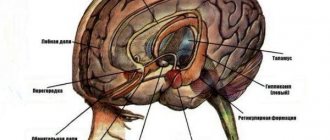
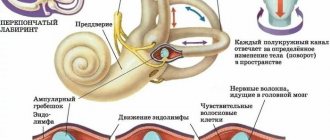
Dizziness and vestibular disorders are related. The human vestibular apparatus is located in the inner part of the hearing organ. The human vestibular apparatus has receptors that are very sensitive and immediately detect any changes in body position. Vestibular vertigo creates a sensation of imaginary rotation of objects around the patient. Most often it is caused by certain damage to the vestibular apparatus; dizziness occurs as a result of damage to the central or peripheral parts of the vestibular analyzer. Other types of dizziness are associated with various diseases and are not related to damage to the vestibular system.
At the Yusupov Hospital they diagnose diseases that cause vestibular vertigo. In the hospital you can undergo examination, treatment and recovery in a rehabilitation clinic. The clinic carries out rehabilitation measures, uses therapeutic exercises, and various types of physiotherapeutic procedures. Instructors select exercises on simulators for patients suffering from dizziness. The vestibular apparatus, which is treated using various methods, is restored in 50-80% of patients after treatment and rehabilitation.
How to treat vestibular vertigo
Dizziness is a common complaint among patients about feeling unwell. Women and the elderly most often suffer from dizziness. Depending on the cause of dizziness, the doctor prescribes treatment. Treating dizziness is a difficult task for a doctor. He refers the patient for examination to determine whether dizziness is caused by diseases. The patient is prescribed symptomatic treatment, which helps to remove symptoms - nausea, vomiting, and stop attacks of dizziness. Vestibular suppressors are used to stop attacks. To prevent attacks from developing, your doctor may prescribe anticholinergic drugs. Such drugs are prescribed with caution to elderly people due to side effects - hallucinations, amnesia, they can cause urinary retention and psychosis in an elderly patient. Some types of antihistamines and benzodiazepines are also prescribed to enhance the inhibitory response of GABA to the patient’s vestibular system.
Vestibular vertigo: symptoms and treatment in older people
Dizziness (vertigo) is manifested by the illusion of rapid rotation of objects around the patient. It may be accompanied by vomiting, nystagmus, nausea, and ringing in the ears. When vestibular vertigo develops in older people, the causes can be varied: lack of blood supply to the brain (cerebral ischemia), multiple sclerosis, head injuries, some types of brain tumors, tumors of the auditory nerve, hormonal imbalance, atherosclerosis, and other disorders. Treatment of vestibular vertigo (vertigo) in older people begins with finding the cause of the dizziness and treating the underlying disease. Vestibular gymnastics for dizziness in older people improves well-being, has a beneficial effect on the heart, musculoskeletal system, and nervous system. Treatment of vestibular vertigo is carried out with the help of drug therapy, physiotherapy, physical therapy, and reflexology.
Examine patients in a standardized setting
The conditions under which a physician examines a patient can have a significant impact on the results of a particular test. For example, it is well known that spontaneous nystagmus recorded after loss of vestibular function can be reduced or eliminated by gaze fixation. This means that at the stage of diagnosis and the period of subsequent observation of the patient, including rehabilitation procedures, the context of the surrounding reality is key.
We recently studied how changes in vestibular and visual cues correlate with the ability to change body orientation in space in patients with Meniere's disease. It was found that body orientation in space in the vertical plane remains impaired 1 week after vestibular neurotomy. In complete darkness, the patient's head was deflected and turned towards the side of the injury; the center of gravity was shifted there too. At the same time, there was also a deviation of the subjective perception of the vertical towards the affected ear. Similar disturbances were observed when the patient was placed in front of a screen with pseudorandom dots without vertical and horizontal visual cues. On the contrary, when the visual background was the environment of the experimental room, which made it possible to perceive the normal coordinates of the vertical and horizontal planes, these disorders were reversible and the patients had a deviation of the head and torso in the direction of the intact side (
).
Shown are the average results obtained in a group of 27 patients with Meniere's disease examined 1 week after unilateral vestibular neurotomy performed for therapeutic purposes. In conditions of complete darkness, the direction of head deflection, lateral rocking movement of the body, and the subjective perception of vertical were shifted towards the lesion in the dark. Under lighting conditions and the absence of a visual vertical reference, no changes in the indicated deviations or their amplitude occurred. On the contrary, in the presence of lighting and a visual reference to the vertical plane, all violations became reversible (deviation of the head, lateral rocking movement of the body) or significantly decreased (subjective visual vertical) (L. Borel et al., 2001).
A schematic illustration of an experimental apparatus is presented that allows recording the orientation of the head relative to the vertical axis (using a two-dimensional motion analysis system), lateral rocking movements of the body (using static posturography - registration of body position) and the position of the subjective visual vertical (using a psychophysical method) in individuals , located in three different types of environments: in complete darkness, under lighting without a visual vertical reference, and under lighting with the presence of a coordinate system in space (the presence of vertical and horizontal plane landmarks in the field of view).
The only parameter that was not influenced by changes in the characteristics of the surrounding environment was the torsional position of the eyes: cyclotorsion of both eyeballs was noted, always directed towards the lesion.
These data convincingly indicate the involvement of more highly organized integrative processes in the process of vestibular compensation, as a result of which the patient can change one spatial landmark to another. In other words, changes in the environment modify the orientation frame and allow the transition from internal to external landmarks and vice versa in conditions where vertical or horizontal coordinates are absent or present, respectively. Consequently, the doctor needs to assess the patient’s condition in a standardized setting and anticipate the result of changes in one or another parameter of the patient’s activity.
Diseases of the vestibular system and dizziness
There are a number of diseases that lead to disorders of the vestibular apparatus:
- Vertebrobasilar syndrome.
- Meniere's syndrome.
- Vestibular neuronitis.
- Thrombosis of the auditory artery.
- Chronic bilateral vestibulopathy.
Vestibular vertigo can be caused by damage to the vestibular nucleus of the brain stem, the vestibular centers of the brain and vestibular connections may be affected. If the vestibular analyzer is affected, the patient will experience certain symptoms:
- Noise in ears.
- Hearing loss.
- Constant dizziness.
When the central parts of the vestibular apparatus (cerebellum, brain stem) are affected, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, vestibular neuronitis or Meniere's disease are most often diagnosed.
New ideas about vestibular rehabilitation and its practical achievements
In addition to the neuroplasticity mechanisms involved in the process of recovery after unilateral loss of vestibular function, there are many factors that can have a powerful influence on the course of vestibular compensation processes by either accelerating or suppressing it. Thus, knowledge about the factors that ensure functional recovery and the factors that inhibit vestibular compensation is of interest from a clinical point of view. Below is a list of factors contributing to the achievement of compensation, which, although they do not claim to be exhaustive, perhaps provide new ideas and useful practical guidelines for otorhinolaryngologists, otoneurologists and physiotherapists who provide rehabilitation to patients with vestibular disorders.
Benign vestibular vertigo
Benign vestibular vertigo is most often considered a pathology of the inner ear; dizziness often occurs when turning the head to the side. The disease may manifest as sudden severe dizziness, nausea and vomiting. Paroxysmal benign positional vertigo develops as a result of the deposition of calcium salts in the ampulla of the semicircular canal. Peripheral vestibular vertigo occurs when the peripheral part of the vestibular apparatus is damaged. Systemic vestibular vertigo is manifested by symptoms of swaying one's own body, rotating objects, bending or falling, accompanied by impaired hearing, balance, nausea and vomiting. Caused by damage to the central or peripheral part of the vestibular system.
FIGHTING SEA SICKNESS
Often, while on a trip, we experience symptoms of motion sickness: dizziness, nausea, headache, lack of appetite.
What is motion sickness and what is its cause? Motion sickness in transport
is the same as the so-called seasickness (in medical language - kinetosis, motion sickness). Kinetosis was called “sea sickness” because people first encountered this phenomenon while traveling on water. Kinetosis occurs when we are exposed to monotonous vibrations - in a car, train, plane, boat, swing or merry-go-round.
Cause of Seasickness
- a malfunction of the vestibular apparatus, which is responsible for keeping us firmly on our feet. It responds to changes in the position of the head and body in space, as well as to acceleration. When a person's body moves and sways in a car or on a ship, the brain receives conflicting information from different senses.
Receptors of the vestibular apparatus say that the body is motionless, but the eyes see that everything around is moving and oscillating. This failure leads to dizziness and nausea. Most people have a vestibular system that is trained enough to easily tolerate these disruptions. People who get motion sickness in transport apparently have some genetic characteristics that cause the vestibular apparatus to fail to cope. Although there may also be provoking external factors: heat, stuffiness, the smell of tobacco, alcohol consumption, overwork, emotional stress, pregnancy. In children, the cause of kinetosis is often insufficient maturity of the hearing organ, where the vestibular apparatus is located, and the autonomic part of the nervous system. As you grow older, these phenomena disappear.
To “deceive” the vestibular apparatus, you can move your feet or shift from heel to toe. This will reduce the discrepancy between signals from different senses to the brain: the vestibular system will decide that you are walking on the ground
TRAINING THE VESTIBULAR APPARATUS:
Stand next to a cabinet or at the back of a chair and make 1 turn clockwise. You can make one more turn to avoid falling. Turn around in the opposite direction counterclockwise 2 times. Do the exercise again, 2 turns in both directions. The next day, increase the number of turns by 1 in each direction, etc.
“Planet Health” talks with Doctor of Medical Sciences Irina Nikolaevna Kholodova, professor of the Department of Pediatrics with a course of outpatient pediatrics named after. G. N. Speransky RMANPO.
— Irina Nikolaevna, is motion sickness a disease?
- This is not a disease, but a symptom. But it may be a signal of some problems or diseases in the body that require mandatory clarification. This is often the result of inflammation of the ear, ailments of the autonomic nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and tumors in the brain. If motion sickness is caused by a disease, it cannot be cured without treating the underlying disease. Nevertheless, motion sickness can be an individual physiological feature in completely healthy people. This greatly complicates a person’s daily life, since even an ordinary trip on public transport turns into a problem for him. And long trips become completely impossible. But motion sickness can be treated if you take this problem seriously and thoughtfully.
—Who usually gets seasick?
— The prevalence of motion sickness is extremely high. Studies have shown that motion sickness occurs in more than 60% of cases in children under 10 years of age. At the age of 10 to 20 years, motion sickness is noted by 45% of respondents. On average, 5–10% of people suffer from systematic motion sickness. Older people are much less likely to complain of motion sickness.
— How does motion sickness manifest itself in adults and children? Is there a difference in symptoms?
— Manifestations of kinetosis are the same in both children and adults: a feeling of nausea, vomiting, cold sweat, severe dizziness, a feeling of lack of air, panic. The only difference is in the causes of its occurrence - in children it is associated primarily with imperfections of the vestibular apparatus and nervous system. Childhood motion sickness most often goes away after adolescence. In adults, it is often not possible to find out the cause of kinetosis. It is believed that it may be caused by genetic characteristics, heredity, a sharp change in position in space, emotional stress, and impaired blood flow.
— What recommendations can you give before the trip?
— If possible, choose night trips. “Motion sickness” is due to the fact that visual signals and the sense of the body’s position in space do not coincide. A difficult journey can go better in the dark. You can try thick sleep glasses. In order to make your life easier, you need to follow simple recommendations. Firstly, two hours before travel it is better not to eat, drink alcohol or carbonated drinks. Secondly, on board the transport you need to be distracted and have fun, even if just to talk with a fellow traveler. In addition, you need to choose the right location. On a sea vessel these are cabins in the middle of the ship, closer to the waterline; on an airplane - seats close to the wings; in a car or bus - the front seats. In any transport, you should avoid seats located in the direction opposite to traffic. If we are talking about traveling on a ship, it is better to be at the stern and look not at the waves, but at the horizon line, which is motionless. In a car, it is optimal to sit in a seat next to the driver and keep an eye on the road. To avoid severe motion sickness, you should not read while in a moving vehicle.
— What to do if the disease takes you by surprise?
- If seasickness takes you by surprise, you need to let the patient swallow small pieces of ice and drink acidified water. Many people find that cold on the face, neck and a warm heating pad on their feet help. Another remedy is to establish deep rhythmic breathing (8-10 times per minute). A radical remedy for seasickness is to stop traffic and not use this type of transport in the future. Of course, if a person becomes ill in an elevator, there is no problem - climbing to the desired floor on your own is only good for your health.
- But what if you get motion sickness everywhere?
- In this case, training the vestibular apparatus will help. You can start riding on swings and rides. Balance exercises are very effective - for example, when you need to hold your body weight alternately on one leg and the other with your eyes closed, rotate your body and head in different planes, or exercise on a large gymnastic ball. Acrobatics, swimming, gymnastics, dancing, somersaults, trampolining, swimming, diving, skating and roller skating will also help strengthen the vestibular system. In the morning, you can do special gymnastics, with bending the torso and head, turns, somersaults, jumps, and various exercises on the horizontal bar. Start with a few repetitions, gradually increasing their number. Looking at the gadget, you can feel nauseous, even if you usually don’t get motion sickness in transport?
— While in motion, for example, in a car, a person feels through the vestibular apparatus that he is moving with a certain acceleration and in a certain direction, but at the same time, the receptors of his muscles, bones and joints send information about his complete immobility. Such a contradiction between two streams of information irritates the centers that control balance and body position in space, which in turn causes dizziness, nausea and vomiting. And if at the same time a person is also looking at the gadget, his eye reacts to movements up, down, and to the side. As a result, random signals begin to enter the brain, which enhance kinetosis.
— What medications can be used to prevent and treat motion sickness?
— If the recommendations do not help, you can use drug therapy. The most promising is the use of natural preparations based on products of natural origin. They have proven effectiveness in practice, are safe, especially for children, and help get rid of the main symptoms of motion sickness without side effects or sedation. As a drug that satisfies all these requirements, the complex drug “Cocculin” can be recommended, which has been successfully used in France since 1969. It contains components that can eliminate all the symptoms of motion sickness described above. The peculiarity of “Cocculin” is that it can be prescribed to both adults and children, has an effect proven in clinical trials, and also has no side or toxic effects.
— What is the regimen for taking the drug “Cocculin” ?
— The dosage regimen is simple: prevention — 2 tablets 3 times a day the day before and on the day of the trip; treatment - 2 tablets every hour until the condition improves.
The tablets should be slowly dissolved 20–30 minutes before meals or 1 hour after meals. The accumulated experience in the use of Cocculin allows us to recommend the drug for the treatment of children from 3 years of age and adults with symptoms of motion sickness in transport.
Buy Cocculin
Exercises for vestibular vertigo
Dizziness often occurs when turning the head or body - this forces patients to try to avoid such movements. Gymnastics for patients with vestibular system disorders includes various types of exercises, including exercises with head and body turns. Exercises can be performed while sitting on a bed, with or without a pillow, sitting on a chair, or standing. The exercises are based on the principle of sensory mismatch between the movements of the eyes, torso and head. Special simulators that work on the principle of biofeedback will help increase the effectiveness of gymnastics. During the training period, you should avoid taking sedatives and alcohol.
A set of exercises to normalize a healthy state
It is recommended to perform physical exercises to treat diseases of the vestibular system daily for at least a quarter of an hour. It is preferable to do them twice a day. At first they are performed slowly, but over time you can increase the pace.
- They stand straight, move their gaze left and right, and then in a zigzag. The head remains motionless. Do twenty repetitions.
- Stand straight and tilt your head back and forth. Do twenty tilts in each direction. Over time, they move on to performing this exercise with their eyes closed.
- They sit on a chair. They shrug their shoulders, and then spread them in different directions and lean forward.
- Take a tennis ball and throw it from your right hand to your left for one minute. Throw the ball above eye level. Next, they raise one knee and repeat the exercise, only this time they throw the ball over the knee.
- You need to walk around the room. Then they close their eyes and walk around the room again. If there are no unpleasant symptoms, you can go up and down some small obstacle, for example, stairs.
Treatment of diseases of the vestibular apparatus should be comprehensive and timely. Next, let's talk about preventive measures.
Tablets for vestibular vertigo
Drugs for vestibular vertigo are Betaserc, Betagistin, Tagista, Vestibo, as well as drugs that support the endocrine system, the heart, and reduce blood pressure. Betaserc improves blood circulation in the brain and promotes the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. Betahistine is often used in complex treatment; it helps with nausea and vomiting. Tagista improves blood circulation in the brain and reduces lymph pressure in the labyrinth of the inner ear. A stable effect is achieved after a month of treatment. Vestibo improves blood circulation in the inner ear and brain; the drug is used in complex therapy.
Use static and dynamic tests that evaluate all broken functions
As already indicated, static and dynamic disorders do not recover over the same period of time and do not involve the same mechanisms. Consequently, the effectiveness of rehabilitation programs or drug therapy cannot be adequately assessed without the use of a significant arsenal of tests that can be used to study all impaired functions of the vestibular apparatus.
Modern tests should be used in clinical practice. It is not enough to conduct only a caloric test to assess the integral functional state of the vestibular apparatus or a classic test on a rotating chair to assess the normal vestibulo-ocular reflex, since they determine the functioning of the horizontal semicircular canal in the low-frequency range. Studies of vestibular function should also be carried out in the high-frequency range in which natural head movements occur (2-20 Hz), and evaluate the functioning of the vertical semicircular canals. For example, the high-frequency active head shaking test (HST, head shaking test) should be used more widely. In addition, simpler tasks make it possible to assess the function of the otolith (myogenic-induced potentials, subjective visual vertical and movement trajectory deviation), that is, to study the state of the sensors involved in the movement (not rotation) of the head in space, which is carried out in everyday life. Bearing in mind that vestibulocortical projections (the representation of vestibular functions in the cerebral cortex) play a key role in spatial orientation, orientation tasks may well be performed in vestibular disorders as routine tests to assess associated perceptual and cognitive impairments.
It is now clearly established that to assess the functional state of the vestibular apparatus, it is necessary to conduct both static and dynamic tests that examine its three main functions (vestibulospinal, vestibulo-ocular and vestibulocortical), which may be impaired in vestibular disorders. Thus, to obtain an idea of the degree of dysfunction of these subsystems, it is not necessary to use complex examination methods.
Treatment in Moscow
The best treatment for vestibular disorders is considered to be exercises for dizziness or vestibular rehabilitation. Vestibular rehabilitation is carried out in many special centers, including the rehabilitation center of the Yusupov Hospital. Therapeutic gymnastics is carried out by an instructor, classes are developed individually for each patient. A preliminary examination by a neurologist will help determine the cause of dizziness, and the doctor will prescribe effective drug treatment. A neurologist will tell you what examination to undergo and how to cure vestibular vertigo during your consultation.