Determination of the severity of harm caused to health due to existing bodily injuries is carried out within the framework of a forensic medical examination.
The concept of harm to health in this case is interpreted as a violation of the integrity of human tissues or organs, a violation of the functional state of limbs or organs, as well as diseases or other pathological conditions caused by bodily injuries. A forensic medical examination to determine the severity of harm caused to health due to existing bodily injuries can be initiated by a resolution of representatives of investigative bodies, inquiry bodies, or a court order. The prosecutor's office, the Ministry of Internal Affairs or the court may issue a written order to conduct a forensic medical examination. In terms of the procedure, these two studies are practically no different from each other. However, the result of the examination is an expert opinion, and the result of the examination is a medical examination report. This act does not have legal evidentiary force, therefore, in most cases, an examination is prescribed to determine the severity of the harm caused to health due to existing bodily injuries.
The severity of harm to health is determined by the following characteristics:
- The danger of the inflicted bodily harm to the life of the victim.
- Total duration of health disorder.
- Stable disability.
- Loss of an organ (limb) or cessation of functioning of an organ (limb).
- Loss of hearing, vision or speech.
- Complete loss of professional ability to work.
- Mental health problems, drug or toxicological addiction.
- Irreversible facial disfigurement.
- Abortion.
To determine whether harm to health has occurred, the presence of at least one of the listed characteristics is sufficient. If there are several signs, the severity of the harm caused to health is determined by the most severe of them. Life-threatening conditions are those that can lead to death.
It should be noted that irreversible facial disfigurement is not a medical concept, so establishing this characteristic is not within the competence of a forensic expert.
Life-threatening serious harm to health
Injuries that are life-threatening to the victim are usually divided into two groups. The first group of bodily injuries dangerous to human life includes:
- Penetrating wounds of the head (skull). Regardless of whether the brain was damaged.
- Fractures of the base of the skull and bones of the cranial vault, with the exception of isolated cracks of only the outer plate of the cranial vault, as well as fractures of the bones of the facial part of the head.
- Severe brain contusions, as well as moderate ones, if there are signs of damage to the brainstem.
- Penetrating spinal wounds, regardless of whether the spinal cord is involved.
- Fractures of the cervical vertebral arches, including fractures-dislocations.
- Unilateral fractures of the arches of the first and second cervical vertebrae, regardless of whether the spinal cord is damaged.
- Subluxations and dislocations of the cervical vertebrae.
- Fracture-dislocation or fracture of one or more thoracic or lumbar vertebrae due to impaired functioning of the spinal cord.
- Injuries in the neck with penetration into the larynx, esophagus, trachea, lumen of the pharynx or damage to the thymus and thyroid glands.
- Injuries in the chest area with penetration into the pericardial cavity, into the pleural cavity or into the mediastinal tissue. Regardless of damage to internal organs.
- An abdominal wound penetrating into the peritoneum.
- Injuries to the abdomen with penetration into the intestines (except for the lower segment of the rectum) or into the bladder cavity.
- An open wound of the pancreas, kidneys or adrenal glands.
- Rupture of any internal organ, including the ureter, membranous section of the urethra, and prostate gland.
- Double fracture of the pelvic ring in the posterior and anterior parts with loss of continuity. Or a bilateral fracture of the posterior pelvic half-ring with loss of continuity of the pelvic ring and rupture of the iliosacral joint.
- Open fracture of the humerus, femur or tibia (long tubular bones), open injuries to the knee and hip joints.
- Violation of the integrity of the main blood vessels (aorta, large arteries and corresponding veins).
- Thermal burn of the third or fourth degree with the affected area exceeding 15% of the skin. Third degree thermal burn with damage to more than 20% of the skin. Thermal burn of the second degree with damage to more than 30% of the skin.
The second group of life-threatening bodily injuries includes injuries that resulted in conditions that threaten human life. Such conditions include:
- Severe shock of the third or fourth degree.
- Coma caused by various reasons.
- Extensive bleeding and large blood loss.
- Collapse, severe cerebral circulatory disorders, acute heart failure, acute vascular failure.
- Acute renal failure.
- Acute liver failure.
- Severe degree of acute respiratory failure.
- Purulent-septic tissue lesions.
- Circulatory disorders causing internal organ infarction, thromboembolism, gas or fat vascular embolism, gangrene of the extremities.
- A complex of several conditions that threaten the life of the victim.
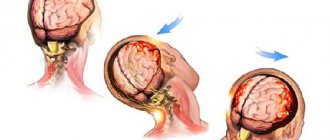
What is a traumatic brain injury?
This is a closed (CTBI) or open (depending on the classification) traumatic brain injury, damage to soft tissues, cerebral membranes, blood vessels and nerves of the brain. Most often, injuries are caused by mechanical impact and most are combined - they include several types of trauma (bruises, fractures, ruptures).
Traumatic brain injury is divided into two main types – open and closed.
- In the first option, there are ruptures of the skin and connective tissue, as well as a possible violation of the integrity of the skull. If an open injury is accompanied by involvement of the subdural membrane, then the injury is considered penetrating.
- With the closed type, there is no damage to the connective tissue aponeuroses of the head, although the skin may be cut.
Moderate health damage
The qualifying characteristics of the average severity of harm caused to the victim’s health are:
- There is no direct danger to the life of the victim.
- Absence of severe conditions characterizing harm to health as serious in consequences.
- Long-term health disorder (loss of ability to work for more than 21 days).
- Persistent loss of ability to work by no more than one third (from ten to thirty percent inclusive).
○ Responsibility and punishment for assault.
The Criminal Code provides for the following as punishment for assault:
- A criminal fine of up to 40 thousand rubles.
- Mandatory work.
- Correctional work.
- Arrest.
- Restriction of freedom.
- Deprivation of liberty.
What punishment will be assigned to your offender will be decided by the court, based on the severity of the harm caused, the presence of aggravating circumstances, such as alcohol intoxication, the offender’s criminal record, relapse, etc.
The procedure for determining the severity of harm caused to health due to existing bodily injuries
The procedure for conducting an examination to determine the severity of harm caused to health due to existing bodily injuries is carried out in accordance with the guidelines for conducting forensic medical research. The research can be carried out exclusively on documents, but in special cases, as well as in the presence of reliable documents that correctly and fully describe the damage inflicted on the victim. Most often, the examination is carried out with an examination and interview of the victim. The research includes the following stages:
- A thorough interview of the victim, inspection of existing injuries or traces of their infliction.
- Collection of all documents available on the case: medical records from the clinic at the place of residence and the emergency room, examination reports, records of the ambulance team, photographs.
- Examination and interview of the victim.
- If there are internal damages, ultrasound or other special studies are performed (if necessary).
- If important documents are necessary or missing, the expert conducting the examination may request the missing papers.
- Study of all provided documents.
- Drawing up an expert report, which contains the conclusions made by the expert.
How to stop beatings and bring the offender to justice?
The sooner you contact a forensic expert, the easier it will be for specialists to establish the fact of harm. This can be done even before writing the application.
You can contact both specialized authorities - a forensic medical examination, and a hospital, having received a certificate from a traumatologist or neurologist.
If you write a statement about beating, then an examination will be ordered by law enforcement agencies.
What to do when contacting the police:
- How to stop beatings and bring the offender to justice? Write a statement with a detailed description of the crime, the characters involved, the methods of inflicting pain and the locations of the blows.
- Examination by an expert in the direction of the police, followed by a conclusion on the severity level.
If you decide to identify harm yourself, then you should adhere to the following algorithm:
- Visiting a clinic, hospital, or emergency room. There, a certificate is issued with the diagnosis upon application, the nature of the injuries and the time of admission to the medical facility.
- With all the documents, go to the police to write a statement.
- Repeated examination with the participation of forensic doctors.
The last point is not always fulfilled, since the investigation may only need documents from the hospital.
Important! Battery is a serious offense. Do not be afraid to seek help from law enforcement agencies; beatings can be repeated and lead to more serious consequences.
What is the legislative framework for the examination of living persons (victims, accused, suspects)?
Federal Law of May 31, 2001 No. 73-FZ “On state forensic activity in the Russian Federation.” Article 25 of the Law describes the procedure for drawing up an expert opinion, as well as the components necessary to be included in it.
Article 111 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation describes the signs of intentional infliction of grievous bodily harm, as well as the degree of punishment provided for such a criminal act.
Article 112 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation describes the signs of intentional harm to health of moderate severity, as well as the degree of punishment provided for such a criminal act.
Article 115 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation describes the signs of intentional harm to health of mild severity, as well as the degree of punishment provided for such a criminal act.
Article 113 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation describes the signs of causing serious or moderate harm to health in a state of passion, as well as the degree of punishment provided for such a criminal act.
Article 114 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation describes the signs of causing grievous or moderate harm to health in case of exceeding the limits of necessary self-defense or in case of exceeding the measures necessary to detain a person, as well as the degree of punishment provided for such a criminal act.
The procedure for conducting an examination to determine the severity of harm caused to health due to existing bodily injuries is subject to the Rules for determining the severity of harm to health, approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 17, 2007 (No. 522).
○ Article of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation for beatings.
Article 116 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation is devoted to the corpus delicti of assault and the punishment that the offender faces if such actions are committed against the victim.
As we already know (see the article on examining battery), battery is repeated blows or other violent acts committed against the victim.
The condition for the use of this composition is the infliction of physical pain by the actions of criminals. In this case, pain and suffering must be caused by the actions themselves, and not by their consequences.
A hit against a wall due to the fact that the victim was pushed will not be regarded as beating. But the actions that consisted of being dragged around the room by the hair, hit in the face, etc. - just fit within the framework of Article 116 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
In my practice, there was a case when parents forced a child to kneel in a corner for a long time, thereby causing him physical pain. The actions of the mother and father in this case were qualified precisely as beatings inflicted on their minor child.
○ What to do if you were beaten?
Current legislation establishes that this crime is a crime of private prosecution, that is, it can only be initiated at the request of the victim and will be proven by him in court. But this does not mean that the victim will be left to the mercy of fate.
If you have become a victim of a beating, the first thing you need to do is contact the police with a statement in which you need to set out all the circumstances of the incident, accurately describe the blows and the place where they were applied, the violent actions that caused pain. You should not hide anything, just as you should not fantasize - the more accurately the facts are presented, the more accurately and quickly the criminal will be punished.
After the victim contacts the police, and such an appeal is mandatory from the point of view of the procedure for collecting and recording evidence in the case, the police will conduct a pre-investigation check, during which the parties to the conflict and witnesses will be interviewed.
The most important thing is that the victim will be given a referral to undergo a forensic medical examination, the conclusion of which confirms the fact of causing physical harm.
It is, of course, better to undergo an examination by a doctor before receiving such a referral, preferably immediately after the beating. This will guarantee the recording of the fact of causing bodily harm - the main subject of proof, and, as a consequence, the punishment of the offender.
Further, based on the results of the audit, the case will be sent to court or closed for lack of corpus delicti.
If you have any questions, I’d be glad to hear them in the comments!
Published by: Vadim Kalyuzhny, specialist of the TopYurist.RU portal