Nowadays there are many drugs for dizziness, including those containing betahistine. Among the names you can often hear Betaserk, Vestibo, Tagista, Betaver, Vesticap and others. At the same time, many people are interested in: how do the drugs differ and which one is the best? What is better to buy at the pharmacy if there are a large number of trade names to choose from, and the doctor is forced to write the generic name? I would like to address this issue in this article.
A little about original drugs
But first, we need a little insight into the question of what is the original drug. The original medicine is called the medicine of the company that invented the formula of the active substance. It should be noted that several years pass before entering the market. The substance undergoes multi-stage testing: theoretical, on animals, after proven safety, clinical trials on humans are carried out. At the same time, the rules governing the entry of funds into the market are very strict.
What happens next? The drug is launched on the market. Moreover, only the manufacturer has a patent for the production of the formula. However, a patent has a duration period, after which the formula must be available to other companies. Of course, this does not happen for free; the rights to implement the formula cost money, but the manufacturing company is not obliged to sell some know-how, as well as ways to obtain the formula. And the aspects of cleaning the product from unwanted impurities and the influence of fillers remain, as they say, behind the scenes.
It is also important that the new manufacturer is not required to conduct clinical trials on effectiveness and safety. This often happens in order to gain a proper reputation for other issues (obtaining the right to be called a bioequivalent of the original drug and other marketing moves, the essence of which is not so important in this article). Happens often, but by no means always. Just as the effectiveness is not always the same, whereas for the original drug it is a priori high and proven by tests.
What am I getting at? I lead to the fact that the original drug of the substance betahistine is Betaserc. But which one is better will be discussed below.
Application of Betaserc in the treatment of patients with subjective tinnitus due to sensorineural hearing loss
Application of Betaserc in the treatment of patients with subjective tinnitus due to sensorineural hearing loss
Rice. 1. Structure of forms of sensorineural hearing loss
Rice. 2. Structure of the causes of the disease
Rice. 3. Scale for assessing the results of treatment of patients with subjective tinnitus
Rice. 4. The effectiveness of Betaserc treatment depending on the form of sensorineural hearing loss
The causes of sensorineural hearing loss are: acute and chronic diseases of the middle ear, circulatory disorders in the vertebrobasilar system, the use of ototoxic drugs [3, 5, 11], work in conditions of noise and vibration, emotional and mental stress [7, 8, 9] , acute infectious diseases. Each of the etiological factors affects certain structures of the sound analyzer; the external manifestation of this effect is: an increase in the thresholds of bone sound conduction, a decrease in the intelligibility of speech perception, and the appearance of subjective tinnitus.
One of the most common symptoms accompanying sensorineural hearing loss is subjective tinnitus. Tinnitus (tinnitus) is a reaction of the sound analyzer, caused by adequate and inadequate stimuli and manifested by noise, crackling, ringing, hum, and musical melodies. “A healthy living organism always sounds,” but this noise or somatic vibrator sounds are usually not audible, since they are masked by external noise (environmental sounds), which act as a so-called damper [1]. When healthy people were placed in a soundproof chamber, a sensation of tinnitus occurred in 94% of subjects with normal hearing.
Subjective tinnitus is defined as a pathological auditory sensation that occurs in the ear in the absence of external sound influence and occurs, as a rule, against the background of various pathologies in any part of the sound analyzer. Subjective tinnitus is not a nosological form of the disease, but a symptom of pathology from the sound analyzer. Of all the ear symptoms, after pain, tinnitus causes the most suffering to the patient. Tinnitus is one of the main and early symptoms of damage to the sound analyzer; it often causes more anxiety to the patient than hearing loss. Subjective tinnitus is observed in patients with acute sensorineural hearing loss in 94.9% of cases, and in patients with chronic hearing loss in 91.8% of cases [2, 9].
It is believed that the cause of tinnitus in sensorineural hearing loss is neurotrophic changes in the sound analyzer. V.T. Palchun (1990) [4] attaches great importance to the disruption of the complex structural and functional organization of intracerebral regulation, with the formation of pathological stable functional connections (PSFC), realized through subcortical structures and the “disease information field” in long-term memory. As a result of these changes, when pathological impulses appear from the affected organ through the PSPS and the “information field of the disease,” a symptom complex of the disease is formed, mainly of the cochlea.
Depending on the severity of the noise and its tolerance by a person, I.B. Soldatov [10] distinguishes the following noise levels:
- I degree – tolerated calmly, does not affect the general condition;
- II degree – irritates in silence, at night, disturbs sleep;
- III degree – constantly bothers, disturbs sleep and mood;
- IV degree – unbearable noise, depriving sleep and reducing ability to work.
Treatment of patients with subjective tinnitus due to sensorineural hearing loss is one of the most difficult tasks for otorhinolaryngologists.
Currently, there are dozens of ways to treat patients with subjective tinnitus. The most effective therapy for this pathology is treatment aimed at improving the blood supply to the inner ear and improving the conduction of nerve impulses.
The basic principles of treatment of patients with this pathology are the following: firstly, if possible, exclude the etiological factor that caused the disease, secondly, start treatment in the early stages, thirdly, be sure to include in complex etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy means aimed at to eliminate oxygen deficiency and normalize microcirculation in the inner ear [6, 12].
According to literature data on experimental histological studies of the auditory nerve, the latter has a lower regenerative capacity compared to other cranial nerves. Therefore, a positive effect in treatment can be obtained if atrophic-degenerative changes have not yet developed in the nerve elements of the sound analyzer, i.e. at least some of the pathological changes in the perceptive apparatus are reversible. These are changes that are caused by capillary stasis, as well as swelling of the nuclei of hair cells. The inability to obtain an effect from treatment for degeneration of the auditory nerve indicates the extreme importance of carrying out therapy in the initial stages of damage to the organ of hearing, which aims to, if not eliminate, then at least stabilize the pathological process, which usually tends to progress.
The most appropriate treatment for tinnitus with sensorineural hearing loss is with drugs that affect the blood supply to the cochlea, can restore the functions of its enzyme systems and improve oxygenation. The emphasis is placed on the reversibility of such pathological changes as impaired blood circulation and microcirculation, swelling of the stria vascularis, disruption of the ionic composition of the labyrinth fluids, capillary and venous stasis with a decrease in the delivery of nutrients, decreased permeability of cell membranes, swelling of the nuclei of hair cells .
In the practice of an ENT doctor, when treating patients with sensorineural hearing loss accompanied by subjective tinnitus, the drug Betaserc (Abbott) is used.
Betaserc is a synthetic histamine analogue that is a weak H1-receptor agonist and a powerful H3-receptor antagonist. Due to the action on these receptors, it has the following effects: improving microcirculation in the vessels of the inner ear, normalizing intralabyrinthine pressure, suppressing the pathological activity of the vestibular nuclei in the brain stem, as well as increasing blood flow in the vertebrobasilar region. In addition, Betaserc accelerates the process of compensation for vestibular disorders (vestibular adaptation).
Betaserc is available in the form of tablets that contain betahistine dihydrochloride. The drug is rapidly absorbed, its maximum concentration in the blood is reached 3 hours after administration. The half-life is 3–4 hours, metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine.
The pharmacological properties of the drug allow it to be used not only in the treatment of dizziness, but also in patients with sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus.
Materials and methods
In order to study the effectiveness of Betaserc, we examined and treated 50 patients, 40% of them men and 60% women, with sensorineural hearing loss aged 18 to 70 years at the ENT clinic of the Moscow State Medical and Dental University. The acute form of the disease was in 10 patients, subacute – in 25 and chronic – in 15 patients (Fig. 1).
Figure 2 shows the structure of the causes of sensorineural hearing loss.
When studying the anamnesis, we took into account the patient’s age, the moment of hearing loss and the appearance of tinnitus, the nature and degree of hearing loss, the connection with past infectious diseases, diseases of the cardiovascular, endocrine, osteoarticular, urinary systems, with the use of ototoxic drugs, with traumatic factors, stress, hereditary predisposition, allergic reactions, etc. As well as bad habits, the nature and degree of noise, the dependence of its intensity on the time of day, on weather changes, on the position of the head and body, complaints of dizziness (constant, periodic, paroxysmal), headache and its localization. Tolerance of tinnitus was assessed as follows: 1st degree – the noise is tolerated calmly, does not affect the general condition; 2nd – noise irritates the patient, especially when nervous, in a quiet environment and at night, disrupts sleep; 3rd – noise is difficult to tolerate, negatively affects sleep and mood; 4th – the patient’s attention is completely concentrated on pathological auditory sensations, they are unbearable, deprive them of sleep and significantly reduce performance.
Examination of the ENT organs included otoscopy using an otoscope with optics, anterior and posterior rhinoscopy, pharyngoscopy, and indirect laryngoscopy. The patency of the auditory tubes was checked. The function of the sound analyzer was studied using whispered and spoken speech, and a set of tuning forks. Tone threshold audiometry and acoustic impedance measurements were performed.
Patients took Betaserc 24 mg 2 times a day. The course of treatment lasted 30 days.
To assess the effectiveness of treatment, a psychological test proposed by Fiedler was used. The initial noise level was taken as 100% and marked on a line of 10 cm (1 cm = 10%). During treatment, the patient noted a percent reduction in noise, if any, on the line. Excellent results included complete disappearance of noise or maintenance of its intensity within 25% of the volume from its original level; to good - when the volume is reduced by half (50%); satisfactory – when the noise remained within 75% of the original volume; to unsatisfactory – when tinnitus remained at the initial level (100%) (Fig. 3).
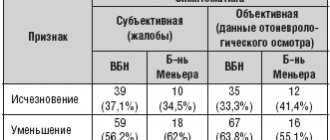
When treating patients with acute sensorineural hearing loss, accompanied by subjective tinnitus, we noted excellent results in 3 patients, good results in 3 patients, satisfactory results in 2 patients, and unsatisfactory results in 2 patients. When treating patients with subacute sensorineural hearing loss, the results were excellent in 5, good in 7, satisfactory in 6, unsatisfactory in 7 patients. In patients with a chronic form of the disease, the effectiveness of the drug was an order of magnitude lower. We noted good results in 2 patients, in other cases these were satisfactory (3) and unsatisfactory results (10). The effectiveness of Betaserc treatment depending on the form of sensorineural hearing loss is presented in Figure 4.
The effectiveness of treatment was directly dependent on the age of the patients and the time between the onset of the disease and the start of treatment. Treatment was least effective in patients over 60 years of age and in patients with chronic sensorineural hearing loss. Treatment is most effective for acute sensorineural hearing loss. For chronic sensorineural hearing loss, the use of Betaserc helps stabilize the process and improve overall well-being.
To stop the further development of sensorineural hearing loss, it is advisable to carry out repeated courses of treatment with Betaserc at a dosage of 48 mg per day 2-3 times a year.
Reference
Noise in ears
is a phenomenon that is described as a sound sensation that occurs in the head and is not associated with an external acoustic stimulus. In the specialized medical literature, ear noise is usually called tinnitus (from the Latin verb tinnire - to ring).
Tinnitus can be objective
, when it can be recorded using auscultation and other instrumental methods of examining the patient, and
subjective
, when the noise perceived by patients cannot be recorded and assessed from the outside; despite the fact that subjective noise occurs in the absence of a real sound source, as a rule, this does not exclude the presence of various pathologies in any area of the sound analyzer. It is impossible to directly register subjective ear noise, as already noted. Of the many proposed indirect methods for measuring subjective ear noise, the most informative are the psychophysical methods of noise metry: “equal loudness” and “overlap”.
Subjective tinnitus
– this is an informational (signal) symptom (similar to the sensation of pain), a kind of “cry for help”, signaling the body about a pathological process. Subjective ear noise is one of the main, constant and often the earliest symptoms in various diseases of the organ of hearing, both conductive and perceptual, but can also occur in cases of dysfunction of other organs and systems.
The prevalence of subjective ear noise among the population is very significant. It has been established that every fifth adult is susceptible to subjective tinnitus to some degree, periodically or constantly, although more than half of them do not seek medical help.
Mechanisms of development of subjective tinnitus
, and in many cases the etiological factors, are not clear enough. To date, many hypotheses have been proposed for the pathogenesis of subjective ear noise, including theories of self-listening, nonspecific irritation, reflex switching, etc. Subjective noise can be regarded as a phantom of auditory perception: the perception of sound heard “in the ears” or “in the head” is very real, but is not connected to an external sound source. Every person hears this sound after exposure to loud noise or while in complete silence. The constant presence of noise in most cases (about 75%) is a habit of reacting to a signal, causing only slight discomfort.
However, none of the hypotheses is able to give a convincing answer why not all patients have tinnitus with the same disease, which parts of the auditory analyzer are responsible for the appearance of this auditory sensation, and how to explain the appearance of such symptoms in a number of people with normal hearing .
It is believed that the main causes of subjective tinnitus may be:
metabolic disorders (vascular atherosclerosis, hepatitis, diabetes mellitus, hypoglycemia, hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism); diseases of the outer, middle, inner ear (cerumen plug, exostosis of the external auditory canal, external otitis, otitis media, otosclerosis, tumors of the tympanic cavity, labyrinthitis, sensorineural hearing loss, acoustic and barotrauma, Meniere's disease); tumors of the cerebellopontine angle, brain, neuroma of the VIII cranial nerve; intoxication (ototoxic drugs, benzene, methyl alcohol); pathology of the cervical spine (osteodystrophic changes, instability); vibration, noise; psychoneurological diseases (multiple sclerosis, schizophrenia, depressive states).
Source: Laesus De Liro
Betaserk, Betaver, Vestibo or Tagista - which is better?
What's better? The question does not have a clear answer. After all, any medicine has many parameters. For some, effectiveness in relation to the symptoms of interest is important (for the drugs we are currently considering, this is, first of all, dizziness and tinnitus). For some, the safety of the drug is more important. For some people, price comes to the fore. And some even look at the availability of the product in the pharmacy near their home.
So which is better? In terms of effectiveness, in my humble opinion, the original drug, Betaserc (Abbot), comes to the fore. However, Vestibo (Actavis) is not much worse than the original and is produced by a self-respecting company. Their safety profile does not differ much (however, all betahistine preparations are quite safe and have virtually no side effects). The drugs Betaver (Veropharm) and Tagista (Shtada) differ significantly in effectiveness, but they also greatly benefit in price. Moreover, according to this indicator, Betaserc is the “worst”. Although, if you compare the effectiveness, time to achieve improvement and the price of the entire course of treatment, this bright line in price is erased in favor of Betaserc.
To summarize the above, I would like to say the following. The original betahistine drug is Betaserc. Not much inferior in efficiency to Vestibo. In terms of price, the cheapest of the above tablets is Tagista. The choice of a specific medicine will be yours, dear site visitors. Be healthy!
Comparison of the effectiveness of Vestib and Betaserc
Betaserc is more effective than Vestib - this means that the ability of the drug substance to provide the maximum possible effect is different.
For example, if the therapeutic effect of Betaserc is more pronounced, then with Vestib it is impossible to achieve this effect even in large doses.
Also, the speed of therapy is an indicator of the speed of the therapeutic action; Betaserc and Vestib are also different, as is the bioavailability - the amount of the drug reaching the place of its action in the body. The higher the bioavailability, the less it will be lost during absorption and use by the body.
Betaserc in solution
If the tablet method of taking betahistine is not suitable for the patient, you can choose the liquid form of the drug. Having settled on Betaserc solution, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for using the dosage form. If the doctor has not prescribed an individual treatment regimen, then the solution is taken as follows:
- for two doses per day, measure 3 ml of the drug;
- For each of the three doses, take 2 ml of medication.
The measured dose of the drug should be diluted with boiled water; you can also take the undiluted substance, but only as directed by your doctor. The required dosage of the medicinal solution is measured with a special syringe with marks, which is included in the package with the liquid form of Betaserc. The cost of a solution for oral use ranges from 1,200 rubles.
When using liquid, it is important to consider that it contains 5% ethanol. Therefore, the liquid form of the drug does not treat signs of vestibular disorders in patients suffering from alcohol dependence. Therapy of asthmatics with any form of medication is carried out under strict medical supervision, but the symptomatic drug does not eliminate the cause of worsening cerebral circulation.
Comparison of ease of use of Vestib and Betaserk
This includes dose selection taking into account various conditions and frequency of doses. At the same time, it is important not to forget about the release form of the drug; it is also important to take it into account when making an assessment.
The ease of use of Vestib is approximately the same as Betaserc. However, they are not convenient enough to use.
The drug ratings were compiled by experienced pharmacists who studied international research. The report is generated automatically.
Last update date: 2020-12-04 13:42:47
Instructions: how to take the medicine
The tablets prescribed by the doctor in a certain dosage are taken with meals, they are not chewed, but washed down with a sufficient amount of water. Treatment begins with a minimum dosage (8 mg), taking one pill 3 times a day. The drug in a dose of 16 mg is taken according to a similar program. If the maximum dosage is selected (24 mg), the tablet is taken 2 times a day. Depending on the patient’s condition, the treatment course can last more than one month.
When using Betaserc, it is important to take into account that when taking tablets simultaneously with food, the absorption of betahistine slows down.
To stop an acute attack of cervical osteochondrosis, let's take 2-3 Betaserc tablets symptomatically, which is 32-48 mg of betahistine.
For course treatment, a dosage of 16 and 24 mg is used, taken three times or twice a day, respectively. If you need to split the tablet in half, this can be easily done by using the notch in the middle of the pill.
The patient feels the first improvements in health after 2 weeks of using the medicine. The onset of a stable therapeutic effect will have to wait several months with constant use of Betaserc. For elderly people, as well as with liver and kidney failure, no dose adjustment is required.
Advertising:
Possibility of side effects
According to the instructions for Betaserc tablets, it became known that the use of the medicine can cause negative reactions in the body. Among the side effects, according to reviews from patients and doctors, one should take into account a certain likelihood of developing the following unpleasant reactions:
- digestive system - the appearance of nausea or vomiting, dyspepsia, discomfort in the abdominal area (pain, bloating);
- taking into account the effect of betahistine on the functioning of the nervous system, the development of headache symptoms is not excluded;
- If you are prone to allergies, there is a possibility of skin itching and rashes like urticaria.
In extremely rare cases, the patient may suffer from angioedema or anaphylactic shock. If Betaserc must be taken together with other drugs, it is necessary to take into account the prohibition on taking the medication together with MAO inhibitors. In case of simultaneous use with antihistamines, the effectiveness of one of the drugs will suffer, which will affect the results of therapy.
During treatment with Betaserc, the patient should refrain from driving vehicles and professional activities that require increased attention and concentration.
If too large a dose of medication is taken, the patient’s body may react with attacks of nausea, a gag reflex, development of drowsiness, and severe abdominal pain. More severe consequences of an overdose can be convulsive syndrome, the development of cardiac and pulmonary complications. In this case, the help of doctors is necessary to provide symptomatic therapy.
Comparison of safety of Vestib and Betaserk
The safety of a drug includes many factors.
At the same time, in Vestib it is quite similar to Betaserk. It is important where the drug is metabolized: drugs are excreted from the body either unchanged or in the form of products of their biochemical transformations. Metabolism occurs spontaneously, but most often involves major organs such as the liver, kidneys, lungs, skin, brain and others. When assessing metabolism in Vestib, as well as in Betaserc, we look at which organ is the metabolizing organ and how critical the effect on it is.
The risk-benefit ratio is when the prescription of a drug is undesirable, but justified under certain conditions and circumstances, with the obligatory observance of caution in use. At the same time, Vestib does not have any risks when used, just like Betaserc.
Also, when calculating safety, it is taken into account whether only allergic reactions occur or possible dysfunction of the main organs. In other matters, as well as the reversibility of the consequences of using Vestib and Betaserc.
When are Betaserc pills prescribed?
The drug, which relieves the symptoms of vestibular disorders, is produced in tablet form. White, round-shaped tablets with a digital inscription contain three dosages of betahistine dihydrochloride - 8, 16 or 24 mg.
In addition to the main substance, the composition is supplemented with auxiliary components, including a certain proportion of talc, mannitol, cellulose, and silicon dioxide.
You cannot independently adjust the dosage prescribed by your doctor, since when choosing a dose of betahistine, the specialist is guided by the severity of the symptoms and the presence of other pathologies in the patient.
Indications for prescribing Betaserc at the selected dosage are signs of the following pathological conditions:
- microcirculation disorders in the labyrinth area;
- Meniere's syndrome, dizziness;
- the presence of dropsy in the labyrinth or inner ear;
- vertebrobasilar insufficiency;
- noise and pain syndrome in the ears.
Advertising:
Also, taking the medication is included in a comprehensive treatment regimen for post-traumatic encephalopathy, atherosclerosis of the arteries that supply blood to the brain, and vestibular neuritis. According to the instructions for the drug Betaserc, contraindications for its use are:
- Diagnosis of pheochromocytoma:
- inadequate reaction to at least one of the components of the drug;
- the patient's childhood (under 18 years).
The instructions also warn that the drug, which has a direct effect on the vestibular system, is prescribed with caution for bronchial asthma and peptic ulcers. Betaserc therapy is contraindicated for women during the 1st trimester of pregnancy and lactation. Prescribing tablets is permissible from the 2nd trimester, but under the supervision of a specialist.
Oralcept belongs to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. It has a pronounced antiseptic, antifungal and analgesic effect. Read more in the article: “what Oralsept helps with.”
Betaserc and cervical osteochondrosis
According to doctors, it makes sense to prescribe Betaserc for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in cases of vertebral artery syndrome, when a lack of blood supply is manifested by dizziness. Painful symptoms of vertebrobasilar insufficiency also include double contours of objects and instability in a standing position, which indicates compression of the artery that supplies blood to the brain structure.
WE RECOMMEND THE ARTICLE!
Neurox is used for VSD, anxiety disorders and cerebral circulatory disorders. Read more >>
The cause leading to the development of vertebral artery syndrome is associated with deformation of bone elements, predominantly of a dystrophic nature. The result of the pathological condition of the cervical spine is the appearance of insufficient blood supply to the brain.
In this situation, the complex treatment regimen for osteochondrosis is supplemented with Betaserc tablets. They help reduce the intensity of characteristic symptoms (headaches, shoulder pains, pain in the arms).