04/23/2019 · Blog · No comments yet
Every person has experienced a panic attack (PA) at least once in their life - a sudden severe anxiety, which is accompanied by a racing heartbeat, increased blood pressure, and a feeling of heaviness in the chest. But not everyone who has experienced panic needs treatment. There is no treatment for panic attacks as such. Help is needed if PAs have become systematized, frequent, and the person cannot cope with the problem on his own. The article will focus on the so-called panic disorder.
Briefly about the problem
Panic disorder is spontaneous, unexpected panic attacks that occur at intervals from several times a year to several times a day and are characterized by the presence of anxious anticipation of the next panic attack.
Patients often have to consult various specialists to get the correct diagnosis. A person with panic disorder can be observed for a long time by a neurologist with a diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD). Panic attacks and VSD are very similar. This is due to the fact that during panic the autonomic nervous system is actively working.
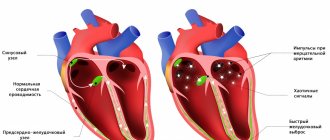
Symptoms during PA are associated with the activity of the autonomic nervous system: during severe anxiety, the hormone adrenaline enters the blood. This is necessary to trigger the biological survival program - the fight and flight reaction, which is genetically programmed. Adrenaline increases the heart rate, increases blood pressure, quickens breathing, blood rushes to the muscles of the arms and legs, flows out of the hands and feet, and the person breaks out in sweat. All this is needed to successfully implement the fight or flight response , nature’s stress response program.
The problem is that nowhere except Russia there is such a diagnosis - VSD. With VSD, the symptoms are vague, and there is no specific cause of the disorder. Therefore, the symptoms of panic disorder easily fit into the criteria for VSD; the person is given an incorrect diagnosis , and accordingly he does not receive proper adequate treatment.
If a person has been correctly diagnosed and has been referred to a psychotherapist or psychologist, then PA therapy for panic disorder can be effective and short-term, even without the use of medication.
How do panic attacks become panic disorder? Initially, there are two reasons for panic attacks: a strong negative or positive experience.
A person experienced stress or had a joyful event, and the body responded to this with physical symptoms. If a person does not attach importance to these symptoms and does not fixate on them, then everything is fine.
If a person fixates on the symptoms and begins to see in the changes occurring in the body an impending disaster - a heart attack, stroke, signs of loss of control and insanity, then this is the first step towards panic disorder .
The second step is to wait for a similar condition to recur, which already leads to the fact that a small amount of adrenaline enters the blood, a vegetative reaction is triggered, and so on in an increasing manner.
Another important criterion for panic disorder is protective behavior. This behavior manifests itself in a person’s actions in order to “save” himself from the consequences of panic symptoms - madness, heart attack, stroke. Protective behavior includes taking medications, calling a doctor, the need to lie down, sit down, and not be left alone.
Protective behavior is a disservice to yourself when dealing with panic disorder. A person has no way to make sure that nothing terrible will happen, that he will calm down over time, without resorting to any means.
This behavior is difficult to refuse. In the short term, it reduces anxiety, but in the long term, it increases it, since each time a person loses faith in his own strength in the fight against the disease.
In the absence of treatment, the repertoire of protective behavior expands, a person becomes more and more limited in life - withdrawal from social contacts, agoraphobia, a constantly high level of anxiety for health, visiting doctors in the somatic network, financial losses, and often the inability to work.
Anatomy
The anatomy and physiology underlying the human body's sense of balance is complex. Many systems are involved, including the brain, spinal cord, eyes, ears, and receptors in the skin, joints, and muscles. Impairment in any of these areas due to injury or illness can negatively impact your sense of balance.
The inner ear, also called the labyrinth, consists of the semicircular canals along with the saccule and the uterus. Collectively, this inner ear system is called the vestibular system or vestibular apparatus.
The inner ear also contains the cochlea, which is the main structure involved in hearing perception.
The three semicircular canals respond to rotational movements of the head. The canals are located at 90 degrees to each other and are filled with a fluid called endolymph. Hair cells are located at the base of each semicircular canal and project into the endolymph. The movement of the head causes movement of the endolymph in the channels, which in turn causes the hair follicles to move accordingly and emit impulses about balance that travel to the brain. Hair cells in the sac and utricle respond to linear acceleration of the head, such as when riding in an elevator or moving forward.
Sensory information from the inner ear is transmitted to the brain through the vestibular portion of the eighth cranial nerve, which is also called the vestibulocochlear nerve. The cochlear part of the nerve transmits hearing information. Certain areas of the brain, particularly the cerebellum and brain stem, as well as parts of the cerebral cortex, process sensory information coming from the inner ear. When both the right and left inner ears send the same information to the brain, the body is balanced. When the body or head moves, the sensory information from the ears is not identical, so the brain perceives the movement and the body adjusts accordingly.
The ears work closely with the eyes to maintain balance. The basis of this is
vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). This is an automatic function of the eyes that stabilizes images on the retina in response to head movements. This reflex causes the eyes to move in the opposite direction to the movement of the head so that the eyes remain stationary on the observed target. Thus, precise information from the vestibular system influences the sense of balance.
If one inner ear is affected by disease or injury, then sensory information sent to the brain will falsely indicate movement from that vestibular system. In this case, the eyes will adjust accordingly and move opposite to the perceived movement despite the fact that the head is actually stationary. The result is involuntary back and forth eye movements. This eye movement is called nystagmus and, if present, makes any healthcare professional suspect a vestibular problem.
There are two other reflexes, the vestibulocervical reflex and the vestibulospinal reflex, which also help the body maintain a sense of balance.
The vestibulocervical reflex works in conjunction with incoming vestibular information and the neck muscles to stabilize the head. And the job of the vestibulospinal reflex is to create compensatory movements of the body in response to vestibular input in order to maintain balance and avoid falling.
Disturbance along any part of the anatomical pathway described above can affect the perception of balance or equilibrium. A problem with the part of the inner ear or sensory information transmitted to the brain through the vestibulocochlear nerve is called peripheral vestibular disorder.
If a problem affecting balance is due to damage to a structure within the brain itself, which then affects the reception and integration of balance information, it is called a central vestibular disorder.
Treatment of panic attacks
The standard treatment for panic disorder worldwide is cognitive behavioral therapy. It has proven its effectiveness in many domestic and foreign experimental studies.
Cognitive behavioral psychotherapy for panic attacks has a number of advantages:
- short-term (6-12 sessions);
- proven effectiveness;
- the ability to do without drug treatment.
Prescribing tranquilizers or antidepressants is advisable:
- the problem with panic has existed for a long time and the anxiety is so strong that starting psychotherapy is difficult;
- Panic disorder is accompanied by depressive feelings.
It should be emphasized that psychopharmacotherapy is only an auxiliary method of treating panic disorder. It does not solve the original problem, which will return after stopping the drugs.
Can a person cope with panic disorder on their own? Yes, with good motivation and good self-help manuals (there are very few of them in Russian).
The main difficulty in self-help remains the lack of a correct diagnosis.
The British NICE system of care for panic disorder places self-help in third place, after cognitive behavioral therapy and psychopharmacotherapy, which is prescribed only if the person has refused psychotherapy.
Causes
There are three groups of etiological factors:
1.
Psychogenic – family quarrels, divorce, betrayal, conflicts at work, etc.
etc. The occurrence of attacks of fear is preceded by the death of a loved one, electric shock, car accident, or illness. Sometimes attacks occur after watching emotional television programs or films. 2.
Biological – changes in hormonal levels (in women during pregnancy, after childbirth, during menopause), taking hormonal contraceptives, the onset of sexual activity, painful menstruation.
Panic attacks do not include conditions caused by diseases of the endocrine system (adrenal adenoma) and hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. 3.
Physiogenic – drug use, alcohol intoxication, weather sensitivity, high physical activity, acclimatization.
Panic attacks occur mainly in patients with certain personality traits: in women with drama and a desire to attract attention; in men – constant anxiety and increased concern for their health.
Benefits of PA psychotherapy
When turning to a psychotherapist in specialized clinics for the treatment of panic attacks, a person has the opportunity to significantly reduce the time of treatment for the disorder. The work follows specialized protocols that take into account all factors in the occurrence and maintenance of the disorder.
Who is psychotherapy suitable for?
Psychotherapy for panic disorder has no special contraindications . The restrictions relate to general contraindications in psychotherapy, for example, cognitive deficits in humans.
Therapy for panic disorder can be carried out without loss of effectiveness online via Skype. This is convenient for remote areas of Russia, where there are no specialists who successfully use methods of treating panic attacks and panic disorder.
How panic attacks are treated by a psychotherapist
The treatment protocol for panic disorder consists of:
- identifying panic triggers;
- psychoeducation of the patient - an explanation of the ongoing processes from a scientific point of view;
- identifying misconceptions about panic;
- withdrawal of protective behavior;
- exposition.
Exposure is the presentation of frightening situations, the experience of which gives the person a new experience that a panic attack is experienced. It helps reduce panic attacks during neurosis. This is a necessary element of therapy, which, through the experience of fear, under the supervision of a specialist, leads to a good result and recovery.