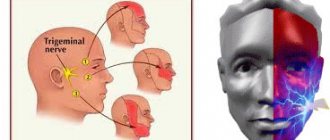
Differences between headaches due to sinusitis and migraines
Their symptoms are very difficult to distinguish. Both with sinusitis and with neurological disease, the pain is characterized as throbbing. When turning or tilting the head, the painful sensation becomes stronger.
The symptoms of these diseases are similar, but they also have differences. Migraine sufferers experience headaches that are aggravated by loud noises. It may be accompanied by vomiting or nausea.
Pain in the head with sinusitis intensifies when turning and tilting the head. However, only a doctor who is well acquainted with the symptoms of these diseases can professionally distinguish the nature of the painful sensations.
Features of headaches with sinusitis:
How to get rid of pain?
To remove pain, it is necessary to eliminate the source that provokes this pain - the accumulation of pus and mucus in the sinuses. As soon as it becomes clear that the disease has moved from the category of a common runny nose to a more serious stage, you should immediately consult a doctor. He will conduct an examination and prescribe medications to quickly relieve symptoms, and a course of physiotherapy. In extremely severe cases, a puncture is made to remove the contents of the sinuses.
You should not prescribe medicine on your own or try to solve the problem using “grandmother’s” methods. Sinusitis is a serious disease that is fraught with dangerous consequences for the body.
Causes of sinusitis
Most often, sinusitis is a complication of acute inflammation in the nasal cavity. Such inflammation can be caused by any infection - viral (ARVI, influenza), bacterial, fungal. Any acute respiratory disease (ARI), expressed in a common runny nose, can lead to sinusitis. When you have a runny nose, the amount of secretion produced by the glands of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity sharply increases, as a result of which the mucous membrane swells, blocking the outlet openings of the sinuses.
Factors contributing to the transition of inflammation to the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses are:
- curvature of the nasal septum and structural features of the nasal passages that prevent the natural cleansing of the paranasal sinuses;
- long-term inflammation in the nasal cavity. This is typical for chronic runny nose (allergic or vasomotor rhinitis);
- blowing your nose. When you blow your nose, purulent secretions from the nasal cavity enter the sinuses, causing inflammation there.
Infection in the paranasal sinuses can also come from other foci of inflammation, for example, from the tonsils (in the case of chronic tonsillitis). In the case of inflammatory diseases of the teeth of the upper jaw (pulpitis, periodontitis), the infection can penetrate into the sinus from the area of the tooth root. Sinusitis of this origin is called odontogenic
.
The development of sinusitis is promoted by general and local hypothermia. Decreased immunity is also a factor favoring the disease. Problems with the immune system, resulting in a tendency to allergic reactions, increase the likelihood of sinusitis.
Treatment methods for sinusitis
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy in combination with drug treatment allows you to quickly and painlessly get rid of an unpleasant illness.
- UHF.
Effectively relieves pain, restores sinus tissue, and also helps improve local immunity. It consists in the effect of an electromagnetic field on the body. This procedure has several contraindications:
- cardiovascular diseases;
- presence of tumors;
- low pressure.
- The procedure is recommended for the treatment of young children and pregnant women. On average, the course of treatment is 12-15 days.
. The principle of action is that medications penetrate deep into the sinuses. The procedure is carried out as follows: a tampon with medicine is inserted into the lower nasal entrance. It is closed using an electrode, the second electrode is placed on the back of the head. The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes. The course of treatment is 10-15 days.
. The procedure is a targeted effect of a magnetic field on inflamed tissue. Effectively relieves inflammation and headaches, reduces swelling of the nasal mucosa. On average, about 10-12 procedures are required. Before performing it, rinse the nose with saline.
. This is a modern procedure that is not only highly effective, but also high in cost. When exposed to a laser, special electrodes are inserted into the maxillary sinuses, which reduce swelling and also strengthen the immune system. As a result, blood microcirculation improves and pathogenic microflora is destroyed. Laser therapy is prohibited for malignant tumors.
. Ultraviolet radiation is one of the most common procedures. It involves heating the affected areas with a special lamp. The duration of the procedure is 5-7 minutes. It is contraindicated in patients with high body temperature, as well as those who suffer from increased sensitivity to radiation or suffer from cancer. It is not recommended to perform ultraviolet radiation on patients who have poor blood clotting.
. When treating chronic as well as acute forms of the disease, ultrasound is used, which penetrates to a depth of 4 centimeters. The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes. Benefits: the contents of the sinuses flow out, the nasal cavity is cleared, and the immune system is strengthened.
. Treatment with infrared radiation has a beneficial effect on patients: both adults and children. The benefits of the procedure include relieving swelling, reducing inflammation and dilating blood vessels.
Puncture
Treatment of an advanced form of purulent sinusitis is carried out using a puncture. The procedure consists of piercing the wall of the sinus with a special needle in order to remove purulent contents from the sinus and also introduce medications into it.
Many patients tolerate the procedure easily. Qualified doctors are fluent in it, so they carry it out quickly and painlessly. Moreover, the effect is noticeable immediately: pain and heaviness go away, and breathing also improves.
The procedure is carried out as follows:
- Anesthesia
of the nasal mucosa. - Piercing the sinus wall
with a special needle. - Removing fluid
with a syringe, as well as rinsing with medications
The puncture is performed in rare cases. For this procedure, the patient must have the following symptoms:
- serious condition (high fever and severe weakness);
- unbearable headache, pulsation in the maxillary sinus area.
A puncture is also prescribed in cases where the infection needs to be cured as soon as possible. For example, during pregnancy.
Drug treatment
When prescribing medications, the ENT doctor takes into account the severity of the disease, as well as the causative agent that caused it.
For sinusitis, medications for various purposes are prescribed to affect a specific symptom of the disease:
- Antibacterial drugs.
Their main task is to destroy the infection, as well as relieve inflammation. - Corticosteroid drugs.
They have an anti-inflammatory effect. - Analgesics
. These medications relieve headaches. - Vasoconstrictor drugs
. Relieves swelling and a feeling of “fullness” in the nose. - Preparations for rinsing the nose.
Important
! Only a doctor should prescribe and prescribe medications for sinusitis. After all, most medications have many contraindications.
When complications develop, injectable antibiotics are used.
In the initial stages of the disease, when the nasal cavity is congested, special nasal drops are used that relieve swelling and ensure free breathing - vasoconstrictor drugs.
Medicines based on sea water not only wash, moisturize and cleanse the mucous membranes of crusts, but also prevent the appearance of mucus and pus. Such drugs include Sialor Aqua.
Sinusitis
Cold
Allergy
Fungus
21942 May 25
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Sinusitis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity. Sinusitis is one of the most common diseases and, although there are no exact statistics on its prevalence, according to various sources, up to 15% of the adult population worldwide suffers from this pathology, and in children it is even more common.
The nose is the initial part of the upper respiratory tract. It is divided into three sections: the external nose, the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses (SNS). OPN are air cavities that are located around the nasal cavity and communicate with it through excretory openings, or ducts. There are four pairs of sinuses: maxillary, frontal, ethmoidal labyrinth and sphenoid sinuses. The largest sinus - the maxillary, or maxillary - is located in the body of the upper jaw, the frontal sinus is in the thickness of the frontal bone, the ethmoid labyrinth is numerous cells in the ethmoid bone, and the sphenoid sinus is located in the body of the bone of the same name.
Causes of sinusitis
The main cause of acute sinusitis is infection. In 90-98% of cases, sinusitis is caused by viruses, in 2-10% of cases - by bacteria. In addition, sinusitis can be fungal in nature, or be the result of exposure to allergens or irritants (substances with an irritating effect).
Secondary bacterial infection of acute renal failure after a viral illness affecting the upper respiratory tract develops in 0.5–2% of adults and 5% of children.
Typically, acute sinusitis is observed against the background of an acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI), most often caused by rhinoviruses. According to research, almost 90% of patients with acute respiratory viral infection showed changes in the form of swelling of the mucous membrane of the acute respiratory tract according to magnetic resonance imaging, which confirms that sinusitis is one of the typical manifestations of acute respiratory viral infection.
Among bacteria, acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of acute renal failure is most often caused by pneumococcus and Haemophilus influenzae. In addition, so-called atypical pathogens - chlamydia and mycoplasma (about 10%) - are increasingly being discovered in both adults and children.
There is no single theory why chronic sinusitis develops. Predisposing factors include a large number of conditions and diseases, including anatomical abnormalities in the structure of the nasal cavity and acute renal failure (for example, deviated nasal septum), chronic rhinitis, atopy (hereditary predisposition of the immune system to an inadequate response to common allergens in the environment), intolerance to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs drugs, immunodeficiency conditions, etc.
Sinusitis can also occur as a result of aero- and barotrauma, gunshot and mechanical injuries (traumatic sinusitis) or in the presence of a focus of acute or chronic inflammation in the oral cavity (odontogenic sinusitis). In odontogenic maxillary sinusitis, the main role is played by the presence of communication of acute renal failure with the oral cavity after the removal of the teeth of the upper jaw and the entry of fragments of foreign material into the sinus during the filling of the canals of these teeth, as well as chronic inflammation of the structures of the upper teeth (pulpitis) and periodontal disease.
Classification of the disease
Sinusitis is classified depending on the causative factor (traumatic, viral, bacterial, fungal, mixed, allergic) and depending on the severity of the process (acute and chronic).
In addition, sinusitis is divided into exudative (serous, catarrhal, purulent) and productive (parietal hyperplastic and polypous).
Depending on which sinuses are affected, there are:
- sinusitis (sinusitis of the maxillary sinus) - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus;
- frontal sinusitis (sinusitis of the frontal sinus) - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the frontal sinus;
- ethmoiditis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth;
- sphenoiditis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sphenoid sinus.
If all sinuses of one half of the nasal cavity are involved in the inflammatory process, the disease is called hemisinusitis, and both halves are called pansinusitis.
Symptoms of sinusitis
The main symptoms of sinusitis are persistent nasal discharge, difficulty nasal breathing, headache or pain in the projection of acute renal failure, decreased sense of smell, stuffy ears, general malaise and cough, fever.
Headache is one of the leading symptoms of acute sinusitis; it occurs due to the effect of the inflammatory process on the membranes of the brain. The pain is localized in the area of the bridge of the nose and eyebrows, and can radiate to the upper jaw. Sphenoiditis is characterized by pain in the crown and back of the head (“casque-like” pain); it is usually diffuse in nature, but with more severe inflammation in one of the sinuses it can be local.
Nasal breathing disturbance can be periodic or constant, unilateral or bilateral. With unilateral sinusitis, difficulty in nasal breathing usually corresponds to the affected side.
Discharge from the nasal cavity can be mucous, mucopurulent, purulent and come away when you blow your nose, or flow down the back wall of the pharynx. With a severe acute process, the intensity of these symptoms usually increases - signs of general intoxication are added. In some cases, reactive swelling of the eyelids and complications in the orbit (especially in children) and swelling of the soft tissues of the face develop.
In children, acute sinusitis is often combined with hypertrophy and chronic inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsil and can manifest itself with nonspecific symptoms - persistent cough and enlarged cervical lymph nodes.
According to the severity of the course, acute sinusitis is divided into mild, moderate and severe.
In mild cases, the temperature does not rise, and nasal congestion, nasal discharge and cough are moderate. Symptoms do not affect the patient’s quality of life (sleep, daily activity) or have a slight effect.
In mild cases, there is no headache in the projection of the paranasal sinuses, and the disease resolves without complications.
Moderate severity of sinusitis is characterized by elevated temperature, but it does not exceed 38°C. Nasal congestion, nasal discharge and cough are severe and affect the patient's quality of life. In the projection of the paranasal sinuses, when the head moves and when the head is tilted, a feeling of heaviness arises. A complication of the middle ear may develop - acute otitis media.
Severe sinusitis is characterized by a body temperature above 38°C. Nasal congestion, nasal discharge and cough are severe, can be distressing, and have a moderate or significant impact on quality of life. Periodic or constant pain occurs in the projection of the paranasal sinuses, which intensifies with movement or tilting of the head, with percussion (tapping) in the projection of the paranasal sinus. Intracranial and orbital complications (orbital complications) may occur.
Diagnosis of sinusitis
To make a diagnosis of sinusitis, the patient must have two or more symptoms: difficulty breathing or nasal discharge, pressure or pain in the area of acute respiratory failure, decreased or loss of smell, as well as rhinoscopic or endoscopic signs (mucopurulent discharge mainly in the middle nasal cavity). course and/or swelling or mucous obstruction predominantly in the middle meatus). If these symptoms are observed for less than 12 weeks, then sinusitis is defined as acute, if more - as chronic.
A general clinical examination may be recommended for all patients with suspected sinusitis, including:
- general blood analysis;
Complications
Many patients do not seek medical help for sinusitis in a timely manner. Unfortunately, the complications of this disease are serious. For example, with purulent sinusitis, complications are possible, including those affecting the brain.
What might patients encounter?
- Orbital complications.
There is a sharp increase in temperature and severe pain. - Intracranial complications.
- Mucocele
. A cyst-like formation forms inside the sinus, which prevents the movement of air and mucus. - Pneumocele
. This is a formation similar in size to a tumor.
To prevent complications from occurring, you need to contact an ENT doctor in time and not self-medicate!
Diagnosis of sinusitis using modern techniques
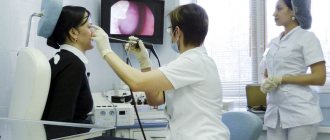
To confirm the diagnosis of sinusitis, the following types of examination are used:
- Video endoscopy of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx to identify features of the anatomical structure and determine predisposing factors for the development of sinusitis;
- radiography of the paranasal sinuses;
- Ultrasound examination of the paranasal sinuses is a safe method with no contraindications, used to diagnose sinusitis and monitor the treatment process;
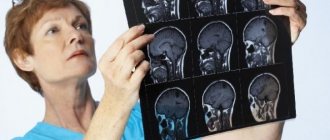
- CT, MRI - according to indications;
- laboratory diagnostics according to indications in full.
Prevention and precautions
To always feel in good shape and not encounter this unpleasant disease, you must follow several recommendations from doctors:
- In winter, be sure to wear a hat.
- Do exercises every morning.
- Ventilate the apartment at any time of the year.
- For prevention, rinse your nose with preparations based on sea water.
The danger of sinusitis is that its symptoms are very similar to those of a common runny nose. If proper measures are not taken, the disease develops into chronic sinusitis. That is why it is important not to self-medicate, but to immediately consult a doctor.