Neurology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the central and peripheral systems. A neurologist has many methods and means in his arsenal that will restore lost health. Some diseases cannot be completely eliminated. In this case, the goal of treatment will be to maximize the patient's quality of life.
According to WHO (World Health Organization), hundreds of millions of people around the world have one or another neurological disease. The most common of them are stroke, epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease, migraine, vegetative-vascular dystonia, etc. However, in practice, a neurologist has to deal with other diseases, as well as their consequences. That is why neurology closely “cooperates” with another branch of medicine – rehabilitation.
What diseases does a neurologist treat?
- cardiovascular - hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke;
- infectious - damage to the central nervous system due to syphilitic and AIDS infections, herpetic encephalitis;
- degenerative - Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases;
- traumatic - bruises of varying severity, concussions, diffuse damage to axons in traumatic brain injuries;
- pathologies of the cerebrospinal fluid system - persistent increase in intracranial pressure, hydrocephalus;
- demyelinating - Guillain-Barré syndrome, multiple sclerosis;
- helminthiasis - opistrochiasis, echinococcosis;
- oncological - gliomas, meningiomas;
- mycotic - candidiasis, cryptococcosis of the central nervous system;
- epileptic - primary (without involvement of the brain matter in the pathological process) and symptomatic epilepsy caused by traumatic brain injury, tumors;
- congenital - cerebral palsy.
When to see a doctor
There are many reasons for the development of diseases of the nervous system. These can be infections, injuries, congenital developmental anomalies, hereditary pathology, bad habits, etc. In this case, various parts of the nervous system can be affected.
You should contact a neurologist if the following symptoms appear:
- Headache;
- Loss of consciousness, dizziness;
- Impaired coordination of movement, sensitivity, tremor;
- Disturbance of sleep, memory, attention, speech, vision, hearing;
- Increased fatigue;
- Convulsions;
- Neuropsychic development disorder.
Symptoms of damage to the nervous system can have mild manifestations, and patients do not pay attention to them for a long time, carry out independent treatment, and are in no hurry to make an appointment with a neurologist. As a result, the underlying disease progresses steadily and its health consequences become more severe.
How does an appointment with a neurologist proceed?
The initial consultation includes a survey and neurological examination of the patient. During the conversation, the doctor listens to complaints and asks additional questions. During the examination, reflexes and the presence of external signs are checked - symmetry of the shoulders and limbs, disorders of posture and motor ability. For a professional neurological examination, special instruments are used, the set of which depends on the nature of the disease. It could be:
- hammer (reflexes);
- needle, brush/cotton wool (deep and superficial pain sensitivity, respectively);
- tuning fork (susceptibility to vibration);
- compass (sensitivity at different points of the body);
- pens, pencils, keys (object sensitivity);
- dynamometer (muscle strength measurement).
Neurological pain and its causes
Pain is a frequent accompaniment of various neurological diseases, and this is exactly what a neurologist treats. However, it can develop for various reasons. The most common painful sensations are caused by the following pathological processes:
- pinched nerve root;
- inflammatory processes localized in soft tissues;
- destruction of articular cartilage due to osteochondrosis and other degenerative diseases;
- muscle spasm;
- influence of external factors (trauma).
In all cases, if pain occurs, you must make an appointment with a doctor. Determining the cause of pain is very important to design effective treatment. In order to eliminate this symptom, a neurologist can prescribe medications or physical procedures that have a good analgesic effect. However, such treatment will be symptomatic, and the result will be temporary. If you eliminate the very cause of the pain, this symptom will disappear forever.
Diagnostic methods
Examination using instrumental and (less often) laboratory methods is an integral part of the diagnosis of neurological diseases and their complications. The choice of a specific technique is carried out taking into account the nature of the violations. In modern diagnostics, one or more studies from the following list may be used:
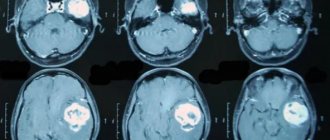
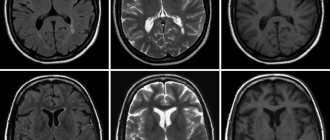
- magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI. The procedure is performed with or without contrast; a contrast tomogram has more accurate results;
- computed tomography, or CT scan, of the brain;
- echoencephalography (ECHO-EG), positron emission tomography (PET/CT);
- angiography of cerebral vessels;
- X-ray, ultrasound of the spinal column;
- myelography;
- ultrasound with Doppler (Doppler scanning);
- electroneuromyography (EEG);
- gamma encephalography (EEG).
For radiculitis and intervertebral hernias, a lumbar puncture may be prescribed. A number of diseases require blood and urine tests.
Neurologist - what does he treat in adults and children?
What symptoms require an appointment with a neurologist?
If you are often tormented by causeless anxiety, the inability to stay in stuffy rooms, you have become very nervous, and are prone to fainting, then you need to pay close attention to your health. Such complaints, even from light loads, are a reason to consult a neurologist.
Who is a neurologist
Before going to a medical institution, you need to understand who a neurologist is and what he treats. Both adults and children may need this doctor. A neurologist specializes in diseases of the autonomic system and disorders of the functioning of the nerves of the spinal cord and brain. He is engaged in careful consideration of complaints and subsequent treatment of identified diseases. This specialization can only be obtained by a person who has a diploma from a higher medical institution. Among the diseases that this doctor treats are the following: neuralgia, tumors of the brain or spinal cord, neuritis, strokes, circulatory disorders, convulsions, head injuries, back injuries, sciatica, Alzheimer's disease, migraines, tremor in newborns, impaired concentration, motor disorders, mental disorders and others. Often, to stabilize the condition of such patients, it is necessary to involve a psychiatrist and psychotherapist.
What does a neurologist do?
A neurologist specializes in diagnosing and treating diseases related to the functioning of nerve fibers. It identifies the primary causes of diseases and their impact on a person’s overall well-being. A good doctor quickly and effectively prescribes competent treatment, which can significantly improve the patient’s quality of life. A neurologist who treats chronic fatigue is the most sought-after doctor in modern medicine. Neurology is a science that studies the connection between the nervous system and human well-being. Neuropathology is the object of research and study of all neuroneurologists. Absolutely all diseases associated with impaired functioning of nerve fibers can be addressed to this doctor. Neurosurgery is a branch of surgery that deals with the surgical treatment of such diseases.
What diseases does a neurologist and neuropathologist treat?
Is there a difference between these specialties? In reality, a neurologist and neuropathologist treats diseases of the nervous system. It’s just that the term “neurologist” was used in the 80s of the last century. In domestic medicine, these concepts are identical. But in foreign practice, a neuropathologist specializes in the pathomorphology of the nervous system, and a neurologist deals with the identification and treatment of diseases of a nervous nature.
What does a neurologist look for?
A neurologist looks at the functioning of the nervous system. Performs an initial examination, checks unconditioned reflexes. The examination also includes a visual examination and palpation. The main task is to identify deviations in a person’s sensory or motor activity. If there are visible violations, he prescribes additional examination or treatment.
What tests does a neurologist prescribe?
When assessing the patient's condition and to facilitate diagnosis of the disease, the neurologist prescribes tests. To accurately determine the disease, a vision or hearing test may be necessary. A specialist may prescribe the following types of tests:
- general blood analysis;
- Doppler ultrasound of the neck, head;
- electroencephalography;
- Brain MRI;
- electroneuromyography.
What complaints are addressed to a neurologist?
This doctor establishes a cause-and-effect relationship between the nervous system and the pathological condition and prescribes treatment. Sometimes you just need to adjust a person’s lifestyle to achieve the desired effect. An abundance of stressful everyday situations and poor environmental conditions are important factors in the manifestation of neurological diseases. The most common complaints that people come to a neurologist with are:
- fast fatiguability;
- frequent dizziness;
- poor concentration;
- constant bad mood;
- behavioral disorders;
- mental disorders;
- sleep quality disorders;
- constant feeling of fear and anxiety.
What symptoms do you see a neurologist for?
The most important thing is to detect early symptoms, this will prevent the development of serious diseases. A combination of negative factors affecting a person, if not promptly contacting a specialist, can aggravate the situation. A neurologist is consulted with symptoms such as:
- regular headaches;
- soreness in the chest on the left;
- fluctuations in blood pressure;
- increased nervousness;
- migraine;
- disturbances in the functioning of the sweat glands.
What problems do people consult a neurologist for?
The reasons for visiting a neurologist are a deterioration in a person’s quality of life. Chronic fatigue and overexertion in everyday life causes disorders of the cardiovascular system. And this brings with it hypotension (low blood pressure), hypertension (high blood pressure). It is fraught with the development of various metabolic disorders. The most important thing is to consult a doctor in time for help. The specialist will prescribe professional therapy and medication.
What does a neurologist treat in children?
The difference between a pediatric neurologist and an adult is that an adult doctor approaches a child with different treatment methods. Parents of children come to us with the following problems: impaired concentration, inability to concentrate, poor performance at school. Any deviations or changes in behavior are a reason to visit a pediatric specialist. This is the first obligatory doctor who examines a newborn baby. It eliminates the risk of developing postpartum pathologies. A pediatric neurologist will help identify early problems in a child’s development and prevent their occurrence.
Take care of your health, do not self-medicate, but consult a specialist! Take care of yourself and your loved ones!
Principles of treatment
What does a neurologist do when there is already a diagnosis? Begins to treat the disease using different methods.
Medicines
To relieve acute pain and inflammation, medications are prescribed, and maintenance therapy is provided if necessary. Problems with blood vessels, concussions, epilepsy, and conditions after surgery almost always require medication.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy is a treatment with hands (from the Latin manus - hand), which helps eliminate functional blocks and muscle spasticity, normalize microcirculation and range of motion. Widely used for diseases of the joints and spine, neuroses.
Massotherapy
One of the most effective methods of treating neurological diseases, along with therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy. Using special techniques, the specialist gently influences the patient’s body to stimulate the body’s natural recovery processes.
Physiotherapy
Through physical techniques, it is possible to accelerate tissue regeneration processes, improve nerve conduction, thereby reducing the intensity of pain and inflammation.
Reflexology
The essence of the method is the impact on bioactive points to restore the disturbed balance. It is based on the idea of the body as an integral system, when one of its elements fails, others suffer.
Traction traction
Used to stretch limbs and muscles in case of bone fractures and diseases of the spine.
Kinesitherapy
“Movement treatment” is how this term is translated from scientific language. This is a type of physical therapy that combines medical, physiological, and biochemical aspects.
Osteopathy
This is a method similar in effectiveness to massage and manual techniques. But, unlike them, it affects the very cause of the disease, helping to restore the well-coordinated functioning of the body.
Therapeutic blockades
For severe pain that cannot be relieved with conventional medications, the sore spot is injected. Injections are made directly into the painful area, hitting the nerve endings. The procedure relieves a person from pain in a matter of minutes for a period of half an hour to several days.
Neurologist consultation
A free or paid consultation with a neurologist in Moscow is divided into several stages: clarifying the patient’s complaints, the characteristics of his life and medical history, as well as conducting a comprehensive examination. As soon as the patient enters the office, the doctor immediately pays attention to his gait and posture. Then he finds out the symptoms that bother the patient, and also asks about the intensity and localization of pain, the state of hearing, vision, smell, memory, sleep, attention, and tolerance to vestibular stress. After listening to all the complaints, the neurologist clarifies the frequency and intensity of various symptoms.
The patient should describe all complaints in as much detail as possible, and also talk about when the symptoms first appeared and whether any previous attempts at examination and treatment were made. In addition, the doctor may inquire about the patient’s daily routine, working conditions, previous injuries, illnesses, and stress.
The doctor must also assess the patient’s psycho-emotional state and ability to navigate in space and time. To do this, he can ask the patient where he is, what month and year it is. After collecting complaints, the neurologist begins to examine and examine the patient. All examination data upon completion are entered into the medical record. It is worth noting that not in all cases a comprehensive examination is necessary - sometimes an abbreviated scheme is sufficient to assess the patient’s condition.
- Inspection
- Audit of the motor sphere
- Sensitivity study
- Motor coordination assessment
During the examination, the doctor identifies such visible signs of neurological disorders as asymmetry of the face and body, hand tremors, hypertrophic and atrophic changes in muscles and skin. At this stage of the consultation, the doctor also assesses the condition of the oculomotor nerves (asks the patient to monitor the movement of the hammer), sense of smell (allows him to smell various substances), glossopharyngeal nerve and facial muscles (asks him to frown, puff out his cheeks, bare his teeth, wrinkle his forehead).
At this stage of the appointment, the doctor examines tone, reflexes and muscle strength. To assess strength, the patient must perform an action, such as shaking a hand or resisting hip flexion. Checking muscle tone is carried out on relaxed limbs by performing passive movements. The reflexes of the legs and arms are tested using a neurological hammer. For this purpose, the neurologist strikes the knee, wrist, elbow or Achilles tendon. The coordination of movements can be assessed during clenching and unclenching of fists.
First, the neurologist performs a surface sensitivity test. This can be done in different ways - with a needle or test tubes of different temperatures. The study of deep sensitivity is carried out in another way: the doctor asks the patient to close his eyes and asks in which direction he moved his finger. In this way, muscle-joint sensitivity is tested. The doctor may also need to evaluate three-dimensional spatial sense. To do this, the neurologist traces with his finger the contours of various figures on the patient’s body, who in turn must guess them. If the patient complains of back pain, paravertebral pain points are checked.
First, the patient needs to stand for a few seconds in the following position - heels together and toes apart, eyes closed, arms extended forward. Then he needs to touch the tip of his nose with his index finger with both hands at once.