Causes of arachnoiditis
In most patients with arachnoiditis, the predisposing factor is infectious diseases. In particular, these diseases include chickenpox, influenza, measles, viral meningitis, cytomegalovirus infection, and meningoencephalitis. The disease can also be provoked by chronic intoxication of the body, inflammatory diseases of the paranasal sinuses, and trauma. Arachnoiditis is often diagnosed in patients who experience reactive inflammation of a growing tumor.
Pathology can also occur due to acute or chronic purulent otitis media. In this case, inflammation is provoked by toxins and low-virulent microbes. Researchers also include various complications of purulent otitis (petrositis, labyrinthitis, sinus thrombosis), brain abscess, purulent meningitis and otogenic encephalitis as the causes of the disease.
In neurology, there are also a number of factors that are considered predisposing to the occurrence of the disease. Such factors include intoxication (for example, alcohol), frequent viral diseases, chronic overwork, hard work in an unfavorable climate, and frequent injuries. In 10% of all cases of the disease, it is impossible to establish the exact etiology.
RESULTS
- RESPONSIBILITY.
- OPTIONAL CONDITIONS RESULTS Ñ Ð½ÐµÑвов.
- OPTIONAL CONDITION. RESULTS RESULTS .
- ROCK. оñ²² ñ ñµññññ ° ° ð¿¿ ° ° ñðð ððññ police ð½ °ð °ð¿ð¿ð¿¿¿½ police ð¶ð¸ð´len ð ²²¿¿ððð police °³ mill " ¾²ð½ices ð> · ð³ ð °.
- RESULTS. RESULTS, RESEARCH ½Ñе ÑаÑÑÑÑойÑва пÑиÑики), ÑÑойкое из менение лиÑноÑÑи.
- RESULTS. RESULTS Ð¿Ð»ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ Ð¶Ð¸Ð´ÐºÐ¾ÑÑи.
- RESPONSIBILITY. RESULTS µÐ½Ð¸Ñ. RESULTS. RESULTS ÑажÑн.
- ROSS. RESEARCH, RESEARCH ÑÑим ÑодеÑжимое.
- RESULTS. RESULTS ие, ÑодеÑжаÑие в Ñебе гной. RESULTS ¸Ð±Ð°ÐºÑеÑиалÑной ÑеÑап¸Ð¸.
Pathogenesis of arachnoiditis
To understand the nature of the disease, it is necessary to become familiar with the anatomical features of the brain. The arachnoid membrane, which is affected by inflammation during arachnoiditis, is located between the soft and dura mater. Moreover, it is not fused with them, but simply fits tightly. Unlike the pia mater, the arachnoid membrane does not penetrate the cerebral convolutions. Small spaces filled with cerebrospinal fluid are formed under it.
All these spaces connect to the fourth ventricle. Through these spaces there is an outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the cranial cavity. The mechanism of occurrence of arachnoiditis is as follows: due to the influence of various causes and provoking factors, the body activates the production of antibodies to the arachnoid membrane, which then provokes its inflammation. In patients with arachnoiditis, there is clouding and noticeable thickening of the arachnoid membrane, as well as the appearance of cystic expansions and connective tissue adhesions in it.
Examination and diagnosis
In order to radically solve the problem of arachnoiditis once and for all, one must understand its true causes. Only then can we talk about real healing. Therefore, treatment in our clinic will begin with a thorough examination, questioning, and studying the results of previously performed studies. Be sure to take with you to the clinic all the medical documents available to you, even those that, at first glance, are not directly related to arachnoiditis (certificates, extracts, epicrises, tests, pictures, ultrasound, ECG, EEG, etc.).
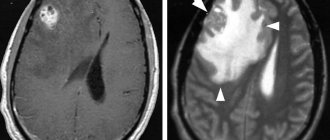
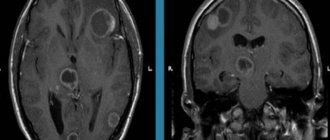
MRI of the brain allows you to see arachnoid cysts, a cystic-adhesive process in the membranes of the brain. Signs of inflammation in the paranasal sinuses and hearing organs are also clearly visible.
We perform blood tests Tests help to find and properly treat the causes of inflammation of the arachnoid membrane.
Neurological examination with examination of reflexes, sensitivity, coordination sphere, autonomics, with a detailed interview of the patient. A complete neurological examination gives the doctor more relevant information about the function of the nervous system than even an MRI scan. We compare the data obtained with the data of analyzes and MRI, on the basis of which we establish a diagnosis. True arachnoiditis is rare; upon examination it is not always confirmed; often we discover and treat another, true cause of the ailment .
Electroencephalography (EEG) to assess the general condition of the brain and look for epileptic discharges.
Examination of cerebral vessels to assess the sufficiency of cerebral circulation.
Classification of arachnoiditis
- Arachnoiditis of the meninges
- Optico-chiasmatic arachnoiditis
- Arachnoiditis of the posterior cranial fossa
- Arachnoiditis of the spinal cord membranes
This type of disease is also called cerebral. Cerebral arachnoiditis is localized in the posterior cranial fossa, on the convex surface of the brain and its base. The clinical picture of this disease is characterized by regular headaches and impaired circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid. In the most severe cases, the disease is accompanied by convulsive seizures, which can even lead to status epilepticus.
Arachnoiditis of the brain is often located in the central gyri and anterior parts of the cerebral hemisphere. Due to the resulting pressure on the sensory and motor centers, the patient may experience sensitivity and movement disorders. If the cerebral cortex is compressed or a cyst forms in it due to arachnoiditis, the patient may experience epileptic seizures.
This type of arachnoiditis is localized mainly in the chiasmal region. Frequent causes of this form of arachnoiditis are tonsillitis, malaria, syphilis, infectious diseases of the paranasal sinuses, and traumatic brain injuries. This type of arachnoiditis is characterized by the formation of adhesions in the area of the intracranial part of the optic nerves and the chiasm. In the most difficult cases, a scar may form around the chiasm.
As a rule, the disease provokes vision problems in the patient. In this case, the degree of decrease in the patient’s vision can vary from its minimal decrease to blindness. In most cases of optochiasmatic arachnoiditis, patients experience optic nerve atrophy. Visual symptoms are often severe, while hypertension symptoms are moderate.
It is the most common type of cerebral arachnoiditis. The severity of the symptoms of the disease depends on the location and nature of the inflammatory process, as well as its combination with hydrocephalus. The formation of cysts and adhesions usually leads to the closure of the openings of the cerebral ventricles, which provokes an increase in intracranial pressure. If intracranial pressure does not increase and is normal, the disease can last a long time.
The acute form of the pathology is characterized by all the symptoms of high intracranial pressure: nausea, dizziness, vomiting, bradycardia, severe headache localized in the back of the head. With a less acute course of the disease, signs of damage to the posterior cranial fossa become most pronounced. Patients may also experience symptoms such as unsteady gait and spontaneous nystagmus.
This is a spinal form of arachnoiditis, which occurs mainly due to purulent abscesses and furunculosis. Symptoms of the disease are similar to those of an extramedullary tumor: patients experience motor and sensory disorders, as well as radicular syndrome (limited mobility, parasthesia, trophic changes, pain in the heart, lower back and stomach, neck and limbs).
Spinal arachnoiditis is localized mainly at the level of the lumbar and thoracic segments, as well as on the posterior surface of the spinal cord. Typically, arachnoiditis of the spinal cord membranes is chronic.
Pathogenesis
In the arachnoid membrane of the brain, reactive inflammation occurs as a result of exposure to a pathogen or its toxins, as a result of which there is a violation of lymph and blood circulation. There are several types of disease depending on the location and nature of the changes - these are cerebral, cystic, adhesive, adhesive-cystic and spinal arachnoiditis. The disease can have an acute, subacute or chronic course.
As a result of impaired circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid, in some cases the development of hydrocephalus may occur:
- occlusive hydrocephalus occurs as a result of impaired outflow of fluid from the ventricular system of the brain;
- Aresorptive hydrocephalus can develop as a result of impaired absorption of fluid through the dura mater due to the occurrence of an adhesive process.
Symptoms of arachnoiditis
The first symptoms of the disease appear long after the exposure of the body to the provoking factor that caused its appearance. During this time, autoimmune processes occur in the patient's body.
The duration of this interval is directly related to which factor affected the body. For example, after a patient has had the flu, the first symptoms of arachnoiditis appear after a long period of time - from three to twelve months. After a traumatic brain injury, this period is reduced to 1-2 hours. At first, the patient is concerned about the symptoms characteristic of asthenia: sleep disturbance, weakness, fatigue, irritability. However, over time, more severe focal and cerebral symptoms of arachnoiditis may appear.
What is arachnoiditis?
Arachnoiditis is an inflammation of the middle layer (arachnoid) of the meninges, which is the protective covering surrounding the brain, spinal cord, and nerve roots of the cauda equina.
The meninges (the lining of the spinal canal) are connective tissue composed primarily of collagen and elastin. Damage, trauma, tumor or infection can cause inflammation of the arachnoid layer anywhere.
Arachnoiditis has been known since the 19th century, when its main causes were infections, mainly tuberculosis and syphilis. It has now become known that the dissolution and degeneration of the arachnoid layer is caused by genetic and autoimmune disorders.
General cerebral symptoms of arachnoiditis
The cerebral complex of symptoms of cerebral arachnoiditis is characterized by liquor-hypertension syndrome. Most patients complain of a sharp headache, which is most active in the morning and can be aggravated by coughing, physical activity and straining. The consequences of increased intracranial pressure include such disorders as pain when moving the eyes, vomiting, nausea, and a feeling of strong pressure on the eyes.
Many patients turn to a neurologist with complaints such as decreased hearing, tinnitus, and attacks of dizziness. Therefore, during diagnosis, the doctor should exclude various ear diseases such as labyrinthitis, chronic otitis, cochlear neuritis, adhesive otitis. It is also possible that symptoms characteristic of vegetative-vascular dystonia may appear.
Patients with arachnoiditis occasionally experience liquorodynamic crises - attacks of headache accompanied by vomiting, nausea and dizziness. Rare crises are considered attacks with a frequency of no more than 1-2 times per month, average - 3-4 times, frequent - more than 4 times. Depending on the severity of symptoms during a crisis, its mild, moderate and severe forms are distinguished. The latter can last about two days.
Complications and consequences of arachnoiditis
The pathological process leads to the development of cerebral hydrocele and increased intracranial pressure. As a result, the vegetative-vascular system, vestibular apparatus, visual and auditory nerves suffer, and epilepsy develops.
Vegetative-vascular disorders:
- changes in blood pressure;
- tingling and burning in the fingertips;
- skin hypersensitivity.
Vestibular apparatus:
- intermittent claudication;
- unsteadiness on one leg;
- falling when landing on the heel;
- inability to connect the fingers with the tip of the nose.
Nystagmus, decreased vision to the point of blindness, hearing loss are complications of arachnoiditis.
Convulsions and convulsive seizures over time can develop into status epilepticus (a seizure lasting more than half an hour or a series of short-term, incessant seizures). A disorder of consciousness and the development of mental disorders occur.
Decreased ability to work is the main consequence of cerebral arachnoiditis. Depending on the severity of the disease, the patient becomes either partially limited in ability to work or completely disabled. High ICP levels at a constant level can lead to the death of the patient.
Focal symptoms of arachnoiditis
Focal signs of the disease occur depending on its location. Convexital arachnoiditis is characterized by mild to moderate disturbances in sensitivity and motor skills of the limbs. More than 35% of patients with this form of arachnoiditis experience epileptic seizures. After the attack ends, the patient experiences a neurological deficit for some time.
Basilar arachnoiditis, which is localized in the optic-chiasmatic region, occurs with serious impairments of attention and memory, as well as a decrease in mental abilities. In addition, patients with this form of pathology complain of a significant decrease in visual acuity and other visual disturbances. In rare cases, opticochiasmatic arachnoiditis is accompanied by inflammation of the pituitary gland, which provokes endocrine-metabolic syndrome, the symptoms of which are similar to those of a pituitary adenoma.
Arachnoiditis of the posterior cranial fossa is characterized by a very severe course. As a rule, patients show signs of facial neuritis and trigeminal neuralgia. Focal manifestations of arachnoiditis also include various cerebellar disorders: cerebellar ataxia, loss of coordination, nystagmus.
Occurrence of the disease
Arachnoiditis develops due to previous diseases, being a complication. Occurs due to injury. These are the main causes of pathology. The true reasons are not fully known. For some reason, the human immune system begins to produce antibodies to the proteins of its own arachnoid membrane. The cerebrospinal fluid circulation holes become clogged, causing fluid to begin to accumulate in the cavities of the subarachnoid space.
The brain is suspended in the skull. It seems to float in liquid - in cerebrospinal fluid. Has nothing to do with the dura mater. What is cerebrospinal fluid? This is processed blood. It contains all the nutrients, important chemical compounds, proteins, amino acids - everything you need to nourish the brain. Through the arachnoid membrane, waste fluid is removed from the body. Arachnoiditis blocks the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, so it accumulates in the cavities, which can ultimately lead to hydrocephalus.
The main reasons for the appearance:
- Up to 60% of all cases of the disease are associated with past infectious diseases. Viral infections: ARVI, meningitis, chickenpox, measles, cytomegalovirus. Purulent inflammation of the ears, paranasal sinuses, teeth.
- a third of cases occur after previous trauma. The degree of injury does not affect the course of the disease, nor does it affect further consequences.
- 10% of cases do not have a clear and complete picture of the reasons for their occurrence. Disorders of the body.
The arachnoid membrane is located between the soft surface of the brain and the hard skull. It does not fit tightly to the structures. Below it is a region of the brain with convex convolutions and spaces between the depressions. These areas are occupied by liquor. The arachnoid membrane has granulations - the paths along which the cerebrospinal fluid leaves the brain area when it has fulfilled its functions and become waste material.
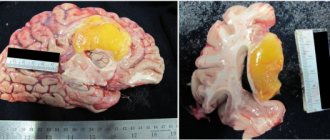
Arachnoiditis involves the body producing antibodies to the arachnoid tissue, causing it to become inflamed, swollen, and cloudy. Adhesions appear both inside and over the entire surface of the shell. She can no longer perform her functions correctly. Arachnoiditis of the brain causes severe symptoms, crises appear, and the person is assigned a disability. The proliferation of cystic formations and the formation of many adhesions thickens the arachnoid membrane.
The arachnoid membrane is also present in the lower part of the spinal canal; under it there is a subarachnoid space filled with cerebrospinal fluid, in which the roots of the spinal nerves rest. It contains many fibroblasts. Many “strings” depart from it, which connect to the brain. There are many types of arachnoiditis.
Doctors say that localization is impossible, since all cells and structures of the arachnoid membrane are completely attacked
Diagnosis of arachnoiditis
Diagnosis of arachnoiditis involves a comprehensive assessment by a neurologist of the characteristics of the course of the disease and its clinical signs. One of the important stages of diagnosis is the collection of anamnesis, during which the neurologist pays attention to the nature and development of neurological symptoms, recent traumatic brain injuries of the patient and infections he has suffered. A study of the neurological status is also carried out, which makes it possible to detect mnestic and psycho-emotional disorders, as well as neurological deficits.
Since arachnoiditis is characterized by visual and auditory disturbances, a neurologist may need to consult an ophthalmologist and otolaryngologist for differential diagnosis. An otolaryngologist checks the degree and type of hearing loss using threshold audiometry. The degree of damage to the auditory analyzer can be determined using the study of auditory evoked potentials, electrocochleography and acoustic impedancemetry.
Instrumental techniques such as skull radiography, electroencephalography and echo-encephalography are not considered sufficiently effective in diagnosing arachnoiditis, since they provide limited information about the presence of the disease in the patient. However, with their help you can detect some symptoms of pathology. For example, cranial radiography detects symptoms of prolonged intracranial hypertension, echo-encephalography detects hydrocephalus, and electroencephalography detects epileptic activity.
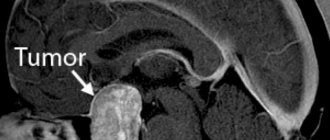
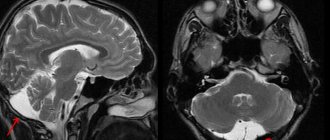
More information about the disease can be collected using MRI and CT scans of the brain. Both of these studies are used to identify morphological changes in the brain (atrophic changes, the presence of adhesions and cysts) and the nature of hydrocephalus. These techniques are also used to exclude tumors, hematomas and brain abscess. The doctor obtains accurate information about intracranial pressure by performing a lumbar puncture.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
To make a correct diagnosis, the following measures are necessary:
- thorough questioning of the patient to identify the fact of previous infectious diseases, injuries, operations using spinal anesthesia;
- neurological examination to identify disorders of sensitivity, motor function, visual impairment, hearing, and vestibular apparatus;
- X-ray examination of the skull bones is carried out to identify changes characteristic of traumatic brain injury, as well as expansion of the cerebrospinal fluid cavities of the brain (ventricles);
- Ultrasound examination of the brain allows one to establish the fact of increased intracranial pressure;
- computer (magnetic resonance) imaging is performed to assess the degree of cystic lesions of the arachnoid membrane, the substance of the brain, determine the size of the cavities (ventricles), and also to exclude a tumor;
- electroencephalography (EEG) – registration and interpretation of electrical signals from the brain, carried out to identify signs of epilepsy;
- an examination by an ophthalmologist is necessary to assess visual acuity, visual fields, and the fundus picture;
- an examination by an ENT doctor is carried out to determine hearing acuity, the function of the vestibular apparatus, to exclude an infectious process in the outer, middle, inner ear, and paranasal cavities;
- examination by a psychiatrist is necessary to identify disturbances in thought processes, symptoms of personality changes;
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following diseases:
- tumor of the central nervous system;
- multiple sclerosis;
- optic neuritis;
- neurosarcoidosis;
- idiopathic epilepsy;
- neurosis and neurasthenia;
Treatment of arachnoiditis
The main goal of drug treatment for arachnoiditis is to eliminate the source of infection using antibiotics. The use of antihistamines and desensitizing medications (diazolin, histaglobulin, diphenhydramine, suprastin, pipolfen, tavegil, calcium chloride) is indicated. Drug therapy also involves improving metabolism and local circulation, as well as normalizing intracranial pressure.
Patients who experience increased intracranial pressure are advised to take diuretics and decongestants (furosemide, mannitol, glycerin, diacarb). To eliminate convulsive syndrome, antiepileptic medications (carbamazepine, finlepsin, keppra) are used. According to indications, the doctor may prescribe drugs from the following drug groups:
- absorbable (rumalon, lidase, pyrogenal);
- antiallergic (loratadine, tavegil, diazolin);
- neuroprotectors and metabolites (mildronate, nootropil, ginkgo biloba);
- psychotropics (tranquilizers, antidepressants, sedatives).
4. Treatment of the disease
There is no cure as such for arachnoiditis. Treatment may be the same as for other chronic pain, where the goal is to relieve pain and other symptoms that directly affect quality of life
. Doctors often recommend a pain treatment program in combination with physiotherapy, exercise therapy and psychotherapeutic sessions. Surgical treatment for arachnoiditis is a controversial option because the results of surgery may not be as expected and will provide only short-term relief. Some patients benefit from steroid injections and electrical stimulation.
Surgical intervention
If drug treatment does not produce the desired results, the patient experiences occlusive hydrocephalus or progressive vision loss, the doctor decides on surgical intervention. During the operation, adhesions are separated and cysts are removed. To reduce the manifestations of hydrocephalus, shunt operations are prescribed.
The prognosis for the patient is often favorable. Only arachnoiditis of the posterior cranial fossa, which is almost always accompanied by occlusive hydrocephalus, can pose a great danger. With frequent relapses of the disease, epileptic seizures and its optico-chiasmatic form, the labor prognosis for the patient may worsen.
Types of disease
Course of inflammation
In most cases, the disorder does not lead to severe pain or fever, which complicates diagnosis and causes late consultation with a doctor. But there are also exceptions.
- Acute course - observed, for example, with arachnoiditis of the cistern magna, accompanied by vomiting, fever and severe headache. This inflammation can be cured without consequences.
- Subacute – observed most often. In this case, mildly expressed symptoms of a general disorder are combined - dizziness, insomnia, weakness, and signs of suppression of the functionality of certain parts of the brain - hearing impairment, vision, balance, etc.
- Chronic – if the disease is ignored, inflammation quickly passes into the chronic stage. At the same time, the signs of a general cerebral disorder become more and more stable, and the symptoms associated with the source of the disease gradually intensify.
Prognosis for arachnoiditis
In most cases, patients with arachnoiditis receive the third disability group. However, if they have severe visual impairment and frequent epileptic seizures, they may be assigned a second disability group. The first disability group includes patients with opticochiasmatic arachnoiditis, which caused complete blindness. Work in transport, at heights, near fire, in noisy rooms, in unfavorable climatic conditions, and with toxic substances is contraindicated for patients with arachnoiditis.
Causes of arachnoiditis
In every second case, the cause of arachnoiditis is infectious diseases or purulent focal inflammation (meningitis, tonsillitis, influenza, otitis media), in every third case it is a traumatic brain injury (hemorrhage, brain contusion), and in every tenth case the exact origin of the pathology cannot be established . But doctors identify risk groups, belonging to which increases the likelihood of developing arachnoiditis:
- if a person lives in harsh climatic conditions, for example, in the Far North;
- if his work involves heavy physical labor;
- if a person lives in a state of constant stress, moral fatigue and emotional exhaustion;
- if he very often suffers from acute respiratory diseases;
- if the body is under constant chemical or alcohol intoxication.
Sometimes the cause of the disease is pathology of the endocrine system and metabolic disorders.
Prevention of arachnoiditis
Arachnoiditis, the symptoms and treatments for which are described above, can be prevented. In order to reduce the likelihood of developing the disease to a minimum, the following recommendations must be followed:
- strengthen the immune system, harden the body;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- Healthy food;
- observe the work and rest schedule;
- If possible, avoid getting into stressful situations;
- walk more, move, play sports;
- promptly treat diseases of a traumatic or infectious nature;
- periodically sanitize foci of chronic infection in the body;
- undergo regular preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist and ENT specialist.
Health to you!
Why does arachnoiditis occur?
The brain is responsible for all processes in our body. Information from various organs is sent to brain cells, where it is analyzed and then transmitted along nerve fibers to various organs of our body. The cause of arachnoiditis (like most other diseases) is a combination of many different factors.
These factors lead to malfunction of various parts of the brain and disruption of neural connections. In other words, the brain stops giving the “correct” orders for the smooth operation of your neural system, which leads to arachnoiditis, and then to more serious consequences.
How to get rid of arachnoiditis as quickly as possible?
We offer an innovative method of color pulse therapy, the discovery of which was awarded the Nobel Prize.
In order to get rid of arachnoiditis, it is necessary to restore the correct functioning of the brain centers responsible for regulating the nervous system. This is exactly the problem that the unique Neurodoctor device solves.
The device is based on the pulse therapy method. This is one of the most progressive and effective treatment methods known to modern world medicine. Thanks to pulse therapy, certain areas of the nervous system are activated, which ensures the elimination of disruptions in its functioning. This occurs due to the impact on the control centers of the brain.
During the treatment of arachnoiditis:
- The general condition of your body will improve.
- Immunity will increase.
- The intensity of headaches, severity and frequency of liquorodynamic crises will decrease.
- The process of resorption of adhesions of the arachnoid mater will accelerate.
- The effectiveness of other methods used to treat the disease will increase.
- The risk of complications will be reduced.
Powerful and effective treatment with the Neurodoctor device will quickly eliminate the clinical manifestations of the disease, localize the foci of pathology, and reduce the dose of medications. This will allow you to live a full life and forget about your illness forever.
How it works?
Neurodoctor affects the control centers of the brain.
The brain begins to produce dozens of neurohormones and form “corrective” nerve impulses.
Neurohormones are many times more effective than the most powerful drugs in quickly curing the disease. Nerve impulses eliminate pathological processes at the cellular level and correct the functioning of other organs and systems of the body.
LEARN MORE ABOUT THE METHOD
Do you need effective treatment for arachnoiditis, but still have doubts?
“Neurodoctor” is currently considered one of the most powerful methods of treating arachnoiditis. It goes well with traditional treatments and allows the body to recover better. Today the Neurodoctor device is:
- A treatment method that won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
- The development history of the device goes back more than 20 years.
- Neurodoctor takes part in medical exhibitions around the world.
- The press writes about the Neurodoctor device (publications such as KP and others).
- Neurodoctor is used by thousands of people in 26 countries around the world.
- Produced in Russia at enterprises of the military-industrial complex.
- Combines well with various medications without causing side effects.
- The device has no contraindications.
What happens if arachnoiditis is not cured?
In most cases, if left untreated, arachnoiditis leads to severe complications that pose a real threat to your health, and sometimes life. Among these complications:
- Severe headaches
- Nausea, vomiting
- Sensory disturbances in the limbs
- Impaired movement coordination
- Deterioration of vision
- Endocrine metabolic syndrome
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Occlusive hydrocephalus
- Epileptic seizures
According to medical research, the rate of development of neurological diseases such as arachnoid, schizophrenia, insomnia and Alzheimer's disease has been growing rapidly in recent years.
If you do not take urgent measures or use ineffective treatment, then powerful pathological processes will inevitably start in your body, which will lead to the development of serious complications causing decrease or loss of hearing, vision and motor activity. Partial or complete loss of ability to work, disability and the need for outside care are possible.
Types of brain arachnoiditis: signs and symptoms
Inflammation of the arachnoid mater is an autoimmune process.
The immune system’s own complexes provoke the pathological process. The clinical symptoms of severe arachnoiditis are quite typical for neurologists to make a diagnosis. Additional diagnostics are carried out by cisternography, electroencephalography, CT and MRI of the brain. Treatment is complex, including neuroprotectors, antiepileptic drugs, absorbent agents, and dehydration drugs.