10.10.2014
Maltseva Marina Arnoldovna
Head of the consultation department - neurologist, specialist in the field of extrapyramidal pathologies, doctor of the highest category
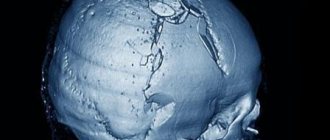
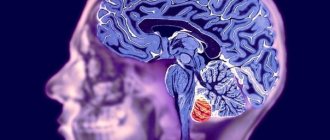
A fracture of the base of the skull is one of the most severe traumatic brain injuries. This condition is accompanied by damage to one or even several bones that form the base of the skull. Damaged in this case may be:
- occipital bone;
- temporal bone;
- ethmoid bone;
- sphenoid bone.
A fracture of the base of the skull can occur from a variety of serious physical injuries: car accidents;
- when a person falls from a great height;
- when hitting the face in the area of the lower jaw or base of the nose.
In most patients, the base fracture occurs from the arch. Statistics say that the number of such patients reaches 59%.
Symptoms of a basal skull fracture
A fracture of the base of the skull is an open traumatic brain injury. It is worth noting that injuries accompanied by the release of blood or cerebrospinal fluid from the ear canals or nose are classified as open penetrating head injuries.
Based on location, injuries are divided into fractures:
- middle cranial fossa;
- anterior cranial fossa;
- posterior cranial fossa;
The most common fractures encountered in medical practice are middle cranial fossa fractures. Such fractures can be longitudinal, transverse or oblique. Most often, doctors fix longitudinal fissures in the temporal lobes. In this case, fractures can spread through various holes, crevices and thinning of the skull bones.
Among the main manifestations of fractures:
- bleeding from the ear canal;
- decreased hearing acuity;
- release of cerebrospinal fluid;
- the appearance of bruises in the area of the temporal muscle.
All of the above damage occurs when there is a blow to the occipital region.
It is worth noting that transverse fractures are clinically characterized by the patient being completely deaf. The patient may also exhibit disturbances in vestibular function, loss of taste in the two anterior thirds of the tongue, and may also experience peripheral facial palsy.
First aid
If you notice signs of a skull fracture, seek medical attention immediately. Before arriving, doctors do not want to give the victim anesthesia, since some medications can significantly increase bleeding or breathing problems, as well as provoke the patient into a coma.
Before the ambulance arrives, it is important to provide first aid:
- The patient should be placed on his back on a hard surface, with his head buried in the ground. The pillow should not be placed under the head. If the patient is unconscious, he should also be placed on his back, but in a half-turn position with a roll of clothing on one side. You need to tilt your head slightly so as not to choke when vomiting.
- Treat the head wound with an antiseptic and apply a sterile bandage.
- Remove the victim's dentures, jewelry, watches, and glasses.
- Remove any clothing that may be tight fitting, obstructing blood flow and breathing.
- Bring a cold object wrapped in a clean cloth to your head.
If the victim is not breathing, empty the vomit from the mouth and perform mouth-to-mouth resuscitation using chest compressions. To avoid direct contact with the victim's mucous membranes, use a piece of clean, permeable cloth.
If there are no breathing problems, it is permissible to give the injured person Analgin with diphenhydramine. When transporting a patient to a medical facility, the following activities are performed:
- Glucose, diuretics and cardiac drugs are administered intravenously. However, in case of severe bleeding, diuretics should not be used. Instead, Polyglucin or Getinol is administered. Lasix is most often used as a diuretic, and cordeamine and sulfacamphocaine are the main medications used to support heart muscle function.
- If breathing problems occur, the patient is inhaled through an oxygen mask.
- Convulsions and increased motor activity are suppressed by Suprastin.
Polyglucinum is prescribed for severe bleeding.
The use of narcotic anesthetics is unacceptable. Such drugs can cause respiratory arrest.
Consequences of skull base fractures and prognosis
Experts note that the future quality of life of patients directly depends on the quality of rehabilitation after TBI, as well as on the nature of this injury, pathologies and possible infections. In the absence of purulent inflammation, in most cases, doctors give a favorable prognosis.
If there are infectious complications, doctors talk about the possibility of developing complications such as encephalopathy, frequent headaches, uncontrolled increase in blood pressure, etc. in the future. This condition may also be accompanied by recurrent epileptic seizures.
Some traumatic brain injuries can cause excessive bleeding, coma, and even death. With such injuries, the prognosis of doctors is extremely unfavorable.
Bleeding of small volumes, intracerebral hematomas, etc. can form. It is worth noting that in this situation, the patient’s future directly depends on the timeliness and adequacy of the treatment.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 3/5 — 10 votes
Share article on social networks
4.Treatment
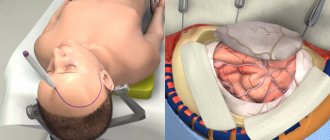
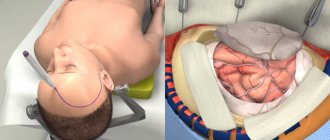
Any depressed fracture of the skull bones is a clear and absolute indication for neurosurgical intervention. As a rule, such an operation is very technically complex and can last several hours. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the mechanical compression of the brain substance; Antiseptic and hemostatic treatment of damaged areas, reposition of bone fragments or reconstructive plastic surgery are performed. Swelling is relieved, and the development of cerebral infections is blocked by loading doses of broad-spectrum antibiotics. Further rehabilitation measures, supportive and preventive therapy depend on the nature and severity of post-traumatic syndrome.
First aid from eyewitnesses boils down to stopping the bleeding (a very careful clean bandage), taking measures to immobilize the patient and immediately calling a specialized ambulance. If for some reason this is not possible, you will have to wait too long, the patient’s condition quickly deteriorates, but there is transport available - the patient is taken with extreme caution to the nearest medical facility, where there is a known neurosurgical sector, or simply to the nearest hospital (this is in any case, it is better to have a long absence of medical care as such).
Rehabilitation
For any skull fracture in an adult or child, in addition to treatment, a long rehabilitation period is required. While the injury is healing and for at least 6 months afterwards, the patient should not undertake any physical activity.
During the recovery period, the patient is advised to periodically use the Chantz collar. It is also possible to participate in sessions of magnetic and acupuncture therapy, massage and electrophoresis. The patient is recommended to attend classes with a psychologist and psychiatrist, and in some cases, classes with a speech therapist are necessary.
Surgical treatment of skull trauma
If conservative treatment methods do not have a positive effect on the process of cerebral fluid leakage, there is a risk of developing recurrent meningitis. In this case, surgical intervention is prescribed, during which the liquor fistulas are eliminated. To determine the exact location of the defect, an MRI is performed with the injection of a contrast agent into the cerebrospinal fluid.
During trepanation of the frontal region, the lumen is closed by suturing the dura mater; in difficult cases, plastic correction of the aponeurosis or fascia is used. The bone defect is corrected by applying a piece of muscle. When liquorrhea is caused by injury to the wall of the sphenoid sinus, tamponade is performed using a muscle or a hemostatic sponge during transnasal intervention.
Violation of the geometry of the skull bones can lead to damage to the optic canal. The nerve suffers from the pressure of the hematoma. The consequences are blurred vision or total blindness. In such conditions, decompression of the optic nerve is indicated; for this, the canal is opened through transcranial intervention.
Extensive comminuted fractures require surgical treatment with cranioplasty. First, the surgeon removes sharp bone fragments from the wound, and the defect in the calvarium is closed with a plate that is attached to the bone. Special fast-hardening plastic is widely used for prostheses. Tantalum plates are also used.
Urgent surgical intervention is required if an intracranial hematoma forms. The accumulated blood is removed and its source is eliminated.
Antibiotics cannot always stop the development of a purulent infection that has entered the skull after an injury. In this case, surgical treatment is also indicated.
The decision on any surgical intervention is made by a neurosurgeon, based on both the diagnosis and the general condition of the patient’s body, and his age.
Subsequently, the patient requires a long rehabilitation process.
Lifestyle after injury
A basal skull fracture is a serious injury that undoubtedly has a major impact on the patient's lifestyle. Immediately after receiving an injury, regardless of its severity, the person is hospitalized in the neurosurgical department. During this time, it is necessary to observe strict bed rest.
A patient with a minor injury requires assistance with self-care. With a severe fracture of the base of the skull, the patient requires careful and complete care.
After the victim is discharged, his lifestyle also differs from his usual one. If the patient had an uncomplicated fracture, then he needs to adhere to the following lifestyle:
- Elimination of physical activity for the first 6 months after injury,
- Alternating periods of sleep and wakefulness. Daytime rest and sleep are required
- Take walks in the fresh air,
- Maintain proper nutrition. It should be dietary and easily digestible. You should completely avoid drinks containing caffeine.
- Quitting bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
After a severe fracture, the patient’s lifestyle changes dramatically. In this case, you will need the help of loved ones. Patients with partial paralysis need to learn to care for themselves in new conditions. After severe brain damage, patients cannot return to their usual way of life.
Rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation after injury is required for absolutely all patients. However, the length of this period will depend on the severity of the injury. For a mild, uncomplicated fracture, rehabilitation consists of:
- Compliance with all recommendations of the attending physician,
- Use of prescribed medications,
- Compliance with the prescribed daily routine,
- Observation by specialized specialists: neurologist, ophthalmologist, traumatologist and otolaryngologist.
After a serious injury, rehabilitation is a multi-stage treatment.
The rehabilitation period after a complicated fracture includes:
- Limiting physical activity. That is, excessive loads are excluded,
- Nutrition correction. Meals should be light, small and balanced. Patients with impaired swallowing function require tube feeding with nutritional formulas,
- Physical therapy and massage course,
- Restoration of cognitive functions of the brain. The patient is given classes to develop attention, speech and memory,
- Restoration of coordination and motor functions in the limbs,
- Psychotherapeutic support for patients with mental disorders. In severe cases, treatment in a psychiatric clinic is required,
- Carrying out medical procedures,
- Taking medications of various groups : vitamins, nootropics (improves nutrition and restoration of brain tissue), analgesics,
- Caring for bedridden patients, which includes feeding, hygiene procedures, and anti-decubitus manipulations.
Main symptoms and signs
When the base of the skull is fractured, the front part is most susceptible to injury, so the main symptoms appear in the area of the eyes, nose and ears. Therefore, the initial examination should be related to these organs.
A fractured skull can cause various disturbances of consciousness: from short-term loss due to injury to falling into a coma. One of the observations with TBI: the more severe the injury, the more impaired consciousness is.
With an intracranial hematoma, periods of loss of consciousness may alternate with moments of clarity. Brain edema may develop, in which the patient experiences severe bursting headaches and blood circulation is impaired.
With a fracture of the base of the skull, the following symptoms are noted:
- Nausea or vomiting;
- dizziness;
- uneven dilation of the pupils, different reaction to light;
- clouding of consciousness;
- decreased heart rate;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- when nerve endings are affected, manifestations of bone paralysis are possible;
- with injured vessels, bleeding occurs from the nose, ears or mouth;
- if the meninges are damaged, liquor fluid may leak;
- memory problems (can't remember what happened).
Due to the injury, the patient may have trouble breathing, and if there is heavy bleeding, the patient may go into shock.