| Cachexia | |
| ICD-11 | MG20 |
| ICD-10 | 64. |
| ICD-9 | 799.4799.4 |
| MeSH | D002100 |
| Media files on Wikimedia Commons | |
Cachexia
(ancient Greek κακός - bad, ἕξις - condition;
obsolete "thinness"
[1]) [2] is extreme exhaustion of the body, which is characterized by general weakness, a sharp decrease in weight, activity of physiological processes, as well as changes in mental the condition of a patient who is not actively trying to lose weight. Cachexia physically weakens patients to a state of immobility associated with loss of appetite, asthenia, and anemia, and the response to standard treatment of the underlying disease is usually poor.[3]
Etiology[ | ]
- Sheehan syndrome
- Esophageal stenosis, which makes it difficult for food to enter the stomach;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), accompanied by symptoms of impaired digestion and absorption of food, including chronic enterocolitis, celiac disease - sprue, condition after gastrectomy, etc.;
- Psychogenic anorexia;
- Long-term use of psychostimulants
- Amyloidosis;
- Debilitating diffuse connective tissue diseases;
- Long-term intoxication in chronic infectious diseases (brucellosis, tuberculosis, etc.) and purulent processes (abscesses, osteomyelitis);
- Acantholytic pemphigus;
- Severe heart failure;
- Malignant tumors (oncological, in particular, cancer cachexia);
- Metabolic and energy disorders in endocrine diseases, especially in panhypopituitarism (hypothalamic-pituitary insufficiency);
- Adrenal insufficiency;
- Thyroid gland insufficiency;
- Acquired immune deficiency syndrome[4].
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
The appearance of symptoms of exhaustion is usually caused by serious causes that cannot be eliminated through self-treatment. In most cases, emergency medical care is required to prevent critical, irreversible changes to internal organs. If symptoms occur against the background of anorexia nervosa, and the patient does not consider himself sick, relatives and close friends can arrange a consultation with a specialist or take the person to a specialized clinic.
Malnourished patients require nutritional supplementation
Conservative therapy
The main goal of treatment is to meet nutritional needs. In mild cases of depletion of the body, the caloric content of the diet is gradually increased; the diet should contain a large amount of protein, complex carbohydrates and vitamins. In severe situations, tube feeding or parenteral administration of special solutions of amino acids and fat emulsions is indicated. Anorexia requires individual and group psychotherapy. For etiotropic treatment of conditions causing exhaustion, the drug treatment regimen includes:
- Enzymes
. To improve digestion processes in chronic enteritis and pancreatitis, enzyme agents are prescribed that replace the function of the pancreas. Taking probiotics helps normalize microflora and prevent the development of SIBO. - Antibacterial agents
. Therapy is carried out for chronic infections that cause intoxication and catabolic reactions. Drugs are selected based on the properties of the pathogen. Antibiotics and antiprotozoal medications are recommended for the treatment of opportunistic infections in AIDS. - Hormonal drugs
. If symptoms of exhaustion are caused by endocrine pathology, replacement therapy is used. Most often, glucocorticoids, levothyroxine and sex hormones are prescribed; for panhypopituitarism, pituitary tropic hormones are sometimes used. - Cardiotropic drugs
. Cardiac glycosides, antianginal drugs (calcium channel inhibitors, beta blockers) fully or partially compensate for heart failure. Thiazide and potassium-sparing diuretics are effective in eliminating edema. - Cytostatics
. The drugs are indicated both for severe connective tissue diseases, amyloidosis, and for the treatment of the tumor cause of cachexia. Medicines and doses are selected individually, taking into account the localization of the pathological process and the presence of metastases.
Surgery
When a malignant neoplasm is identified as the cause of exhaustion, radical interventions are necessary to remove the neoplasia along with the affected tissue and lymph nodes. For stage 1-2 cancer, organ-conserving surgery is the method of choice. In advanced cases, advanced techniques are used. To treat exhaustion of the body, which is caused by obstruction of the esophagus, stenting of the narrowed area is performed. If necessary, esophagoplasty is performed with gastric or intestinal grafts.
Symptoms[ | ]
Symptoms of cachexia include severe weakness, loss of ability to work, and sudden weight loss, often accompanied by signs of dehydration. Weight loss can reach 50% or more.
Subcutaneous tissue decreases sharply or disappears completely, and there are signs of hypovitaminosis (vitamin deficiency). As a result, the skin of patients becomes flabby, wrinkled, turns pale or acquires an earthy-gray tint.
Trophic changes in hair and nails are also present, stomatitis may develop, and severe constipation is typical.
In patients, sexual function decreases; in women, amenorrhea may occur, as the patient’s circulating blood volume decreases.
Glomerular filtration in the kidneys often decreases. Hypoproteinemia, hypoalbuminemia, as well as iron anemia or B12-deficiency anemia are manifested.
Mental disorders are often observed with cachexia. At the beginning of its development, asthenia appears, which causes irritable weakness, tearfulness, and subdepressive mood. With the development of cachexia and asthenia, the adynamic component begins to manifest itself to a greater extent. During exacerbations of the underlying disease, which caused cachexia, clouding of consciousness in the form of amentia, twilight stupefaction, severe or rudimentary forms of delirium, which are replaced by anxious and melancholy states, apathetic stupor, and pseudoparalytic syndrome, may often occur. Despite the favorable outcome of the underlying disease that caused cachexia, prolonged asthenia always remains. In some cases, it is combined with manifestations of psychoorganic syndrome of varying intensity.
Diagnostics
To clarify the cause of exhaustion, a consultation with a therapist is usually required, who is responsible for the initial examination and excludes the most typical factors that cause weight loss. A comprehensive study of the condition of internal organs and assessment of neurological and mental reactions is necessary. The following methods have the greatest diagnostic value:
- Sonography
. First, an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is performed, during which signs of inflammatory and degenerative processes, the presence of stenoses and space-occupying formations are revealed. The motility of the stomach and intestines is assessed. An ultrasound of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands is performed; in women, the mammary glands are examined to exclude cancer. - X-ray method
. In case of exhaustion, the condition of the gastrointestinal tract must be checked, for which a series of X-rays with contrast are performed. The method is effective for stenosis and tumors of the esophagus and allows one to evaluate the rate of chyme movement. To exclude damage to the pituitary gland, a targeted radiograph of the sella turcica is recommended. - Endoscopic studies
. Endoscopy helps to study in detail neoplasms and strictures in the upper part of the digestive canal, which often cause depletion of the body. During the procedure, a methylene blue test is performed to detect metaplasia, as well as an endoscopic biopsy of suspicious formations to exclude an oncological cause of cachexia. - Blood tests
. The degree of depletion of the body is judged by the level of decrease in protein levels in a biochemical blood test. Determining the concentration of nitrogen metabolism products and basic electrolytes makes it possible to assess the severity of damage to internal organs. The level of tropic hormones of the pituitary gland, liberins and statins of the hypothalamus is measured. - Neurological examination
. The examination is indicated if there are signs of nervous and physical exhaustion. They examine the level of consciousness and cognitive capabilities, check muscle tone and coordination of movements. To exclude severe lesions that are accompanied by refusal to eat, CT and MRI of the brain are prescribed. The functional activity of brain cells is recorded on an EEG.
If the symptoms of exhaustion of the body are accompanied by “minor signs” of oncological pathology (fatigue, lethargy, general malaise, anemia), it is necessary to examine the blood for tumor markers, carry out additional instrumental procedures - CT scan of the abdominal cavity and chest, scintigraphy of the body. All patients undergo a screening test for HIV infection. When exhaustion is combined with a dysmorphomanic state, consultation with a psychiatrist is required to exclude a neurotic or psychotic cause of the disorder.
Treatment[ | ]
Treatment of patients with cachexia is aimed primarily at the underlying disease, but necessarily includes the necessary measures to restore the patients’ nutrition, as well as careful general care for them. The diet must include proteins and fats, vitamins, and it is advisable to use easily digestible foods. For symptoms of impaired digestion and absorption of food, multienzyme drugs are prescribed, such as pancreatin, etc. To relieve patients with cachexia from a serious condition, glucose, electrolytes, vitamins, protein hydrolysates, and amino acid mixtures are administered parenterally. Anabolic steroids are used according to indications. For psychogenic anorexia, treatment is prescribed and carried out by a psychiatrist; Appetite stimulants may be used.
Fatigue of decisions, or Why “the head doesn’t think well”
Exhaustion attacks more than just our ability to self-control. It extends to many forms of self-regulation. Most of all, it influences decision making. The more decisions we have to make—from buying a new car to scheduling conference attendees—the more difficult it is for us to continue to act in the same spirit.
Researchers call it “decision fatigue,” a condition that causes us to do one of two things:
- make frivolous choices;
- To do nothing.
What to choose? The question is complex
Due to decision fatigue on Wednesday, we return the ridiculous purchases we made on Tuesday, because the next day, when the fatigue passes, our heads are clearer. This is why we put off making decisions when we are too tired to do it now.
But exhaustion affects more than just decisions. Interpersonal relationships and the ability to change are under attack. If purchases, decisions, and resistance to temptation are depleted, then complex behaviors are also subject to depletion (scientists confirm this).
Notes[ | ]
- Skinny // Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron: in 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional). - St. Petersburg, 1890-1907.
- Merriam-Webster Dictionary
definition of cachexia - Mitja Lainscak, Matej Podbregar, Stefan Anker.
How does cachexia influence survival in cancer, heart failure and other chronic diseases? (ENGLISH) // Current Opinion in Supportive and Palliative Care. — Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (English) Russian, 2007-12. - T. 1, issue. 4. - pp. 299-305. — ISSN 1751-4258. - doi:10.1097/SPC.0b013e3282f31667. - Rapini, Ronald P.;
Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. Dermatology: 2-Volume Set (undefined). —St. Louis: Mosby, 2007. - P. 1169. - ISBN 1-4160-2999-0..
Causes of premature ovarian failure syndrome
To understand why this pathology develops, it is necessary to have an idea of how healthy ovaries work. This paired gland organ performs 3 functions in the body at once:
- Produces sex hormones (estrogens) that regulate reproductive and sexual function and are responsible for a woman’s age-related maturation;
- They produce eggs - sex cells, which, when fertilized by sperm (during sexual intercourse or during IVF), form an embryo, which subsequently develops into a full-fledged child.
The peak performance of the ovaries occurs from 15 to 35 years. The supply of eggs in them (ovarian reserve) is formed during the period of intrauterine development of a woman. Unlike men, she does not develop new germ cells - only those that are already present mature. With age, this supply gradually dries up - normally this process ends at 40-45 years of age (with some variations up or down), after which menopause (female menopause) occurs, characterized by the complete extinction of reproductive function. the inability to have children, serious hormonal changes in the body.
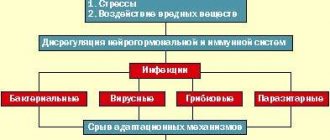
The depletion of the ovarian reserve itself is a normal process that every woman faces. It becomes a pathology if it occurs earlier than the biologically established norm - that is, before the age of 40. SIS is a rare disease and occurs in only 3% of women. At the same time, no changes are observed in the ovaries themselves, so the disease is not organic, but functional in nature. The exact mechanism by which the pathology appears has not been established for certain, but there are several working hypotheses:
- Genetic. Currently, most researchers are inclined to believe that hereditary predisposition is considered the decisive factor in the formation of SLI. It has been clinically established that ovarian hypotrophy is most often observed in women whose mothers or sisters also encountered a similar problem. In patients with established ovarian wasting syndrome, an extra X chromosome is more common.
- Autoimmune. Another possible cause of SIJ is the production of immune antibodies that inhibit the functioning of the glandular tissue of the ovaries. Such a reaction of the body to its own organs can occur independently or with various autoimmune disorders - hypothyroidism, vasculitis, systemic lupus erythematosus and other pathologies of a similar nature.
- Neurological. This hypothesis calls the main cause of early ovarian depletion organic damage to the parts of the central nervous system responsible for the functioning of the gonads (sex glands). In particular, dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system of the brain can lead to such consequences.
- Iatrogenic. In this case, the main factor causing early ovarian dysfunction is exposure to drugs or damage caused by external mechanical stress - for example, trauma, surgery (surgeries to remove cysts or other ovarian tumors). Actually, this hypothesis is not fundamental, since it explains only those cases of SSI in which disruption of the gonads is caused by obvious organic disorders.
Also, factors contributing to early ovarian failure syndrome include:
- Poisoning with toxic substances (including nicotine, alcohol, psychotropics) and medications, exposure to ionizing radiation (radiation);
- Anatomical abnormalities of ovarian development caused by genetic disorders or trauma;
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, endocrine disorders, traumatic injuries to the ovaries.
- Psycho-emotional disorders, accompanied by frequent and sudden mood swings and nervous breakdowns.
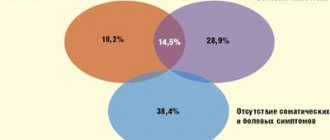
In addition to premature decline of reproductive function, there are the following symptoms of ovarian wasting syndrome:
- amenorrhea - cessation of menstrual bleeding and, consequently, renewal of the uterine endometrium, necessary for normal conception and development of the child;
- cessation of ovulation - the production of healthy eggs involved in the conception of children;
- decreased libido (sexual desire), decreased natural moisture in the genital organs and, as a result, a feeling of dryness, discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse and movement (running, walking);
- sudden changes in mood, increased aggressiveness, tearfulness, frequent attacks of depression or apathy, indifference to oneself and others, panic attacks;
- decreased cognitive function, difficulty concentrating, memory, general decrease in performance;
- physiological symptoms - sudden bouts of sweating, increased body temperature and blood pressure, redness of the skin in the shoulders, chest and neck;
- increased bone fragility associated with endocrine and metabolic disorders accompanying SSI.
Thus, ovarian wasting syndrome negatively affects all aspects of a woman’s life, from the ability to have a child to the ability to perform professional tasks and everyday activities. Increased suspiciousness and a tendency to depression contribute to the development of an inferiority complex and social distancing in a patient suffering from SUS.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Links[ | ]
- Merriam-Webster Dictionary
definition of cachexia - Cachexia // Kazakhstan. National Encyclopedia (Russian). - Almaty: Kazakh encyclopedias, 2005. - T. III. — ISBN 9965-9746-4-0.
| Dictionaries and encyclopedias |
|
| In bibliographic catalogs |
|
Prevention of early ovarian failure
SSI is caused by very specific medical reasons, so a woman may not encounter this problem at all if she follows simple recommendations:
- avoid exposure to toxic substances and ionizing radiation;
- do not self-medicate with medications;
- eliminate or minimize stressful situations at work or in your personal life;
- visit a gynecologist in a timely manner and undergo regular examinations of your reproductive system;
- monitor your diet, and also eliminate the use of alcohol, psychoactive substances, and smoking.
Another way to prevent and overcome this disease is egg cryopreservation. As a rule, SIA occurs after the age of 30, so a woman has a lot of time to preserve her genetic material in a cryobank while the ovarian follicular apparatus is still functioning. Freezing does not reduce the fertility of the germ cells, and they can be used for artificial insemination many years later.