Hospitalization and treatment under the compulsory medical insurance quota. More details after viewing the pictures.
Arnold-Chiari malformation in adults is accompanied by the descent and exit through the foramen magnum of the brain structures that are located in the posterior cranial fossa. At the same time, nearby brain structures are compressed. This leads to disruption of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and the development of hydrocephalus. Most often, the signs of Arnold-Chiari malformation are combined with syringomyelia. This is a chronic disease of the central nervous system, which is accompanied by the formation of cavities in the medulla oblongata and spinal cord.
Neurologists find it difficult to establish the true causes of the disease. Symptoms of Arnold-Chiari malformation may occur due to shrinkage of the posterior fossa. As a result, the brain structures gradually exit through the foramen magnum. The cause may also be an increase in brain size due to hydrocephalus or traumatic brain injury.
What is Arnold-Chiari Malformation?
Arnold-Chiari malformation is a condition in which a part of the brain at the back of the skull, called the cerebellum, protrudes through the foramen magnum into the spinal canal (normally through this opening the spinal cord exits the skull).
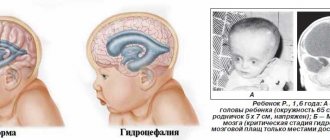
This protrusion of part of the cerebellum creates a disruption in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the cranial cavity, which can cause increased intracranial pressure with the development of hydrocephalus and symptoms of varying severity. In most cases, this problem is congenital.
In rare cases, malformation may develop at a later age, in which case it is referred to as acquired or secondary malformation.
There are several types of Arnold-Chiari malformation, but the most common is type I, also called primary Arnold-Chiari malformation type I. Although it is congenital, the first symptoms of the disease may appear in infancy or early childhood, but they are most often detected in adolescence or early adulthood.
Get an MRI of the brain in St. Petersburg
Treatment in adults
The main treatment method is surgery. Conservative therapy can only be considered as an additional method. But in most cases, the disease is accompanied by significant neurological disorders, including the development of paresis and other life-threatening complications. In this case, surgical treatment cannot be delayed.
Most often, specialists use craniovertebral decompression. The operation involves removing a bone fragment with widening of the foramen magnum. Specialists also eliminate signs of compression of neurological structures, remove the cerebellar tonsils and parts of the first two cervical vertebrae. To restore the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid, artificial materials and transplants are used, which are sutured into the area of the dura mater as patches.
Carrying out bypass operations
In neurosurgery, shunt systems are actively used to eliminate hydrocephalus. The purpose of this surgical intervention is to restore the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. Shunts have one-way valves. In the future, it is possible to replace these systems or revise them during repeated neurosurgical interventions.
The outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is achieved by draining the ventricles of the brain. The shunt system can be connected to the right atrium or the abdominal cavity. It is possible to use modern endoscopic methods of surgical treatment. They are characterized by minimally invasiveness and a short rehabilitation period.
With a highly qualified neurosurgeon, operations take place without any complications. The risk of infection increases if the basic rules of infection safety are not followed, the shunt is disconnected, or a sharp decrease in intracranial pressure. By using special shunt systems, such adverse consequences can be avoided.
Causes of Arnold-Chiari malformation type I
The exact causes of Arnold-Chiari malformation type I are not known. The problem may arise during fetal development due to some defect, presumably associated with exposure of the fetus to harmful substances. But it is possible that the appearance of the disease is caused by heredity and genetic mutations.
Arnold-Chiari malformation type I occurs after birth. Its causes are the flow of cerebrospinal fluid into the lumbar or thoracic spine. This usually occurs due to injury, infection, or exposure to harmful substances.
Filum terminale disease
After the research of Dr. Royo Salvador and his doctoral dissertation (1992), it was found that several diseases whose cause was previously unknown, such as: Arnold Chiari I syndrome, idiopathic Syringomyelia and Scoliosis, Platybasia, Basilar Impression, Axial vertebral tooth displacement, An angular bend at the level of the arch of the atlas is part of a new pathology - Diseases of the filum terminale - and arises for the same reason: tension in the spinal cord and the entire nervous system.
The tension force of the entire nervous system during filum terminale disease is present during the formation of all human embryos; to a greater or lesser extent, everyone suffers from its consequences and various forms of manifestation and intensity.
The following diseases may be associated with filum terminale disease: intervertebral hernias, some cerebrovascular insufficiency syndromes, facet syndrome, Bostrup syndrome, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue, nocturnal enuresis, urinary incontinence and acute paraparesis.
For accurate diagnosis, selection of treatment and monitoring of a patient with filum terminale disease, the Filum System® method was created.
Symptoms and manifestations of Arnold-Chiari type malformation
The main manifestations of malformation are:
- Syrinx. This formation is a fluid-filled cavity in the spinal cord (syringomyelia) or cysts. As it grows, this formation puts more and more pressure on the spinal cord. In some cases, this can lead to impaired neuromuscular functions and weakness of the limbs. Difficulty moving or breathing. To clarify this diagnosis, patients are prescribed magnetic resonance imaging.
- Scoliosis. In children under 16 years of age, in whom the formation of the spine has not yet completed, as a result of the appearance of cavities, lateral curvature of the spine (scoliosis) may occur.
- Headache . Children up to and including adolescence with undiagnosed Arnold-Chiari malformation type 1 may experience headaches localized to the back of the head and neck, aggravated by exercise.
- Sleep apnea. With this symptom, a short-term cessation of breathing is observed during the patient’s sleep. The presence of this symptom can be determined during a sleep study of the patient.
Other symptoms include hoarseness, difficulty breathing, rapid side-to-side eye movements, muscle weakness, difficulty maintaining balance, abnormal reflexes, and neurological problems including paralysis.
Symptoms
Neurological symptoms of types 0 and 1 Arnold-Chiari malformation most often begin to bother people at the age of 20–40 years. The degree of dislocation of the cerebellar tonsils can increase under the influence of unfavorable factors. The most common complaints with MAC type 0 are headache, predominantly of the cervical-occipital localization, as well as pain in the neck. Arnold-Chiari malformation type 1 in adults is more often manifested by complaints of nystagmus, dysarthria, ataxia, intention tremor (tremor during voluntary movements), headache, dizziness, sensory disturbances, paresis, dysfunction of the pelvic organs, disturbances in the frequency and rhythm of the pulse, breathing rhythm , lability of blood pressure, symptoms of damage to the caudal group of cranial nerves (IX, X, XI, XII pairs) - impaired facial sensitivity and bulbar disorders (swallowing and speech disorders).
Arnold-Chiari syndrome grade 2 first appears not in adults, but in newborns or early childhood. MAC type 2 is more severe; children with this pathology are already born with a hydrocephalic skull shape. Hydrocephalus interferes with normal development. In addition, such children suffer from breathing, heartbeat and swallowing problems. The disease is often accompanied by convulsive seizures. Children develop nystagmus, apnea, stridor, vocal cord paresis, dysphagia with regurgitation, and impaired tone in the limbs. The severity of neurological symptoms primarily depends on the severity of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics disorders, and not on the degree of ectopia of the cerebellar tonsils.
Diagnosis of Arnold-Chiari malformation type I
If the disease is asymptomatic, it can be detected during examinations (computer or magnetic resonance imaging) prescribed by a doctor for other diseases. If there are symptoms and suspicion of Arnold-Chiari malformation type 1, the doctor will refer the patient for a CT or MRI. A CT scan creates a three-dimensional image of an area of the body using X-rays, while an MRI uses a powerful magnetic field for this purpose. The resulting images are processed using a computer, creating three-dimensional visualization.
Get an MRI of the brain in St. Petersburg
General information
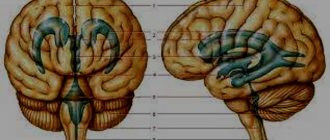
Arnold-Chiari syndrome is a malformation of the cerebellum, a part of the brain responsible for coordination, muscle tone and balance.
The pathology is assigned the ICD-10 code Q07.0 and it represents a descent of the cerebellar tonsils down to the level of the first, and sometimes the second cervical vertebra (below the Chamberlain line) and blocks the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid. The disease is most often combined with microgyria , compression of the posterior part of the brain, stenosis of the cerebral aqueduct, basilar impression, invagination, underdevelopment of the quadrigeminal and other malformations of the nervous system. The syndrome most often occurs in individuals aged 12-71 years and does not exceed 000.9%.
Localization and structure of the cerebellum
Treatment of Arnold-Chiari malformation type I
Typically, the treatment method for the disease depends on the symptoms and their severity, the general health of the patient and his age:
- If there are no symptoms, doctors carefully monitor the patient's health with frequent examinations or regular MRIs.
- If symptoms occur, your doctor may prescribe pain medication or suggest surgery to relieve pressure on the brain and restore normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- If you have few or no symptoms but have fluid-filled cavities, your doctor may order an MRI with contrast. This type of MRI is excellent for examining the flow of cerebrospinal fluid and identifying areas where these flows are blocked. If symptoms worsen, surgery may be suggested.
- If there are signs of sleep apnea, a sleep study is performed, based on which the doctor develops a further treatment plan.
Diagnostic tactics
If the patient has certain complaints or a developmental anomaly was discovered by chance, he should contact a qualified neurologist for further diagnosis and treatment. The neurologist will take a medical history, conduct a full examination of the patient, and assess his neurological status. To make a final diagnosis, Israeli specialists use the following diagnostic methods:
- X-ray examination of the skull reveals only bone abnormalities.
- MRI of the brain and spinal cord, as well as CT using contrast, demonstrates the presence of abnormalities in the development of bone tissue and reveals a violation of the location of the soft tissues of the brain.
- Echo-EG, EEG and REG provide information about the state of intracranial pressure.
Second opinion for Arnold-Chiari malformation type I
Despite the fact that the malformation is clearly visible on MRI and CT, errors often occur during these examinations. Some of them are related to the use of outdated equipment or its poor performance. These are objective reasons. Subjective reasons include the fact that doctors often cannot make the correct diagnosis based on MRI and CT. For example, the diagnosis of Arnold-Chiari malformation is often made in children with a simple low location of the cerebellar tonsils (a normal variant), or can be confused with other anomalies of the craniospinal junction. In addition, the description of MRI images may be performed inaccurately and incorrectly by the radiologist.
If we talk about experience, then in a city of half a million there may be an average of 25 people with Arnold-Chiari malformation, and doctors rarely observe this condition. Therefore, when looking at the results of CT and MRI, they may assume diseases that are more familiar to them, which will lead to incorrect treatment, wasted money, wasted time and health.
In order to avoid misdiagnosis, it is vital for the patient to obtain a second opinion on the scan results and it is advisable that this opinion be from a doctor of higher qualifications than the doctor who gave the first opinion.
The National Teleradiological Network (NTRS) provides every patient with free access to obtain an alternative opinion from leading specialists in the field of radiology (radiodiagnostics) and magnetic resonance imaging. No matter where you are, all you need is access to the Internet and scan results in electronic form. Upload them to our server and within a day you will receive the most qualified conclusion that can be obtained in our country.
NTRS is your opportunity to avoid misdiagnosis and treatment.
Consequences and prognosis for life
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment should begin as soon as possible. Certain diagnostic problems may arise due to the asymptomatic course of the disease. Chiari malformation grade 3 is often fatal. But timely surgical treatment allows you to avoid adverse consequences. The operation is the gold standard of modern neurosurgery.
Even minor neurological manifestations are an indication for contacting specialists. Ideally, treatment should begin immediately after the pathology is identified. The disease in its advanced form ends in disability and death of the patient.
Timely treatment using surgery allows you to avoid irreversible atrophic processes in the central nervous system. At the Burdenko Research Institute, such surgical interventions are performed at a high professional level. Experienced neurosurgeons work with patients, paying special attention to each stage of treatment, including preparation for surgery and conducting a thorough comprehensive examination.
After surgery, patients are under the supervision of neurosurgeons, rehabilitation specialists, and resuscitators. Specialists monitor vital signs of the body. If necessary, professionals provide first aid and slow down the development of complications and other adverse health consequences. Modern techniques used in neurosurgery make it possible to reduce the degree of tissue damage during work with the brain and avoid unnecessary injuries and blood loss.
CT
Modern volumetric scanning with high quality sagittal reformation visualizes the foramen magnum and tonsils relatively well, although the lack of contrast (compared to MRI) makes accurate assessment difficult. More often, pathology can be suspected on axial images when the medulla surrounds the tonsils and there is little or no cerebrospinal fluid. This condition is called “overfilling” of the foramen magnum.
Bypass surgery
To treat Chiari malformation, your doctor may also recommend bypass surgery. It involves the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid from the central canal of the spinal cord. With the help of a lumboperitoneal shunt, this substance can be diverted into the abdominal or thoracic cavities.
The effectiveness of surgical intervention is about 50-85%. However, doctors emphasize that the operation should be performed before the onset of serious neurological disorders, since otherwise, after surgery, the patient’s recovery may be partial or not occur at all. The main task of the doctor in such cases is to stabilize the patient and prevent further development of the disease.