Hyperventilation syndrome (increased breathing) is one of the common manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia. It occurs as a result of dysfunctions in the central nervous system due to various reasons. It manifests itself as a whole group of symptoms, including respiratory, autonomic, mental, vascular, pain and muscle manifestations. The result of the changes is abnormal breathing and increased pulmonary ventilation. Requires complex treatment, first of all, regulation of processes in the central nervous system. From this article you can learn about the causes, symptoms and methods of treating hyperventilation syndrome.
General information
Hyperventilation syndrome is one of the types of disorders of the autonomic nervous system, which is manifested by difficulty breathing.
The pathology is quite common and is diagnosed in approximately 15% of the population. Hyperventilation syndrome is in no way associated with diseases of the pulmonary system, bronchi or heart. The feeling of lack of air occurs solely against the background of disruption of the autonomic nervous system , which is responsible for the vital processes of the body that are beyond the control of our consciousness.
A person can control the frequency and depth of breathing only for a certain time. Breathing can be deep and shallow, rare and frequent, with or without delay.
The pathology occurs in people of various age groups, but the peak incidence is recorded in people 30-40 years old. Females among patients are 4-5 times more common than males. The syndrome is characterized by a predominantly chronic course, with acute cases accounting for only 2% of calls.
How does respiratory distress manifest in hyperventilation syndrome?
Breathing is influenced by both the autonomic and somatic nervous systems. That is, it is in close relationship with a person’s emotional background, and if the emotional state turns out to be unstable, breathing disorder occurs. In a person, this process may become more frequent or, on the contrary, slow down, and so-called “failures” of breathing may occur. Most often, respiratory distress is expressed by:
- a constant or occasional feeling of lack of air;
- it seems to the patient that he cannot take a deep breath or that air cannot pass into the lungs;
- the attack is accompanied by a feeling of difficulty breathing;
- it is accompanied by a dry, obsessive cough, sniffling, yawning, and frequent sighs.
Pathogenesis
The psycho-emotional state of a person quite strongly influences the functioning of the respiratory system. Various psychogenic triggers (for example, anxiety) lead to biochemical shifts that affect the balance of calcium and magnesium. The development of hyperventilation is potentiated by changes in the functioning of respiratory enzymes.
Due to excessive release of carbon dioxide, its concentration in the blood decreases, which leads to a shift in pH to the alkaline side, hypocapnia and the development of respiratory alkalosis . Against the background of the changes described above, specific symptoms appear:
- tetany;
- algic disorders;
- disturbances of consciousness;
- autonomic and sensory disorders.
The result is increased anxiety, which supports hyperventilation. Even after eliminating the provoking etiological factor, the vicious circle continues to exist and negatively affect the patient’s health.
What is hyperventilation: causes, symptoms and treatment
Hyperventilation is breathing excessively fast and deeply, which many people have probably already experienced.
Movies depict hyperventilation as a popular way to show people under severe mental stress: the sufferers suddenly begin to breathe faster and deeper, turn chalky white, and finally someone bursts in with a plastic bag into which the unfortunates must exhale and inhale.
In fact, acute mental stress can lead to acute hyperventilation, but the symptom can also be chronic. And it's not always the fault of the psyche. Read on for all the important information about "hyperventilating" and why a plastic bag is perfectly legal in many cases.
Hyperventilation: description
The term hyperventilation describes excessive ("hyper") ventilation of the lungs. It sounds strange at first, but this can happen with rapid and deep breathing .
As a result, the so-called partial pressure of carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) in the lungs and in the circulating blood decreases, which in turn shifts the pH of the blood into the alkaline (basic) range.
Hyperventilation has nothing to do with the normal acceleration of breathing during physical activity.
In fact, a decrease in CO2 partial pressure automatically triggers an unconscious reflex to reduce respiratory activity, but hyperventilation disrupts this loop. All this in more detail:
The lungs are responsible for vital gas exchange in the blood. It supplies it with fresh oxygen and, in turn, CO 2 produced by cellular respiration, which is released through the lungs.
When you hyperventilate, your breathing becomes faster, but at the same time your breathing becomes deeper. Since during normal breathing the blood is already almost 100 percent saturated with oxygen, hyperventilation does not cause additional oxygenation of the body.
However, the concentration of CO 2 in the blood decreases more and more, which has far-reaching consequences.
Under normal circumstances, the resulting CO 2 dissolves in the blood and binds there as carbon dioxide . As the name suggests, this in turn has an acidifying effect on the pH levels in the blood.
As the CO 2 content and therefore the carbon dioxide content decreases, the blood becomes alkalinized, so the pH , which should be around 7.4, thus increases.
The condition created in this way is called “respiratory alkalosis.”
Hyperventilation and the brain
The human body is equipped with a number of protective functions and reflex mechanisms, which are usually very significant and do their job well. However, under certain circumstances, such a reflex mechanism may also be disadvantageous. This is also true in the case of hyperventilation in relation to cerebral blood flow.
If the concentration of CO 2 in the blood is increased, this is usually accompanied by a decrease in oxygen content. Special receptors in the paired carotid artery and aorta (main artery) are able to measure the level of CO 2 in the blood and report this to the brain, where the signal is processed.
Classification
Pathological types of breathing:
- terminal;
- periodic;
- dissociated.
Types of periodic breathing:
- Biota;
- Cheyne-Stokes;
- wavy.
Periodic breathing is characterized by alternation of respiratory movements and pauses in the form of apnea . The pathology occurs against the background of a disorder of the automatic respiratory control system.
Terminal breathing types include:
- gasping breath;
- apnestic breathing;
- Kussmaul's breath.
Pathological terminal types of breathing are accompanied by gross disturbances of rhythmogenesis. Kussmaul breathing is characterized by a deep inhalation followed by an extended, forced exhalation. Kussmaul is described as deep and noisy breathing, which is recorded in unconscious patients due to uremic, diabetic or hepatic coma. Kussmaul breathing is triggered due to a pathology of excitability of the respiratory center in individuals with cerebral hypoxia , metabolic acidosis and toxic phenomena .
Dissociated breathing is characterized by:
- asymmetry of the right and left halves of the chest;
- paradoxical movements of the diaphragm.
Da Costa syndrome is named after the monk and is manifested by a paroxysmal increase in pulmonary ventilation, which is accompanied by changes in consciousness, pain, sensitivity, muscle-tonic and autonomic disorders. Da Costa syndrome occurs after psychological trauma in the form of acute and chronic stress.
Normalization of breathing during an attack
Normalization of breathing during hyperventilation syndrome
To prevent disruption of pulmonary ventilation during stressful situations, special exercises will help that will bring the respiratory system to a state of rest.
The first thing to do is lie on your back and place one hand on your chest and the other on your stomach (left and right don't matter). Bend your knees and pull them towards your chest. This reduces the amount of air the lungs receive because it prevents the diaphragm from actively moving.
In this position, you need to make measured breathing movements, counting to 4 while inhaling and exhaling. At the same time, it is important to constantly monitor the work of the abdominal muscles, chest and diaphragm, so that as much oxygen enters the lungs as necessary, but not more.
Causes
Hyperventilation syndrome occurs due to the combination of the respiratory regulation system. During periods of stress, or when the patient is overtired or afraid, the depth and rhythm of breathing movements changes involuntarily, which leads to a feeling of lack of air. This is what provokes panic attacks , which further aggravate the course of hyperventilation syndrome.
Also, increased suspiciousness or the patient’s exposure to outside influences can lead to pathological breathing. For example, an attack of suffocation may occur after a person has seen an attack of bronchial asthma in another patient. This event can be recorded in memory and even after a few years lead to the formation of hyperventilation syndrome.
Etiological factors:
- Organic. These include various lesions of the central nervous system (dyscirculatory encephalopathy , hydrocephalus , arachnoiditis ), as well as diseases of internal organs (recurrent bronchitis , arterial hypertension , diabetes mellitus ). The influence of only organic factors occurs in 5% of patients with hyperventilation syndrome.
- Psychogenic. They are provoked by mental disorders ( neurasthenia , depression , anxiety or phobic disorders, and extremely rarely – hysterical neurosis ). Pathology can develop against the background of acute and chronic stressful situations. In some cases, the syndrome develops as a result of psychogenic behavior in childhood, when the child witnessed an episode of suffocation of a drowning person or asphyxia .
- Mixed. In these cases, the psychogenic trigger is triggered in response to organic pathology. Occurs in 35% of cases.
Hyperventilation syndrome can also be triggered by taking certain medications (methyl xanthine derivatives, salicylates, beta-agonists, progesterone ).
Hyperventilation in diving[edit | edit code]
Controlled hyperventilation
Effective use of the lungs is of paramount importance in diving. To increase the supply of respiratory gas before diving, controlled hyperventilation is used - the diver takes several deep and quick breaths (in no case allowing hypocapnia) and dives while inhaling. Excessive hyperventilation before a dive can lead to loss of consciousness at shallow depths (and thus become uncontrollable).
Uncontrolled hyperventilation
Uncontrolled hyperventilation can occur due to any physical activity and leads to unwanted brain hypoxia. So, this can happen when running or cycling, but it is especially dangerous during intense swimming, since in the latter case loss of consciousness will lead to drowning.
Prevention of loss of consciousness during hyperventilation
For most healthy people, the first signs of hypoxia are pre-fainting or unconsciousness, a state of anxiety, and a lack of bodily sensations, which due to inexperience may be noticed too late. But if symptoms are detected in a timely manner, it is enough to stop swimming on the surface of the water, turn over on your back and hold your breath while inhaling until carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood and brain tissue.
Symptoms of hyperventilation syndrome
The disease is characterized by polymorphism and a multiplicity of symptoms. However, it is customary to distinguish a typical triad in the clinical picture of HVS:
- emotional disturbances;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- muscle-tonic phenomena.
There are 4 forms of breathing disorder:
- Empty breath is a subjective feeling of lack of air, which encourages the patient to breathe more often and deeper.
- Labored breathing. Patients describe the condition as “a lump in the throat”, “stiffness when inhaling.” It takes some effort to take a full breath. Accessory muscles take part in the act of breathing, and arrhythmic increased breathing is recorded.
- Respiratory automaticity disorder. It seems to the patient that breathing stops, which encourages him to independently control the breathing process and correct it.
- The use of hyperventilation equivalents (coughing, yawning, deep sighs, sniffling).
Psycho-emotional disorders are manifested by feelings of fear and anxiety. The most commonly reported disorder is generalized anxiety disorder . Patients complain of loss of the ability to relax on their own, note increased anxiety and constant nervous tension. Quite often, fear of public places (social phobia) and open spaces (agoraphobia), aggravated by respiratory disorders, is detected.
Muscular-tonic syndrome develops due to changes in the electrolyte composition of the blood, which is responsible for neuromuscular excitability. Patients complain of " paresthesia ", which is manifested by burning, numbness, tingling and a crawling sensation. Tetanic phenomena also appear in the form of muscle spasms and tonic convulsions in the distal limbs. Carpopedal spasm is extremely rarely recorded.
Classic symptoms of hyperventilation:
- cardialgia;
- headache;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- dyspepsia;
- confusion;
- cardiopalmus;
- syncope.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of the disease may appear spontaneously. In some cases, a person needs immediate help. Rapid breathing is accompanied by:
- deep breathing;
- dizziness;
- dry mouth;
- tingling in the limbs;
- pain in the heart area;
- panic attacks;
- loss of consciousness.
The symptoms that appear should not be ignored. There remains a high probability of developing severe disorders throughout the body. If the person is conscious, laboratory tests must be performed. Symptoms alone will not help determine the pathology; you need to study the level of hemoglobin, the ratio of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Similar attacks can occur repeatedly. In some cases, they go away on their own, without any special consequences for the body. Sometimes the symptoms are so pronounced that it is impossible to cope with them on your own. If the person's condition is serious, it is necessary to call an ambulance. Respiratory system disorders can affect overall well-being.
You can cope with controlled hyperventilation; an uncontrolled process is especially dangerous and can threaten a person’s life.
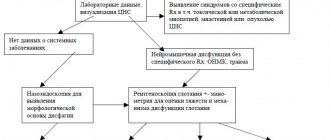
Tests and diagnostics
In addition to instrumental diagnostic methods, the most important components when examining a patient are a thorough examination and a detailed history taking. Hyperventilation syndrome is always accompanied by a huge number of complaints about the functioning of organs and systems. The final diagnosis can be made only after the examinations show the absence of organic pathology. It is for this purpose that patients are prescribed spirography, echocardiography, ECG, and ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
When you first interview a patient, you can easily identify high emotional tension or a certain amount of anxiety. If a positive result is obtained from a psychogenic test, the doctor may immediately suspect hyperventilation syndrome.
Also, to identify pathology, the patient is recommended to breathe frequently and deeply for 5 minutes. Specific symptoms will appear immediately if the patient actually suffers from HVS. There is also a unique questionnaire that allows you to easily diagnose pathology in 9 out of 10 patients.
The diagnosis cannot be made only based on the results of additional research methods or on the basis of one specific symptom. It is important to remember that disturbances in the respiratory system may also indicate other more serious diseases ( bronchial asthma , heart failure , etc.). Only thanks to the individual approach of the attending physician in combination with modern diagnostic methods can the only correct diagnosis be established.
How to diagnose?
Pulmonary hyperventilation syndrome is very difficult to diagnose; it is arrived at by the method of exceptions, since the symptoms are very similar to other diseases. Most often, the patient needs to undergo a number of examinations.
But the most effective method for making a diagnosis is capnography. The equipment calculates the concentration of carbon dioxide in exhaled air. If the indicators are normal, the occurrence of breathing problems is considered accidental. Otherwise, respiratory neurosis is diagnosed.
Also, to more accurately determine the manifestation of symptoms, a special questionnaire is used. The table lists all the symptoms of dysfunctional breathing, and the patient must mark the degree of manifestation of each indicator according to points.
Treatment of hyperventilation syndrome
Therapy for hyperventilation syndrome should take an integrated approach and combine both pharmacotherapy and non-drug methods. It is important for the attending doctor to conduct explanatory conversations about the reasons for the occurrence of violations. It is necessary to show the patient the connection between the emotional component and somatic symptoms, to convince the patient of the absence of organic pathology. Treatment consists of several areas:
- Psychotherapy. When psychogenicity is detected in childhood, psychoanalysis sessions are required. Psychoanalytic and cognitive-behavioral techniques are also effective.
- Formation of correct breathing. Regular breathing exercises have a positive effect on the course of the disease. Auxiliary methods include courses on relaxation and relaxation techniques. It is necessary to teach the patient the technique of breathing into a bag to relieve a hyperventilation crisis.
- Biofeedback therapy. Special equipment allows not only to obtain objective information about the respiratory system, but also to teach the patient how to breathe correctly.
- Drug treatment of mental spheres.
- Elimination of electrolyte disturbances. Taking magnesium and calcium with the drug can not only reduce the tendency to tetany, but also have an anticonvulsant, calming effect.
Complex treatment is carried out over 4-6 months. Regular monitoring of the patient is recommended to prevent relapses.
Breathing exercises
There is another good exercise to prevent hyperventilation. It should not be done at the time of an attack, but should be practiced in advance if there is a tendency to respiratory disorders. Exercise will not only help to avoid hyperventilation, but will also improve the functioning of the lungs and respiratory system as a whole. You need to exercise daily.
Performance:
Breathing exercises for the syndrome
- lying on your back, close your eyes and relax for 5 minutes, trying to feel warmth and lightness in your body;
- take a deep, slow breath, protruding the abdominal wall as much as possible (at this time the lower sections of the lungs will fill);
- then gradually raise the chest;
- Now you need to exhale smoothly, first lowering your stomach and then your chest.
It is important to count in your mind the time of inhalation (4 seconds) and exhalation (8 seconds). To avoid stretching of the lung tissue, you need to inhale not 100% of the possible, but 90%. If, while doing the exercise, a person notices shortness of breath, dizziness, anxiety, then it is necessary to shorten the inhalation (3 sec.) and exhalation (6 sec.).
At first, you need to repeat this exercise 10–15 times, after a month begin to gradually increase their number to 50 (1 every 3–5 days). The duration of inhalation and exhalation should also be increased strictly in the proportion of 1:2 (for example, 5 seconds for inhalation and 10 for exhalation or 10:20). It is important to remember that without the help of a specialist it is better not to make the breathing cycle too long (more than 1 minute). When breathing exercises are performed correctly, a feeling of peace and comfort appears in the body. Alcohol, cigarettes and psychotropic drugs are prohibited while mastering respiratory exercises.
Alcohol and cigarettes are prohibited while mastering respiratory exercises
Medicines
For the purpose of drug correction of mental areas, the use of antidepressants with a pronounced anxiolytic effect ( Amitriptyline , Fluvoxamine ) is indicated.
Also, patients with hyperventilation syndrome are prescribed antipsychotics, tranquilizers and sedatives. During a crisis, taking benzodiazepine drugs ( Diazepam ) is indicated. When the vegetative component is strongly expressed, vegetotropic medications are prescribed.
Symptoms of increased alveolar ventilation
During an attack, the following occur:
- difficulty breathing;
- spasm of blood vessels, muscle tremors, feeling of cold;
- tachycardia - rapid heartbeat;
- dizziness;
- feeling of lack of air when breathing;
- pain behind the sternum;
- loss of balance and inability to control the body;
- feeling of mild nausea;
- perspiration, increased sweating;
- tingling, pins and needles sensation, feeling of tightness in the limbs;
- Derealization is a short-term feeling of unreality of what is happening around.
Often, during the precursors of an attack, other disorders occur:
- aching pain in the abdominal cavity;
- excess pressure in the human arterial system;
- intestinal disorders;
- a sharp drop in blood flow intensity;
- legs give way;
- severe weakness in the body, muscles;
- slight increase in temperature;
- spontaneous muscle contractions;
- feeling of impending blackout.
Prognosis and prevention
Hyperventilation syndrome does not threaten the patient’s life, but significantly reduces its quality. In the absence of timely and competent treatment, the symptoms worsen and a vicious circle occurs. In the future, the influence of trigger factors may resume and provoke a relapse.
To prevent hyperventilation syndrome, it is necessary to promptly correct emerging psychological problems, learn to adequately respond to stressful situations and form an optimistic, friendly outlook on life.
What to do during an attack
The following actions will help alleviate the condition during an attack of hyperventilation and prevent serious consequences:
During an attack of hyperventilation, do not panic
- feeling an attack approaching, sit up straight, close your eyes and calm down;
- even if you feel a lack of air in your lungs, do not inhale deeply;
- breathe only through your nose, closing one nostril at a time to reduce the amount of oxygen entering the lungs;
- if you still breathe through your mouth, you need to clench your teeth tightly;
- Make sure that at the moment of inhalation the peritoneum works, and not the chest.
List of sources
- N.V. Daragan, S.Yu. Chikina “Hyperventilation syndrome in the practice of a pulmonologist: pathogenesis, clinical picture, diagnosis”, article in the journal “Pulmonology” No. 5, 2011
- Kovalenko T.G. “Hyperventilation syndrome. A new look at the problem", Electronic collection of scientific works "Health and education in the 21st century" No. 7, 2011
- Shchekotov V.V., Barlamov P.N., Urban P.I. “Hyperventilation as a risk factor for endothelial dysfunction in patients with hypertension,” Medical Almanac No. 3, 2011
When should you see a doctor?
For physical causes, hyperventilation is often chronic and can lead to other symptoms such as swallowing air with flatulence , frequent urination , heart problems and seizures due to absolute calcium deficiency and severe headaches . Therefore, the causes of hyperventilation must be found and eliminated, so in any case you should consult a doctor.
In contrast, psychogenic hyperventilation is usually acute, and symptoms quickly subside once the person has calmed down a bit and their breathing has returned to normal. However, visiting a doctor is also advisable since hyperventilation, especially in cases of increased illness, can seriously affect the exact cause of the disease. If necessary, you can call a psychologist.
Indications for treatment
The main indication is a clinically confirmed diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia. Since VSD is a syndrome, the indications for its therapy correspond to disorders of various etiologies: vascular, psychological, neurological, cardiological and many others.
If your professional responsibilities involve high mental and emotional stress, stressful situations, overwork, or if you have a hereditary predisposition to VSD, sign up for a consultation with a specialist. Timely prevention will help avoid worsening problems, because the disease is easier to prevent than to treat.