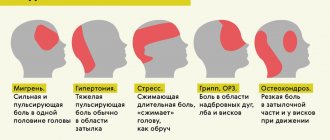
What's better for headaches?
As soon as a headache starts, most people look into the medicine cabinet looking for something to take for the headache. At the same time, few people are puzzled by the reasons - they simply relieve the symptom that bothers them and calm down. But in vain. Everything will happen again or become more complicated.
The most common causes of headaches are serious illnesses that go unnoticed, or muscle tension caused by a sedentary lifestyle, incorrect position during sleep and wakefulness, excessive stress or lack thereof.
These days, the main causes of constant headaches are the improper use of smartphones, tablets, and computers. This causes the cervical vertebrae to suffer, the blood supply to the head is disrupted, and headaches occur that last for several days, hours, or weeks.
While the patient is taking the best pills for headaches, he develops osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. What does the patient do to quickly get rid of this disease? He also takes pills for cervical osteochondrosis or uses ointments. But the cause of the problem does not disappear: the muscles still do not work correctly, the pain returns.
That is why proper relief of headaches in most cases is possible only after experienced doctors have carried out therapy for cervical osteochondrosis, including a set of exercises for muscles and vertebral stretching, massage to improve blood supply.
The nature of pain in different locations of the hernia
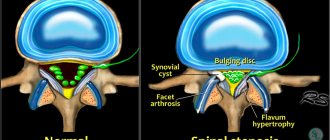
Intervertebral discs are spacers that perform a shock-absorbing function. They consist of a fibrous ring and an elastic nucleus pulposus located inside it. With a hernia, the fibrous nucleus cracks and the nucleus pulposus extends beyond the spinal column, compressing the surrounding tissues.
Intervertebral hernia always occurs with pain. Based on their location, they are divided into cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral. In each department, the pain syndrome occurs with its own characteristics. Small differences are also observed at the level of individual intervertebral discs. More than 90% of hernias are localized in the lumbosacral region, mainly at the level of L4–L5 and C5–S1. Cervical hernias are much less common, and thoracic hernias are even less common; they account for 1–2% of all vertebral hernias.
The pain syndrome in this disease can be a consequence of compression of the spinal roots by a hernial protrusion or irritation of the nerve endings by proteins of the nucleus pulposus, leading to the development of inflammation, swelling and also compression of the nerve roots. Painful sensations intensify due to reflex tension of the spinal muscles.
Pain due to hernia of the cervical spine
Most often, pain from a herniated cervical spine is a consequence of compression of the nerve roots and tension of the neck muscles due to prolonged uncomfortable positioning of the head. Aching pain spreads to the side and back of the neck, collarbone and arm. The upper cervical vertebrae C1 – C3 are rarely affected; usually hernial protrusions develop in the middle and lower sections. Thus, characteristic pain sensations appear when the following nerve roots are compressed:
- C4
– in the clavicle area; - C5
– along the upper and outer edge of the shoulder; - C6
– outside along the shoulder on the forearm and thumb; - C7
– from behind the shoulder to the back of the hand, index, middle and ring fingers.
Radicular pain may have a moderate aching character, intensifying with movement. But with a sharp turn of the head, severe pain (lumbago in the neck) may appear due to pinched nerve roots. The pain is so severe that the person cannot move. It can go away as suddenly as it began, but its duration is difficult to predict: it can be from several minutes to several days, so the patient will need urgent help.
Autonomic pain associated with compression of the autonomic nerve fibers of the spinal nerves C6 - C7: from constant aching to short-term paroxysmal pain. Headache is also one of the characteristic symptoms of cervical hernia. It develops when a hernial protrusion compresses the vertebral artery entering the spine in the region of the 6th cervical vertebra.
When an artery is compressed by an intervertebral disc, the supply of oxygen to the brain is disrupted, which leads to dizziness and headaches. Often attacks develop paroxysmally and have the character of migraines, when one half of the head hurts.
Pain due to thoracic hernia
The thoracic spine is the most stable, so hernial protrusions are rare here. The disease develops with a sedentary lifestyle in combination with work in a forced position, for example, at a computer, if the workplace is not equipped correctly and the back is constantly bent. This contributes to the development of not only intervertebral hernia, but also spinal curvature. In the thoracic region, kyphoscoliosis (lateral and posterior curvature) often develops in combination with a vertebral hernia.
Characterized by aching pain on one side of the chest. With a sharp turn of the body, they can become acute - very painful intercostal neuralgia develops. Without medical help, it is almost impossible to cope with pain.
Pain from a thoracic hernia usually occurs on one side
But the most characteristic symptoms of a thoracic disc herniation are autonomic pains associated with infringement of the autonomic nerves that innervate the internal organs in our body. First of all, these are heart pains that occur when the nerve roots of the thoracic spine Th1 - Th4 are pinched. More often they are of a constant aching nature. Patients have been trying for a long time to identify and treat cardiac pathology to no avail. Sometimes acute short-term painful attacks appear, similar to angina attacks. You can distinguish them from angina attacks by taking Nitroglycerin: it instantly relieves spasm of the coronary vessels and the associated pain, but has no effect on neurological pain.
When the Th5–Th8 nerve roots are pinched, a sensation of painful inhalation or exhalation appears; painful attacks can imitate the symptoms of pancreatitis.
A hernia in the Th9 - Th12 area causes pain in the stomach, duodenum and biliary tract, which is difficult to distinguish from true diseases of these organs.
Pain due to hernia of the lumbar spine
The pain initially has a periodic, aching character, then becomes constant, and with sharp turns, bends or lifting heavy objects it can become acute. If acute pain is localized only in the lumbar region, then they speak of an attack of lumbago (lumbago). Only those who have suffered an attack of lumbago know how much a hernia in the lumbar region hurts. An attack can find the patient in any uncomfortable position, which he is no longer able to change. It starts suddenly and can go away just as suddenly. Sometimes an attack lasts several moments, minutes, hours. But in some cases, lumbago can last for several days and can only be relieved with medication.
If acute pain in the lower back due to a hernia radiates to the buttock and back of the thigh, then this condition is called sciatica or lumbosacral radiculitis when the L5, S1 nerve roots are pinched. Pain from a hernia is often accompanied by convulsive muscle spasms that extend to the heel. With a hernia L1 - L2, pain waves appear in the lumbar region and spread along the front of the leg; with a hernia L3 - L4, the pain will spread to the inner ankle.
Pain due to a hernia of the lumbar spine becomes acute during sudden movements
Causes of cervical osteochondrosis
Most often, the development of this pathology is caused by everyday sedentary work, in which a person does not control the correct position of the body in the chair, and his head is constantly tilted forward. The same can be said about the long stay of the head in a tilted back state, which is typical for construction workers when performing repair work.
As a rule, excessive load on the cervical spine inevitably leads to degenerative disorders in the vertebral discs. In addition, cervical-vertebral osteochondrosis, the symptoms of this disease and the need for its treatment may be due to the following factors:
- Violation of calcium metabolism;
- The reasons are genetic;
- Thermal irritants;
- When doing extreme sports (treatment of sports injuries);
- Physical inactivity;
- Long-term stay of a person in one position due to professional affiliation;
- Obesity;
- Prolonged stressful situations;
- Injury to the neck and back of the head;
- Autoimmune processes that can provoke the destruction of cartilage tissue.
Adopting a healthy diet and moderate physical activity can minimize the likelihood of developing osteochondrosis.
Make an appointment Online booking
- Clinic on Krasnopresnenskaya +7 (499) 252-41-35 Volkov lane, 21
- Clinic on Varshavskaya +7 (499) 610-02-09 Varshavskoe highway, 75, building 1
- Clinic in Annino +7 (495) 388-08-08 Varshavskoe highway, 154, building 1
How to get rid of pain from a herniated disc
It is impossible to do this without the help of a specialist. Even if an acute painful attack passes on its own, you should consult a doctor, as the next attack may be more painful and prolonged.
What can you do at home?
You can try to reduce the intensity of pain on your own.
- For moderate pain, you can apply an anesthetic to the painful area:
- ointment or gel with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects - Pentalgin-gel, Ketoprofen, Fastum-gel, etc.;
- any anesthetic rubbing (Menovazin, etc.).
- For more intense pain, you can take a tablet from the same group of NSAIDs: Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nise, etc. and at the same time apply an ointment, gel or anesthetic solution externally.
- In case of severe pain, if the above procedures do not help, take a position that minimizes pain and ask your loved ones to call an ambulance.
Primary health care
Done by a doctor who will:
- Anesthetic injection - the same painkillers only in a solution intramuscularly. Sometimes glucocorticoid hormones are added to eliminate swelling, which helps reduce pinching. At the same time, a medicine is administered to relieve muscle spasm.
- If there is no effect, a paravertebral block is performed - the injection of an anesthetic substance (Novocaine) near the site of infringement.
- If the pain remains intense, the patient is hospitalized.
After eliminating the pain, you should go to the clinic and undergo an examination. The sooner you see a doctor, the greater the chance of stopping the progression of the hernia.
Specialized assistance
Treatment in a hospital depends on how painful the hernia is in the lumbar (or any other) region. For very severe pain that cannot be relieved, the following is carried out:
- Epidural block - an anesthetic is injected into the area of the spine between the dura mater of the spinal cord and the periosteum of the spinal canal.
- Electrophoresis with an anesthetic solution - a double effect is obtained - electric current and a medicinal solution.
- Acupuncture (acupuncture) – pain can be eliminated quickly and effectively.
Acupuncture and epidural block help relieve severe hernia pain.
In case of severe pain, the patient is prescribed bed rest. During this period, gentle massage and manual therapy techniques are possible. These methods relieve muscle spasms and eliminate pinching. Therapeutic exercises begin after pain is eliminated. Exercises should be done regularly, without breaks, gradually increasing the load. This allows you to strengthen the muscles that support the spine and prevent pinching of the nerve roots.
Each type of intervertebral hernia has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easy it is to get rid of a hernia in 10 sessions
Features of the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in “Health Plus”
In our medical center, patients with cervical osteochondrosis can undergo a course of ultrasonic wave therapy with permission from several specialists. These are fairly simple procedures for the patient, lasting 10–15 minutes. The duration of the course is determined individually and is 5–10 procedures 1–2 times a week.
During therapy, a sound wave of a given frequency and energy created by an ultrasonic therapy device acts on the diseased area of the spine, relieving pain and swelling, which allows you to restore normal neck mobility. The crunching sound decreases when moving the head. After the first procedure, the processes of regeneration of cartilage tissue are launched. In many cases, a course of shockwave therapy allows one to avoid surgical intervention, completely destroying osteophytes and returning patients to normal life.
Medical clinics have all the necessary diagnostic and treatment facilities, thanks to which we are able to diagnose cervical osteochondrosis, identify its symptoms and carry out effective treatment. The staff consists of experienced specialists who are constantly working to improve their skills and have become experts in the field of UVT. An initial consultation on the shock wave therapy method can be obtained free of charge, prices are lower than the market average. It is possible that after 1–1.5 months you will be able to practically forget about the troubles with your neck, headaches will reduce their frequency and intensity, and all that remains is to follow preventive measures.
What can hurt with spinal hernias?
It is worth knowing about the characteristic back pain associated with a herniated disc in order to seek medical help in time. In this section you will find answers to your questions related to back, neck and lower back pain.
Lower back pain
Pain due to a herniated disc in the lower back is the most characteristic symptom, known to absolutely everyone.
- Can my lower back hurt from a hernia?
Yes, maybe the pain can be of a very different nature. - Why does it hurt?
The most common cause is compression of the spinal nerve roots. Sometimes this is due to an inflammatory process or tissue irritation by proteins of the nucleus pulposus of the disc. Most patients know firsthand how a hernia hurts in the lumbar region. - Probable location and type of hernial protrusion
. If the lower back hurts, then most likely it is pinched nerve roots L1 - L. Sometimes pain waves spread along the front surface of the thigh, in such cases you can think about a lateral hernia. When the L3, L4 roots are affected, pain from the lumbar region can spread along the anterior inner surface of the thigh. The most characteristic pain is lumbar pain, spreading to the buttock area and the back of the thigh, which is typical for foraminal hernia L5 - S1. - What to do
? You can take a pain reliever, but then consult a doctor immediately. - How to relieve pain?
This is not easy to do. Sometimes severe pain goes away as suddenly as it started. But it is difficult to eliminate it with pills or some folk remedies. This can lead to increased pinching and complications. Therefore, there is no need to endure, it is better to immediately call an ambulance.
Leg pain
Pain from a spinal hernia in the leg can spread to the thigh or even lower - to the lower leg and foot.
Knee pain
- Can a hernia hurt?
Maybe, but rarely. Most often it hurts in the popliteal region, along the sciatic nerve and its branches. - Why does it hurt?
The joint may hurt when the sciatic nerve is involved, as it gives nerve branches to the knee joint. - Probable location/type of hernial protrusion.
L5 – S1, lateral or foraminal type. - What to do?
Undergo examination and the course of treatment prescribed by your doctor. - How to relieve pain?
Painkillers from the NSAID group (Diclofenac, Nise, etc.) internally in the form of tablets and externally in the form of an ointment.
Buttock pain
- Can a hernia hurt?
This may be one of the most common pains. - Why does it hurt?
Due to pinching of the spinal nerve roots. They give off fibers that then form the sciatic nerve. This nerve crosses the gluteal region and goes to the back of the thigh. - Probable location/type of hernial protrusion.
L4, L5, S1 – S3, lateral or foraminal hernias. - What to do?
Seek medical help. - How to relieve pain?
Painkillers for oral administration and ointments.
Pain from a herniated disc may spread to the leg
Shin pain
- Can a hernia hurt?
It may be that the pain occurs more often on the posterior outer surface of the lower leg and is often combined with muscle cramps. - Why does it hurt?
Due to pinching of the sciatic nerve. In the popliteal fossa, it is divided into tibial (runs in the middle of the back surface of the leg) and fibular (runs along the outer surface). - Probable location/type of hernial protrusion.
L4, L5, S1 – S3, lateral or foraminal hernias
. - What to do?
Contact your doctor immediately
.
Painkillers do not always help. - How to relieve pain?
Rubbing with Menovazine and taking NSAIDs orally.
Heel pain
- Can a hernia hurt?
It may hurt often. - Why does it hurt?
This is the same damage to the sciatic nerve due to pinched nerve roots. The tibial nerve, which arises from the sciatic nerve, innervates the heel. - Probable location/type of hernial protrusion.
L4, L5, S1 – S3, lateral or foraminal hernias. - What to do?
Examine and treat the identified disease. Painkillers alone cannot cure it. - How to relieve pain?
Rubbing with Menovazin, starting from the popliteal fossa to the heel.
Pain in the neck
With a cervical hernia, pain always occurs, but it is of a different nature.
- Can a hernia hurt?
Maybe this is one of the main symptoms. - Why does it hurt?
Due to the infringement of the nerve roots by hernial protrusion, tissue swelling and compression of the roots, irritation by substances of the nucleus pulposus. - Probable location/type of hernial protrusion.
Soreness is most often associated with lateral and foraminal hernias, since it is with these types of disease that the nerve roots are infringed. Median hernial protrusions are often accompanied by movement disorders. - What to do?
A cervical hernia is not something to joke about, because this section is connected to the medulla oblongata, which contains vital centers - the cardiovascular and respiratory. Therefore, you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible. - How to relieve pain?
Painkillers internally and externally in the form of ointments. But only in the form of emergency assistance, after which you should immediately consult a doctor.
Arm pain
Pain from a spinal hernia in the arm is also one of the characteristic symptoms.
- Can a hernia hurt?
Maybe it hurts very often. - Why does it hurt?
In the arm, pain due to a spinal hernia appears due to the involvement of the brachial plexus, formed from the nerve roots C4 - C7 and Th, in the pathological process - Probable location/type of hernial protrusion.
With a hernia of C5 - C6, pain radiates along the outer surface of the shoulder, forearm to the thumb. With a C7-Th1 hernia, the back of the shoulder, forearm, back of the hand, index, middle and ring fingers hurt. Most often this is the side type. - What to do?
Carry out courses of conservative treatment prescribed by your doctor. - How to relieve pain?
Severe pain can only be relieved in a clinical setting. At home, you can take a painkiller tablet and apply pain-relieving ointment to the painful area.
Side pain
This symptom is of the most vague nature; it is often mistaken for manifestations of other diseases.
- Can a hernia hurt?
Maybe. - Why does it hurt?
The nerve roots of the thoracic spine become pinched or become inflamed and swollen. The pain is usually one-sided, aching, paroxysmal, and difficult to relieve. - Probable location/type of hernial protrusion.
For disc herniation Th1 – Th12 of any type. - What to do?
Get examined and treated in a good clinic. - How to relieve pain?
The aching pain is exhausting and difficult to eliminate. Painkillers act slowly and for a short period of time, so it is best to seek medical help right away.
Headache
- Can a hernia hurt?
Maybe the pain is similar to migraines, half of the head hurts, often accompanied by dizziness and fainting. - Why does a hernia hurt?
Due to compression of the vertebral arteries that supply the brain, nerve cells cannot fully function without oxygen. - Probable location/type of hernial protrusion.
C6 – C2 – the vertebral arteries pass at this level. - What to do?
Contact your doctor immediately. - How to relieve pain?
Painkillers can dull the pain, but complex treatment is necessary to eliminate the lack of oxygen in the brain.
Heartache
When the hernial protrusion is localized in the cervicothoracic direction, headaches and pain in the heart area often occur
Pain in the heart with cervicothoracic localization of hernial protrusion is of a very different nature and often misleads not only patients, but also doctors.
- Can it hurt from a hernia?
Maybe. The pain is either constant aching or acute paroxysmal (like angina pectoris). - Why does a hernia hurt?
Compression or inflammation of the autonomic fibers of the roots of the spinal nerves of the cervical and thoracic regions. - Probable location/type of hernial protrusion.
C7 – TH5, giving branches of the autonomic nerves to the heart. Hernia of any type. - What to do.
Be examined not only by a neurologist, but also by a therapist or cardiologist. It is also worth remembering that cervicothoracic hernias are often combined with angina pectoris. In this case, treatment of two diseases is required. - How to relieve pain.
If such pain appears for the first time, take Nitroglycerin. If it doesn’t help, then the pain is purely neuralgic, you need to take any NSAID drug. In any case, call an ambulance to rule out myocardial infarction.
What types of intervertebral hernias are most difficult to treat?
4 stages of treatment for intervertebral hernia
How does a spinal hernia hurt?
With a hernia, not only the location of the pain, but also its nature can differ significantly. Each type of pain may indicate a specific condition or stage of the disease.
Acute pain due to intervertebral hernia
Attacks of acute pain can begin suddenly and also end suddenly.
Cervical lumbago – cervicago
Sudden severe pain in the neck, radiating to the head, collarbone or arm, occurs with a sharp turn or tilt of the head and has an acute shooting nature that does not allow the patient to move. Hence the name - cervical lumbago. It cannot be in an empty place; usually before this a person feels pain in the neck, but does not attach any importance to it. And the disease progresses, the disc protrudes beyond the spinal column and, with sudden movement, the nerve roots are pinched.
What to do in case of cervical lumbago:
- provide rest to the head and neck, no need to move;
- make a wide tourniquet out of a towel and place it around the neck - this will partially relieve tension from the neck muscles;
- apply cold to the neck - any solid product from the freezer, wrapped in a cloth;
- take a medicine from the NSAID group - Diclofenac, Nise, etc.;
- apply ointment or gel from the same group of drugs, for example, Voltaren, to the neck.
- Seek medical help.
Intercostal neuralgia
When the roots of the spinal nerves of the thoracic spine are pinched, severe pain appears along the intercostal nerves. The same symptoms can develop with inflammation of the intercostal nerves. The pain is very strong, often one-sided. This condition is especially dangerous on the left side, as it can easily be confused with an attack of angina.
Therefore, if an attack of intercostal neuralgia has developed for the first time, and you cannot understand why and what hurts, it is better to immediately call an ambulance. And then take a Nitroglycerin tablet: if it is an attack of angina, it will help relieve spasm of the arteries that supply the heart muscle and prevent myocardial infarction. With intercostal neuralgia, Nitroglycerin, of course, will not help, but it will not harm either.
Wait for the doctor and carry out treatment only as prescribed. If a doctor offers you hospitalization, do not refuse it: it is better to spend several days in the hospital and understand the situation (clarify the diagnosis) than to die from a myocardial infarction.
Lumbar lumbago - lumbago
Sometimes, against the background of habitual aches in the lower back or in the midst of complete health, severe pain in the lower back suddenly appears, forcing a person to remain in the position in which the pain found him. Most often this is associated with lifting weights or a sharp turn of the body with an already existing pathological process in the spine (osteochondrosis).
The attack is associated with infringement of the nerve roots of the lumbar discs. It can start abruptly and end just as suddenly. The duration of the attack varies, from several minutes to several days and even weeks.
First aid for lumbago:
- take the position in which the lower back hurts the least; better - lying on your back without a pillow with your legs slightly bent at the knees; you can put a small pillow under them;
- use medications from the NSAID group: take a Nise tablet orally and apply Voltaren gel to the lower back.
- Be sure to seek medical help, undergo examination and treatment.
Constant, aching pain due to a hernia
Constant aching pain with a herniated spine is very characteristic of this disease. When localized in the cervical region, one half of the neck, the area of the collarbone, shoulder blades, shoulder, and even one or more fingers may hurt. Aching pain may intensify at night due to tissue swelling and compression of the nerve roots.
If the thoracic region is affected, constant aching pain in the side or in the form of attacks may appear. Attacks of aching, wave-like pain in the side are often debilitating.
It is very difficult to get rid of constant aching pain due to a herniated spine.
Complaints of dull pain in the lower back are the most common. It can be constant, periodically disappearing or intensifying after physical activity. Unpleasant dull pain may appear in the buttock, lateral and posterior thighs. But more often they appear in the lower leg and foot area, especially in the heel area.
To get rid of such pain, painkillers alone will not be enough. A full course of conservative treatment will be required, selected by the doctor individually for the patient.
It is quite possible to live without pain, you just need to seek medical help. And choose the right clinic, the specialists of the Paramita clinic, Moscow, will relieve you of both acute and aching old pain.
Pain after hernia surgery
We use non-surgical hernia treatment techniques
Read more about our unique technique
Experts have long come to the conclusion that surgery for a herniated disc is not a panacea at all - it is a necessary measure. Despite the fact that today there are carefully verified gentle technologies for such operations, no one can guarantee the absence of subsequent relapses and pain.
And this is not always due to the skill of the neurosurgeon. Statistics show that the main reason is insufficient postoperative rehabilitation. Many operated patients either completely ignore it or perform it in an abbreviated version. And since the cause of the disease has not gone away, it can recur in the same disc, in adjacent discs, or even in other parts of the spine.
What to do? Remember that a hernia does not develop out of nowhere and treat a chronic disease according to all the rules using conservative methods.
The duration of rehabilitation and the techniques used within its framework should be chosen by the attending physician. As for painkillers and ointments, you need to understand that this is a forced temporary measure that does not in any way contribute to healing.
Diagnostics
The main and most informative methods for diagnosing osteochondrosis include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI images with a high degree of detail reflect the condition of not only the bone tissue of the spine, but also soft tissue - muscles, cartilage, blood vessels, nerves and intervertebral discs. If there are contraindications to MRI (presence of metal prostheses, pacemakers), computed tomography is prescribed, but the information content of the method is much lower in terms of diagnosing osteochondrosis.
Frequently asked questions about the disease
Can a hernia cause joint pain?
They can, if large nerves are pinched, for example, the sciatic, sending branches to the joints.
Can my stomach hurt from a hernia?
Maybe when the pathology is localized in the cervical and thoracic spine. This is due to infringement of the autonomic nerves innervating the internal organs.
Why does a hernia hurt at night?
At night, the body warms up, blood vessels dilate, tissues swell, and nerve roots are compressed, which increases pain.
Hernia hurts during pregnancy - what to do?
If the disease was identified before pregnancy, it must be treated before conception. During pregnancy it will help:
- weight control;
- wearing a bandage;
- therapeutic exercises and swimming;
- Most painkillers are contraindicated, so you cannot take them yourself, but an obstetrician-gynecologist can choose a safe remedy.
Pain due to a herniated spine indicates that it is necessary to undergo an examination and complex treatment prescribed by a doctor. This is the only way to stop the destruction of the spine and disability.
Self-treatment with folk remedies can lead to serious complications. But it’s never too late for treatment; the Paramita clinic will help you in any case.
Literature:
- Ibaturin I.A., Tarasko A.D. Pathogenetic basis of the action of paravertebral novocaine blockade / Kazan Medical Journal. - 1995. - v. 76, no. 2. - p. 93-96.
- Kuzmenko V.V., Fokin V.A., Sokov E.L. and others. Psychological methods for quantitative assessment of pain./ Soviet Medicine.-1986, No. 10.- p. 44-48.
- Shostak N. Back pain, diagnostic and treatment options // Doctor - 2005. - No. 5. - P. 3-5.
- Braddom RL Physical medicine and rehabilitation. Philadelphia, 1996. 1301 p. 12.
- Sturzenegger M., Newell DW, Douville C., Byrd S., Schoonover K. Stroke 1994, 25:. 1776-1783.
Themes
Intervertebral hernia, Spine, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 09.16.2020 Date of update: 12.11.2020
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (1)