Before moving on to the issue of rehabilitation after neurosurgery and traumatic brain injuries, you need to have a clear understanding of both.
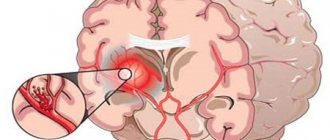
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a set of contact injuries (soft tissues of the face and head, skull bones and facial skeleton) and intracranial injuries (damage to the substance of the brain and its membranes), having a single mechanism and age of formation. TBI is the third most common cause of death in the country (after cancer and cardiovascular diseases).
Neurosurgical surgery involves surgical treatment of diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system that arise both as a result of TBI or independently. The consequence of severe TBI and any neurosurgical intervention is a disruption of brain function of varying duration and severity, requiring further rehabilitation under the supervision of a neurologist. The rehabilitation program after TBI is highly individual and depends on the severity of the injury, the period of occurrence and the nature of the complications.
Differentiation of traumatic brain injuries
According to communication with the external environment, traumatic brain injuries, like fractures, can be open (penetrating, non-penetrating) and closed.
According to morphology, TBIs are divided into subtypes:
- Shake. The most gentle at first glance, but also the most insidious damage. The period of pronounced symptoms is up to several days.
- Squeezing. Pressure on the brain is exerted by a hematoma or the presence of air in the skull, or less often by a foreign body.
- Mild, moderate and severe brain contusion.
- Diffuse axonal damage - diffuse ruptures or tears of axons (coma with symptoms of brain stem damage).
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage is cerebral bleeding with a sharp headache and loss of consciousness in combination with hyperthermia and a meningeal symptom complex.
The combination of these injuries can be different, for example, bruise and compression or hemorrhage with bruise. Often there may be hemorrhage with the presence of a bruise and compression of the brain by the hematoma. Brain injury most often occurs at the site of impact, but often damage occurs on the opposite side of the skull - in the impact zone.
Most common in TBI
- movement disorders;
- sensitivity disorders;
- speech and swallowing disorders (bulbar disorders);
- disturbances of consciousness;
- disorders of liquorodynamics;
- psychoorganic syndrome;
- secondary disorders.
Rehabilitation after a traumatic brain injury begins as early as possible, sometimes physical rehabilitation measures are already carried out on the first day.
The goals and objectives of rehabilitation measures will vary depending on the timing of the injury, the degree of its severity and the location of the damage.
Symptoms for various degrees of TBI severity
The severity of TBI is determined by the Glasgow Coma Scale (assessing the patient’s eye opening, movement and speech): mild – 13–15 points, moderate – 9–12 points, severe – 3–9 points. In other words, three factors are taken into account: state of consciousness, vital functions, neurological symptoms. In this case, the patient’s condition is assessed as satisfactory, moderate, severe, extremely severe, terminal (between life and death). The more serious the injury and the deeper its penetration, the more difficult the patient’s recovery.
Symptoms of TBI with:
- Mild severity: headache (cephalalgia), dizziness, nausea and vomiting, sleep disturbance, irritability, fatigue.
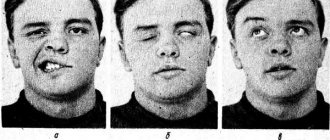
- Moderate: speech impairment, partial loss of vision, paroxysms of the limbs, mental disorders, memory loss, heart rhythm disturbances, high-intensity cephalgia, increased frequency of respiratory movements while maintaining rhythm, loss of consciousness for up to several hours.
- Severe: convulsions, paralysis, hypo- or hypertonicity of muscles, lack of consciousness for up to several weeks, coma, critical impairment of vital functions, deep brainstem and cerebral disorders.
Recovery from a concussion
A concussion occurs as a result of injuries and bruises. When the brain comes into contact with the skull in a person, a temporary change in the chemical properties of neurons occurs, as well as a disconnection of signal transmission between synapses, resulting in the development of disorders that can be eliminated by effective rehabilitation after a concussion.
When a person has a concussion, they experience the following symptoms:
- confusion;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased fatigue, drowsiness;
- headaches, dizziness;
- increased blood pressure;
- memory impairment;
- increased breathing;
- pale skin, which quickly gives way to redness.
For many patients, the relevant question is how long does recovery after a concussion take with an integrated approach. Before starting rehabilitation measures, the patient is examined.
The Yusupov Hospital has modern diagnostic equipment that allows you to identify the consequences of a concussion and begin treatment and recovery after a concussion. Highly qualified specialists allow us to assess the patient’s condition using special scales. When making a diagnosis, in some cases magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography is performed.
Rehabilitation after a concussion is carried out to eliminate the consequences of the injury, stabilize the patient’s condition, adapt to physical activity and improve the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. At the rehabilitation center of the Yusupov Hospital, experienced exercise therapy instructors, neuropsychologists, physiotherapists and other specialists interact with patients.
Periods, consequences and complications of TBI
The so-called traumatic disease includes three periods:
- Acute (duration 2 weeks – 2.5 months) – development of defense reactions to a damaging factor.
- Intermediate (duration 6 months – 1 year) – the process of lysis and repair in damaged areas.
- Long-term or final (duration 2-3 years, with complications - until the end of life) - completion of tissue degeneration and restoration of functions.
Complications of TBI in the acute phase:
- Impaired function of the respiratory system (respiratory depression and gas exchange disorders).
- Problems with central and regional (cerebral) circulation.
- Hemorrhagic complications (cerebral infarction, intracranial hemorrhage).
- Dislocation (displacement) of brain parts.
- Complications of a purulent-inflammatory nature: intracranial (abscesses, osteomyelitis, meningitis, encephalitis), extracranial (pneumonia, for example).
Possible consequences of TBI:
- Paralysis of the limbs (partial, complete) on one or both sides.
- Loss of vision, hearing, ability to speak, swallow, and breathe.
- Loss (weakening) of control over the function of the pelvic organs (the patient is not able to control the processes of urination and defecation).
- Tremor (shaking) in the limbs.
- Partial memory loss, deterioration of attention, changes in character and other consequences associated with higher nervous activity (usually after a coma).
In the long-term post-traumatic period, the development of epilepsy (acquired epilepsy), occlusive hydrocephalus, neuroses, and parkinsonism is possible. Also, cases of arachnoiditis and arachnoencephalitis (a disease of the central nervous system - serous (non-purulent) inflammation of the arachnoid membrane of the brain or spinal cord) are not uncommon.
Treatment and recovery after TBI
If a person has suffered a head injury, the first thing to do is call an ambulance. Before her arrival, place the victim on his back and apply a bandage to the wounds. The ambulance takes the patient to the traumatology or intensive care unit. In the hospital, the patient is examined, X-rays of the skull, spine, neck, limbs, and pelvis are prescribed, an ultrasound of the internal organs is performed, and tests are performed. The patient's condition is assessed by a neurologist using the Glasgow scale every 4 hours. Antibiotics, antiseptics, analgesics, sedatives and anticonvulsants are prescribed. If the patient is in a coma, he requires artificial ventilation. In case of hematoma or cerebral edema, surgical intervention is necessary; the earlier the operation is performed, the lower the risk of death.
Recovery prognosis
The most favorable prognosis for concussion . But it is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations. Such patients may still have cognitive disorders and frequent mood swings, but these symptoms disappear after about half a year.
moderate injury can hope for a positive prognosis for the restoration of all body functions , but they still have consequences associated with coordination, speech impairment, and headaches.
The most unfavorable prognosis is if a person has suffered a severe . In this case, deaths are common. And if a person survives, he almost always remains disabled, with epilepsy, meningitis, and encephalitis.
To return the patient to a normal and active life, it is necessary to carry out a set of rehabilitation measures, but only after the acute phase has passed.
An individual rehabilitation program is developed for each patient, which depends on the severity of the injury.
For movement disorders, therapeutic physical training . In such classes, the instructor can perform passive exercises, or demonstrate exercises for the patient to perform them independently, starting from the simplest ones, gradually moving to more complex ones, increasing the load.
If there are no contraindications, then massage . Massage improves blood circulation, normalizes the digestive system, and puts the mental state in order. Massage can be relaxing or tonic, acupressure, general or for specific areas.
They also use a method such as manual therapy to normalize the muscle tone of the body and increase the range of motion in the joints.
Reflexology in combination with other methods gives good results, since the doctor uses schemes aimed at restoring the nervous system.
Very often, after a TBI, the victim has speech disorders; a speech therapist . Classes with this specialist are aimed at normalizing the tone of speech muscles; he performs gymnastics and massage of the muscles of the tongue, cheeks and lips, producing sounds and correct pronunciation. The speech therapist also develops fine motor skills and hand placement for writing.
To relearn how to take care of yourself in everyday life, dress yourself, take a shower, or just eat, an occupational therapist .
will help relieve inflammation, tissue swelling, and pain . It includes currents, magnetic field, laser, ultrasound, cryotherapy, paraffin therapy, ozokerite therapy, hydromassage.
Psychotherapy is a very important part of recovery from TBI. Psychologists and neuropsychologists work with patients to help cope with apathy and depression.
Today, there are a large number of different simulators that are considered an integral part of restoring motor functions:
· Exercise bike (Ortorent)
Vibration platform (Galileo Med)
· Walking simulators (Innowok Pro, Corvit)
· Exercise machines for coordination of movements and muscle relaxation (Gross simulator)
· Verticalizer for vertical body position.
The recovery process is different for everyone, depending on the severity of the disease. This is a long-term effort for the patient and all family members. Everyone needs to be patient and not give up, perform the exercises you have learned not only in class, but also at home. To achieve good results, you need to contact a specialized medical institution that has experience and positive results in this area.
You can sign up for a recovery course after receiving a TBI by calling: 8 (351) 225-3315
Rehabilitation after a brain contusion at the Yusupov Hospital: benefits
Recovery from brain contusion and concussion is one of the priorities of the Yusupov Hospital Rehabilitation Center. Experienced specialists provide patients with high-quality medical services and create a comfortable psychological environment.
Recovery after a concussion, carried out by specialists at the Yusupov Hospital, has a number of advantages:
- fast and highly accurate diagnostics, allowing to identify the consequences of the injury. The rehabilitation center has a modern material and technical base, which is regularly updated;
- when choosing methods of treatment and recovery, specialists give preference to the safest and most effective means;
- development of an individual recovery plan, including therapeutic and recreational procedures and medication;
- in patients with a concussion, rehabilitation takes place in a comfortable hospital to consolidate the results obtained and comprehensively eliminate the consequences;
- professional care and round-the-clock supervision by medical staff.
Bruises and concussions, for which rehabilitation is mandatory, are most often detected in modern people leading an active lifestyle. The main task of specialists at the Yusupov Hospital when treating patients with traumatic brain injuries is to provide emergency care and subsequent recovery.
Patients experiencing intense symptoms after a fall or various types of injuries can immediately contact the rehabilitation clinic, which is open daily. Pre-registration for an appointment is carried out by employees by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
How to cure TBI and get rid of the consequences?
Modern science has proven that nervous tissue can and can recover. Therefore, treatment for traumatic brain injuries should perform the following tasks:
- Elimination of the causes of death of nerve cells (elimination of intracranial hematomas, reduction of ICP, etc.);
- Stopping secondary damage to brain tissue;
- Creating conditions for active nutrition and oxygen supply to all areas of the brain;
- Stimulation of restoration processes and the formation of new neural connections.
"Semax 0.1%" - neuroprotector Neuroprotectors
Medicines that prevent damage to nerve cells in the brain from adverse effects.
Their influence is aimed at eliminating or reducing disturbances in nerve cells. and neurometabolic Neurometabolic
A drug intended to influence higher brain functions.
Improves memory, stimulates mental activity, increases and facilitates the learning process, the properties of which allow you to effectively perform several of the listed tasks at once. Therefore, it is successfully used after any type of TBI, including concussion, for the treatment and prevention of consequences. The use of Semax 0.1% after TBI reduces mortality among patients, reduces the degree of disability and significantly reduces the length of hospital stay.
Concussion: recovery period
Patients recovering from a concussion are interested in how long it takes to resolve the effects of the injury. Rehabilitation at the Yusupov Hospital includes a set of measures individually selected for each patient, so its duration is determined by a specialist.
After a concussion, until the symptoms are eliminated, the patient must follow the recommendations of a specialist:
- maintain a sleep and rest schedule;
- eat rationally;
- limit physical activity and exclude work that requires concentration;
- avoid stress and emotional tension;
- do not drink alcohol.
If a patient is diagnosed with a concussion, recovery of the body should take place under the guidance of an experienced specialist. In some cases, patients require a hospital stay, so comfortable conditions have been created for patients at the Yusupov Hospital.
Signs and symptoms
TBI can cause a wide range of functional short-term and long-term changes affecting cognitive, emotional, and behavioral areas.
As a result of brain damage, the following suffers:
- thinking (the process of modeling environmental patterns);
- attention (concentration and retention);
- memory (memorization, storage, reproduction of information);
- functions of the sense organs (vision, hearing, taste, smell, touch);
- speech activity (communication, expression and understanding of words);
- emotions and behavior (depression, anxiety, aggression, social unacceptableness).
Symptoms that may occur after a TBI:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- convulsions;
- loss of coordination of movements.
TBI can also cause epilepsy and increases the risk of conditions such as Alzheimer's-type dementia, Parkinson's disease and other brain diseases that become more relevant in old age.
Repeated mild brain injuries occurring over a long period of time (i.e., months and years after the initial episode) lead to cumulative neurological and cognitive deficits. Repeated moderate to severe TBIs occurring within a short period of time (i.e., hours, days, or weeks after the first event) can be catastrophic or fatal.