Trigeminal neuritis is sometimes mistakenly called trigeminal neuritis of the facial nerve, but more often another term is used - “neuralgia” - which literally means pain. This is an inflammatory process in the fifth pair of cranial nerves.
Our expert in this field:
Lashch Natalia Yurievna
Neurologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor. Laureate of the Moscow City Prize in the field of medicine.
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Some facts about the disease:
- On average, it occurs in 6-8 people out of every 100,000.
- Women get sick more often than men.
- In most cases, the disease is diagnosed in people over 40-50 years of age.
There are two types of trigeminal neuralgia:
- Primary occurs as an independent disease.
- Secondary – a symptom of other pathologies.
How does the trigeminal nerve work?
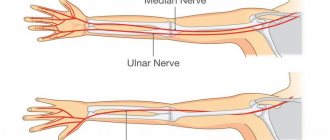
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth pair of cranial nerves (there are 12 pairs in total - they innervate the organs of the head and neck). It is paired - that is, it is on the right and left. It consists of two types of nerve fibers - sensory and motor. After exiting the skull, the trigeminal nerve divides into three branches, which seem to cover the entire face:
- Ocular - is sensitive, innervates the eyeballs, eyelids, lacrimal sacs, mucous membrane of the nose and its paranasal sinuses, lacrimal gland, forehead skin.
- Maxillary - also sensitive, innervates the skin of the cheek, temple, teeth and gums of the upper jaw, mucous membrane of the palate, nose.
- Mandibular - responsible for both sensitivity and movement, innervates the muscles of mastication, muscles of the palate, eardrum, mucous membrane of the cheek, anterior 2/3 of the tongue, skin of the temple, the front of the ear and external auditory canal, teeth and gums of the lower jaw.
Description of the pathological condition
The disease of the nerve branches located in the tongue and lower jaw is accompanied by pain and salivation disorders. Nerve clusters (nodes) located in this area belong to the peripheral parts of the NS. Despite the fact that neurologists anatomically separate the sublingual and submandibular nodes, degenerative processes occur in them simultaneously. This is due to the fact that numerous neural connections are distributed between the channels. This allows the pathology to be classified as one disease.
Treatment of trigeminal neuritis
Typically, treatment of the disease begins with medications:
- Anticonvulsants . Usually the drug carbamazepine or phenytoin, oxcarbazepine is prescribed; the doctor selects the dose individually. Over time, these medications may become less effective, in which case your doctor will increase the dosage. However, anticonvulsants have some side effects that may make it difficult to use them.
- Antispasmodics . Used together with anticonvulsants. For example, a neurologist may prescribe baclofen for you.
- Physiotherapy . Diadynamic currents, ionogalvanization with novocaine, and ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone help to cope with the symptoms of trigeminal neuritis.
If neuralgia manifests itself in the form of severe toothaches, painkillers are used, and ointments with anesthetics are rubbed into the gums.
If medications no longer help, the neurologist raises the question of surgical treatment of trigeminal neuritis. The following operations are possible:
- Microsurgical decompression . During the intervention, compression of nerve fibers by blood vessels is eliminated. Typically the incision is made behind the ear. The operation effectively eliminates pain, but after it a relapse may occur, complications such as hearing loss, numbness of the face, paresis and paralysis of the facial muscles.
- Transection of nerve branches . In this case, the transmission of pain impulses is disrupted.
- Radiosurgery (gamma knife). A special device generates a high dose of ionizing radiation, which damages nerve fibers. If painful attacks begin to bother you again in the future, the procedure can be repeated.
There are other surgical methods for treating this type of neuritis.
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
The trigeminal nerve provides sensation to the skin of almost the entire face and front of the head. It is mixed in structure, that is, it is responsible for both sensitivity and movement, but the motor fibers are thinner. Still, the trigeminal nerve is mostly sensitive. This determines the characteristics of the symptoms of the disease.
Possible complications
Over time, symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can give rise to neuropathic complications and lead to the development of secondary pain syndrome in the head. In the chronic form of the disease, the auditory and facial nerves are irritated. Without treatment, trigeminal neuralgia can lead to more serious complications:
- dystrophy of masticatory muscles;
- decreased sensitivity of the affected area;
- Sykinesia (cooperative movements in which one nerve controls many muscles);
- contracture and spontaneous contraction of the facial muscles;
- conjunctivitis.
What are the symptoms of trigeminal neuritis?
I am bothered by excruciating attacks of shooting, stabbing pains. They usually last for a few seconds or minutes and then suddenly go away. Most often, pain occurs in the area of innervation of the two lower branches of the trigeminal nerve: in the jaws, cheeks, teeth, gums, lips. In the area of innervation of the upper first branch of the nerve (forehead, eyes), pain occurs less frequently.
Usually only the right or left half of the face is affected. During an attack, a grimace of pain appears on the face, the person freezes, is afraid to move, and holds his breath. Sometimes the patient, on the contrary, begins to breathe heavily and frequently and rubs the sore spot.
Over time, attacks become more frequent and severe. There are certain “trigger zones” - most often they are on the lips and gums. Touching them, exposure to high or low temperature (cold or hot food) provoke painful attacks.
Often, pain due to neuritis is accompanied by vegetative symptoms, such as redness of the facial skin, lacrimation, and the release of large amounts of saliva.
Are you experiencing similar symptoms? Perhaps this is trigeminal neuritis or another disease, for example, arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint, multiple sclerosis. Only an experienced neurologist will be able to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Symptoms of arthrosis of the jaw joint and diagnosis of the disease
The first signs of the disease usually appear between the ages of 32 and 50 years. If the patient is well informed about the symptoms and treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint, the disease can be recognized in its infancy.
Symptoms of arthrosis of the jaw - a reminder for self-diagnosis!
You should be alert to the following changes:
- regular clicking in the joint when moving the lower jaw - the crunching seems to “send to the head”;
- limited mobility - for example, when yawning, the mouth does not open as wide as before;
- deterioration of hearing - sounds become muffled, the ears are often blocked, a characteristic noise is heard (as if a seashell was applied to the ear), deafness develops over time;
- blurred vision, which is usually accompanied by pain in the eye from the affected joint;
- pressing and bursting headaches, especially in the temporal, parotid-masticatory region;
- frequent cramps, usually painful;
- nasal congestion;
- dizziness and other problems with the vestibular system;
- abnormalities in the functioning of the salivary glands (usually dry mouth);
- facial asymmetry that has not been observed before - caused by misalignment of the jaw, the formation of bone spurs or swelling of the joint;
- fatigue when chewing food, discomfort when chewing hard and tough foods;
- morning stiffness in the jaw joint;
- decreased facial expression and difficulty swallowing food;
- increasing pain in the joint;
- toothache and tooth wear;
- numbness of the skin or mucous membranes near the affected joint;
- a feeling of “jumps” in the joint - sometimes even noticeable from the outside.
Acute piercing pain with arthrosis of the jaw joint can radiate to the ear, temple or back teeth on the affected side. However, more often patients suffer from a dull, aching pain in the jaw. In old age, pain due to arthrosis of the lower jaw may be absent, giving way to aches (including when the weather changes), heaviness and discomfort in the joint.
If, shortly before the onset of symptoms of jaw arthrosis, you have suffered from arthritis of the jaw joint, an acute infection, an exacerbation of chronic otitis, facial trauma or tooth loss, consult a doctor immediately.
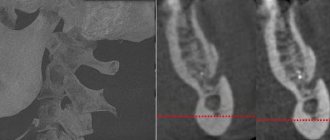
Medical diagnosis of arthrosis of the jaw
When diagnosing arthrosis of the lower jaw, the doctor uses X-rays to determine the type of changes in the joint - sclerotic (replacement of normal bone tissue with abnormal one) or deformational (associated with bone abrasion or the growth of bone growths - osteophytes).
Also, x-ray examination allows us to determine the stage of arthrosis of the facial jaw:
1st - onset of the disease without significant changes in the bone;
2nd - destruction of the articular head with noticeable signs of the recovery process;
3rd - pronounced growth of bone tissue, which prevents movement in the joint;
4th - complete immobility of the jaw due to the fact that the elements of the joint are not consistent with each other.
In addition to x-rays of the jaws, the doctor may prescribe a general blood and urine test, a biochemical blood test, zonography of the affected joint, or diagnostic arthroscopy.
Between the onset of the disease and its final stage, 20-30 years may pass, or maybe 6-12 months. Do not ignore the first symptoms of arthrosis of the jaw joint. Arthrosis of the jaw is completely reversible only at the 1st stage!
Long term forecast
With treatment (and in rarer cases, without it), remission - the symptoms of trigeminal neuritis do not bother you for several months or even years. Many patients are helped by medications, but over time they begin to act weaker, and they have to resort to surgical treatments.
Frequent and severe pain attacks can reduce performance and quality of life. In young patients, the prognosis is more favorable, in older people (and it is in them that the disease occurs more often) it is more serious.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
The cause of trigeminal neuritis is not always found. In this case, the disease is called idiopathic . If the damage to the nerve trunks is caused by some other disease, they speak of symptomatic , or secondary , neuritis.
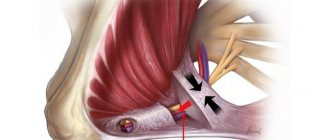
Most often, the disease develops as a result of compression of the nerve by improperly located vessels. In most cases, the superior cerebellar artery is to blame.
Modern medicine sees the mechanism for the development of inflammation and pain as follows. Chronic compression causes the trigeminal nerve to lose myelin , a sheath that is made of fat and is important in conducting nerve impulses. An inflammatory process develops. Subsequently, degeneration of axons - the long processes of nerve cells that make up the nerve fiber.
Causes of neuralgic anomaly
Factors in the development of neurological disorders in the jaw area are both internal and external primary sources. Internal reasons include:
- frequent hypothermia;
- systematic damage to oral tissues by inflammatory processes;
- complications after medical and dental procedures;
- infections of the mouth and throat, sore throats, inflammation of lymphatic deposits;
- chronic diseases of the peritoneum, gastrointestinal tract, pelvis, sternum.
External provocateurs of the disease are:
- severe intoxication or chronic poisoning with industrial poisons;
- constant interaction with household chemical compounds;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- accumulation of slag, intoxicating substances that are not excreted by the liver;
- metabolic disorders as a result of diabetic syndrome;
- damage to the endocrine system.
A variety of allergic conditions, vegetative-vascular dystonia, chronic blood pressure disorders, hypotension, and hypovitaminosis can aggravate the situation.
What other causes can lead to trigeminal neuritis?
In addition to vascular compression, other causes can lead to the disease:
- Age-related changes in the body.
- Compression of the nerve branches in the bone canals of the skull in which they pass. These canals can be narrowed from birth, or as a result of certain diseases: caries, sinusitis.
- Compression by intracranial tumors.
- Injuries to the face, head.
- Multiple sclerosis. This is a chronic disease in which the myelin sheath is destroyed. Trigeminal neuritis affects 3-4% of patients with multiple sclerosis.
- Postherpetic neuralgia. Its cause is herpes zoster.
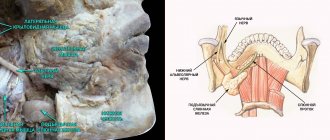
What is mandibular nerve injury?
By this concept, dentists mean injury to one of the nerves:
- chin;
- lingual;
- alveolar.
Types of injuries include sprain, compression, crushing and rupture - partial or complete. The cause of the stretching is the long-term retraction of the mucoperiosteal flap, which is created by an implant of greater length than necessary. Crush injuries and compression are caused by needle injuries during the administration of anesthesia. Rupture occurs in two cases: when cutting the mucosa or during preparation of the hole for the implant.
Causes of pain attacks in trigeminal neuritis. What are triggers?
Triggers are irritants, “triggers” that provoke an attack of pain. These can be a variety of mechanical or temperature effects on the skin of the face and mucous membranes.
Most often, the following factors act as triggers: shaving, eating food (especially cold or hot), any touching the face, drinking, talking, brushing teeth, wind, applying makeup, washing, smiling. When habitual daily actions always lead to excruciating pain, this significantly reduces the quality of life and interferes with work.
When you see your doctor, tell your doctor what triggers lead to attacks in your case.
Why might this happen?
The reasons are obvious:
- Dental nerves are sensitive to cold.
- Prolonged exposure to wind on an unprotected face.
- Lack of headwear in cold weather.
- General hypothermia of the body.
Possible provoking factors should also be highlighted
- Development of caries.
- Tooth chips and injuries.
- Tooth infection.
- The use of low-quality fillings in dental treatment.
- Poor quality prosthetics.
How does the treatment of neuritis depend on the causes?
If the cause of trigeminal neuritis is not known, all that remains is to deal with its main manifestation – pain. The neurologist prescribes various medications, and if they stop helping, he recommends surgery.
If the cause of the disease is known, you need to try to eliminate it. For example, if a patient is diagnosed with multiple sclerosis, special therapy is prescribed that helps slow down the progression of the pathology. If the nerve is compressed by an artery or the walls of a bone canal, the compression must be removed.
Get a consultation with a doctor
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Sometimes, before the correct diagnosis is finally established, a patient suffering from trigeminal neuritis has to see more than one doctor. It is extremely important to start treating the disease as early as possible. It has been proven that the longer a person suffers from trigeminal neuralgia, the more difficult it is to cope with the pathology.
Causes and prevention of mandibular nerve injuries
The only cause of such damage is considered to be medical errors. Since in preparation for implantation, X-rays of the jaw are taken, which the doctor must carefully study so that when choosing an implant and a place for it, he does not injure the nerve, the injuries are caused by his unprofessionalism or negligence.
Damage to the mandibular nerve most often occurs when:
- improper administration of anesthesia - needle injury;
- choosing an implant that is too long;
- damage by an instrument - when preparing the site for the implant.
The only way to avoid such an injury is for a doctor to responsibly approach the stage of preparation for surgery, carefully studying the condition and structure of his patient’s jaw. The only way of prevention for the patient is to choose a trusted clinic and a highly qualified doctor. Specialists at the Implantmaster clinic have been able to reduce the number of injuries of this kind to 2%, since they carefully study three-dimensional photographs of a person’s jaw before implantation, and can correctly assess the condition of the bone tissue, the location of nerves and blood vessels, and select the optimal size of the implant.
Diagnosis of trigeminal neuritis: what happens during an appointment with a neurologist?
An appointment with a doctor begins with a conversation. First of all, it is important for a neurologist to get answers to three questions:
What is the nature of the pain? Is it typical for this disease ? With trigeminal neuritis, pain attacks occur suddenly, they are strong, painful and pass quickly.
Where does the pain occur ? When the trigeminal nerve is damaged, pain is localized on the face, in certain places.
What triggers lead to seizures ? Usually this is touching the face, exposure to wind, high and low temperatures.
You will be asked how long you have been experiencing symptoms, whether you suffer from any chronic diseases, and whether you are receiving any treatment. Then the neurologist will examine you and press on certain points on your face where the branches of the trigeminal nerve enter the skin. A general neurological examination will be performed to diagnose any possible medical conditions that may be causing your symptoms.
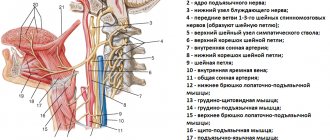
Diagnosis of neuralgia of the submandibular and sublingual nodes
A neurologist can detect and diagnose diseases of the vegetative nodes during a personal examination of the patient. To establish an accurate diagnosis, topical diagnostics is used, which includes:
- patient interview;
- analysis of complaints;
- examination using palpation and additional techniques;
- as well as identifying objective signs of pathology.
Since there are several vegetative nodes in the head and face area, and the symptoms of their diseases are very similar, the main task of the neurologist during the initial examination will be to identify the location of the disease.
Using sliding and fixing palpation, the specialist identifies the localization of the pathological process. Sometimes pinching or superficial pain stimulation methods are used for accurate diagnosis.
If the doctor has doubts about the results of topical diagnostics, a diagnostic blockade technique is used, which makes it possible to absolutely accurately establish the source and localization of neuralgia. The blockade is carried out on an outpatient basis by injecting local anesthetics (novocaine, lidocaine, trimecaine) into the painful area. Pain relief for a while allows the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis.
Symptoms of neuralgia of the submandibular and sublingual nodes often have similar symptoms to inflammation of the gums and internal structure of the teeth. To rule out dental diseases, you may need to consult a specialist in this field.
What diagnostic methods can a doctor prescribe for trigeminal neuritis?
The disease can be caused by various reasons, sometimes very serious (for example, cancer). Diagnosing them is not always easy. Depending on your complaints and information obtained during the examination, the neurologist may prescribe various instrumental studies and laboratory tests.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the head is most often used. This diagnostic method helps to identify pathological changes in the brain characteristic of multiple sclerosis and intracranial tumors.
The doctors of the medical center International Clinic Medica24 adhere to modern current standards - this guarantees that you will be prescribed all the tests necessary in your case, the doctor will not miss anything. At the same time, the coordinating doctor in our clinic will make sure that only truly necessary procedures are prescribed to you, so that you do not overpay for unnecessary things. All types of diagnostics are carried out using our medical center’s own equipment.
The material was prepared by Natalya Yurievna, a neurologist at the international clinic Medica24, Candidate of Medical Sciences Lasch.
Home remedies
Before treating trigeminal neuralgia at home, you should consult a doctor, since many remedies can only worsen the situation. If the specialist allows it, it is also possible to use various home recipes.
According to recommendations for trigeminal neuralgia, it is worth consuming orally or lubricating the affected side with birch sap. You need to drink 4-5 glasses per day. Heated buckwheat folded in cotton cloth will help relieve pain. The compress is made 2 times a day, keeping it at the site of inflammation until it cools down. At home, it is useful to massage the sore area: rub, stroke and lightly knead the area of inflammation.