Post-puncture syndrome
The symptoms of this syndrome are not caused by the extraction of cerebrospinal fluid during the puncture itself, but are the result of damage to the dura mater, which forms after insertion of the needle.
The entry of cerebrospinal fluid into the epidural space of the spinal cord contributes to the displacement and expansion of the dural sinuses and intracranial vessels. It forms several hours after lumbar puncture and has three degrees of severity:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
This manifests itself as a headache in the occipital or frontal region, and in more severe cases, nausea and vomiting. Postpuncture syndrome lasts about four days, less often up to two weeks, and even more rarely more than two weeks. The use of needles of a smaller diameter or sharp disposable needles, turning the needle 90° during lumbar puncture (the bevel of the needle runs parallel to the fibers of the dura mater), and avoiding excessively accelerated flexion can reduce the incidence of post-puncture syndrome.
Chronic post-puncture syndrome is treated by injecting 10 ml of autologous blood into the epidural space, which promotes forced closure of liquorrhea. If conservative treatment is ineffective, direct surgery is indicated, in which the defect is closed with two special Cushing clips.
Composition of cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal substance is produced, on average, at a rate of about 0.40-0.45 ml per minute (in an adult). The volume, rate of production, and most importantly, the component composition of CSF directly depends on the metabolic activity and age of the body. Typically, tests show that the older a person is, the more reduced production is.
This substance is synthesized from the plasma part of the blood, however, both the substrate and the producer differ significantly in ionic and cellular content. Main components:
- Protein.
- Glucose.
- Cations: sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium ions.
- Anions: chlorine ions.
- Cytosis (presence of cells in the cerebrospinal fluid).
An increased content of protein and cell aggregates indicates a deviation from the norm, which means it is a condition that requires further tests and mandatory consultation with the attending physician.
Regimen after lumbar puncture
Some doctors believe that bed rest does not prevent the development of post-puncture syndrome, and therefore they are allowed to walk immediately after a lumbar puncture. However, most of the authors conclude that bed rest has a positive effect, and the position of the patient and the duration of bed rest are discussed (most stopped at 3-4 hours). The patient should be in a horizontal position, lying on his stomach. After a lumbar puncture, general cerebral symptoms may occur (nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness), in combination with the body’s autonomic reaction, it has a characteristic feature - deterioration when trying to get up. The patient needs to create peace, lower his head, offer plenty of warm drinks and (or) intravenous administration of plasma substitutes. When contrast agents or oxygen (air) are administered, bed rest can last up to three days.
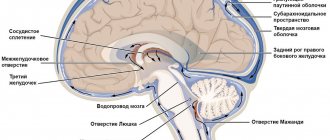
Characteristics of cerebrospinal fluid
The difficulty of understanding cerebrospinal fluid, what it is and for what purpose it is present in the human body, experts draw an analogy with tissue. After all, it contains cells and vitamins, organic as well as inorganic compounds and salts. This composition and structure allows it to perform basic functional duties:
- absorb - in fact, the brain is practically not attached to the bone structures, therefore, in the process of moving a person, it is subject to load and friction, which is leveled by the cerebrospinal fluid;
- participation in metabolic processes - since nervous tissues are independently unable to extract and deliver nutritional components, as well as oxygen molecules, the cerebrospinal fluid performs this function for them.
The circulation of cerebrospinal fluid occurs constantly and continuously - this ensures support for the internal environment. In the event of chemical or functional failures, a person immediately feels a deterioration in health in the form of pain, difficulty moving, and general intoxication. Based on the nature of the unpleasant symptoms, doctors judge the possible causes and prescribe laboratory tests of the brain fluid.
How is the procedure done?
The fear experienced by patients who are about to undergo a lumbar puncture procedure may arise against the background of insufficient awareness of the patient about the features of lumbar puncture and a misconception about the procedure for its implementation.
Where is a lumbar puncture performed?
Lumbar puncture is a medical procedure that requires strict adherence to asepsis. For this reason, such manipulations are carried out in the operating room, and the patient is hospitalized for one day in a neurological hospital in the neurosurgery department. It is permissible to perform a puncture in a day hospital: if there are no complications, the patient is sent home 2-4 hours after puncture.
In adults, lumbar puncture is usually performed in the L3-L4 space.
Preparation
Before undergoing the procedure, the patient must sign an informed consent for medical procedures, as well as undergo the necessary examination. The list of mandatory diagnostic minimums before performing lumbar function includes:
- fundus examination (to identify possible symptoms of increased intracranial pressure);
- computed tomography of the brain and spinal cord to exclude tumor formations and hydrocephalus;
- general blood test (if platelet deficiency is detected, drug correction is required).
Before the puncture, examinations are carried out
If the patient is taking drugs from the group of anticoagulants (thinning the blood and increasing its fluidity), treatment must be discontinued 72 hours before the scheduled procedure.
Posture for puncturing
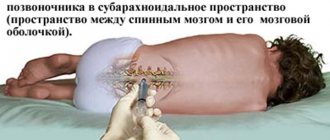
The classic and most effective position for a lumbar puncture is considered to be the position when a person lies on the edge of the operating table (on his side), with his legs bent at the hip and knee joints pressed to his stomach. The head should also be tilted forward (the chin extends towards the knees). This position ensures maximum expansion of the interspinous spaces between the vertebrae and facilitates the passage of the needle into the spinal canal.
In some cases, for example, with a large amount of fat in the back area, inserting a needle while lying down is difficult. In such situations, manipulations are carried out in a sitting position: the patient sits on the edge of a table or couch, puts his feet on a special stand, crosses his arms in the chest area and lowers his head on them.
Poses for puncturing
Needle insertion technique
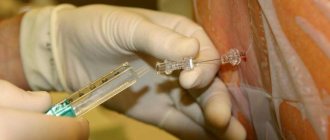
To perform a puncture, a special Beer needle with a rigid rod is used to close holes in tubular instruments (with a mandrel). It is inserted into the space between the spinous processes at the level of L3-L4 or L4-L5. In children, the spinal cord is located slightly lower than in adults, so puncturing for children is performed strictly at the L4-L5 level. The criterion that the needle has reached the subarachnoid space is the feeling of “failure” (the instrument descends into an empty cavity). If everything was done correctly, a clear liquid, cerebrospinal fluid, begins to flow from the needle.
Before puncturing, the skin within a radius of 15-25 cm from the puncture site is treated with an alcohol solution of iodine. Subarachnoid puncture does not require general anesthesia and is performed under local anesthesia, for which a local anesthetic (most often a 0.25% novocaine solution) is injected at regular intervals while the needle is advanced.
Puncture and biopsy needles
For research, from 1-2 ml to 10 ml of cerebrospinal fluid is usually taken, which is immediately placed in three test tubes, after which its chemical composition, rheological properties, and microbiological parameters are examined.
Preparing for the examination
Preparation for cerebrospinal fluid analysis is as follows:
- Blood tests are taken (general, clotting tests).
- At the preliminary consultation, an anamnesis is collected. The patient needs to inform the doctor about past illnesses, the presence of chronic illnesses, and negative reactions to medications.
- It is necessary to donate cerebrospinal fluid on an empty stomach - eating is prohibited 12 hours before the procedure.
Before the examination, taking medications that thin the blood, as well as analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is not allowed.
Contraindications
An absolute and categorical contraindication for performing a subarachnoid puncture is the displacement of some segments of the brain relative to other structures, since the introduction of instruments into the subarachnoid space in this case leads to a difference between cerebrospinal pressure in different areas and can cause sudden death of the patient right on the operating table .
Contraindications to lumbar puncture
All possible risks and their relationship with the expected benefits are carefully weighed and assessed in the presence of the following contraindications, which are considered relative:
- infectious and pustular skin diseases in the lumbar region (furunculosis, carbunculosis, fungal diseases, etc.);
- congenital anomalies, malformations and defects of the spinal tube, central spinal canal and spinal cord;
- impaired blood clotting ability;
- previously performed blockade of the subarachnoid space.
If there are these contraindications, which most neurosurgeons and neurologists consider conditional, the procedure is postponed until the existing restrictions and diseases are eliminated. If this is not possible and diagnosis must be carried out urgently, it is important to consider all possible risks. For example, in the case of infectious skin diseases at the puncture site after puncture, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents to prevent infection of the internal tissues of the body and the development of inflammatory reactions.
What is lumbar puncture
Risks of axial herniation during the procedure
Axial (cerebellar-tentorial) herniation is the descent of the brain into the foramen magnum, which is the natural opening of the skull bones. Clinically, the pathology is manifested by the onset of coma, stiffness of the neck muscles, and sudden cessation of breathing. In the absence of emergency assistance, acute ischemia and hypoxia of brain tissue occurs, and the person dies. To prevent herniation syndrome during the procedure, the doctor uses the thinnest possible needle and takes the minimum required amount of fluid to prevent sudden changes in cerebrospinal pressure.
The maximum risks of axial herniation are observed in the presence of the following pathologies:
- hydrocephalus 3-4 degrees;
- large neoplasms;
- greatly increased ICP (difference between cerebrospinal fluid pressure and atmospheric pressure);
- violation of the patency of the liquor-conducting pathways.
Complications of the procedure
In the presence of these four factors, the risk of sudden brain herniation is maximum, therefore these pathologies in most cases are absolute contraindications for lumbar puncture.
Decoding the results
Normally, cerebrospinal fluid has moderate viscosity, a transparent and colorless structure. Even before the analysis, the doctor evaluates the appearance of the cerebrospinal fluid, the presence of impurities in it (for example, blood), the consistency of the liquid and the rate of its flow. Normally, cerebrospinal fluid should be released at a rate of 20 to 60 drops per minute. Deviation from these indicators may indicate inflammatory processes, tumor diseases or metabolic disorders (for example, leukodystrophy).
Normal indicators for studying the composition of cerebrospinal fluid
Normal cerebrospinal fluid values and possible abnormalities
| Parameter | Norm | The indicator is increased (possible reasons) | The indicator is lowered (possible reasons) |
| Cerebrospinal fluid density | 1,005-1,008 | Any inflammatory (including infectious and purulent) diseases of the spinal cord | Excess fluid (possible signs of hydrocephalus) |
| pH level (acidity) | 7,3-7,8 | Neurogenic syphilis, epilepsy, organic lesions of the nervous system | Inflammation of the brain and its membranes |
| Protein | 0.44 g/l | Neuroinfections, inflammation of the meninges and various structures of the brain and spinal cord, hydrocephalus, malignant tumors | Neuropathy |
| Glucose | 2.3-4.0 mmol/l | Strokes | Meningitis and meningoencephalitis |
| Lactic acid salts | 1.0-2.5 mmol/l | Inflammation of the brain and its membranes due to infection with pathogenic bacteria and any inflammatory pathologies of the central nervous system | Viral cerebrospinal meningitis |
| Hydrochloric acid salts | 115-135 mmol/l | Neoplasms and accumulation of pus in the cranial cavity | Inflammation of the soft membranes of the brain, neurogenic syphilis, brucellosis |
Cloudiness of the cerebrospinal fluid indicates increased infiltration of leukocyte cells, and a dark yellow color indicates possible metastases from skin cancer.
Video - Spinal tap
Spinal cord puncture is an effective therapeutic and diagnostic neurosurgical procedure that has a high degree of reliability and information content in cases of suspected various diseases of the central nervous system. Today, sufficient practical experience has been accumulated in carrying out such manipulations, and the risk of possible complications is minimized, so you should not be afraid of a lumbar puncture. All actions are performed under local anesthesia, and the patient does not feel pain during the procedure, except for the initial discomfort from the injection itself.
Pathologies of cerebrospinal fluid and their consequences
First of all, of course, experts pay attention to changes in the color of the liquor. So, with a yellow-brown or greenish-gray tint, a tumor neoplasm in the brain, or, less commonly, hepatitis, should be excluded. Whereas a reddish color indicates possible hemorrhage in the ventricles and subarachnoid space. Sometimes this result is a consequence of a traumatic brain injury.
Turbidity and the presence of sediment in the cerebrospinal fluid are an indication for emergency medical intervention. Most often, pathogenic microorganisms are implicated as the cause of infectious brain damage. An increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure is an indication of its excessive accumulation in the brain cavities, for example, during concussions and bruises, fractures of the cranial bones or pressure on tumor tissue.
Detection of glucose in the cerebrospinal fluid is a harbinger or consequence of diabetes, encephalitis or even tetanus. The doctor will recommend additional examinations - magnetic resonance imaging, bacteriological culture of fluid, blood for tumor markers, PCR diagnosis of various infections. After all, establishing an accurate diagnosis contributes to the optimal selection of a treatment regimen. If you contact a doctor late, this is due to the functions of the cerebrospinal fluid, which aggravates the situation - metabolic disorders, paresis and paralysis, epilepsy and dementia, as well as death, develop.
To prevent various complications, doctors urge people to take care of their own health, give up bad habits, eat right and undergo preventive medical examinations in a timely manner.