The disease COVID-19, which is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 strain of coronavirus, has led to a pandemic in 2021. It is characterized by a polymorphic clinical picture. This means that the symptoms and severity of the disease depend on many factors: the age of the infected person, the presence of chronic diseases, etc. The disease has different symptoms in different categories of patients, which makes it difficult to diagnose.
Causes of symptoms
Low body temperature (hypothermia) is a decrease in thermometer readings of less than 35 degrees.
The clinical picture occurs in many acute and chronic diseases. This may be a dysfunction of the liver, stomach, or adrenal glands.
A common cause is vegetative-vascular dystonia. This term is often found in modern medicine, but does not refer to officially recognized concepts in medicine. The diagnosis is most often given to those who experience panic attacks, uncontrolled increases in blood pressure, and shortness of breath for no apparent reason.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia has other symptoms:
- weakness;
- short-term decrease in body temperature;
- redness or vice versa – blanching of the skin;
- dizziness, sometimes headache.
At the initial stage of development of the infectious process, a decrease in body temperature is observed. The mechanism of symptom development is associated with the body’s specific reaction to the action of the virus.
Another cause of headaches and decreased body temperature is general hypothermia of the body. In this case, it is enough to drink hot tea and relax, wrapped in a warm blanket.
The cause of low body temperature and headache may lie in emotional stress, for example, due to exposure to a stressful situation. You need to calm down, take the appropriate medication or drink lemon balm tea for the symptoms to disappear.
Low fever and headache in adults often accompany pregnancy. During this period, hormonal changes occur in a woman’s body, which enhance the work of all endocrine cells.
Failure to eat a balanced diet may also result in headaches and decreased body temperature. In this case, you need to normalize your food intake, include sufficient quantities of vegetables, fruits, meat, fish, and dairy products in your diet.
Other conditions that occur with a decrease in body temperature and headache:
- diabetes;
- inflammatory and tumor-like processes in the cerebral region;
- alcohol and drug intoxication of the body;
- chronic fatigue;
- anemia.
Fluctuations in body temperature depend on many factors: time of day, age, the presence of chronic inflammatory foci in the body, and characteristics of the body.
Causes of headache and fever
Symptoms such as headache and fever are common symptoms of a wide range of disorders. At home, it is difficult to understand what caused the deterioration in health, so it is important to undergo a full diagnosis. These may be infectious diseases, in which it is recommended to limit contract with others, as well as chronic non-contagious internal diseases in the initial stages.
Viral diseases
Fever and headache are signs of colds, which often appear during the cold season. The viral infection multiplies on the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. Flu, sore throat, ARVI are often diagnosed in adults and children. The severity of these diseases depends on the patient's age, treatment regimen and other factors. It is important to understand that before the first signs appear, the patient already becomes a carrier of infection and poses a danger to others. On average, this period lasts from 3 to 7–10 days.
Tests for infectious viral diseases are carried out if the patient develops characteristic symptoms:
- fever, temperature, headache;
- cough, difficulty breathing, possible sputum production;
- nasal congestion;
- sore throat, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx;
- general weakness, deterioration of health.
One of the stages of diagnosis is fluorography of the lungs. If in the initial stages a viral infection affects only the upper respiratory tract, then it can further spread to the lower sections. This goes away if the patient is not given bed rest in time and a course of treatment is not prescribed. The body's immune defense is not enough to fight infection during periods of seasonal immunodeficiency, in the presence of any chronic diseases in the anamnesis. To quickly regain strength and cope with the virus, rest and plenty of fluids are prescribed, a course of vitamins and antiviral drugs is prescribed, and antibiotics are included if necessary.
Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses
Sinusitis is inflammation of the sinuses. Normally, they are sterile cavities formed by the bones of the skull, inside which there is air. However, when a bacterial infection occurs, purulent inflammation develops, which is accompanied by a severe headache and fever. The disease can be triggered by viral diseases of the respiratory tract, polyps in the nasal passages, swimming in contaminated water, and is also a complication of otitis media and ARVI.
Headache at a temperature of 38 degrees or more may be a sign of the following diseases:
- sinusitis - the most common form of sinusitis, purulent inflammation of the maxillary sinus;
- frontal sinusitis - affects the frontal sinus;
- ethmoiditis - a purulent process in the ethmoid labyrinth;
- sphenoiditis - inflammation of the sphenoid sinus.
Treatment of sinusitis and other sinusitis is prescribed individually. In some cases, taking antibiotics, vasoconstrictor drugs and regular nasal rinsing is sufficient. However, sometimes conservative treatment is ineffective, and to remove purulent contents it is necessary to puncture the maxillary sinuses. This is a painful procedure that doctors try to avoid and prescribe only when absolutely necessary.
Meningitis
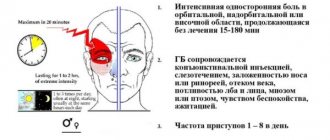
One of the dangerous diseases that requires urgent hospitalization and treatment in a hospital is meningitis, an inflammation of the membranes of the brain. The process can develop independently or manifest itself as a complication of infectious pathologies. The first symptoms are chronic headache, which is accompanied by fever. The thermometer readings can remain within 37.5 degrees, but in some patients they rise to a critical level.
There are several types of meningitis, depending on its cause, nature of the course and other features:
- bacterial – develops when a meningococcal infection enters the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract and spreads through the body through the blood;
- purulent - secondary inflammation, which manifests itself as a result of the addition of staphylococcus, E. coli and other bacterial pathogens;
- serous - meningitis, which occurs without purulent complications, is often caused by enteroviruses, as well as polio viruses and other types;
- tuberculous - a specific type provoked by Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- protozoan - the causative agent is the intracellular parasite Toxoplasma, which enters the body with raw meat and offal.
High fever and headache are a reason to urgently consult a doctor. It is important to understand that some types of meningitis develop due to a viral infection. The disease is transmitted to others, so the patient requires hospitalization in a virus hospital. The process is dangerous because as a result of inflammation, brain cells are destroyed and cannot perform their functions. In the chronic course of meningitis, disruption of the functioning of internal organs, developmental delay in children, as well as complete or partial paralysis are possible. Treatment is aimed at relieving inflammation and preventing purulent complications, as well as restoring neural connections.
Toothache
One of the reasons why you get a headache when you have a fever is dental disease. Tooth decay, nerve inflammation, abscesses and other pathologies can cause severe pain. It spreads to the entire surface of the face, temples and the back of the head. The patient is worried about chronic migraines, fever up to 37 degrees or more. The pain intensifies during chewing and often worsens at night. It is important to see a dentist in a timely manner, and it is not recommended to take painkillers before visiting a doctor.
Poisoning
Headaches and fever in adults and children accompany various poisonings. The main reason is the ingestion of toxins that accumulate in the bloodstream and internal organs. They cause disruption of the digestive tract, liver and excretory system, and can also affect nerve tissue. If toxins reach the brain, the condition is dangerous due to neuronal necrosis and disruption of vital functions. Poisoning can be caused by poor-quality food, poisonous gases, salts of heavy metals, pesticides, certain medications, and alcoholic beverages.
Poisoning can be identified by characteristic symptoms:
- general weakness, sharp deterioration in health;
- headaches, dizziness, possible fainting;
- sharp abdominal pain, disruption of the digestive tract;
- with damage to the nervous system - hallucinations.
Food poisoning can be successfully treated at home. The patient is prescribed a starvation diet and plenty of fluids, sorbents and drugs to restore the microflora of the digestive tract. If your health sharply worsens, it is possible to relieve intoxication only in a hospital setting. In this case, drip infusions of electrolyte solutions are prescribed, as well as drugs to remove toxins from the body.
Thermoneurosis
If the temperature rises with a headache, but tests do not show any deviations from the norm, this may be a symptom of thermoneurosis. The patient’s health is deteriorating, and the patient suffers from chronic migraines. The condition is the body's reaction to the following factors:
- irregular daily routine, lack of rest, night work;
- stress, anxiety;
- disorders of the autonomic nervous system.
The main sign of thermoneurosis is a persistent increase in temperature up to 37 degrees and chronic headaches. The examinations do not detect any pathologies, inflammatory processes, viral infections or other disorders that could provoke a deterioration in health. Doctors recommend proper rest and restoration of a normal daily routine, as well as a course of vitamins. In most cases, such changes have a positive effect on health and help against fever and headaches.
Neoplasms
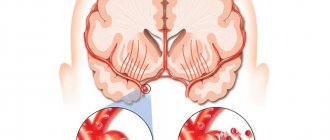
One of the reasons why it is important to undergo a comprehensive examination for chronic headaches and fever to 37–38 degrees is neoplasms. Brain tumors can be benign or malignant and vary in shape, size and growth rate. They are determined using MRI, and treatment tactics are prescribed individually. It is important that at the initial stages, neoplasms can remain asymptomatic, but then they cause necrosis of nerve tissue and disruption of brain function. Their timely detection is the key to effective treatment, since most functions of the nervous system can be preserved in the initial stages.
Other reasons
Fever and headaches in children and adults are symptoms of a number of pathologies and conditions that can go away on their own or require emergency treatment. They may indicate the following violations:
- intestinal infections - at the initial stages they resemble a cold or flu, but then cause acute digestive upset;
- high blood pressure - with chronic hypertension, the temperature can rise to 37 degrees or more;
- nephritis, pyelonephritis – inflammation of the kidneys;
- any chronic inflammatory processes during the period of exacerbation.
Even a healthy person can experience headaches from time to time. However, if it is accompanied by fever, weakness and other symptoms, this indicates the initial stage of the disease. To select an effective treatment, it is necessary to accurately determine the nature of the pathological process and its cause.
Clinical picture
At low temperatures, dizziness may occur.
Low body temperature and headache are complemented by other clinical manifestations:
- weakness, decreased ability to work;
- paleness of the skin;
- trembling;
- dizziness;
- increased drowsiness;
- decrease or increase in heart rate.
If the body temperature is below 34 degrees Celsius, a person’s speech becomes slurred, motor activity is impaired, the nasolabial triangle turns blue, and hallucinations may occur.
Diagnosis of the cause
If symptoms appear, you should consult a therapist.
If you have a headache and a decrease in body temperature, you should consult a therapist. The scope of diagnostic measures is determined depending on the general condition of the patient. If there is a pronounced decrease in indicators, hardware and laboratory diagnostics are prescribed:
- Blood tests. Biological material is examined for the level of glucose, hemoglobin and red blood cells. Based on the results of a biochemical blood test, signs of dysfunction of internal organs and the inflammatory process can be determined.
- Hormonal studies. To identify diseases of the thyroid gland, thyroxine, free T3, and thyroid-stimulating hormones of the pituitary gland are determined for quantitative indicators.
- X-ray analysis, computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. Based on the results of diagnostic measures, pathological formations in the cerebral region can be identified.
If necessary, the patient is referred for consultation with a specialized specialist: neurologist, oncologist, endocrinologist, etc.
Hypoglycemia: causes and prevention
Hypoglycemia is a rather narrow topic related to diabetes mellitus. However, it is still unrealistic to fully cover diabetes mellitus in one article. Therefore, today I will talk about one of its serious consequences, which occurs due to a lack of glucose in the body. The hypoglycemic state develops rapidly, leads to severe disturbances in brain function and is potentially fatal.
Physiology of the phenomenon
At first, a boring and dry definition. Hypoglycemia is an metabolic-endocrine syndrome that occurs when plasma glucose levels decrease by at least 0.5 mmol/l from the lower limit of normal and is accompanied by symptoms of dysfunction of the central nervous system. Let me remind you that the norm is 3.5–5.5 mmol/l.
The fact is that the brain is a highly energy-consuming organ (especially its gray matter), one might say - a spender. Yes, yes, compared to other organs, it consumes an enormous amount of energy and at the same time lives in isolation (the cranium).
This means that any starvation, be it oxygen or glucose, can lead to organ death within a few minutes. And the fact that the brain lives in the cranium, which is unable to expand even with cell swelling, further aggravates the problem.
Here I must explain that any tissue damage leads to swelling: bite your finger and it will swell, but after a couple of days (or even hours) the swelling will go away and the finger will return to its previous appearance and functionality, but the swollen brains will increase in size, will rest against the walls of the prison (skull) and begin to flow away to where there is free space. The blood vessels will contract, nutrition will stop, damage to nerve cells will increase, the brain will swell even more and proceed into the foramen magnum. The first to suffer will be the neurons of the medulla oblongata, which contains the oldest centers of respiration and control of the cardiovascular system, and this will completely finish off the body.
And I ask you not to think that the brain swells only from hitting a wall - it swells from any damaging factor, including a lack of oxygen, glucose and other substrates that lead to cell damage.
Causes of hypoglycemia
Undoubtedly, patients suffering from diabetes mellitus are most susceptible to this condition, for example, due to an overdose of insulin, errors in the method of its administration (administration of insulin without preliminary shaking in the bottle, administration of the drug to places where rapid absorption of the drug can occur). Some manage (apparently, thinking that for some reason it didn’t work) to inject insulin into a vein along with subcutaneous injection.
Features of treatment
Warming - first aid at low temperatures
If the thermometer reaches more than 32-34 degrees Celsius, as a first aid measure you can limit yourself to warming up, for example, by wrapping yourself in a warm blanket and drinking warm tea. You can take a hot bath.
If hypothermia persists for a long time, but the patient's condition remains satisfactory, no specific therapy is performed. It is enough to correct your lifestyle: proper rest, sleep for at least 8 hours, and maintaining a balanced diet.
In case of a critical decrease in body temperature and headache, inhalation of warm humidified oxygen and intravenous administration of a special heated solution are prescribed. In some cases, extracorporeal blood purification is indicated.
With a slight decrease in body temperature, depending on the etiology of the symptom, the following methods are used:
- Taking antibacterial drugs. Prescribed if the patient has a bacterial infection, which at the initial stage of development can occur with a low temperature. Broad-spectrum agents are used by intravenous infusion.
- Taking hormonal drugs. Prescribed to accelerate metabolic processes in the body and restore normal body temperature.
- Drugs from the group of antidepressants. Designed to improve neural connections between different parts of the brain. The restoration of normal temperature is due to stimulation of the hypothalamus and an increase in contractile thermogenesis.
- Products from the group of vitamins. Prescribed drugs containing group B, which improve the transmission of impulses along nerves and muscle fibers, as well as restore trophic processes in tissues.
- Means for suppressing intoxication of the body. These contribute to the binding and destruction of toxic substances.
If a headache and low temperature are symptoms of the development of an oncological process or the presence of a formation of a different etiology in the body, surgical intervention is performed.
Preventive measures
For prevention, it is necessary to follow a work and rest schedule.
To prevent diseases and conditions that cause a similar clinical picture, it is recommended to adhere to the recommendations:
- lead an active lifestyle;
- maintain a balanced diet;
- carry out hardening procedures (contrast shower, etc.);
- adhere to the work and rest schedule;
- avoid overwork;
- be less nervous.
If you cannot avoid the appearance of a headache and a decrease in body temperature, it is better to undergo a comprehensive examination of the body and begin treatment immediately. Any disease is easier to treat at the initial stage of development.
Light form
Up to 80 patients have a mild form of COVID-19. As a rule, these are young people without any concomitant diseases. The symptoms of the disease, in this case, are similar to those of ARVI. However, there are certain differences that make it possible to recognize infection with coronavirus infection.
Full recovery occurs within 14 days without any negative consequences for the body:
- 1 day. Body temperature rises slightly, rarely exceeding 37.2°C. There is also a slight malaise, which can easily be attributed to fatigue. Nasal congestion may occur and your sense of smell may deteriorate.
- 2-4 days. General weakness and increased fatigue persist, but no critical temperature is noted. Additionally, there is a sore throat and a slight unproductive cough. Problems with the sense of smell are intensifying; sick people characterize them as “lack of odors.” Sometimes an additional disorder of the digestive system occurs, and there is no appetite.
- 5-6 day. All of the above symptoms subside and the condition improves. The intensity of the cough decreases, but the sense of smell does not return.
- 7-14 days. There is a complete recovery, all symptoms of COVID-19 completely disappear.
In children, the mild form, in most cases, does not manifest itself with any symptoms. Sometimes there may be signs of a mild cold without fever. But at the same time, the infection persists in biological fluids and waste products for a long time. This means that after infection the child becomes an active virus carrier.