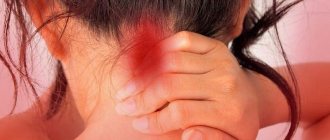
A headache in the back of the head is a very unpleasant phenomenon, causing a lot of inconvenience and often limiting performance. The causes of pain in the occipital part of the head can be very different, from diseases of the cervical spine to neuralgic pathologies.
If you don’t know why the back of your head hurts, then this article is for you. It collects the main causes and describes methods of treating headaches in the back of the head. In any case, you must remember: if you have a headache in the back of your head, you should not self-medicate, you need to seek medical help. Of course, we are not talking about isolated cases of pain in the occipital region. As a rule, they are caused by prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position, stress, extreme hunger, and also due to excessive consumption of foods with caffeine or chemical additives.
Features of pain
Attacks can be either constant or periodic. Quite often, patients note that the back of their head hurts more during physical activity or bright light.
On the right, other unpleasant symptoms are possible:
- Tremors and cramps of the fingers.
- Deterioration of hearing and vision.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea.
You should not endure it if the right side of the back of your head hurts and the above symptoms are observed. After all, a similar symptomatic picture is recorded in many diseases.
At the Doctor Pozvonkov Center for Progressive Medicine, a therapist, vertebrologist, and neurologists receive daily consultations, and the latest medical equipment is used to conduct comprehensive diagnostics.
Headaches in the back of the head
A headache in the back of the head is a type of pain syndrome that is accompanied by a feeling of tightness in the back of the head. In addition to the feeling of squeezing, a person may complain of nausea, ringing in the ears, and pain radiating to the neck or temporal region. Pathology of the musculoskeletal system, cerebral vascular incompetence, neck injury and much more can cause headaches, which you will learn about after reading the article.
Causes and symptoms
The problem of headaches is so pressing that there is not a single person who has not complained of pain in the back of the head at some point in their life. So what could be the reason?
Voltage
Constant work at the computer, reading books, being forced to be in an uncomfortable position causes spasm of the back muscles. As a result of the spasm, the blood flow to the brain worsens, which makes itself felt by pressing pain. This reason is the most common, so if you have a headache in the back of your head, first of all remember what you did the day before. If the symptom does not go away for a long time, and you are monitoring the condition of your back, then read the next point.
Pathology of the musculoskeletal system
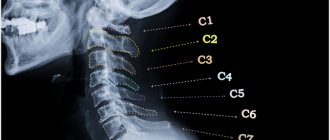
As you know, destructive processes in the spine begin at the age of 20–25 (osteochondrosis), so if you begin to notice constant aching pain in the back of the head and neck, dizziness, spots before your eyes, you should not put off visiting a therapist. After an examination and medical history, the doctor will prescribe a diagnosis and recommend contacting specialists, if necessary. Osteopathy often helps patients in such cases. A course of procedures restores mobility to the musculoskeletal system and pain disappears.
Vascular pathology
If your head hurts in the back, this may indicate high or low blood pressure. Changes in vascular tone are accompanied by a characteristic headache, sometimes pulsation. Hypertensive patients may experience dizziness, nausea, tinnitus, and redness of the facial skin. In people with hypotension, pain in the head can radiate not only to the back of the head, but also to its entire surface, and is more characterized by patients as bursting from the inside. If headaches are of a similar nature, you should consult a neurologist. You should take problems with blood vessels seriously; you cannot constantly relieve such pain with painkillers; serious treatment is necessary.
Injuries
Bruises and sprains can also cause discomfort in the back of the head and neck. They will be especially pronounced when trying to turn your head to the side. In such cases, a course of osteopathy can help.
Hormonal disbalance
Less commonly, the cause may be endocrine pathology associated with diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and brain.
Neuralgia
Damage to the nerve bundle or nerve roots (particularly due to hypothermia) leads to occipital neuralgia, which is characterized by shooting acute pain. Typically, rest, being in a warm room, special massage and painkillers help relieve a pain attack. In this case, consulting a neurologist will help.
Migraine
Despite its favorite location in the temples, sometimes migraines can occur in the area where the neck meets the occipital part of the skull (cervical migraine). In addition to severe throbbing pain, a person may experience photophobia and nausea. If headache attacks coincide with migraine symptoms, you should consult a neurologist. Proper treatment helps not only reduce pain, but also prevent new attacks.
Viral and bacterial infections
If the back of your head hurts, and your general health leaves much to be desired (runny nose, cough, etc.), then there is a consequence of ARVI. In this case, the headache goes away on its own after recovery. But if it is intense, is not relieved with analgesics, the neck muscles are tense and unable to relax - this indicates possible meningitis. If you suspect an infectious component of your headache, you should consult a physician to diagnose and treat the disease.
Myogelosis
Often the disease occurs after exposure to a draft, prolonged stress, poor posture, or is a complication after myositis. As a result, there is a tightening of the neck muscles, which is accompanied by discomfort in the shoulder joint and pain in the back of the head. An osteopathic doctor can help you cope with such problems.
Diagnostics
If you have a headache problem, you should first consult a neurologist, since pathologies of the spine or vascular bed are a common cause of the symptom. To identify the cause, our medical office takes a general blood and urine test (to rule out the inflammatory nature of the disease), and an x-ray of the spine is taken. If necessary, the patient is examined by other specialists.
Treatment
Although this symptom is unpleasant, sometimes you can get rid of it without the help of pills. It is enough to ventilate the room you are in, allow yourself a neck and back massage, drink mint tea and lie down on the bed for at least half an hour. If the pain does not disappear and nausea increases, then it is better to take an analgesic. Remember: painkillers only treat the symptom, not the underlying disease. If, at the height of pain, your temperature rises and intoxication increases, do not hesitate and consult a doctor for qualified help.
Pain in the head is rarely primary; most often it develops against the background of concomitant diseases. At our medical center, you can undergo a comprehensive diagnostic examination, which will help make a diagnosis as early as possible and relieve you of painful symptoms. You can make an appointment with a neurologist any day of the week from 09:00 to 21:00.
You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling
+7+7 (495) 980-13-16
Why does the right back of my head hurt?
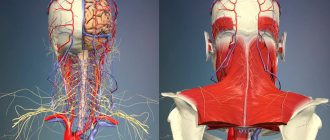
Pain always indicates a deterioration in blood supply or nerve conduction.
The cause is focal pinching of nerves and blood vessels due to displacement of the vertebrae and a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs. In this case, a long-term pathological condition provokes a number of serious diseases:
- Hypertension.
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
To prevent such conditions, the correct position of the structures of the spinal column and the tone of the muscle frame are restored.
It is worth remembering that the human nervous system covers the entire body, and often the source of damage is in a completely opposite area.
Therefore, a comprehensive examination is important, and not just work on the affected area.
What to do if you have a headache in the back of your head
As you can see, there is a reason why you have a headache in the back of your head. And if you can deal with the cause of overwork or stress on your own, then other diseases are an urgent reason to consult a doctor. Timely diagnosis of the disease and adequate treatment will not only relieve you of pain, but also keep you healthy and active for many years.
It is better to start the examination with a visit to a therapist. Book a consultation with a doctor right now by calling our clinics' multi-line number 8 or using the online appointment form.
Administrators will select a convenient time and day for your appointment. You don’t need to take anything with you, we will give you everything disposable both for your appointment and for undergoing additional studies, such as tests or ultrasound of blood vessels. #Doctor therapist headache neurology
Treatment
If the back of your head hurts, there is numbness on the right side, and at the same time you feel strong muscle tension, in our Center you can always visit the necessary specialists.
And you should start by restoring the position of the spinal column using spinal traction.
The procedure is aimed at returning the physiological position of the vertebrae, reducing the load on the cervical spine, as well as stabilizing blood circulation and nerve conduction.
In this case, the safest method is water stretching, since treatment in water promotes a gentle effect and additional relaxation of the muscles.
Manifestations of headache and accompanying symptoms
We call any pain in the head area a headache, but the mechanism of its occurrence varies. It is caused by irritation of pain receptors in the dura mater, as well as blood vessels, nerves - trigeminal, glossopharyngeal, vagus, skin nerves, head muscles, cervical spinal roots. It can also manifest itself in different ways: it can be dull, pulsating, squeezing, bursting; can concentrate in the forehead, temples (on one or both sides), back of the head, crown of the head. Attacks can be strong, moderate or weak, and vary in duration and frequency. Pain may be accompanied by other symptoms (nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances, dizziness, increased or decreased blood pressure, etc.). All these characteristics are important for making a diagnosis.
Primary headache. Major diseases.
The most common forms of primary headache are “tension pain” and migraine, more rarely – cluster headache and other forms.
Tension headache (TTH)
can occur in anyone. This is the most common form of headache and is often characterized as a “normal” or “regular” headache. Attacks can last from 30 minutes to several days. The frequency of attacks varies from person to person, and it can also vary from one person to another during different periods of his life. The pain is described as squeezing, squeezing the head like a hoop or tight hat, usually bilateral, and moderate. In some people it can become chronic (chronic pain is diagnosed if there are more days with a headache than without it). A person experiencing chronic headaches becomes irritable. Weakness, fatigue, decreased appetite, and sleep disturbances may occur. The cause of TTH is physical tension in the muscles and ligaments of the head and neck - the so-called “muscle stress”, which can be a consequence, for example, of working in an uncomfortable position. TTH often occurs in those who work at a computer or whose work involves the need to look at details (jewelers, watchmakers, assemblers of electronic equipment, masters of artistic embroidery, etc.). The emotional factor is also important: emotional tension caused by stress or a state of increased anxiety can also lead to pain.
Migraine
characterized by severe and painful attacks of headache, which are often accompanied by nausea (and in some cases vomiting), as well as intolerance to light and sound. The perception of smells changes, thermal sensations are disrupted. Migraine attacks last from 4 hours to 3 days and can be repeated with a frequency of 1-2 times a year to several times a month. During an attack, so-called “precursors” may be observed - irritability, depression, fatigue, occurring several hours or even days before the onset of pain. In a third of cases, pain is preceded by phenomena called “auras”: 10-30 minutes before the attack there may be visual disturbances (blind spots, flashes, zigzag lines in front of the eyes), tingling and numbness starting from the fingertips and spreading up the body and etc.
Predisposition to migraine is congenital and is associated with disorders in the brain structures responsible for pain and other sensations. Every seventh adult suffers from migraines, with women three times more likely than men. In girls, migraines usually begin during puberty.
Factors that contribute to the development of migraine attacks: chronic fatigue, anxiety or stress, in women - menstruation, pregnancy and menopause.
But a predisposition to seizures does not mean that an attack will definitely happen. There are factors that act as a “trigger” for an attack. An attack can be triggered by: skipping meals, insufficient fluid intake, certain foods, sleep disturbances, physical activity, changes in weather, sudden changes in emotions.
Cluster (or beam) headache
characterized by one-sided sharp (“dagger” or “drilling”) pain. The intensity of the pain rapidly increases within 5-10 minutes, and the attack itself lasts from 15 minutes to 3 hours, during which the patient cannot find a place to rest. The pain is usually localized in the eye area, and the eye may become red and watery. Recurrent attacks form a cluster (that is, they follow each other), the duration of the cluster is from 6 to 12 weeks. This form of pain occurs five times more often in men than in women. However, those who smoke a lot or have smoked in the past are more susceptible to it.