What is femoral nerve neuritis? How is the femoral nerve structured, what functions does it perform in the body? Why does the disease occur? Modern methods of treatment.
Our expert in this field:
Lashch Natalia Yurievna
Neurologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor. Laureate of the Moscow City Prize in the field of medicine.
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
The femoral nerve is a fairly large nerve of the leg. It is mixed in function, that is, it contains both motor and sensory nerve fibers. With the development of the inflammatory process - neuritis - their functions are disrupted.
The main causes of femoral neuritis:
- Poisoning with certain substances.
- Diabetes mellitus is a disease that leads to disruption of blood flow in small vessels, as a result of which the nutrition of the nerve is disrupted and an inflammatory process develops in it.
- Vasculitis is an inflammatory process in blood vessels.
- Violation of the ratio of various proteins in the blood serum (dysproteinemia).
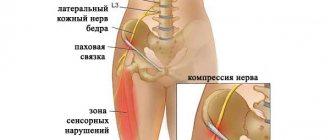
- Impairment of blood flow to the nerve as a result of compression.
- Tunnel syndrome is a condition in which a nerve is compressed in a canal formed by bone and ligaments. There are characteristic places where compression of the femoral nerve can occur with subsequent development of neuritis, for example, under the inguinal ligament.
Why is this happening?
There is evidence that risk factors for compression of the pudendal nerve are:
- Chronic microtraumas (non-systematic exercise according to the principle: “it’s better rarely, but wear it out.” This includes cycling, exercise in the gym, team sports).
- Hormonal disorders (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, etc.)
- Systemic connective tissue diseases (collagenosis, etc.)
- Chronic intoxication (alcohol)
- Genetic predisposition
- Congenital anatomical features of the pelvis
What is hip neuritis?
"Neuritis" is a term that refers exclusively to inflammation in the nerves and has nothing to do with the joints. The inflammatory process in the hip joint is called coxitis.
Usually, neuritis of the hip joint is mistakenly called the same femoral neuritis, or damage to another nerve - the obturator, which is responsible for adducting the hip inward. A characteristic sign of obturator neuritis is the inability to cross your legs.
Often a person comes to the conclusion that he has “neuritis of the hip joint” because he heard this term from someone before, and he began to be bothered by pain in the hip joint. The reasons may be different: damage to the joint, nerve, muscles, bones. You need to visit a doctor and get examined.
If you notice symptoms of neuritis - pain, numbness in the leg, muscle weakness, impaired movement - consult a doctor immediately. Early treatment may provide the best prognosis.
Enduring pain is dangerous!
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Pain in the perineum in pregnant women
Patients often come to the gynecological department of our clinic with the question of why the perineum hurts during pregnancy and how dangerous it is. Normally, such symptoms are associated with the growth of the fetus and its descent. It is typical for the 3rd trimester - it is during this period, due to the development of the child, that there is an impact on the ligaments, nerves and muscles of the mother’s body, which are stretched. However, the occurrence of such symptoms in the early stages may be a sign that there is a high risk of miscarriage.
It is not uncommon for the fetus to put pressure on the nerve that runs nearby. The pain that occurs in this case limits movement and does not stop until the fetus changes position. Modern medicine cannot help in this case.
Perineum hurts before childbirth
Severe pain symptoms that occur over a long period of time are a sign that labor is approaching. It is caused by the expansion of the pelvic bones and other processes of preparation for the process, along with the approach of the fetus to the birth canal.
Perineum hurts after childbirth
Painful symptoms are felt by almost all women afterward, although its strength may vary. It depends on the presence/absence of injuries during childbirth. So, it goes away 3-4 days after birth when it occurs due to swelling and stretching of tissues, and persists much longer with ruptures of the perineum and sutures.
Treatment of neuritis of the femoral nerve
For femoral neuritis, the following types of treatment are performed:
- B vitamins - to improve the functioning of nervous tissue.
- Drugs that improve blood flow - to improve nerve nutrition.
- Drugs that improve metabolic processes in the nervous system and the conduction of nerve impulses.
- Drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - they help cope with pain and inflammation.
- Your doctor may also prescribe diuretics to relieve swelling in the area of the inflamed nerve.
- Physiotherapy procedures help: electrophoresis with novocaine, ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone, UHF therapy.
- They provide massage and physical therapy.
If femoral nerve neuritis is caused by an infection, the neurologist will prescribe antibiotics or antiviral drugs.
If, despite treatment, there is no improvement within 1-2 months, the question of surgical intervention arises. Usually, during the operation, the doctor frees the nerve from the tissues compressing it or restores its integrity and sews together the torn fibers.
Do not self-medicate. At the international neurology clinic Medica24, effective medical care is available at any time. Administrators are ready to take your call every day, including holidays and weekends. Contact us by phone +7 (495) 230-00-01.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
What functions does the femoral nerve perform? What are the main symptoms of femoral neuritis? Manifestations of the inflammatory process in another nerve of the leg – the obturator nerve.
The femoral nerve can be compared to an electrical cable, with many individual “wires” running inside it. They perform different functions: some are responsible for movement, others for sensitivity. Such nerves carrying different types of nerve fibers are called mixed. So is the femoral nerve. Here are the main functions it performs:
- Skin sensitivity: on the front of the thigh, on the inner surface of the lower leg.
- Movements: hip flexion (the femoral nerve helps tuck the legs toward the abdomen), calf extension.
Accordingly, violations of these functions will act as the main symptoms of femoral neuritis.
What diagnostics are performed for pain in the perineum?
Often, when pain symptoms occur in the perineum, the patient does not know which doctor he needs to see. First of all, you should make an appointment with a therapist who, depending on the situation, will give a referral to a urologist, gynecologist, proctologist or surgeon. Diagnostic methods in all cases are specific, the main ones are the following:
- interviewing the patient to determine the nature of the pain and the presence of additional symptoms;
- physical examination by a gynecologist or urologist;
- careful history taking;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- bacterioscopy in women, urethral flora smear in men;
- radiography;
- ultrasonography;
- intestinal colonoscopy;
- examination of the rectal mucosa;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging;
- X-ray of the colon of the bladder with the introduction of a contrast agent into it.
Characteristic symptoms of neuritis of the femoral nerve
If the neuritis occurs in the upper part of the femoral nerve, before it exits the pelvis, the clinical picture of the disease will be most striking. All possible symptoms of femoral neuritis occur:
- Impaired hip flexion. This makes it difficult to lift the body from sitting and lying positions.
- Impaired leg extension. It becomes difficult to walk, run, or climb stairs. A person tries not to bend his leg at the knee again, because after that it is difficult to straighten it. The leg is constantly strongly extended, because of this the gait changes - the patient throws his straight leg forward and places the entire sole on the floor at once.
- Atrophy of the thigh muscles. The affected leg becomes thinner than the healthy leg, which may be noticeable externally.
- Impaired sensitivity. The person does not feel touch or pain on the front surface of the thigh or inner surface of the lower leg.
- Pain. They occur in the same places where sensory disturbances occur.
An experienced neurologist will be able to understand the symptoms that are bothering you and prescribe the correct treatment.
Symptoms of pain in the perineum
The clinical picture that complements pain in the perineum in women and men may be different, since it depends on the pathology that caused it. This means that symptoms vary. The most common ones are:
- Discharge from the urethra or vagina;
- Radiating pain to the pelvis, lumbar region and lower abdomen;
- Increased pain during physical activity;
- Frequent urge to urinate;
- Pus and blood in urine and semen;
- Increased pain during sexual intercourse;
- Sensation of a foreign object in the rectum;
- Increased body temperature.
Clinical manifestations characteristic of a particular disease are presented in our table below:
| Diseases | Additional symptoms |
| Prostatitis |
|
| Perineal injuries |
|
| Malignant prostate tumors |
|
| Inflammatory processes of the vagina |
|
How does obturator nerve neuritis manifest?
Not far from the femoral nerve there is another nerve - the obturator. If neuritis develops in it, the following symptoms occur:
- I can't cross my legs.
- Difficulties arise when trying to turn the leg outward.
- The sensitivity of the skin on the inner thigh is reduced.
In order to correctly understand the symptoms of the disease, you need to be examined by a neurologist. Contact a doctor at the Medical Center International Clinic Medica24 immediately after you notice the neurological disorders described on this page. Call at any time of the day.
The material was prepared by Natalya Yurievna, a neurologist at the international clinic Medica24, Candidate of Medical Sciences Lasch.
Surgery
The operation is indicated if conservative therapy is ineffective and severe pain that cannot be eliminated by conservative methods persists for more than 6 weeks, as well as in the presence of:
- large intervertebral hernias;
- spondylolisthesis;
- spinal deformities;
- hemangiomas, chondromas and other spinal tumors;
- severe dysfunction of the pelvic organs, leading to urinary or fecal incontinence.
In such situations, conservative therapy will, at best, slow down the development of these pathologies, but not eliminate them completely. But if in the isolated existence of, for example, an intervertebral hernia, this is enough to improve the patient’s condition, then in cases where the presence of spinal pathology provokes the addition of sciatica, such measures will not be enough.
After all, the cause of the pinched sciatic nerve remains, it continues to suffer and cause the corresponding clinical picture. Therefore, in such cases, surgery is the only way to achieve a lasting improvement in the condition, restore a normal quality of life and eliminate the risk of loss of ability to work.
But even if there are indications, surgical intervention cannot always be performed. It is contraindicated for:
- pregnancy;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- serious respiratory or heart failure.
A timely operation can completely eliminate the causes of sciatica.
Surgical treatment of sciatica for intervertebral hernias
Herniated discs are a common cause of sciatica. Moreover, the severity of symptoms of nerve entrapment does not always depend on the size of the protrusion. Sometimes even small hernias can cause serious pain, limited mobility and neurological disorders.
Today, the problem of intervertebral hernia can be completely solved only by surgery, but the type of operation directly depends on the size, location and other features of the hernia. For small protrusions, preference is given to percutaneous surgical methods: nucleoplasty and hydroplasty.
In both cases, the essence of the operation is to destroy part of the nucleus pulposus of the disc, which leads to a reduction in the size of the hernia or even its retraction due to the creation of reduced pressure inside the disc. Percutaneous surgery techniques involve the use of thin cannulas, the diameter of which does not exceed several millimeters.
Operations of this type can be performed under general or local anesthesia. The instruments are inserted into the disc under the control of the image intensifier, which allows the neurosurgeon to precisely control the direction and depth of needle insertion, and also practically reduces the likelihood of injury to nerves or large blood vessels to 0.
Using cold plasma, radio waves, thermal laser energy or liquid pressure (during hydroplasty), part of the nucleus pulposus is destroyed. The volume of intervention is clearly controlled by the surgeon. Once the desired effect is achieved, the cannula is removed, and the remaining postoperative wound does not even require sutures. It is covered with a sterile bandage, and within a few hours the patient can leave the clinic and return to daily activities.
But nucleoplasty and hydroplasty are effective only for hernia sizes up to 0.7 cm. In other cases, other methods are used:
- Microdiscectomy – involves removing the hernia through an incision of about 3 cm in the projection of the affected disc. Special miniature instruments are used to perform the operation. Microdiscectomy allows you to remove a hernia of almost any size and location, while the small size of the incision ensures ease of rehabilitation and speed of recovery.
- Endoscopic surgery is a gentle method of surgical treatment of intervertebral hernia, which involves removing it with special instruments that are inserted into the patient’s body through punctures up to 1 cm in diameter. Through endoscopic surgery it is also possible to remove almost any hernia, but if its location is complex, the technique is powerless.
Surgery for sciatica caused by spondylolisthesis
Surgical treatment is indicated for spondylolisthesis, accompanied by a displacement of the vertebra by more than 50% relative to the normal axis. It can be carried out in two ways, and the choice of a particular one is based on the results of the MRI. But with sciatica, stabilization of a displaced vertebra in a normal position is permissible only after removal of the anatomical formation that provokes compression of the nerve and the development of neurological symptoms of sciatica.
In almost all cases, stabilization of a displaced vertebra is carried out using a special plate, which is fixed to a healthy and slipping vertebra using screws. This eliminates the possibility of it being re-displaced from its anatomically correct position. But first it is necessary to carry out:
- Discectomy – removal of the intervertebral disc is indicated if, against the background of spondylolisthesis, an intervertebral hernia forms and impinges on the spinal root. If complete removal of the disc is required, it is replaced with an endoprosthesis or a graft of the patient's own bone. The first option is preferable, since modern endoprostheses are in no way inferior in functionality to natural intervertebral discs.
- Foraminotomy - is performed when a nerve is pinched in the foraminal openings of the spine as a result of a decrease in their size due to the proliferation of bone tissue or other reasons.
- Laminectomy is a radical operation used only in extreme cases when spondylolisthesis has led to stenosis of the spinal canal. During a laminectomy, both individual anatomical structures and entire vertebrae can be removed. In the latter case, the removed vertebra is replaced with appropriate implants.
Surgery for sciatica caused by scoliosis
Scoliotic deformity of the spine often provokes pinching of various nerves and the development of sciatica in particular. Therefore, if the deformity cannot be corrected conservatively, surgical intervention is resorted to.
There are several types of operations performed for scoliosis. The specific tactics for restoring the correct axis of the spine are determined individually, but in all cases special metal structures are used that fix the vertebrae in the correct position. Sometimes they involve correcting the position of the vertebrae after surgery with gradual tightening of the screws to form a more correct axis of the spine.
But if previously all operations to correct scoliosis involved long incisions along almost the entire length of the spine, today this is possible even in a minimally invasive way. As a result of eliminating spinal deformity, the nerves are freed, which helps eliminate the causes of sciatica and progressively improve the patient’s condition.
Prevention measures
It is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it later. Sciatica is no exception. To prevent this disease, women planning pregnancy, like everyone else, should lead an active lifestyle, attend aerobics classes, yoga, go to the pool, and so on several times a week. Strong physical activity, which can negatively affect the condition of the spine, should be avoided. You also need to avoid sudden movements and hypothermia. If, in the process of treating any disease, a doctor prescribes intramuscular injections, they should only be given by a trained specialist. For this purpose, almost every hospital or clinic is equipped with a treatment room. Incorrect insertion of the needle can result in it touching a nerve (which, by the way, is not difficult, because the thickness of the sciatic nerve is approximately equal to a centimeter). Such an injection will cause severe pain, and its consequences can be unpredictable.
Symptoms
Pinching of the sciatic nerve during pregnancy does not go away without symptoms and often treatment of the disease is required urgently. Typically, this pathology is manifested by pain, which occurs in various areas of the lower body and has different intensity and frequency of occurrence. The main symptoms of sciatica include:
- Discomfort or pain in the lumbar region or just below it. Further, the pain can move to the sacrum area, and then down to the foot.
- The pain can manifest as shooting and can be observed only at certain points along the path of the sciatic nerve.
- Pain can occur when bending the body, making sudden movements, or turning the body.
- In cases where the compression of the sciatic nerve is too severe, a pregnant woman may experience problems walking. There may also be numbness and loss of sensation in the areas where the nerve is affected.
- When inflammation of the sciatic nerve occurs due to pinching of the sciatic nerve, body temperature may increase.
- Disturbance in the process of urinary excretion, disruption of bowel function.
A pregnant woman should tell her doctor about any of the listed symptoms, and especially if they are observed in combination.