Numbness in the hands is the first signal to make an appointment with a neurologist. Numbness often indicates inflammation, damage, or compression of sensory nerves. With numbness of the limbs, pain and tingling may occur, muscle tone may decrease and movement of the limbs may be impaired - this is the result of damage to mixed nerves, which include both motor and sensory fibers.
People of certain professions should pay more attention to the numbness that occurs. There is a group of professions that are more likely to be susceptible to carpal tunnel syndrome, which causes frequent pain, numbness and tingling that affects the entire hand. If you are: a driver, a cashier, involved in jewelry making, programming or music, then you are more at risk than others of getting an occupational disease, you should monitor your health more carefully.
If you have direct or indirect symptoms, you should be examined by a neurologist; these symptoms may include:
- Sudden numbness, localized or spreading throughout the body.
- Prolonged feeling of weakness.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Numbness in the arms or legs.
- Loss of sensation in the face and torso.
Content:
- Causes of numbness
- Typical clinical picture
- Other symptoms
- Treatment
Alcohol in excessive quantities has a negative effect on all organs. The nervous system is also very sensitive to its effects - central (CNS), as well as peripheral. One of the consequences of this effect on the nerve structures is numbness after heavy drinking, which is felt in the hands.
At first it is insignificant, then it progresses - it causes discomfort and interferes with performing various types of work with your hands.
There is another side to the “coin”: such a feeling is not only unpleasant in itself, but can signal the possible development of a stroke.
Causes of numbness
In alcoholics, this pathology occurs due to acetaldehyde. This organic substance is formed in the body as a result of the breakdown of ethanol. Acetaldehyde is characterized by pronounced toxic properties. During an alcoholic binge, it is not completely eliminated from the body (in addition, the liver, damaged due to prolonged use of alcoholic beverages, does not fully neutralize it), it enters the organs and tissues through the bloodstream and poisons them.
Numbness due to the toxic properties of acetaldehyde occurs for two main reasons - due to its influence:
- on the structures of the central nervous system;
- directly to the nerve endings in the soft tissues of the hands.
Once in the brain, this substance disrupts intracellular processes. Because of this, the functions of the organ suffer significantly, including the function of recognizing and evaluating impulses that come from various structures. This mechanism of occurrence of the described pathology is called central.
In addition, acetaldehyde enters the soft tissues of the hands through the bloodstream, where it affects peripheral nerve endings. Impulses through them begin to be transmitted to the brain centers with malfunctions - the hands become numb, and other symptoms also appear.
There are several mechanisms of the negative impact of acetaldehyde - this effect is:
- directly on the nerve fibers of the hands;
- on the myelin sheaths covering them;
- on brain tissue;
- on its vessels, because of which the blood supply to the brain structures suffers with all the ensuing consequences.
Diagnostics
At the first visit, the doctor interviews the prospective patient about the nature of the discomfort, the frequency of occurrence of the symptom, and other clinical manifestations that occur in combination with numbness. They also collect information about cases of paresthesia in the past, the nature of professional activity, and lifestyle. The hereditary factor (cases of neurological and vascular diseases in close relatives) is of no small importance. Find out whether there have been previous surgical interventions that could lead to paresthesia.
Next, the level of sensitivity of the skin is examined in areas that are affected by paresthesia, as well as in adjacent areas. When examining the epidermis, the doctor pays attention to the shade of the skin, the volume of hair on the head near the face (are there areas with hair loss), local temperature (as the inflammatory process develops, it increases).
Symptoms of paresthesia:
- tingling or burning sensation on the skin;
- "goosebumps" on the face;
- blanching of the epidermis in the area with paresthesia;
- numbness.
Paresthesia occurs suddenly, without precursor symptoms, or gradually, supplemented by other clinical manifestations. As a rule, sensory disturbances are short-lived and occur in “flares.” Rarely is the symptom continuous, which is possible with the development of severe multiple sclerosis.
To determine the cause of paresthesia, that is, a neurological or vascular disease, instrumental and laboratory diagnostics are prescribed:
- blood tests for sugar levels;
- blood tests for levels of toxic substances;
- biochemical blood test;
- ultrasound diagnostics of vessels of the neck and head;
- X-ray examination of the spinal column in the cervical region;
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the spinal cord and brain.
One of the common methods for diagnosing the primary pathological process is electroneuromyography. The study makes it possible to estimate the rate of transmission of excitation factors along nerve fibers and, as a result, to identify a violation of this process.
If there is a suspicion that paresthesia is caused by filling material entering the dental canal, diagnostic measures are carried out by a dentist.
Typical clinical picture
Numbness of the fingers after heavy drinking can be observed in isolation or the entire hand may become numb.
This pathology is often accompanied by distortion of sensitivity:
- painful - with mechanical impact on the tissues of the hands and fingers, pain sensations are muted or do not occur at all;
- thermal - such patients are often susceptible to frostbite and burns, because they do not feel high and low temperatures and do not control their influence;
- tactile - the patient may not feel touch.
If alcoholic delirium (fever) has developed, then tactile sensations are often distorted - up to the appearance of tactile hallucinations. An alcohol addict feels as if someone or something is touching his hands. This creates the following sensations:
- “goosebumps”;
- crawling insects;
- tickling;
- tingling (even painful);
- burning;
- superficial touch with soft or hard objects;
- blowing wind
and others.
If alcohol dependence progresses over time, then there is a high risk of developing polyneuropathies - this term refers to multiple lesions of peripheral nerves. This is usually observed in alcoholism of 2-3 degrees. Symptoms appear that are generally characteristic of polyneuropathies:
- glove-like pain in the upper extremities. Accompanied by a similar disorder in the legs, similar to “socks”;
- loss of sensitivity like “gloves” with the presence of the same “socks”;
- convulsions;
- movement disorder.
In severe cases, the hand curls.
Why do my hands go numb?
Doctors believe that if a person is young, the cause is in the nervous system, and if an elderly person, it is in the blood vessels or endocrine system.
Are common
In most cases, both hands may go numb due to illness.
Household
The reasons for numbness are simple - a person sat in an uncomfortable position, which pinched the nerves and blood vessels. This disrupted blood flow and impulse transmission. This occurs most often in the following cases:
- The man raised his arms above his chest.
- He was carrying a heavy bag.
- Wears tight clothes.
- Performs work manually.
- Sleeps on one side.
If negative factors are eliminated in a timely manner, the discomfort will also disappear. But if it becomes a habit, chronic diseases may appear.
Problems with the circulatory system
Blood enters the arms through the aortic arches, passing through the chest cavity. The following arteries are found in the arm:
- Radial.
- Elbow.
- Palmar.
There are many small vessels in the palm. And if some stop functioning, others replace them. If the body is healthy, sensitivity will be restored quickly.
But if pathologies are present, some symptoms last a long time. Vascular thrombosis is considered a dangerous disease. If the blood clot is in the artery that supplies the arm, the person will lose sensation from the fingers to the entire arm.
Numbness may result from vascular aneurysms. These are small formations that fill with blood, pinching the nerves. Another disease is vasopathy or angiopathy. The tone of the vascular walls decreases, the lumen narrows, and blood circulation is disrupted. This causes ischemia. The tissues that feed from these vessels lack oxygen.
Lack of vitamins
Numbness may occur if the body does not have enough vitamin B or minerals. At the same time, a person quickly gets tired, and his memory deteriorates. And if there is not enough vitamin A and E, the performance of bone marrow cells is impaired, and the development of red blood cells and other blood cells slows down.
Atherosclerosis
This is a disease in which cholesterol accumulates in the blood vessels. Lipids do not allow normal blood circulation. The symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- Cramps when relaxing.
- Insomnia.
- Itching and burning.
Hands look pale and nails become thicker. Hair density decreases.
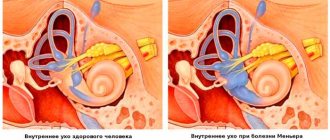
Raynaud's disease
A common disease in women. The small arteries of both arms are affected. The disease usually occurs in car drivers and pianists.
Numbness appears as a result of spasms in the blood vessels. The skin turns pale, becomes colder, and sensitivity worsens. As soon as the spasm passes, the skin returns to its original state. But relapses are possible, sometimes every day.
Herniated discs
This can also be a cause of numbness. If a person experiences numbness in his fingers, changes occur in the neck area. There are signs by which a hernia can be identified:
- Arms and shoulders hurt.
- Blood pressure rises.
- My head is spinning.
Metabolism problems
Typically the causes are the following diseases:
- Diabetes.
- Cholesterol deposition.
- Lack of calcium and potassium.
In the latter case, bruises appear on the person’s body, and the wounds do not heal well.
Nerve problems
The hands have many nerves that control sensation. The system contains the following nerves:
- Elbows.
- Radiation.
- Musculocutaneous.
- Axillary.
- Median.
If nerve function is impaired, impulses are transmitted more slowly. There may also be pain in the arm or a burning sensation.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Neuralgic disease, when the fingers go numb and the hand hurts. The cause of the disease is compression of the median nerve between the elements that form the wrist and hand. Often found in older women.
Diabetic neuropathy
Another disease that causes numbness in your hands is diabetes. At the same time, a person may feel tingling in the limbs, cramps, and muscle weakness. Sometimes severe pain appears in the muscles, similar to an electric shock.
Osteochondrosis
When the spinal cord nerves are compressed, numbness may occur.
Stroke
If a cerebral artery ruptures or thrombosis occurs, there is a risk of stroke. Usually a person loses sensitivity in the limb for which the damaged hemisphere is responsible. First, the little finger and ring finger go numb. A stroke can also be identified by other symptoms:
- Muscle weakness.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Incomprehensible speech.
- Deterioration in coordination of movements.
- Dizziness.
- Increased pressure.
- Numbness of fingers.
A numbness in the finger may also indicate an illness:
- Little finger of the left hand – heart problems, for example, heart failure.
- Unnamed - compression of the nerves in the elbow area. Perhaps they are injured.
- Thumb. Osteochondrosis or vitamin deficiency.
- Pointing. Diabetes mellitus, joint inflammation or diseases of the endocrine system.
- Average. Raynaud's disease or spinal diseases.
Numbness can also occur with fungal infections.
Chronic kidney disease
Uremia may develop if the kidneys are affected. Toxins begin to accumulate in the blood, which affects the nerves. As a result, the limbs go numb. If the disease is advanced, only an organ transplant will help.
Injury
Hand numbness can occur after injury:
- Tendon rupture.
- Stretching.
- Fracture.
Injuries usually result from frostbite or shock. Blood circulation is disrupted, which leads to symptoms.
Other diseases
There are other diseases that can cause numbness in the hands. For example, HIV, which activates an infection that affects the nerves.
Other symptoms
If numbness in the hands after binge drinking occurs due to a pathology of the central nervous system, then other clinical symptoms may occur, including not only in the hands. Observed:
- change in gait;
- deterioration in the mobility of the fingers of the upper and lower extremities;
- feeling of weakness in half of the body.
Caution should arise if:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- diplopia (double vision);
- difficulty swallowing (even when trying to swallow liquid);
- speech disorder;
- feeling as if the tongue is pulling;
- insomnia.
Such failures indicate the possible development of a stroke - a cerebrovascular accident.
In what areas can numbness occur?
If your arms and legs often feel numb, pay attention to where the loss of sensation occurs. Sometimes this criterion is of value to the doctor during diagnosis.
- Numbness of the hands and feet - observed with a spinal injury, hernia or pinched spinal nerves.
- Loss of sensation in the fingers - occurs with carpal tunnel syndrome, when the nerve is compressed by swollen muscles.
- Numbness in the arm and leg at the same time indicates serious disorders in the body. The causes may be neurological, orthopedic and vascular.
- Numbness combined with dizziness - the most common cause is neuralgia.
- Numbness of the limbs and face - here one should suspect damage to the brain or blood vessels. Consultation with a doctor is required.
- The right arm and leg are numb - a one-sided lesion indicates pinched spinal nerves. Often occurs with curvature of the spine, hernias.
- Reduced sensitivity in the left arm and leg - indicates neurology, the presence of heart and vascular diseases. You should see an orthopedist. Often the cause is a curvature of the spine.
To identify provoking factors, it is necessary to analyze the characteristics of working conditions. Poor posture often contributes to loss of sensation in the limbs.
Treatment
In the treatment of the described pathology, the following are used:
- vasodilators;
- diuretics;
- anticoagulants (drugs that prevent increased blood clotting);
- drugs that improve the conductivity of nerve structures;
- nootropics - drugs that improve blood circulation in the brain;
- vitamins and vitamin complexes;
- painkillers. They are taken orally or injected. If necessary, novocaine blockades are performed.
Simultaneously with neurological treatment, he detoxifies the body to remove acetaldehyde from it. For this purpose the following are involved:
- infusion therapy - various solutions are injected intravenously, along with them the dangerous metabolite of ethyl alcohol is removed from the body;
- detoxification using hardware methods - plasmapheresis, hemosorption.
Physiotherapeutic methods that are also successfully used are :
- galvanization;
- UHF;
- Microwave;
- ultrasound;
- paraffin applications;
- mud applications and wraps;
- massage.
After completing the course of therapy, if necessary, sanatorium treatment is prescribed.
If the upper limbs of an alcoholic become numb due to a pre-stroke condition, he should be hospitalized in a hospital.
This pathology can occur repeatedly. Therefore, it is of great importance to rid a person of alcohol addiction - if he does not give up the addiction, he will continue to be haunted by diseases and pathological conditions caused by the negative effects of alcohol on the body. Competent specialists in a good clinic will help you get rid of addiction.
Treatment of headaches and hand numbness
Treatment is individualized and depends on the final diagnosis. Its goal is not only to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and pain, but also to get rid of their underlying cause. So, the doctor may prescribe:
- for stroke - a comprehensive rehabilitation program aimed at restoring nerve conduction in the affected areas, therapeutic exercises, exercises to improve memory and speech;
- for neck diseases - a set of exercises to perform at home, muscle relaxants, wearing a hard collar if necessary;
- for vascular diseases - a gentle diet, moderate physical activity, drugs to improve blood circulation in the brain;
- surgery - may be required to remove hernias and aneurysms; in some patients it is indicated for injuries.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, it is possible to receive treatment both on an outpatient basis and in an inpatient setting. Also in our center you can select an individual rehabilitation program after a stroke and undergo it under the supervision of doctors. It is important to understand that the effectiveness of treatment will depend not only on the correct prescriptions, but also on their implementation at home.
Literature:
- Guide to neurology according to Adams and Victor: textbook. manual for the postgraduate system. prof. physician education / Maurice Victor, Allan H. Ropper; scientific ed. V. A. Parfenov; lane from English edited by N. N. Yakhno. — 7th ed. — Moscow: Med. information agency, 2006. - 677 p.
- Peripheral nervous system in normal conditions and pathologies: educational manual / N. S. Subbotina; Federal Agency for Education, State. higher educational institution prof. Education Petrozavodsk State univ. - Petrozavodsk: PetrSU Publishing House, 2006. - 129 p.
- General medical practice according to John Nobel / S. Adhikari et al.; edited by J. Nobel, with the participation of G. Green and others; lane from English edited by E. R. Timofeeva, N. A. Fedorova; ed. trans.: N. G. Ivanova [and others]. — M.: Praktika, 2005.