Signs
Symptoms directly depend on which part of the brain the tumor is located in and how large it is. Pain begins to bother you if the tumor is growing or has already grown to an impressive size. The functioning of certain organs may also be disrupted.
Can appear:
- headache;
- problems with the musculoskeletal system;
- epileptic seizures;
- paralysis;
- lack of coordination;
- swallowing disorder;
- paralysis;
- breathing disorder.
Such a cyst is removed only as a last resort, when there are clear indications and the symptoms are life-threatening and disrupt the most important functions of the body. If the cavity grows rapidly, emotional and mental disorders, convulsions, and seizures appear; these are also clear indications for surgical intervention.
All ages are submissive: cysts in infants
In newborns, cystic formations formed either during intrauterine development or appeared as a result of birth trauma. The same reasons precede the appearance of cysts in infants, and, in addition, new prerequisites are added, for example, infectious and inflammatory processes or hematomas resulting from injuries, which result in cerebral circulatory failure, leading to hypoxia and ischemia, and, consequently, to the death of neurons in some part of the brain (the place where the cyst forms).
Subsequent degeneration of the nervous tissue, its necrosis, will serve as a good place for the formation of a cavity, which will begin to accumulate fluid, enlarge and compress neighboring areas and liquor-conducting pathways. This will most likely result in hydrocephalus and give certain neurological symptoms, delayed growth and development of the child.
A cyst in a child’s head can form anywhere; therefore, the main types of cystic formations localized in the brain are distinguished:
- Arachnoid cyst resulting from trauma and inflammatory processes. The habitat can be any part of the brain, characterized by rapid growth, manifested by hydrocephalus with its characteristic symptoms.
- The most severe forms of the cystic process include the subependymal cyst. Its cause is circulatory failure in the brain followed by ischemia. Such a cyst requires increased attention to itself and constant monitoring of the child (MRI annually to avoid excessive growth)
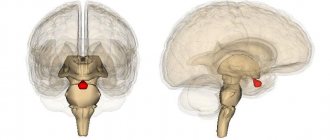
- A choroid plexus cyst, which develops in the fetus and by the time the baby is born, usually disappears safely.
Choroid plexus cysts (pictured) - in most cases, a phenomenon that does not require concern
The cystic process is diagnosed in early infancy using neurosonography (ultrasound), and the cyst is removed surgically.
Kinds
Cystic cavities are differentiated according to the following characteristics:
- Localization. The arachnoid cyst of the brain is located between the soft tissue and the membrane. Cerebral - directly in the brain tissue. An arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst rarely causes symptoms. This is explained by the fact that the subarachnoid cyst does not directly affect the brain itself, but is located between it and the outer membrane.
- Location. A lacunar cyst develops in the frontal lobes. In the pineal body - pineal. There may also be a cyst of the posterior cranial fossa, left temporal lobe, right, etc. A retrocerebellar cyst is located in the cerebellum. In severe cases, neoplasms can affect the entire hemisphere (hemisphere). This can cause critical conditions. Damage to the occipital, frontal region, and pyrineural septum is dangerous. Sometimes the spinal cord may be affected.
- Etiology. Takes into account the reasons for the appearance of cysts. Primary is formed due to genetic disorders. This is a congenital anomaly that affects the tissues of the head. At some stage of fetal development, brain tissue is formed with disturbances. The baby may be born with a cyst or it will grow later. If the baby develops normally, parents may not even be aware of the congenital anomaly for many years. Often newborns with it are no different from healthy peers. Secondary - the result of birth injuries, operations, stroke, coronary artery disease, infections, etc. Most often, one lobe of the brain may be affected.
Any cyst can capture healthy tissue or displace it. In severe pathogenesis, brain tissue can be compressed and pinched. On one side they are pressed by the cyst, on the other by the bones of the skull. The consequence is that the functions of the department that is affected are disrupted. This is dangerous as it threatens health and life. This option requires immediate medical attention.
Sometimes neoplasms can spread to the spine. This can provoke dangerous consequences.
When a brain cyst appears, size and growth rate are of no small importance. Most often these are tiny tumors. They do not compress brain tissue and practically do not interfere with normal life. But large tumors require urgent treatment and constant monitoring of the patient’s condition.
Due to a post-ischemic cyst, the blood supply can be seriously impaired. The tissues do not receive proper nutrition and atrophy, and zones of necrosis form.
It is necessary not only to detect the neoplasm itself, but also to find out for what reasons it appeared. Only by knowing the reasons can you effectively build a treatment regimen.
Features of therapy
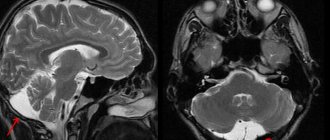
As a rule, treatment of a cyst is prescribed only after a full diagnostic examination, which is performed using computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, which allows you to see the clear contours of the formations, determine their size, as well as the degree of impact on surrounding tissues.
It should be borne in mind that the presence of such cavities is not necessarily associated with cancer and usually responds well to treatment. During a magnetic resonance imaging study, the patient is injected with a special contrast agent, which makes it possible to determine what exactly is in his brain: a cyst or a malignant tumor. MRI is recommended to be performed repeatedly to constantly monitor the dynamics of the disease.
Methods for treating a brain cyst are selected based on the reasons as a result of which it arose. Emergency assistance is usually needed in the following cases:
- constantly recurring seizures;
- hydrocephalus;
- rapid increase in cyst size;
- hemorrhages;
- damage to brain structures located next to the cyst.
As a rule, non-dynamic brain cysts do not require intervention, while dynamic ones are treated using medicinal and surgical methods.
Traditional treatment involves the use of various medications, the main purpose of which is to eliminate the causes of the disease. Doctors may prescribe medications to patients that resolve adhesions, such as caripain or longidase. In order to restore blood circulation, they prescribe medications aimed at reducing cholesterol concentrations, normalizing blood pressure and blood clotting.
You can provide brain cells with the necessary amount of oxygen and glucose with the help of nootropics, for example, picamilon, pantogam, instenon. Antioxidants will help make cells more resistant to intracranial pressure. In addition, immunomodulatory, antibacterial and antiviral agents are sometimes used, which are necessary in case of detection of autoimmune and infectious diseases.
The appearance of arachnoiditis signals, first of all, that the patient’s immunity is greatly weakened, which is why it is necessary to actively restore the defenses. In order to select a consistent and safe course of immunomodulatory and anti-infective treatment, you need to take a blood test. As a rule, all medications are prescribed in courses lasting about three months, repeated twice a year.
What is the danger
It is believed that four out of five cavity cerebrospinal fluid formations pose no threat to humans. They do not appear in any way and practically do not grow. In most cases, cysts are found by chance during an MRI. Surgeon intervention is not required for such development of the tumor.
Sometimes such intracranial anomalies can behave aggressively. Most often these are the disorders that develop according to the second type. Cysts grow quickly after a concussion or an inflammatory process. They can reach impressive dimensions.
If the cyst grows, it begins to put pressure on the brain tissue. This provokes pain and functional disorders. It is very dangerous that blood circulation and the respiratory reflex are disrupted. This leads to irreversible consequences and tissue necrosis. Over time, if the tumor behaves aggressively and does not slow down its growth, neurological disorders appear. Convulsions and partial or complete paralysis may occur. As a result, this condition can lead to disability. You cannot live with such cysts; they need to be treated.
It is important that a person listens to his feelings. It is necessary to notice signs of an anomaly at the earliest stages of its development. If we are talking about a child, then parents should monitor as carefully as possible any change in his behavior or physical condition.
The most dangerous thing is rupture of the cyst tissue. Exudate gets inside the skull. The result is severe intoxication and death of the patient. If the compaction has reached a large size, the cavity is removed or drainage is installed.
If the cyst is located on the transparent septum of the brain, even small-sized neoplasms can cause pain and neuralgia. To reduce tension and pain, the doctor may prescribe diuretics in combination with analgesics.
Causes
If the appearance of cysts was preceded by a difficult pregnancy in the expectant mother, experts call such tissue defects primary. Provoking factors are:
- uncontrolled use of medications by a woman;
- alcohol abuse;
- past infectious diseases;
- abdominal injuries.
If the formation of a tumor occurred in the postneonatal period of life, then the reasons may be:
- neuroinfections - for example, meningitis, or encephalitis, tuberculosis or syphilis;
- surgical interventions on brain structures;
- agenesis of the corpus callosum – absence of an anatomical unit or its replacement with a cyst;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- helminthic infestations;
- intracerebral bleeding.
From the editor: Causes of epilepsy in adults
Sometimes an arachnoid vesicle is identified as a result of examinations that were performed for other indications. The reasons for such formations are not reliably known - the person himself does not remember what could have been the impetus for the formation of the intracerebral cavity.
Symptoms
Symptoms appear if the cyst is medium to large in size. It can be:
- visual impairment;
- hearing loss, tinnitus;
- headache that is not relieved by medication;
- pulsation in the head area;
- nausea that does not go away after vomiting;
- problems with coordination;
- changes in skin sensitivity;
- involuntary movements of arms and legs;
- violation of muscle tone;
- lameness;
- paralysis;
- convulsions;
- hallucinations, mental disorders.
How to live
If there are no symptoms of the anomaly, it does not grow, you can calmly live with it. Such patients only need to undergo regular MRI scans to monitor whether it has begun to enlarge. Such benign anomalies rarely develop. To help the patient, the doctor may prescribe restorative conservative treatment. There are medications that improve blood circulation and oxygen supply to tissues.
It is important for patients with cysts to be monitored and undergo regular examinations.
Treatment
Two treatment methods are used:
- Conservative. Medicines are used to maintain the patient's condition. They improve blood circulation and metabolism. Drug therapy is especially advisable if there are many cysts. It is important to decide on treatment tactics. It depends on the cause of the appearance of neoplasms, their size, location, and growth rate.
- Operational. It is not always necessary to have surgery. And a cyst may be inoperable if it is located in the deep structures of the brain. If surgery is indicated, there are different types: bypass surgery, drainage, surgery with an endoscope. In fact, it is very rare to resort to the help of a neurosurgeon in the presence of a cerebrospinal fluid cyst. This is a last resort. Sometimes complete removal of the cyst tissue is required to maintain quality of life. The prognosis depends on the location of the anomaly, its size, the condition of the patient’s body, age, etc. The percentage of successful operations is quite high.
If a congenital cyst is discovered in a newborn, it can be promptly removed using a bypass or endoscope. Microsurgery is possible. An arachnoid cyst in a child does not resolve on its own. Such cases require close attention from doctors. It is important to immediately decide how to deal with it, for what reasons it appeared. The baby should be carefully monitored by a neurologist. If the tumor progresses, surgery is required.
To avoid complications, rehabilitation treatment is required after surgery. Otherwise, a postoperative cyst may form.
Types of brain cysts
K»Ã°ÃÂÃÂøÃÂøúðÃÂøàðÃÂðÃÂýþøôðûÃÂýààúøÃÂà÷ðòøÃÂøÃÂ:
- Ã] ²²Pa · ãâtely · ãâte ¸.
- ÃÂàÃÂÃÂúÃÂÃÂÂÃÂ: ÿÃÂþÃÂÃÂþù (ø÷ úûõÃÂà¾Ãº ðÃÂðÃÂýþøôðûÃÂýþù þñþûþÃÂÃºà ¸) øûø ÃÂûþöýþù (ÃÂüõÃÂø ð ÃÂðÃÂýþøôðûÃÂýÃÂàúûõþú ø ôÃÂÃÂà ³Ã¸Ã ÃÂúðýõù).
- ÃÂàÃÂÃÂõÿõýø ÃÂð÷òøÃÂøÃÂ: ÿþûþÃÂÃÂà ¸, ÃÂòõûøÃÂøòðÃÂÃÂøõÃÂàò ÃÂð÷üõÃÂð àøûø ÿÃÂõúÃÂà°ÃÂøòÃÂøõ ÃÂþÃÂÃÂ.
From the editor: Treatment of stroke and rehabilitation after it
ÃÂÃÂòðõàø ÿþ üõÃÂÃÂàþñÃÂð÷þòðý øÃÂ: ðÃÂðÃÂýþøôðûÃÂýðà(ýð ÿþòõàÃÂýþÃÂÃÂø üþ÷óð), ÃÂõÃÂÃÂþÃÂõà»ÃµÃ±ÃµÃ»Ã»ÃÂÃÂýðà(ò óûÃÂñøýõ ÃÂõÃÂþà³Ã¾ üþ÷óþòþóþ òõÃÂõÃÂÃÂòð).
ÃÂõÃÂÃÂþÿþûþöõýøõ úøÃÂàò óþû þòýþü üþ÷óõ:
- ÷ðôýÃÂàÃÂõÃÂõÿýðàÃÂüúð;
- ÿÃÂðòðàòøÃÂþÃÂýðàôþûÃÂ;
- ûõòðàòøÃÂþÃÂýðàôþûÃÂ;
- ÃÂõûàüõöôàÿþûÃÂÃÂðÃÂøÃÂüø;
- ûþñýðàÃÂðÃÂÃÂÃÂ;
- ÃÂõüõýýðàÃÂðÃÂÃÂÃÂ;
- üþ÷öõÃÂþú;
- ÃÂøÃÂúþòøôýðàöõûõ÷ð.
ÃÂÃÂðÃÂýþøôðûÃÂýðàúøÃÂÃÂð üþöõà A ÷óþòþü úðýðûõ, ýð úþýÃÂõ ýõà VALUE The úÃÂõÃÂÃÂÃÂð.
What will resolve it?
If the cyst is not subject to surgery, drug treatment is indicated. There are drugs that can resolve scars and sutures after surgery. They can shrink cerebrospinal fluid cysts.
One of these drugs is Actovegin. It is considered quite effective. Before prescribing the drug, the doctor sends the patient for a full examination. He must know in which area the tumor is located, what size it is, and most importantly, why it appeared.
Do not underestimate the capabilities of modern medications. They can improve metabolism and blood circulation. This is a good stimulus for the body. It is important to complete the full course. It is possible that for prevention it will be necessary to repeat it regularly. It is difficult to completely remove such tumors with the help of medications.
Prevention
Prevention of congenital cerebrospinal fluid cysts is based on the prevention of congenital malformations and includes the following areas:
- eliminating the impact of teratogenic factors on a pregnant woman;
- rational management of pregnancy;
- careful delivery.
Prevention of acquired cerebrospinal fluid cysts is based on timely and complete treatment of vascular and inflammatory cerebral diseases, traumatic brain injuries.
How can traditional medicine help?
The task of folk remedies is the same as traditional ones - to improve blood circulation, metabolism, and eliminate symptoms. Properly selected recipes will help cope with annoying headaches and can even slow down the growth of the cavity.
In folk medicine it is common to use:
- Hemlock. The crushed seeds of the plant can be infused in half a liter of olive oil. You need to mix and leave the product for three weeks in a cool place. It is recommended to instill this oil solution 2 drops into the nose 2-3 times a day.
- Dioscoreim Caucasian (root). 4 parts of the root need to be crushed and poured with vodka (1400 ml). The infusion is poured in stages. First, take half the roots and pour 700 ml of vodka in a glass container. You need to leave it for 5 days. Then you need to drain all the liquid and pour a fresh portion of vodka (700 ml) over the roots. Leave again for 5 days. The infusion should be taken one teaspoon three times a day.
- Decoctions of raspberries, licorice, wormwood, elecampane, chamomile, and calendula will help reduce intracranial pressure.
For some reason, many people believe that folk remedies are safe. This is wrong. To avoid unpleasant consequences, you should definitely ask your doctor whether you can use them specifically. It is the doctor who must select the folk remedy. Otherwise, it may not only not help, but also seriously harm. In addition, some medications are incompatible with herbs or alcohol.
Classification
By origin, cystic neoplasms are:
- congenital (primary) – arise even at the stage of intrauterine development;
- acquired (secondary) - their causes are pathological processes (bleeding, inflammation, traumatic injuries) occurring in the meninges.
Depending on the characteristics of the morphological structure, cavity arachnoid formations are divided into two types:
- simple - their cavity is lined with cells that produce cerebral fluid;
- complex (retrocerebellar) - their structure includes various tissues (arachnoid membrane cells, neuroglia).
According to the characteristics of the clinical course, the following are distinguished:
- frozen - they are characterized by a latent course, lack of growth;
- progressive - accompanied by a gradual increase in neurological symptoms, which is associated with an increase in the size of the formation and compression of brain structures.