Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death among the population of most European countries. Most often, doctors are faced with arterial hypertension, which is a common cause of vascular accidents such as stroke or heart attack. But sometimes an increase in pressure leads to the rupture of a vessel aneurysm, if it exists in the brain. Rehabilitation after a brain aneurysm (more precisely, its rupture) consists of restoring the function of areas of the cortex and white matter affected by hypoxia.
- 6 Expected prognosis for cerebral aneurysm
- 7 Consequences after surgery for cerebral aneurysm: Video
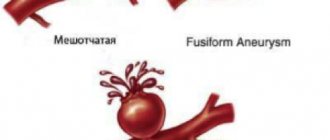
Concept of cerebral aneurysm
An aneurysm is a change in the structure of the vessel wall, which results in the formation of a cavity inside the lining of the artery. It occurs against the background of a congenital defect of the vascular wall, endothelial infections, high blood pressure, and atherosclerotic process. The exact cause of the pathological condition is unknown.
There are several types of aneurysm. Among them are:
- saccular (at the site where the branch of the arteriole branches off from the main vessel, a bulge filled with blood appears);
- dissecting (for unknown reasons, the integrity of the vascular wall changes, resulting in the formation of a space between the endothelium and the muscle layer, where blood sweats).
In a physical sense, an aneurysm is a pathological increase in the diameter of a vessel, which leads to its rupture and further hemorrhage
Features of the postoperative period
Brain surgery always causes consequences for the body. However, with proper rehabilitation and following the doctor’s recommendations, they can be overcome. Here's how the process begins:
- after the surgery department, the person is transferred to the neuro intensive care unit for several days,
- every day the surgeon examines the patient, studies the emerging consequences and prevents complications,
- if unfavorable symptoms occur, a computed tomography scan is performed,
- the most common consequences are vascular spasms and hypoxia of brain cells, sometimes hemorrhages occur under the arachnoid membrane,
- in the absence of exacerbations, clipping and other operations do not lead to death,
- if a large aneurysm was located near the basilar basin, the risks increase,
- Also, the risk of mortality is high in people admitted with hemorrhage.
Disability after embolization of a cerebral aneurysm occurs only in 4% of cases. Statistics show that 8 out of 10 patients return to their normal lives, but only 4 of them begin working.
Consequences of clipping
Complications after artery clipping occur in approximately 10% of cases. This 10% includes consequences such as:
- disturbance of attention, concentration,
- constant headaches,
- minor and significant speech problems,
- ischemia, pulmonary edema - in rare cases.
Mortality occurs only in very difficult situations . If possible, you should not refuse the operation.
Restorative procedures
In the first days after the intervention, to prevent the consequences of the operation, the patient is monitored by medical personnel. It is important to notice bleeding and other symptoms in time.
In the first days of recovery, the patient is prescribed nootropics, analgesics, diuretics and neuroprotectors if bleeding occurs.
Open trepanation and operations near brain tissue are complicated by additional consequences:
- repeated hemorrhages,
- infections and inflammations (in very rare cases),
- neurological disorders,
- necrosis of nervous tissue and neurological deficit - vasospasm.
Recovery after surgery for a cerebral aneurysm
The only option to save the life of a patient with a brain aneurysm is immediate surgery. This involves clipping the affected vessel using a metal clip, which eliminates the damage.
Rehabilitation after surgery for a cerebral aneurysm requires a fairly long period. In the early stages, it involves the prevention of thrombotic complications and the fight against hypertension, as well as relieving the consequences of a hemorrhage that has occurred.
The early postoperative regimen involves keeping the patient in the intensive care unit and administering antibiotics to prevent infections.
Hemorrhagic stroke, which often accompanies an aneurysm, requires treatment according to all the rules of modern protocols, and the most severe complication of aneurysm rupture with the development of subarachnoid hemorrhage is cerebral vasospasm, which leads without treatment to the formation of secondary foci of ischemia.
Having moved to the general ward, the patient requires stable drug support in the form of cholesterol-lowering drugs and powerful antihypertensive therapy using central blocking drugs.
Recovery is noticeably accelerated with the inclusion of medications that improve cell metabolism and their energy efficiency.
Key points of rehabilitation after cerebral aneurysm
The patient can be discharged from the hospital only if there is confidence in the stability of blood flow in the affected segment of the vessel. Achievement of target blood pressure values and satisfactory results of cerebral angiography are also necessary. The absence of focal changes on the tomogram confirms the beginning of restoration of the damaged area of the brain parenchyma.
Further rehabilitation of the patient at home involves taking prescribed medications and following an individual program of exercises to restore functions controlled by the affected area of the brain. If this is part of the motor or sensory cortex, the patient is prescribed therapeutic exercises, massage procedures, and exercises on simulators.
If the functions of the limbic system, speech center, sensory organs, and the like are involved in the process, the patient needs classes with specialized rehabilitation therapists, a speech therapist, as well as verbal training methods.
Also, a patient who has suffered an aneurysm is recommended for annual planned hospitalization in a therapeutic hospital, a visit to a sanitary-resort institution that has a profile such as rehabilitation after removal of an aneurysm.
Every three months, such a patient, according to the protocol, must be examined by a neurologist, who is obliged to conduct basic screening tests (coagulogram, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring, general blood test).
What medications should a patient take after a cerebral aneurysm?
The patient’s medication plan depends on many factors: the presence of concomitant diseases, laboratory and instrumental indicators. Let's try to provide a drug treatment regimen for a typical representative of this group of patients.
The patient's first priority is to take statins (cholesterol-lowering drugs). It is also imperative to prescribe rational combination antihypertensive therapy, preferably using a diuretic.
One of the key medications will be a beta blocker, the selectivity of which must be chosen according to the situation. The purpose of this appointment is to reduce the force of heart contractions and slow down the pulse wave.
You can use metabolic support in the form of meldonium, arginine. Choline ascylate has proven itself well as a drug for restoring microcirculation of the brain parenchyma
Important elements of therapy are a disaggregant (clopidogrel) and a venotonic (detralex), thanks to which rehabilitation after a cerebral aneurysm will be free of high risks of endothelial complications.
Dietary patterns of patients who have had an aneurysm
Patients should avoid fatty foods, alcoholic beverages, and substances that can sharply increase blood pressure. It is worth paying attention to the consumption of unsaturated fats, which have a positive effect on cell metabolism. It is necessary to increase the intake of antioxidants in the form of fruits, vegetables, and juices.
There is evidence of the beneficial properties of dried fruits and nuts due to a large number of microelements that affect the functioning of the heart.
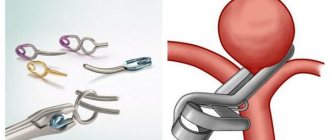
Aneurysm clipping
Clipping of a cerebral aneurysm is performed on an open organ. The process requires craniotomy. The goal of such an intervention, as with embolization, is to disconnect the neoplasm from the blood supply. The effectiveness of open intervention is much higher, but the operation cannot be performed if the aneurysm is deep.
When opening the skull, the doctor finds a bag filled with blood, and a clamp is applied to it. The process is controlled by an endoscope, and all manipulations are carried out with microsurgical instruments. The probability of complications after surgery does not exceed 8%, but the possibility of damage to the aneurysm sac is almost completely eliminated.
The most common mistakes: loose closure of the base of the sac, repeated manifestations of the disease and bleeding. To avoid such consequences, you need to carefully choose a clinic, study doctors and trust only real professionals.
What should such patients avoid?
Under no circumstances should you violate the established regime of mobility and physical activity. This can lead to a sharp increase in cardiac output and rupture of the clip (recurrent hemorrhage).
You should not stop taking prescribed medications without permission, as this can lead to complications in the postoperative period. Chronic lack of sleep, fatigue and nervous stress are contraindicated, which negatively affects the condition of the heart.
You should not skip scheduled visits to the doctor or refuse necessary diagnostic measures even after a successful operation.
How to prepare
Before surgery, you should undergo a number of standard examinations. These include:
- urine analysis for general indicators;
- blood test (for general and biochemical parameters, blood group, platelet aggregation, coagulogram, syphilis, HIV, hepatitis C and B);
- angiography;
- computed tomography (CT) of the abdominal aorta with contrast;
- fluorography;
- Ultrasound of abdominal vessels.
Preparation for the procedure also involves early cessation of smoking, alcohol, hormonal drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs. On the eve of the intervention you should not eat or drink. In addition, you need to shave the operated area.
Consequences of surgery for cerebral aneurysm
As a rule, successful surgery for an aneurysm leads to saving the patient's life. Of course, everything depends on related factors, such as the timeliness of assistance, the size of the aneurysm, the strength of the vascular wall, etc. Even in the case of successful surgery, it is often not possible to completely restore the function of the part of the brain affected by hemorrhage or compression to the patient.
In any case, since an aneurysm is, first of all, a physical deformation of a vessel, causing a change in the functioning of the adjacent section of the parenchyma, it is important for a patient with a morphologically confirmed diagnosis to undergo surgery in a timely manner.
What a patient may encounter if an aneurysm ruptures
The consequences of a ruptured aneurysm are the most severe. They are more difficult to treat and are accompanied by residual effects:
- difficulties with perception and processing of information,
- decreased visual sharpness, appearance of “blind spots”,
- difficulty moving, convulsions and involuntary movements,
- tingling, numbness, decreased sensitivity of different parts of the body,
- difficulty swallowing food,
- speech disorders,
- epileptic seizures,
- character changes, pronounced apathy or aggressiveness may appear,
- pain syndrome in different parts of the body,
- problems with bowel movements.
If any unpleasant sensations or sudden changes occur, it is necessary to urgently undergo a computed tomography scan.
Expected prognosis for cerebral aneurysm
With timely seeking medical help and successful coordinated actions of doctors, you can count on a good result. Of course, a prerequisite is to perform vessel clipping according to modern techniques and high-quality postoperative drug support. The type, size and location of the aneurysm also plays a role. If there is a large lesion in a hard-to-reach area, the prognosis is significantly worse.
It is worth paying attention to the improvement in prognosis for patients who do not suffer from concomitant diseases, such as diabetes mellitus or chronic heart failure.
How is the procedure performed?
During the operation, an aortic prosthesis is used - a mini-tube made of synthetic material. Its size and diameter correspond to a healthy aorta. A sewn-in prosthesis will allow the blood supply to normalize and reliably replace the removed section of the vessel.
- First, the patient is given sedatives. Preference is given to epidural anesthesia with a needle inserted into the space surrounding the spinal cord. This measure will turn off vascular tone and facilitate manipulation of the aorta.
- Next, the patient is immersed in a state of anesthesia. An anesthesiologist monitors the vital signs of the body. If necessary, he increases or decreases blood pressure by introducing the necessary drugs.
- Access to the aorta is performed retroperitoneally (from the side) or by laparotomy (in the middle of the abdomen). But before this, the surface must be treated with special antiseptics.
- Then the aortic aneurysm is isolated from the dissected tissue. Particular attention is paid to the zone of transition to the low-lying part and the so-called “neck” of the aneurysm.
- After resection, prosthetics begins, choosing one of two suitable methods. The fact is that, depending on the segments involved in the lesion, it can be bifurcational or linear.
- Having completed the connection, the blood flow is checked, the clamps are finally removed, the incision is sutured layer by layer and a bandage is applied.
Observation program after treatment method
Experts recommend following basic rules to keep your blood vessels healthy:
- Quitting smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Exclusion from the diet of fatty foods, smoked meats, and red meat.
- Compliance with diet.
- Adequate physical activity.
- Normalization of body weight.
- Complete rest.
- Optimal working mode.
- A calm life without stress and conflicts.
- Periodic medical examinations with the necessary studies, in particular, duplex scanning of the neck vessels.
- If necessary, preventive use of medications that thin the blood and prevent blood clots.
- Regular examination by a doctor and compliance with his recommendations.
Systematization of manifestations of aortic aneurysm
Currently, there is no unified approach to systematizing the manifestations of peritoneal aortic aneurysm. Most often, doctors and authors of medical works use the method of A. Pokrovsky and R. Ermolyuk, according to which aneurysms are divided:
- by etiology
– acquired (non-inflammatory or inflammatory) and congenital; - according to morphology
- into false (traumatic origin), true and stratifying; - by shape
- diffusion and saccular; - according to the course of the clinical process
- into diseases with an uncomplicated course, complicated and dissecting; - by type and location
- on the proximal segment of the peritoneal aorta, on the infrarenal section, as well as with total damage to the entire section of the abdominal aorta.
According to medical statistics, up to 95% of aneurysms are localized in the infrarenal region.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm - main diagnostic methods:
- Physical examination - includes palpation of the abdomen, percussion, i.e. tapping, listening to the peritoneum using a phonendoscope, measuring pulse and blood pressure.
- Laboratory tests of physiological fluids - urine and blood. They help diagnose and determine the cause of the aneurysm.
- Duplex ultrasound examination is the “gold standard” for screening patients (detection and follow-up);
- CT angiography is the “gold standard” of preoperative examination and in cases where information from ultrasound scanning is insufficient;
- X-ray of the abdominal organs;
- Contrast-enhanced MRI angiography;
- X-ray contrast aortography.
Treatment tactics for abdominal aortic aneurysm
- If the size of the aortic aneurysm is less than 5.0 cm in diameter, the patient needs correction of risk factors under the dynamic supervision of a cardiologist, cardiovascular surgeon, and regular monitoring studies;
- If the size of the aortic aneurysm is ≥ 5.0 cm, then the patient requires surgical treatment to eliminate the risk of aneurysm rupture and other life-threatening complications.
- If the aneurysm is more than 3.0 cm and its size increases ≥ 6 mm per year, then the patient also needs surgical treatment.
An established diagnosis of an abdominal aortic aneurysm is an indication for surgery (at any age).
Contraindications for surgery:
- acute disorders of coronary and cerebral circulation with severe neurological deficits,
- circulatory failure stage IIB-III.
Causes of development of abdominal aortic aneurysm
- atherosclerosis, in which the appearance of cholesterol plaques on the wall of the aorta gradually reduces its strength, which contributes to protrusion in one of the areas;
- congenital predisposition, transmitted through the male line, confirmed by many years of observations: the presence of an aneurysm in the father indicates a 50% chance of this disease occurring in his son;
- an inflammatory process of a chronic, sluggish nature that occurs in the aortic wall itself or in the adipose tissue that surrounds the vessel;
- traumatic damage to the wall due to trauma or injury to the abdomen, surgery or endovascular intervention.
Atherosclerotic manifestations become the cause in 85-90% of cases of the development of acquired aneurysm in the abdominal aorta. Signs of predisposition to the development of the disease are smoking, arterial hypertension and chronic pulmonary diseases.
Preparing for treatment
Before proceeding with resection of a carotid artery aneurysm, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient in order to identify the area of localization of aneurysmal expansion, determine the speed of blood flow, the diameter of the lumen of the arteries and other parameters of cerebral circulation. Necessary diagnostic measures include:
- duplex ultrasound scanning;
- computed tomography;
- angiography;
- magnetic resonance angiography.
A week before the date of surgery, the patient is prescribed medications that help reduce blood clotting.