A baby is born with most of the brain cells that this organ should have. In the first 12 months of life, the cerebrum (CB) becomes more complex; by the time it reaches 2 years of age, it has 75% of the weight of the adult brain. At the age of 3 years, the percentage of weight increases to 90%. Almost 50% of brain cells present at birth weaken or die during the first years. This process organizes and optimizes brain activity. Events in a child’s life provoke electrical impulses and create nerve fibers. The more fibers are used, the more stable an important organ becomes, the fewer neurons are susceptible to death. Similar to muscles, children's brains operate on a “use it or lose it” principle.
Brain waves
Brain waves are an expression of the frequency at which an organ operates. During the day they change, which causes a change in the person’s condition. Waves are divided into 5 types:
- delta;
- theta;
- alpha;
- beta;
- gamma.
All waves are active, consciousness is influenced by the dominant brain wave. Each wave type plays an important role in the formation of intelligence in childhood.
The activity and capabilities of the brain are described in a number of books by V.M. Bekhterev (they can be downloaded from many specialized sites).
Below is a diagram of wave frequencies and corresponding states of mind.
Beta (14-30 Hz):
- concentration, excitement, alertness, cognition;
- high levels are associated with anxiety, illness, loneliness, and arguments.
Alpha (8-13.9 Hz):
- relaxation, wakefulness, light trance, increased serotonin production;
- drowsiness, meditation, entering the subconscious.
Theta (4-7.9 Hz):
- REM sleep phase;
- increased production of catecholamines (important for learning and memory), increased creativity;
- integrative, emotional experiences, potential behavioral changes, increased knowledge retention;
- hypnotic imagination, trance, deep meditation, penetration into the subconscious.
Delta (0.1-3.9):
- "sleepless sleep";
- release of growth hormone;
- deep, non-physical state, trance;
- entrance to the subconscious.
Ultrasound of the child's brain
Ultrasound of the brain in a newborn baby may also be called neurosonography
(NSG). With its help, the specialist receives a two-dimensional image of the structure of the brain, information about the condition of the tissues and head. The method is based on the various properties of tissues to reflect high-frequency sound waves. The procedure does not involve the use of magnetic fields or ionizing radiation, so ultrasound can be used to examine the brain of even newborn children.
Prenatal development
Consideration of the question of how a child’s brain develops should begin from the time the embryo is formed. It is formed in the womb from the anterior part of the neural tube, which appears in the 3rd week (20-27 days of development). The neural tube is formed by primary and secondary neurulation. At the head end of the neural tube, 3 primary cerebral recesses are formed - anterior, middle, posterior. At the same time, the frontal, parietal, and occipital lobes are created. The neural disc arises from the neuroectoderm.
At week 5, secondary medullary pads form, forming the main parts of the adult organ. The forebrain is divided into the intermediate telencephalon, the hindbrain into the medulla oblongata, pons, and cerebellum.
Gyrification of the hemispheres occurs sequentially. First, a longitudinal fissure is formed (determined by the fact that the hemispheres grow separately), then the lateral sulcus (separates the temporal lobe), after which the central sulcus.
Features of the prenatal stage of child brain development:
- Week 3: creation of a medullary (spinal) tube;
- Week 4: expansion of the proximal tube into 3 primary and 5 secondary follicles;
- Week 6: Neuroblasts begin to develop into mature neurons;
- 2nd month: the cerebellum, the base of the neurohypophysis, rhinencephalon (olfactory center), hippocampus, basal ganglia develop; at this stage, the cerebral hemispheres begin to develop;
- 3rd month: the corpus callosum begins to form;
- 4th month: brain development in children continues with intensive separation of the hemispheres (gyrification), an increase in their surface;
- then the children's brain experiences proliferation, differentiation, migration, maturation of nerve cells, growth of supporting elements; Myelination begins from the end of intrauterine life.
Briefly about the main elements of the brain
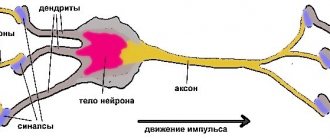
The brain consists of a huge number of neurons connected to each other via synapses. Neurons form various large structures: the cerebral cortex, brain stem, cerebellum, thalamus, basal ganglia - everything that is very often called “gray matter”. But nerve fibers—“white matter”—are responsible for connecting these structures. The white color of nerve fibers comes from myelin, an electrically insulating substance that covers these fibers.
Let's look at the features of the three pillars, without which brain development is impossible, and disturbances in which lead to serious illnesses.
Neurons:
- They are building blocks for the brain
- They form different parts of the brain
- They exchange information within the brain
Synapses:
- Provide communication between each pair of neurons
- Each neuron is surrounded by thousands of synapses
- Thanks to synapses, areas of thousands of neurons communicate
Myelin:
- Covers the fibers of adult neurons
- Necessary for efficient transmission of electrical impulses
- Increases the efficiency of connections between neurons by 3,000 times
Neonatal development of GM
Humans are the only mammals whose GM increases 3 times in size in the first 2 years of life. If it had been larger at birth, the baby's head would not have been able to pass through the birth canal. If the volume were small, the baby's life would be at risk.
Insufficient size of the brain is observed in microcephaly, an anomaly accompanied by mental impairment.
How does a child's brain develop before one year of age?
- at birth it weighs about 350 g, up to 1 year - about 1 kg;
- At birth, the brain has about 200 trillion neurons (nerve cells) - about the same as in adulthood;
- each neuron responds to stimulation of a growing system of dendrites (branched nerve cells) and synapses (the place where signals are transmitted from one neuron to another);
- each neuron ends in dendrites with approximately 15,000 synapses;
- dendrite formation becomes more complex over time, with 3-4 branches before the age of 6 months;
- the more stimuli the GM captures, the better the dendrites become;
- the anterior lobe (the part responsible for emotions) becomes metabolically active from 6 months (the neural basis of emotional intelligence is formed before 18 months);
- over the course of 2-4 months, the number of synapses in the visual center increases 10 times (approximately 20,000 neurons);
- up to 12 months, the neurons responsible for identifying the native language find their permanent place.
The difference between reason and education is that it is reason that can provide you with a good life (A.V. Semenovich)
Early development is the active position of adults towards the child in the first years of life. This is a continuous process, it is painstaking work that requires constant “involvement” in the child’s life.
Brain maturation is a long and uneven process, across its zones and levels, in accordance with age stages. Brain development proceeds by layering and superstructure of new levels over old ones, as noted by L.S. Vygotsky. The old level passes into the new one, exists in it, creating its basis (foundation). Our brain is so delicate and complex that it is better to protect it from negative influences at any age. Neurophysiologists believe that there are two periods in childhood when a child’s brain deserves especially careful treatment: from one to three years of age and in adolescence.
Different brain structures reach maturity at different stages of ontogenesis (individual human development from conception to the end of life), therefore, each age period is characterized by specific neurophysiological conditions for the formation and development of mental functions. In turn, each child has individual development and learning characteristics.
“There are neurophysiological laws of brain development. Its energy potential is limited at any given time, so if we waste energy on the untimely development of some mental function, then a deficit arises where this energy should have been actually directed. Since the external environment requires the completion of a certain task, the brain will perform it, but at the expense of some other structures of the psyche” (A.V. Semenovich, Candidate of Psychological Sciences).
Early age can be called the age of sensory knowledge of the world around us. During this period, children experience the formation of all types of perception (visual, tactile-motor, auditory, etc.).
It is well known in practical psychology and psychotherapy that early childhood is the time when a child’s basic relationships with the world are established.
The period from 1-3 years provides regulation of body tone and wakefulness. At this time, the brain of a small child performs a fantastic amount of work to assimilate a huge amount of information, and the second year of life is especially difficult in this sense. First, the child recognizes speech, then attempts to speak independently begin - this is a complex, complex task that the brain has to solve. Also, in the second year of life, a child has to simultaneously cope with another difficult task. He is learning to walk. From the point of view of brain activity, this is also more than serious. According to Tara Swart (a neurophysiologist), mastering these tasks can be accompanied by serious emotional overload and a feeling of exhaustion. The early formation of positive emotions based on the establishment of social connections with adults, and later with peers, is the key to the development of a child’s personality. The emotional sphere also has a great influence on the formation of children’s cognitive abilities. It has been proven that if children are limited in receiving information and processing it, in accordance with their age, the pace of their development becomes slower. Therefore, it is important that the lives of children be varied and rich in impressions. Sensory needs cause high motor activity, and movement is a natural state baby, promoting his intellectual development. Since the sensorimotor level is basic for further development, preference should be given to motor methods. Updating and consolidating any bodily skills presupposes the development of such mental functions as emotions, memory, perception, self-regulation processes, etc.
Therefore, at this age it is necessary to develop:
1 Sensory and motor skills (move, learn colors, add by size and color, etc.)
2 Memory (learn short poems, retell fairy tales, short stories)
3 Attention (watch, observe, repeat)
4 Explore the “world” with all senses (allow the child to touch everything with his hands: feel, stroke, look at, make crafts from scrap materials together with his mother).
Help your child develop by following the rules of brain function.
- Physical activity stimulates brain function.
- The brain has a survival program.
- Supporting children's creativity, self-expression, and establishing contacts with people.
- Each person's brain is unique.
- The child's emotional environment should be positive and safe.
- All games and activities should follow the principle “from very simple to simple, from simple to complex, and then to very complex.” If your child can't cope with something, simplify the task.
- The brain does not respond to boring things.
- Don't overload your child.
- The human body can withstand stress for no more than 30 seconds. If stress lasts more than 30 seconds, it interferes with the brain's ability to learn.
- Vision is the most powerful of the senses. Use pictures when learning and remembering.
- Encourage your child's curiosity.
- Rejoice at your child's success, even the slightest attempt to prove himself, especially if this is the first time.
- Be active in your baby's life.
- Ensure your child gets good sleep.
Let your child grow up healthy and happy!!!
GM development during the first years of life
The newborn's brain is anatomically and functionally immature. During the breast period, it grows rapidly, the number of glial cells increases, and hydration decreases.
At the end of the 1st year, the weight of the GM doubles. The development of a child’s brain occurs intensively over the years; in the process of ontogenesis, innate unconditioned reflexes are replaced by conditioned ones.
At 3 years of age, the brain weighs approximately 3 times more than at birth. The ability of abstraction, learning, and memory is used; the child realizes his personality and becomes a social creature.
The first years of life are a critical stage for a child's brain development and provide the neurological foundation for intellectual development in adolescence and adulthood.
In the early years, children are very open to science through play. For young children, play is a way of preparing for a successful future life. Therefore, during this period, parental love and plenty of time spent together are important.
At 6 years of age, the weight of the brain is almost equal to the weight of the adult human brain (1250 g). The hemispheres are expressively grooved. Branching of neurons, myelination (creation of a covering that protects large nerve fibers from damage) are completed, memory and the ability to recreate memories improve. In the activity of the GM cortex, the ability of internal blocking is used; the child distinguishes between what he says, thinks, and reads.
During the first 8 years of life (especially the first 3 years), there are several critical periods for the acquisition of certain types of intelligence. If these “periods of opportunity” are closed, learning becomes more difficult, sometimes even impossible.
In adolescents, the GM grows mainly in the anterior lobes, its weight is about 1400 g.
Development of the frontal lobes of the brain in children under 3 years of age
The founder of neuropsychology, Alexander Romanovich Luria, identified three brain blocks that are involved in the implementation of higher mental functions:
- Block 1 – regulation of tone and wakefulness, energy block. These are the reticular formation, the limbic system and other subcortical structures. As you know, even the smartest computers cannot work without a power supply.
- Block 2 – reception, processing, storage of information. These are the cortical ends of the analyzer systems, primarily auditory, visual, and skin-kinesthetic (everything is not so simple there, for example, the vestibular system does not have its own separate cortex, so it is integrated with the visual and kinesthetic). This includes modality-specific activities.
- Block 3 – control, regulation and programming of activities. This includes the motor, premotor and prefrontal cortex, that is, the entire forehead (front and back).
The “forebrain” creates and implements programs for various types of activities. It is responsible for praxis, including the motor side of speech, thinking, consciousness, planning, volition, initiative, and will. If globally, it determines a person’s personality.
Each part of the brain has its own time of maturation and activation of functional systems. The same mental functions during development can be performed by different “ensembles” of brain zones. That is, as we grow older, a restructuring of functional systems occurs.
For example, parents of children with mental retardation often say that the child had a setback in speech: until the age of 1.5-2 years he spoke simple words, and then fell silent. This could happen precisely at the stage of restructuring of the speech system: at this age, global changes occur. Specialization of the hemispheres for speech occurs, and the function moves to the left hemisphere. That is, new structures included in the work must be ready. Plus, any restructuring is a critical period during which any stress (illness, vaccination, allergic reaction, etc.) can have a strong negative impact.
The frontal lobes are the most late maturing part of the brain. According to various sources, the prefrontal cortex matures between 20 and 23 years of age. But this does not mean that it does not work until this age.
One well-known specialist on the Internet recently wrote, they say, how can neuropsychologists write in their conclusions to a child “immaturity of the prefrontal cortex”! She matures already at a conscious age!
It is not true. Of course, one cannot talk about full maturity at 3, 7, 12, 18 years old. But at these age stages, the frontal cortex is already working and increasing its capabilities. The prefrontal cortex does not “sleep” until age 23! Moreover, in childhood, according to the results of instrumental studies, metabolic processes in this zone are twice as fast as adults.
Child development:
2-6 months The child is no longer a reactive being. It develops communicative and cognitive activities. He lets you know by shouting if you don’t like something. Uses facial expressions and humming, movements to interact.
6-12 months The child is involved in object-manipulative activities together with an adult. By 6-8 months. the metabolic rate in the frontal regions increases significantly (which indicates intensive maturation). The arsenal of means of demonstrating the child’s initiative and will is expanding: he uses babbling and the first words, intonations, and rich facial expressions. There is an integration of various mental functions. Visual-motor coordination develops. The baby begins to gradually understand spoken speech. The first internal motives for activity, attention, and delayed reactions develop. The first signs of speech regulation of the child’s behavior appear: he becomes able to follow the simplest instructions of an adult (for example, look for the required object with his eyes). But, of course, at this age attention is still unstable. The child quickly switches to bright side stimuli. At this stage, emotions serve for self-regulation and stimulation of the child to cognition and speech development. The connections between the prefrontal cortex and the limbic system (which is responsible for emotions) are intensively maturing. Thus, the child’s motivational sphere is formed.
As the child approaches one year of age, the child’s attention becomes more stable, and distracting bright stimuli interfere less. The ability to follow the instructions and requests of an adult becomes stronger. 1 year is a turning point for the development of the brain and its anterior region in particular. By the beginning of the second year of life, it becomes possible to follow instructions with a time delay and resist distracting stimuli.
1-3 years . The first voluntary actions appear. At the same time, the speech of an adult still plays only a stimulating role, but not an inhibitory one! Adults often want the child to listen and stop unwanted actions. But at this age, verbal prohibitions do not work, it has been experimentally proven. Therefore, it is better to distract and switch the child in such situations. In this case, inhibition in the studies was able to be “turned on” with visual accompaniment of the corresponding part of the instructions.
From the age of 2, a child can already learn a simple system of rules given through speech, but with visual reinforcement. The regulatory function of speech is not yet sufficiently formed.
By the age of 3, acting on an adult’s verbal instructions becomes a more stable skill. A three-year-old can solve conflict problems (that is, situations where two conditions are in opposite directions), unlike a two-year-old child.
At the age of 2-3 years, rapid morphological maturation of the frontal region occurs: neural complexes are formed, connections are formed, the number of synapses reaches a maximum; The volume of simultaneously processed tasks is growing.
At 3 years old we can talk about the child’s voluntary objective actions - praxis. That is, the cortical level of movements (parieto-premotor) matures.
In conclusion, I will say that 3 years is truly a critical period in a child’s development. The most important. Often, parents of non-speaking children close to 3 years of age try to convince themselves (and me at the same time in consultations) that “the child has the right not to speak until the age of 3.” Unfortunately, this is not just a matter of speech, but the fact that the absence of speech only illustrates that something is wrong in development, there is a problem.
At 3 years old, a child already has internal speech (which develops after external speech), with the help of which he regulates his behavior, directs attention, and carries out cognition. There is a body diagram, an image of “I”. Therefore, often when speech is delayed, we also observe problems with the corresponding processes in the child.
Neuropsychologist Alexandrova O.A.
Make an appointment with a neuropsychologist by phone or fill out the form on the website.
Brain diseases in children
Because the brain develops during fetal life and relatively long after birth, its individual structures are more susceptible to damage. On the other hand, the nervous system of a child, compared to an adult, has better plasticity and the ability to regenerate, for example, after a blow, concussion, or inflammation.
The following pathologies are recorded in pediatric neurology and neuropsychology:
- cerebral palsy and other disorders of the nervous system - congenital malformations and various genetic syndromes, developmental delay, autism, as well as inflammation, tumors, injuries;
- heredogenerative diseases, metabolic defects that can (not necessarily) affect other organs;
- epilepsy - in addition to idiopathic epileptic syndromes (without apparent causes), seizures can be a symptom of another GM disease - cancer, birth defects, degenerative, metabolic diseases; epilepsy is more common in children with cerebral palsy.
Diseases in premature babies
Premature babies undergo regular ultrasound examinations. Because the blood vessels are fragile and unable to respond to changes in blood flow and intracranial pressure, bleeding into the brain may occur. This is the most common problem in the first few days after birth in very low birth weight babies.
Another specific brain disease of premature infants is cystic periventricular leukomalacia. It is a white matter disorder that leads to the formation of cysts. The basis of this disease occurs during fetal development or immediately after birth, but the diagnosis can only be determined after several weeks.
J. Stamm, P. Spencer. Smart kid. How to develop a child from birth to 3 years.
Publisher: Peter, 2010
The buyer chooses a book based on clothes. By design, name. Complex titles are not welcome; the reader must be motivated to pick it up and look through it. Call the book “Functional mapping of the internal picture of the brain, developmental methods,” and it will gather dust on the shelf, despite the excellent contents. As a result, endless clones of a “smart child” are born: how to develop a child, how to raise a child correctly, how to increase intelligence... and so on. These books have different authors and were published by different publishers, but are similar to each other like twins. It is difficult to understand under which cover another hack is hidden, and where the treasure is hidden. There is definitely a treasure in this book. She is very good. Despite the banal name.
Children are born into a wide variety of living conditions and situations. Where the arctic cold reigns, they are wrapped in blankets made of bear skins, and in the tropical jungle a mother carries a naked child on the simplest harness, holding her close to her body. Children hear different languages, not to mention countless dialects. These native voices can be loud, harsh and drunk, or soft, melodic and friendly. The child will be deliberately protected from the harsh realities of life or abandoned to the mercy of fate. And from the very beginning, the child’s brain begins to adapt to the circumstances in which it finds itself. There is no single model of what is required for the survival of a growing brain because there are many environmental variations. The brain begins only with a general instruction to “increase connections as necessary,” and changes in it occur in this way solely for the purpose of survival! It depends on constant adaptation to changes in external conditions and flows of incoming information. This survival instinct is unconscious, but very powerful. The speed with which the young brain adapts to the outside world allows the baby to take maximum advantage of the family and cultural conditions into which he was born.
The book begins with a heartbreaking story: the author, Dr. Jill Stamm, gave birth to a child weighing 500 g. Despite a whole bunch of disappointing diagnoses, the girl managed to be born. The author covers in detail the features of child brain development from birth to three years, including in “special” children. Here is the physiological structure of the brain and nervous system, the development of attention, fears, stress, the influence of emotions, education, care... And, of course, useful tips, techniques, games.
A striking feature of the book: it is very nicely written. The author really worked and tried to convey his truth to readers; there is no doubt that he passed everything written through himself, experienced it, felt it .
“A child watching a video of, for example, a flower, no matter how professionally the filming is done, does not experience anything similar to the real sensations that he experiences when touching a real flower. Feeling its soft, velvety petals and strong, flexible stem, picking a flower and feeling its pieces in his hands, smelling its aroma... Likewise, when he watches a video of a child frolicking under the streams of a sprinkler, this does not even remotely resemble the sensations that arise when drops of cold water glisten on the skin, and bare feet touch the prickly and wet grass.”
Figuratively, exactly. It's like watching a movie.
Sleeping and eating at the same time, a familiar approach to the child is an important part of learning self-regulation. When you create this support, the brain and body systems learn to become aware of these smooth, predictable patterns and adjust accordingly for calm, secure confidence. Over time, this helps your child manage himself better. This is how self-discipline arises, teaching self-control or self-regulation.
Reasonable Limits: When I say reasonable, I mean age appropriate. Any one-year-old will reach for the TV remote control “one more time” after you say, “No,” because his brain is geared toward learning by repeated testing. (When I did this, my mother said “you can’t.” What would happen if I did press at least one button?) All two-year-old children experience outbursts of anger, partly because, due to development, they want more than they are physically capable of do. Knowing what is “normal behavior” for a child at a given age will help you guide his behavior in a constructive direction. Instead of punishing a child who cannot resist interest in an object that intrigues him, it is better to remove this object from his reach or remove the child from the current situation.
Here's everything you want to know about the child's brain and the development of its connections. This important information will help parents of children diagnosed with ADHD or other neurological problems. The author also writes about this. As well as about age-related needs to explore the world and children's reactions, which sometimes look strange and even outrageous. We lose a lot by not trying to find out the deep essence of what is happening; we have no idea how difficult our one-year-old (two-year-old, five-year-old, but still small) child is. It is also interesting to learn about the impact of massage, communication, reading, touching on brain development, and about properly teaching a child speech skills and increasing IQ.
The book is on the publisher’s website: https://www.piter.com/book.phtml?978549807238.
How to promote the development of children's GM?
The intellectual basis of a person is largely formed already in the prenatal period. Therefore, in order to give birth to a smart, physically healthy baby, it is important for the expectant mother to focus on her lifestyle.
Just as calcium is the main building block of bones, protein is a component of muscles, one of the most important substances for the brain is fat. It accounts for about 60% of the dry part of the GM, about 1/3 is unsaturated fatty acids, in particular α-linolenic and docosahexaenoic acid, which are responsible for the proper formation of the nervous system and the mental development of children. B vitamins are also important, especially B1, B6, B12, B9 and other substances such as iron, iodine, zinc, protein.
Factors influencing brain development in adolescents
The most interesting period from the point of view of brain development is adolescence. This means that at this time he absorbs almost everything he encounters - from positive relationships with friends or teachers to risks, stress. Therefore, experts encourage parents to take care of how to develop their child's brain and help children avoid the risks of adolescence that could negatively affect their lives.
- Shake. A very dangerous problem for teenagers; can occur with any sport that children engage in during this period. If this situation occurs, you should consult a doctor, preferably a sports professional.
- Stress. Although the areas of the brain that deal with the rational aspects of things are often stuck in teens, their emotional brains are firing on all cylinders. Therefore, even minor criticism, banal for an adult, can be an important development factor for a teenager.
- Drugs and alcohol. The excessive activity of a teenager’s brain makes him literally a “sponge”, absorbing all information from the environment. The brain responds quickly to any new challenge, both positive and negative, such as various addictive substances.
Hypnosis is not recommended for children. MRI revealed significant functional changes in the brain after hypnosis.
Child brain development. What is important for parents to know?
Modern pedagogy and psychology have a huge arsenal of scientific data, among which neurosciences occupy a special place. Despite the fact that scientists do not yet have a complete understanding of the process of human brain development, there is a sufficient number of facts, the understanding of which can greatly facilitate the life of parents and specialists working with children. Montessori staff has prepared an overview of the basic facts about the work of the child's brain.
Brain development before and after birth. Why an expectant mother should eat well and avoid stress, while established parents should take their baby’s leisure time more seriously
Brain development begins even before the baby is born, and scientists consider the brains of people over twenty years of age to be fully mature. The most complex human organ undergoes multiple changes, is incredibly sensitive to external influences, and also largely depends on hereditary factors. How does the human brain develop?
What happens before birth?
The moment your baby took his first breath, his body has already done a lot of work and laid the foundation for the entire future functioning of the baby. Despite the fact that the size of his brain will increase another 4 times before it fully matures, the bulk of the neurons in it already exist, and its biochemistry has already been adjusted.
The fact that the brain that controls our feelings, thoughts and abilities is formed in the womb places great responsibility on pregnant women. We cannot underestimate the scientific evidence that lifestyle, quality of food and even the emotional state of a woman during pregnancy have a huge impact on the development of the baby.
For example, there is clear evidence that stress during pregnancy disrupts the formation of the structure of the limbic system tracts, which, in turn, is responsible for the emotional reactions of the future person. Scientists have been able to link the use of various medications, including the seemingly harmless paracetamol, with hyperactivity in children, and sugar abuse during pregnancy has affected the cognitive abilities of children.
Newborn brain. What is he like?
The uniqueness of man is that his brain is huge relative to the rest of the body, therefore, to pass through the birth canal, the child is born slightly underdeveloped, and the brain reaches almost full size (about 80%) by the age of three. You probably know about the fontanel, a soft area on the head of a newborn. It is this zone that is responsible for the possibility of a person being born naturally and for that very rapid growth of the child’s brain.
So, a child is born, and in front of him is a huge world and an incredibly complex society in which he needs to learn to live independently as quickly as possible. The baby’s brain is literally designed to learn huge amounts of information, because synapses (nerve cell connections that are the basis of all knowledge and skills) are formed much faster than in adults and even teenagers.
The principle of synapse formation is simple. The more often certain information reaches a child, the more significant the body considers it, the connection strengthens, and skill and memory in this area improves. This way, vital skills (for example, speech and walking) remain with the baby for life, and random events are forgotten with age. The same process is characteristic of the adult brain, but their speed of assimilation of information is significantly lower.
A child's brain craves new information and learns to sort it into important and unimportant categories. That is why it is important for preschoolers to have regular and extensive contact with a diverse environment. Thanks to the balance between various activities (creative and developmental activities, communication with elders and peers, playing alone, being in the city and in nature, outdoors and indoors, and so on), the baby’s harmonious development occurs, because his brain regularly encounters a variety of situations and learns to respond adequately to different stimuli and solve diverse problems.
How does the brain grow?
The structure of the brain changes not only due to synapses. Entire areas of the brain and nerve cells of a newborn are not yet fully formed by the time the baby is born.
Visual cortex
Everyone knows that babies do not acquire keen eyes right away, and when they are born they can barely distinguish the boundaries of objects and colors. This is because cells in the visual cortex develop and learn to recognize images in front of them within the first six months!
It is surprising that even with such an immature vision system (newborns hardly even know how to focus), they are already able to distinguish the most important image - the human face. It is during visual contact with their mother that newborns train their vision and learn to see the world.
The development of the visual organs and areas of the brain responsible for visual information begins with visual contact with the mother. Early development specialists recommend looking at and talking to the baby as much as possible, especially during breastfeeding, because with this simple action you stimulate the baby's development.
Cerebellum
Many people remember from their school biology course that the cerebellum is responsible for the development of movements, and is also involved in memory, attention, speech acquisition, and even the formation of emotions. It is easy to guess that the harmonious development of this most important area of the brain largely depends on the child’s sufficient physical activity. From rolling over and crawling to sports clubs and dance classes, moderate physical activity stimulates the active development of the cerebellum. To understand how necessary movement is for the well-being of a child, it should only be mentioned that the cerebellum increases three times in size only in the first year of a baby’s life.
The cerebellum, which is involved in a huge number of brain processes, develops only under conditions of adequate physical activity. That is why it is important for parents of infants to give their children the opportunity to move, crawl and grab objects around, certainly testing them.
Myelination of neurons
If we imagine that neurons are the wires of the body, then myelination is their high-quality insulation. Coating cell processes with a special substance (myelin) allows the nervous system to transmit signals faster and more accurately. It is because of the incomplete process of myelination that it is more difficult for infants to process information and quickly respond to changes in the environment. For the same reason, they cannot perform subtle and complex actions.
From simple to complex
Solving increasingly complex problems becomes within the capabilities of a young brain thanks to the completion of increasingly complex chains of neurons, as well as the configuration and automation of the joint work of these chains. The rule is simple: the more individual operations a task includes, the later it will become available to the brain. That is why babies first learn to move their legs, and only then can use walking to get to the right place or object.
More detailed information about the children's brain can be obtained from the head of the laboratory of brain and cognitive research, Sergei Kiselyov:
How to create optimal conditions for the harmonious development of a child’s brain?
As you already understand, despite the role of heredity in the development of the nervous system of children, a well-organized environment is much more important. In this section, we would like to pay attention to the main characteristics of a truly developmental environment that has a positive effect on the harmonious development of the child’s brain from birth.
Social environment
The desire to be among other people is inherent in us at the level of instincts, so it is not surprising that for normal development a child simply needs contact with other people. Our brain has undergone many changes precisely thanks to the advent of culture (for example, humans have especially developed frontal lobes, which are responsible for arbitrariness and complex information processing), therefore, for its normal development, a child simply needs communication with his own kind. A wide range of acquaintances and the opportunity to communicate with adults and peers in various conditions stimulates the areas of the brain responsible for the development of speech, self-control and emotional intelligence.
Researchers studying the brains of people who were socially isolated as children have noted that even as adults, their brains react more strongly to stress, are more sensitive to criticism, and are less susceptible to conscious control.
Attending educational activities, evenings with family, joint walks with other families and any other forms of communication are necessary even for the youngest children, because they stimulate the development of the child’s brain, as a result of which his communication and cognitive abilities improve.
Balanced diet
It is important for parents to remember one obvious fact: being an organ of the human body, the brain needs a varied and balanced diet. Even the adult brain is highly dependent on the quality of nutrition, and for the child's brain, a healthy diet is critical. We are talking about both a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals and a balance of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Neurologists are currently actively studying the effects of various types of diets on children’s brain development, but there is already evidence of a connection between increased sugar consumption and cognitive impairment in children, as well as the harmful effects of obesity on the brain function of adolescents.
Many parents go to extremes and, instead of a varied diet, begin to feed their children whole handfuls of vitamin and mineral supplements. Remember that any nutritional supplements and medications should be given to children only after consultation with a doctor and based on test results. A healthy diet, including vegetables, cereals, herbs, animal and vegetable protein, vegetable and animal fats in moderation, as well as the maximum exclusion of unnatural additives and semi-finished products, is quite enough for a healthy diet.
Physical activity
We have already written that physical activity is critical for children’s health. Try to instill in children a love of movement from the first months of life, use gymnastics for babies, allow the baby to crawl and touch different objects, introduce him to different surfaces. A little later, feel free to include physical education sessions, walks in the fresh air, games in children’s playgrounds, dance classes, gymnastics and sports interesting for the baby into your daily routine. Try to be an example for your child and do not reduce your own physical activity!
New experiences are the key to health!
We have written many times that in order to feel stability, develop a sense of time and improve control, a fairly strict daily routine is important for children. However, it is important to understand that the content of the classes must change. Use different types of creative materials, visit different playgrounds and parks, go on visits, invite other families to your place, learn new songs and poems. New information stimulates the formation of connections in the brain: the more positive and varied experiences a child has at an early age, the easier it will be for him to cope with new tasks in adulthood.
In each new task, our brain looks for similarities with its past experience, in this it is similar to search engines on the Internet. Imagine that in childhood, each person develops his own database, and the quality of the search engine depends on its vastness. New experiences broaden a child’s horizons and make him more successful and adaptive at an older age.
Avoid traumatic situations
Undoubtedly, difficulties and disappointments are also necessary for the child, as are positive emotions, but only problems that the child is able to solve on his own or with the help of his parents do not traumatize his psyche. Agree, it’s one thing to catch a baby crying because the shoelaces don’t want to tie themselves, but it’s another thing to calm a child who has prematurely encountered violence, illness or family disadvantage.
Hundreds of studies have shown that the effects of childhood trauma affect entire areas of the brain, disrupting their connections with other areas and interfering with the normal process of processing information, leading to post-traumatic disorders, depression and other disorders.
conclusions
The human brain is the most complex organ of the body; it is not surprising that its development requires more than one year, and the quality of its functioning depends not only on genetic factors, but also on the characteristics of the environment. Understanding the principles of brain development by parents allows them to create an optimal environment for the child.
Conclusion
Brain development is a complex process that is still not fully understood by scientists. However, there is already enough data that allows child development specialists to make their classes as beneficial as possible for kids. Montessori children's teachers and psychologists use only proven methods based on scientific data on child development.
Children attending preschool clubs and various developmental activities has many advantages: the child expands his circle of acquaintances, becomes more independent and confident, gains new life experiences and simply spends time usefully, and parents get several hours of free time, which are so necessary. The specialists of our children's clubs always try to choose the optimal program for children in accordance with the preferences of the family. Come get acquainted with our children's center for a free trial lesson, we will definitely select a suitable schedule for your baby!
The article was prepared by Montessori teacher Oksana Sokolova
How to help children's brains develop properly
What does the harmonious development of a child’s brain depend on?
Answering this question, scientists name a whole range of factors - from the nature of nutrition and the safety of the social environment to diseases suffered in infancy and injuries received.
Of course, the course of pregnancy is also of great importance. Generally speaking, taking care of your child's brain health should begin at the planning stage. It is in order to prevent possible disorders of the brain’s development that doctors prescribe folic acid to expectant mothers (it should be taken before conception and continued after pregnancy) and preventive vaccinations: against influenza, whooping cough, rubella. They also recommend giving up smoking and drinking alcohol.
How does nutrition relate to brain development?
It seems that the postulate about the importance of adequate nutrition for a child has been internalized by all modern parents. But what is behind it? How is nutrition related to the brain? Here's how: it turns out that brain development can be disrupted if a child does not receive the necessary nutrients. As a result, we may experience inadequate development of the sheath of nerve fibers (myelin) and/or insufficient size of the brain itself.
Of course, we remember that intellectual potential depends not only on the size of the brain. But if the size is reduced due to malnutrition, this can lead to a decrease in the child's ability to learn and communicate adequately.
If the supply of nutrients is insufficient, the growth of the brain of the fetus and newborn slows down. And this has long-term consequences: it negatively affects the child’s behavior, including his goodwill. This is how food is related to brain development!
However, do not be alarmed: unless the nursing mother and her baby are in starvation conditions - whether for social reasons or due to some unnatural diet - the likelihood of a deficiency in the infant's brain mass is minimal.
What happens to a baby's brain during and after pregnancy?
How do nutrients get into the fetus during pregnancy? When food enters the stomach of the expectant mother, under the influence of enzymes, food begins to disintegrate into tiny particles, which are absorbed by the intestinal villi and enter the blood of the pregnant woman. Since mother and fetus have a single blood flow, the fetus also receives beneficial substances. That's why it's so important to include seasonal vegetables and fruits, poultry, beef, nuts, and foods containing whole grains in your diet during pregnancy. During pregnancy, add 10-12 extra grams of protein to your daily diet - for example, in the form of low-fat cottage cheese, cheese, lactic acid products - and the proteins will become the “building blocks” for building new cells in the developing body of the fetus.
And if proteins are definitely needed by both the unborn child and the mother, then such an important component of a healthy diet as polyunsaturated fatty acids is needed mainly by the woman during pregnancy. The fact is that during pregnancy they do not have a significant effect on the fetal brain and its future intellectual potential, but they can increase the elasticity of the birth canal, which will be important during childbirth.
How does nutrition affect a baby's brain up to six months?
Try to establish breastfeeding - this is the best way to get all the necessary nutrients for the baby. In addition, in breastfed children, the formation of white matter in the brain occurs more intensively. Perhaps this is facilitated by breast milk lipids - arachidonic (ARA) and docosahexaenoic (DHA) fatty acids. They are actively involved in the early development of the nervous system, the formation of myelin (the main component of the white matter of the brain) and the formation of connections between neurons.
However, if breastfeeding is not possible, there is no need to panic. The baby's (and his brain's!) need for fatty acids can be met with breast milk substitutes. When choosing a mixture, pay attention to those enriched with fatty acids. The more long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids ( look for the labels ARA and DHA on the packaging ) in a child’s diet, the better: they have a beneficial effect on the development of the nervous system and the functions of the entire body as a whole.
What to feed a child so that his brain develops well?
Experts recommend starting to give your baby complementary foods (that is, new types of food other than breast milk and infant formula) when he is six months old. This is important not only because the child needs to grow and gain a healthy weight, but also for brain development: proteins, unsaturated fats, carbohydrates, macro- and microelements - nerve cells use all these components for their functional activity and as building material.
How do you know when it’s time to introduce complementary foods? As a rule, you can start when the baby demonstrates a set of the following skills:
- sits with virtually no support;
- controls head position well;
- shows food interest, that is, he opens his mouth and leans forward when he is offered food.
There are many schemes for introducing complementary foods, but the classic recommendations are as follows: you should start with single-ingredient cereals or vegetables. By seven to eight months, the diet can be diversified: in addition to vegetables and cereals, offer your baby meat (or other proteins), fruits, vegetables, yoghurts, and cheese. Take a closer look at new types of cereals - multi-component ones: they contain a sufficient amount of ingredients that promote brain development.
Despite the fact that fish and greens are not children’s favorite foods, you should still try to accustom your child to them. Not only because it will help expand your menu and establish healthy eating habits. Fish and greens contain folic acid and polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are the physical foundation for the formation of intelligence.
Pay attention to vegetable oil: if the fatty acids from olive oil go directly to the brain cells for their quality work, then the components of sunflower oil may be involved in inflammatory processes that we would like to avoid.
What is a stimulating environment and what does it have to do with children's brains?
The results of many years of research show that in the first year of life, the child’s social environment can also influence the development of the brain. Under its influence, such a property of the brain as neural plasticity is formed - the ability to physically change in response to acquired experience. The more attention and care a child receives, the more integral a person he grows and the better his brain develops. In contrast, lifelong malnutrition and childhood abuse reduce the activity of a gene that protects the brain from the effects of stress hormones.
What needs to be done to create the right environment around the child? Here are its main components:
- parental attention - eye contact and a sense of security contribute to the formation of new connections between brain neurons, which will later be involved in the process of learning and establishing contacts with new people;
- communication with family is the child’s first experience of communication; if it is positive, then the child gets used to generating positive emotions and forms positive emotional intelligence; in turn, the negative emotions that a child experiences if he is shouted at, subjected to emotional and physical violence, make the child withdrawn, closed to new knowledge and the realization of his potential;
- games and communication - the child should have the opportunity to look at pictures and objects, hear a variety of sounds and speech, touch different things; this stimulates various analyzers and involves certain parts of the cerebral cortex in the active functioning.
As you can see, the development of a child’s brain is a complex process that you and I can control by performing the most basic parental actions: feeding, caring, monitoring health and creating a nurturing environment. It's not difficult, but so many benefits! And to understand the issue even better, read the recommendations on the #FoodForMind website.
Find out about foods that are good for your child's brain
Read about the benefits of fatty acids in a child's diet
Learn about the three main components of baby food