September 24, 2019
37004
0
3.9 out of 5
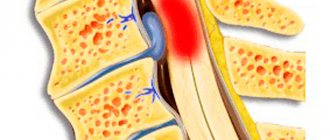
Stenosis or pathological narrowing of the spinal canal is a dangerous disease that often accompanies intervertebral hernias and other spinal pathologies. It provokes severe back pain, paresis and paralysis, and stenosis of the spinal canal at the lumbar level can cause disruption of the pelvic organs and be accompanied by involuntary defecation and urination.
The disease seriously reduces the quality of life and threatens the development of severe complications. In a short time it can lead to compression myelopathy and myeloradiculopathy. Therefore, if symptoms of stenosis occur, treatment should be started immediately.
Types of spinal canal stenosis
There are several classifications of the disease. The main one was a change in the sagittal size of the spinal canal. Highlight:
- Absolute stenosis of the spinal canal is diagnosed when it narrows to 10 mm and its area reaches 75 sq. mm. This is invariably accompanied by compression of the nerve roots of the cauda equina.
- Relative - the size of the spinal canal is at least 12 mm, area - up to 100 square meters. mm. Signs of relative spinal canal stenosis appear when another factor is added that causes compression of the nerve endings.
A combination of absolute and relative stenosis of the spinal canal of the lumbar and cervical region is possible. In such situations they speak of a mixed form of pathology.
Depending on the location of the narrowing site, lateral and central stenosis are distinguished. In the first case, there is a decrease in the root canals to 4 mm, while in the second, there is a reduction in the distance from the posterior surface of the vertebral body to the base of the spinous process located opposite it.
There are also congenital and acquired forms of the disease. The first occurs as a result of exposure to infectious and toxic factors during intrauterine development of the fetus at 3–6 weeks. In such situations, moderately severe central spinal stenosis is more often diagnosed.
Acquired or secondary occurs when:
- injuries;
- degenerative-dystrophic changes in intervertebral discs and facet joints;
- spondylolysis;
- compaction of the yellow ligaments;
- Bekhterev's disease;
- undergoing spinal surgery;
- tumor processes, etc.
Secondary degenerative spinal stenosis can be either absolute or relative. More often it forms in the lumbosacral spine at the L5–S1 level. Depending on the cause of its development and accompanying signs, discogenic, discarthrogenic, etc. are distinguished.
Accurate determination of the type of pathology using an MRI examination allows you to choose the best treatment option and surgical technique. To obtain a complete picture, patients are also prescribed radiography and CT.
Adults and children can undergo a full diagnosis of the disease using the latest generation equipment from the specialists at SL Clinic. The vertebrologist will explain the diagnostic results in detail and, if necessary, select the optimal treatment tactics for the detected disorders. Since our neurologists, traumatologists - orthopedists and neurosurgeons work in close cooperation, our patients are completely protected from diagnostic errors and, if indications for surgical treatment arise, they will be immediately consulted about the possible options, consequences and risks.
Diagnostics
- Studying the patient's complaints - the doctor asks about the location of the pain, its manifestation, and the presence of accompanying symptoms.
- Physical examination - the patient’s posture is studied, the presence of scoliosis, palpation and percussion diagnostics are performed.
- X-ray – X-ray will show bone formations and can also evaluate narrowing of the intervertebral canal to confirm the diagnosis of relative stenosis. If a narrowing of the lumen of less than 10 mm is detected, the patient is diagnosed with absolute stenosis.
- Multislice CT scan – detects degenerative processes of bone and cartilage tissue.
- A myelogram is an x-ray with contrast that allows you to evaluate the degree of pressure on the nerve roots.
- Magnetic resonance imaging – visualizes the condition of soft tissues and the spinal cord.
Treatment methods
Spinal stenosis can be treated conservatively or surgically. But inexorable medical statistics indicate that only 32–45% of patients experience positive dynamics due to the use of medications, physiotherapy and exercise therapy. But even in such situations, treatment of stenosis without surgery does not lead to recovery, but only contributes to a slight improvement in the condition, especially if stenosis of the left or right root canal L5-S1 or another segment is diagnosed.
Conservative therapy includes:
- taking individually selected drugs from the group of NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, vitamins, drugs to improve blood flow, chondroprotectors, etc.;
- blockades with anesthetics;
- corticosteroid injections;
- phonophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- SMT therapy;
- Exercise therapy.
Therefore, today the only way to avoid the development of complications and achieve complete elimination of unpleasant symptoms is surgical treatment. Stenosis surgery is designed primarily to eliminate those factors that led to compression of the spinal cord and its nerve roots. For this purpose, decompression operations are performed. During these procedures, the herniated disc or vertebral arch that causes canal stenosis is removed. If necessary, stabilization of the spine is performed in order to fix the vertebrae in the anatomically correct position and avoid their displacement in the future, i.e., to prevent relapse.
Decompression interventions
Initially, decompression interventions are used to eliminate the effect of compression of the spinal canal. Today, in the arsenal of spinal surgeons there are 3 types of techniques that are used for disc herniation with stenosis, including L5-S1:
- Classic discectomy is an operation that involves removing the entire intervertebral disc through an incision of up to 10 cm. It is indicated for anterior compression of the spinal cord by a herniated protrusion of the intervertebral disc, including if there are 2 hernias and stenosis. Although there are more gentle methods for removing pathological formations, open discectomy leaves no chance for their re-formation in the same area of the spine, which completely eliminates the risk of relapse of the disease. A titanium implant (cage) is installed in place of the removed disc, providing reliable support for the vertebrae.
- Microsurgical discectomy - surgical intervention has the same goals as open surgery, but is carried out with special instruments through a miniature incision, the length of which does not exceed 3 cm. Therefore, after it, patients recover easier and faster. But microsurgical discectomy does not allow fixation of the vertebrae with anterior stabilization systems, which is necessary when spinal stenosis and hernia are interrelated.
- Decompression laminectomy – This operation is used for posterior compression of the spinal cord. It consists of partial removal of the vertebral arches in the affected area, followed by stabilization of the spinal column with special structures.
All types of surgical interventions are performed in the medical field. Some of the best spinal surgeons in Moscow are capable of performing operations of any degree of complexity, and the availability of modern equipment makes it possible not only to accurately pre-assess all the risks and potential benefits of each procedure, but also to perform it with precise accuracy.
Stabilizing interventions
After compression of the spinal cord is removed, surgeons must fix the spine in a physiological position and create optimal conditions for proper load distribution during physical work. Depending on the location of the narrowing, the following can be used:
- Systems that stabilize the anterior support columns are cages with bone chips.
- Posterior stabilization systems – used for fixed connection of vertebral bodies, titanium structures for transpedicular fixation.
Both options for stabilizing systems are considered the optimal treatment option for the disease. Interbody cages allow you to reliably fasten the anterior column of the spinal column and prevent relapse of the disease, and transpedicular implants reliably stabilize the spine, preventing it from moving.
Special dynamic stabilization systems are also used. There are several types of such structures, each of which has its own strictly limited scope. This:
- Interspinous U-implants – systems of this kind are designed for dynamic fixation of the spinous processes of the lumbar spine, including spinal canal stenosis at the level of L3–L4, L4–L5, which may be an indication for their installation. The U-system allows you to slightly reduce the load on the posterior support columns and increase the area of the spinal canal, thereby relieving pain caused by spondylous joints of the vertebra.
- A transpedicular fixation system with nontinol rods is also indicated for installation in the lumbar spine for reliable connection of adjacent vertebral bodies. This system makes it possible to maintain a large range of movements, due to which motor abilities are practically not limited.
- Dynamic interbody implant – designed for installation in place of a removed disc when spinal canal stenosis of the cervical or lumbar spine is diagnosed. Its design features allow you to maintain a fairly good range of motion.
Their disadvantage can be considered the impossibility of use in cases of spinal instability, since they do not provide a pronounced therapeutic effect and are unable to hold the vertebrae in the desired position. Also, over time, their mobility is lost.
Possible complications if left untreated
Without timely and adequate treatment, absolute stenosis can have extremely serious consequences. And irreversible paralysis of the limbs is far from the only thing. Thus, due to impaired nutrition of spinal cord cells and deterioration of its oxygen supply, an ischemic stroke of the spinal cord may occur. And if the spinal canal is critically narrowed at the level of the thoracic or cervical region, death may occur due to respiratory distress or sudden cardiac arrest.
Cervical decompression surgery
With cervical spinal stenosis, there are practically no symptoms. They begin to appear in advanced stages of the disease in the form of:
- severe pain in the neck on one or both sides, radiating to the shoulders, shoulder blades, arms and back of the head;
- painful spasms throughout the body;
- the appearance of numbness and weakness in the arms when moving the neck;
- the presence of a sensation of “goosebumps” on the skin of the upper extremities;
- breathing disorders when the pathology is localized at the C3–C4 level.
Surgical treatment of cervical spinal canal stenosis is performed through an anterior or posterior approach. The choice depends on the nature of the current situation and the presence of concomitant neck pathologies.
The operation to eliminate stenosis of the cervical spinal canal using an anterior approach involves making an incision on the frontal surface of the neck. It is performed from a microsurgical approach and is not traumatic; it requires a high level of skill from a vertebrologist. Usually the surgeon tries to make it in a natural fold of skin so that over time the postoperative scar becomes invisible.
Indications for this type of intervention are:
- kyphosis;
- anterior compression accurately determined on MRI;
- severe spinal instability;
- degenerative cervical spinal canal stenosis, involving more than 2 vertebrae.
The essence of treatment for neck stenosis is discectomy and spinal fusion. After removal of the intervertebral disc, an interbody implant is installed in its place, which securely holds the vertebrae.
Operations with a posterior approach are also less traumatic and therefore safe in experienced hands. Laminectomy or laminoplasty is expected; if indicated, spinal fusion can also be performed, and spinal stability is ensured by installing suitable structures.
Indications for performing surgery using a posterior approach are:
- confirmation by MRI results of posterior compression;
- congenital stenosis;
- cervical kyphosis;
- detection of ostification of the posterior or anterior longitudinal ligament.
Traditionally, all manipulations are performed through a posterior approach when osteoporosis, ligamentous insufficiency, or the risk of developing pseudarthrosis are diagnosed.
Causes
| Congenital pathology is caused by abnormalities in the structure of the vertebrae: | Causes of acquired stenosis: |
|
|
Stenosis occurs in the part of the spine that is affected by the above diseases.
Often the causes of stenosis are intervertebral hernias and osteochondrosis
Decompression surgery for lumbar stenosis
Signs of lumbar spinal stenosis include gradually increasing pain in the back and legs. Initially, they appear during walking or physical work, but subsequently they can persist at rest. The discomfort does not have a clear localization, so patients often describe it as an unpleasant sensation in the legs. My legs ache especially at night. A symptom of restless legs appears.
Symptoms of lumbar spinal stenosis may also appear:
- increasing weakness in the legs when walking;
- lameness forcing the patient to stop and sit down;
- the onset of relief after bending the legs at the knees and hip joints, bending forward;
- numbness, the appearance of “pins and needles” in the legs;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs, which is manifested by a sudden urge to urinate or defecate, decreased potency in men.
Before the development and introduction of spinal stabilization systems into spinal practice, treatment of lumbar spinal canal stenosis was carried out by decompressive laminectomy without fixation. Today, decompressive surgery in combination with fixation of the vertebrae with posterior or anterior stabilization systems is the gold standard.
For lumbar spinal canal stenosis, surgery is most often performed using transpedicular systems. Thanks to their installation, it is possible to achieve high functionality of the operated area and significantly reduce the rehabilitation period.
Statistical data also supports such systems. According to them, central and lateral lumbar spinal stenosis can be treated with 90% efficiency by posterior decompression followed by stabilization.
Symptoms
Absolute stenosis has a clear clinical picture.
Typical symptoms of the disease:
- Sharp pain in the spine. It decreases when bending and sitting down and increases when walking. This is due to the increase in the distance between the vertebrae as the back rounds. This sign is the main diagnostic criterion.
- Neurogenic intermittent claudication (localized in the lower back). It manifests itself as pain in one leg when walking. When sitting or bending over, the pain disappears. In this case, the patient can perform any work for a long time in a sitting position, for example, riding a bicycle, driving a car.
- Lasègue's symptom. The patient experiences sharp pain along the sciatic nerve when he lifts his straightened leg while lying on his back. When bending the leg, the pain goes away.
- Decreased sensation in the arms or legs.
- Paresis.
- Weakness of the muscles of the upper and lower extremities.
- Calf cramps.
- In men, sexual dysfunction; in women, menstrual irregularities.
- Deterioration of the pelvic organs (urinary incontinence, etc.).
With thoracic stenosis, the patient experiences chest pain, difficulty breathing, and increased heart rate. The sensitivity of the upper chest also decreases, and the hands become numb. Pathology of the cervical spine is manifested by headaches, fainting, nausea, numbness of the face and back of the head.
Find out more about one of the main causes of stenosis:
- Osteophytes of the spine
- Osteophytes of the lumbar spine
- Spondylosis
- What is spondylosis deformans?
Diagnostics
Did you know that...
Next fact
Initially, the diagnosis is made based on the patient's complaints and external examination. The main diagnostic criteria are: the presence of intermittent claudication, Lasegue's symptom. However, this may not be enough to assess the severity of the pathology.
You can accurately determine the degree of compression using the following methods:
- Ultrasound of the spine . Detects hernias, neoplasms, foci of inflammation.
- MRI is the most informative method. Allows you to detect the slightest changes in the structure of bone and cartilage tissue, impaired blood flow, and vascular damage.
Video: “Diagnostics of spinal stenosis”
Treatment of complicated stenosis
The most common comorbidity is spinal instability. In such situations, the use of only interspinous fixation systems or decompression interventions is impossible. This will lead to increased loosening of the vertebrae and worsen the patient's condition. In such situations, only front and rear stabilization systems can be used.
If a patient is diagnosed with a L5-S1 hernia and spinal canal stenosis or protrusion in another segment, the “gold standard” of treatment includes 2 stages:
- Performing microdiscectomy or open discectomy in combination with the installation of transpedicular implants.
- Spinal stabilization with a titanium cage.
With timely surgery, patients have a high chance of a full recovery and return to a full life.
Causes of spinal stenosis
The pathology can be congenital, but most often it is a consequence of an incorrect lifestyle, mainly sedentary, or traumatic back injuries. Diseases that can lead to stenosis:
- Bone tuberculosis;
- Osteochondrosis;
- Arthrosis of the joints;
- Rheumatic joint pathologies;
- Neoplasms of the spinal cord - they can also fill the space and put pressure on the nerve endings, similar to cartilage and bone tissue.
Features of rehabilitation
Once surgery is completed, patients are allowed to get up on their feet the same day or the next morning. During the normal course of the recovery period, discharge from the hospital occurs after 3–4 days. Each patient receives detailed recommendations from the doctor, strict adherence to which is the key to obtaining the most pronounced effect from the operations performed.
All patients are recommended:
- during the entire rehabilitation period, do not lift anything heavier than 3 kg;
- it is important to avoid vibration, shock, sudden movements, turns, and monotonous movements;
- Serious physical activity is unacceptable;
- Light household work is allowed, but if you experience pain, weakness or other symptoms, you should consult your doctor;
- on the recommendation of a doctor, it is necessary to begin performing special exercises and then regularly engage in exercise therapy under the guidance of a rehabilitation specialist;
- 4 weeks after surgery you should start swimming.
On average, the recovery period is 6–8 weeks. Accurate implementation of all medical recommendations allows you to reduce it and speed up the patient’s return to their usual lifestyle.
Prevention
The most effective way to prevent the development of the disease is regular moderate load on the spine. This may be an exercise program developed specifically for you, or coordinated with doctors ( orthopedist
and vertebrologist) a course of classes in any sports club.
It is important to constantly monitor the position of the spine - correct posture should become habitual; it is important to remember this not only when sitting on a chair, but also while walking, lifting a load and even resting.
Children
Children, no less than adults, are susceptible to spinal diseases. In approximately 6% of cases of diagnosing stenosis, it is of a congenital nature. In other situations, narrowing of the spinal canal occurs due to degenerative changes and injuries. The peculiarities of the anatomy of a child’s body determine the possibility of developing pathology even as a result of falling from his own height onto his knees or somersaulting.
Therefore, often when examining previously absolutely healthy children who have recently complained of short-term weakness in the legs, spinal canal stenosis L4–S1 was discovered. The disease also often provokes scoliosis and spondylosis.
The main difficulty in treating children is early diagnosis of the disorder. Since they cannot always accurately describe what worries them, or do not attach due importance to alarming symptoms, parents may be unaware of the development of the disease for a long time. Patients are often referred for an MRI after undergoing a number of other studies carried out regarding emerging lameness or other manifestations of pathology.
Treatment of stenosis in children is carried out using conservative therapy. If it is ineffective or there is a risk of complications, the help of surgeons is required. In mild forms, non-surgical treatment often gives good results, but the presence of spinal column deformities almost always requires surgical interventions. They are aimed not only at eliminating stenosis, but also at eliminating the prerequisites for its development. Therefore, surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis and correction of scoliosis are often performed simultaneously or in several stages.
Treatment of absolute stenosis
If the diagnosis of absolute spinal stenosis is confirmed, the patient must undergo surgical treatment as soon as possible. Drug therapy or exercise therapy are powerless in this case, and the time lost on them does not benefit the patient.
The operation protocol may be different:
- Discectomy – the disc at the level of which the maximum narrowing of the canal has formed is completely or partially removed. If a hernia is to blame for the narrowing, only it can be removed. Next, the patient receives a disc implant.
- Laminectomy - the surgeon removes part of the vertebral arch, resulting in the release of the spinal canal. Most often, such intervention is performed if the stenosis is of traumatic origin. After eliminating the compression factor, the patient is given an implant that ensures normal motor function of the spine and protects it.
Stenosis surgery
Our clinic performs a full range of surgical interventions indicated for stenosis, including the installation of transpedicular stabilization systems.
The cost of surgical treatment of stenosis starts from 450,000 rubles and depends on: - The implant manufacturer; — Clinic (where the operation will be performed) and the class of the ward. The price includes: — Stay at the clinic before and after surgery; — Implants. — Operation; - Anesthesia; — Postoperative observation. — Observation and consultation during the rehabilitation period. All clinic services and costs are shown in the price list
Consequences
Absolute stenosis is a dangerous condition that requires urgent help.
Due to deterioration in oxygen supply to tissues, serious complications develop:
- paralysis of the lower extremities (with lumbar stenosis);
- respiratory depression and death from suffocation if the outbreak is localized in the thoracic region;
- stroke due to pathology of the cervical spine.
Important! As a result of these complications, the patient may remain permanently disabled or die.
Prevention and prognosis
The prognosis of the disease depends on the degree of compression, the cause and the presence of concomitant diseases. If the operation is performed in a timely and correct manner, the patient is able to recover and return to his normal lifestyle . A less favorable prognosis is observed for incurable progressive diseases (Bechterew's disease). With them, a relapse is possible.
Prevention of stenosis is as follows::
Familiarize yourself with the principles of preventing spinal stenosis; active lifestyle, physical education;- avoiding spinal injuries;
- prevention of obesity, metabolic disorders, which are the causes of spinal pathologies;
- timely treatment of exacerbations of osteochondrosis and other back pathologies;
- undergoing regular MRI if hernias, protrusions, spondyloarthrosis, etc. have been diagnosed.
Secondary prevention is aimed at preventing the re-development of stenosis. It can be avoided if you follow all medical recommendations in the early and late postoperative periods.
Lumbar stenosis
This is the most common type of stenosis. It occurs as a result of age-related changes and entails life-threatening complications. At the beginning of the development of pathology, conservative treatment is used, later - surgery. The symptom is pain; the diagnosis can only be determined after examination, since lower back pain can indicate many other pathologies.
Self-medication and the use of traditional methods are not only inappropriate, but also pose a real threat to the health and life of the patient. To carry out any manipulations, an examination in a specialized clinic is necessary.