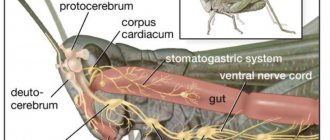
Emotional lability is instability of mood. It occurs after shocks, experiences and other significant events. This phenomenon is characterized by certain symptoms, signs and treatments.
Human emotional lability is a pathology that is important to monitor and treat. An advanced stage can provoke the formation of more serious diseases.
The word “lability” itself means mobility and instability. Simply put, the emotions of a particular person are changeable, rushing from one extreme to another, irritating not only the nervous system, but also. In physiology, the term is used to denote the mobility of cells and tissues, their response to a stimulus.
In psychiatry and psychology, emotional lability is the property of the psyche to respond with inadequately expressed affect to an external event. For example, a person with a healthy psyche will calmly react to spilled coffee, but an “unhealthy” person may become very angry.
Increased emotional lability indicates a central manifestation of the disease, personality disorder, and is also a symptom of vascular diseases of the brain and endocrine diseases. Experts note that older people and children are most susceptible to this phenomenon.
Emotional lability syndrome in children is associated with knowledge of the world. Children under 5 years old actively explore everything around them: from the sand under their feet to the contents of upholstered furniture. Their reaction may be inappropriately strong to unexpected “research” results. For example, a soft and fluffy cat suddenly bit or released its claws. For an adult, this situation will be normal, but a child will get scared and start screaming. In this case, increased lability does not indicate pathologies and disorders.
For adults with a healthy psyche, increased emotional lability is not typical. Its signs indicate disorders in the body. The most common cause of pathology is stress.
Inappropriate expression of emotions is typical for many people. Increased emotional lability, which manifests itself regularly, requires specialist intervention and correction. Unfortunately, people often ignore such problems and prefer to call the disease special.
Unstable emotionality can flare up suddenly, be expressed in an inadequate attitude towards certain events and disappear just as suddenly. Short-term stress has this effect on the nervous system. However, similar cases do not signal serious mental health problems.
Emotional expression disorder is formed due to the following reasons:
- prolonged stress;
- a situation that traumatizes the psyche;
- endocrine imbalance;
- vascular and neurological diseases;
- mental disorders.
Prolonged stress is the most common cause of increased emotional lability. In critical conditions, the body experiences difficulties with an adequate assessment of the situation, which results in intolerance to certain events.
A situation that traumatizes the psyche can knock any person out of his usual way of life. This could be the death of a loved one, a sudden change of place of residence, or failure in your personal life. Any event that is important for a specific person.
Endocrine imbalances, mental disorders, vascular and neurological diseases are problems in the body that require treatment. Pronounced emotional lability indicates that it is time to see a doctor and check your health.
The concept of what emotional lability in adults is consists of a definition and symptoms. Timely identification of signs of the disease will allow you to solve problems at an early stage of development and avoid major difficulties in the future.
Emotional lability: what is it in adults? Pathology is accompanied by symptoms that can be used to determine the presence of problems. The very definition of the term suggests that the symptoms express emotional instability. This manifests itself in an inadequate reaction to familiar events.
Most often, people with the syndrome react sensitively to touching films and emotional conversations, small children and animals. They often cry, but they themselves cannot explain why. Yes, kittens and puppies are cute, but not to the point of tears.
Aggression and self-aggression also take place. In most cases, they flare up sharply and subside just as abruptly. This symptom is considered a defensive reaction when people try to hide their problems. An unobtrusive question about your well-being or mood can lead to inappropriate shouting and attempts to avoid answering.
Frequent mood swings are a clear symptom. A person can enthusiastically play a game for 20 minutes, and a minute later decide that it is all nonsense and a waste of time. He may study the cinema's repertoire with interest and plan to attend a show, and later give up and burst into tears.
The next symptom is expressed in passion for the task. For example, a constant and rapid loss of interest indicates emotional lability. Immersion in the study of the history of Ancient China, a quick change of this hobby to cross-stitching, and then to football - all these are symptoms of pathology.
Let us highlight the main symptoms of emotional lability syndrome:
- frequent mood changes;
- immoderate passion;
- aggression;
- auto-aggression;
- increased tearfulness.
All these symptoms are characteristic of each individual at different periods of life. If you notice them, there is no need to immediately sound the alarm. It is worth thinking about help when they are expressed quite clearly and are repeated regularly.
Pathology in the form of emotional lability is of two types:
- border;
- impulsive.
The borderline type is expressed in frustration, indifference. A person susceptible to this type of lability expresses emotions weakly and inactively. Increased anxiety and absent-mindedness may occur.
The impulsive type is the opposite of the borderline type. People suffering from this type of pathology are characterized by a negative mood, anger, and addiction. Auto-aggression can result in suicidal tendencies, so it is important for such people to promptly contact specialists for help in solving problems.
Any type of emotional lability is destructive to the nervous system and mental health, which affects all areas of an individual’s life.
Inappropriate expression of emotions is typical for people of different age categories. If in adults this is a pathology that requires correction, then does the same apply to children?
First of all, it must be said that a person is exposed to stress at any age. An adult can control his emotional state, but this is more difficult for children.
Adults influence the development of a child’s psyche and emotional state. Peers also matter, but parents and other close people are more important. Children are exposed to stress equally from excessive care and complete indifference on the part of their parents. It is important to find a balance that will allow the little person to grow into a healthy person.
Regardless of upbringing, the child throws tantrums, screaming and lying on the floor in the most inappropriate places. For the first time, he tests how adults will behave. If this situation repeats regularly, the moment is lost. A little manipulator can get carried away and get into the role so much that regular hysterics will lead to constant tension in the nervous system, which results in emotional lability.
Emotional lability: what is it in children - lack of upbringing, pathology or characteristic? Regular manifestation of symptoms signals a problem, and a one-time “action” is a routine check of the extent of what is permitted.
As for teenagers, the question remains open. During puberty and alienation from their parents, children experience a lot of stress due to changes in their body and appearance. In this regard, many of them face problems in choosing a hobby, and in behavioral strategies. The same algorithm applies here: regular and vivid manifestation of symptoms is a cry for help, rare manifestations are simply a period of growing up.
It doesn’t matter who suffers from emotional lability - a child, an adult, a man, a woman, an elderly person. Anyone can need help, so it is important to use corrective methods and seek professional treatment.
Emotional lability and its treatment are an important aspect in the formation of the personality of children. Adults also require correction, since the pathology does not disappear on its own. Before working with the nervous system, it is necessary to establish the cause of the symptoms.
If this is regular stress, you will have to find its root cause and try to eliminate it. If this is a disease of the cerebral cortex, endocrine or nervous system, therapy with a psychiatrist will be only a small part of the treatment program. In any case, it is worth undergoing an examination of the body and contacting.
Doctors prescribe special medications for adults that can control their emotional state and suppress outbursts of anger, aggression, and expressiveness. Treatment of childhood syndrome occurs differently. Most medications are intended only for adult patients, but other methods of work are used with children.
To a greater extent, parents influence the correction of emotional lability in a child. Adults must explain, cope with failures and overcome difficulties. It is upbringing that can instill in a child calmness and adequacy from early childhood.
Prevention of emotional lability is implemented throughout life. It can be roughly divided into 4 important stages:
- child;
- teenager;
- adult;
- elderly.
Each life stage has its own characteristics. Tantrums and unstable emotional state of the child are corrected by patience and personal example of parents and other adults. Children are a mirror image of their parents, so you need to take care of yourself first of all.
Teenagers are a special category, since development during this period is characterized by rebellion. There are exceptions, but they are rare. It is important to talk to teenagers who are prone to emotional swings as if they were adults and try to understand them. Shouting, threats and punishment will not lead to positive results. And again - personal example. When a teenager sees that a parent is calm, trusts his child and perceives information adequately, then he himself becomes the same.
An adult must control himself and monitor outbursts of emotions. Ignoring the problem does not help solve it, but only makes the situation worse. Here it is important to listen to the opinions of loved ones. If they notice emotional instability, mood swings and other symptoms, then they still need to monitor themselves. In other words, for an adult, the prevention of emotional lability consists mostly of self-control.
Older people are more likely to suffer from mental illnesses, such as senile dementia. Prevention for this category of people should be a continuation of work on oneself. Tracking your emotional state will help you avoid serious problems in the future, so you need to avoid stressful situations and take care of your nervous system.
Human life is filled with stressful situations, problems and difficulties. Everyone has to overcome these difficulties, but not everyone can adequately perceive them. If from childhood a person gets used to the fact that all problems are solved by their parents, in adulthood it will be quite difficult for them to cope with them on their own.
Emotional lability syndrome is familiar to most people. If you learn to control emotions, adequately assess difficulties, balance ambitions and opportunities, life becomes much easier.
Emotional lability is a deep area of knowledge in psychology. Experts constantly conduct research, study symptoms and correction methods, and develop treatment. The phenomenon affects both a person’s physical condition and his mental health.
Prevention of emotional lability largely involves reflection and self-control. It is important to remember that a person’s main ally is himself.
Sincerely, Department of Psychological Support and Career Guidance at PSU
Dormitory No. 7 room 77, 81
Slave. tel.: 053379567
What is lability
In the general sense of the word, lability is mobility, instability, variability, mobility. The term was introduced in 1886 by N. E. Vvedensky (Russian physiologist, student of Sechenov). It reflects many characteristics of the nervous system:
- speed of occurrence of the exciting impulse;
- the speed with which he reaches his goal;
- the rate of occurrence of the reverse reaction - the braking impulse;
- frequency of tissue irritation in response to a nerve impulse;
- the time it takes the tissue to recover after each cycle of excitation.
Many people differentiate this concept in different areas. For example, in psychology, mental lability is, first of all, instability of mood, emotional hyperexcitability, too sharp and sometimes inadequate reaction to what is happening. In physiology, this is a disorder of the autonomic nervous system, when a call from the outside provokes a malfunction in the body.
In fact, many scientists say that the concept of lability should be considered equally in both psychology and physiology, since it reflects the borderline state between them. To clearly demonstrate this, let's give an example.
Situation. A person unexpectedly finds out that he was fired from a well-paid, beloved job to which he devoted many years of his life.
The reaction of a person whose nervous system is normal: he will get upset, try to find out the reasons, draw conclusions for the future and go look for a new job. Even if he was fired unfairly and resentment lurks in his soul, he will not sort things out and start scandals. Even if he is choleric, he can say something harsh, express his opinion, but nothing more. Explanation: the processes of excitation and inhibition are balanced.
Reaction of a person with increased lability: depending on the accentuation of the character, he will either begin to cry hysterically with wringing of his hands, or start a scandal. At the same time, such people will always experience symptoms of a disorder in the autonomic system: sweat on the forehead, pressure surge, tachycardia, hand tremors. It will be visible to the naked eye that he is not able to control himself. Despite the fact that the attack passes quickly, the consequence is often prolonged depression. Explanation: the excitation speed is too high, but the inhibition process cannot keep up with it.
The reaction of a person with low lability: he will take the documents and calmly leave without sorting things out. Moreover, this will not be an ostentatious demonstration; he really won’t care. Explanation: the speed of the exciting impulse is extremely low for there to be any response to the challenge from the outside.
In such borderline cases, they say that the second person has a labile nervous system (instantly reacting to everything with a low speed of inhibitory impulses), and the third has a rigid nervous system (not responding to stimuli or not resisting them).
The main phases of stuttering development
In its development, stuttering goes through 4 main stages or phases.
The initial stage is formed in the earliest years
The person does not yet understand the essence of the problem, therefore he does not believe that there is anything wrong with him. The symptoms are still scant, but are already noticeable to any observer. Problems are attributed to an early age. But the “maybe it will go away on its own” strategy does not work. Time moves on, but self-elimination of the violation is not observed. Attempts to put pressure on a young patient lead to an even worse result: the stuttering gets worse.
The 2nd phase is formed several years later
The number of speech situations that are difficult or undesirable for a person is increasing. The patient strives to replace constructions that are difficult to pronounce with something similar in meaning. If the vocabulary is sufficient for the age, everything is fine. It is possible to temporarily achieve compensation for the pathological process. Depending on the etiology of logoneurosis, it is possible to cope with the problem or it continues to progress. In some cases, the child does not understand that something is wrong with him, although he is aware that his speech is different from the speech of others. Persistent neuroticism has not yet been observed.
Phase 3 develops in early adolescence
In some cases, even earlier. By 9-10 years old. There are two possible options for the progression of the pathological process. Some patients never experience any awkwardness in communication. They strive for sufficient communication despite the persistent consolidation of the anomalous state. Others are embarrassed by their problem, so they try to avoid verbal contact if possible. The convulsive syndrome becomes automatic. It is already quite difficult to cope with him. Especially if therapy has not been carried out previously. In the first case, the patient perceives treatment proposals with skepticism. In the second, he does not seek therapy because he is afraid of ridicule from the doctor.
4th phase, also the final one
It does not always develop. Basically, “those patients who are ashamed of their problem get to her. A real personal problem is forming. The patient is afraid to speak. Avoids speech situations at all costs. Especially unusual ones for him. There is a persistent fear of speaking. This seriously complicates the patient's social life. Leads to isolation, refusal of society, interaction with society except for the most basic actions: going to the store, etc. Here you need the help of not only a speech therapist-defectologist, but also a psychotherapist. The problem becomes especially acute in late adolescence and towards adulthood.
The general rule is one - treatment should begin as early as possible. This makes it easier to cope with the pathological process. It is possible to eradicate stuttering completely. Don't delay with the correction.
Kinds
Depending on the speed of excitation processes:
- low lability - characteristic of a rigid nervous system, when the reaction to an external challenge is minimal;
- high lability is an immediate response to it, and the restraining factors (inhibition impulse, level of upbringing, character type) do not work.
Depending on the manifestations:
- impulsive - pronounced both at the psychological and physiological levels;
- moderate (borderline) - depending on the situation, it can manifest itself quite restrainedly.
By degree of neglect:
- mild - minor but noticeable deviations in behavior are observed;
- moderate severity - mental and vegetative manifestations are diagnosed;
- severe - development of various complications.
Depending on the scope of manifestation:
- emotional is mental lability, which is characterized primarily by instability of mood and too strong reactions to what is happening;
- vegetative is physiological lability, in which a malfunction in the functioning of various body systems comes to the fore.
These two types of deviations rarely exist in their pure form: most often their symptoms are intertwined and lead to a diagnosis that is registered in ICD-10. Organic emotionally labile asthenic disorder (abbreviated as simply labile disorder) is treated by psychiatrists, psychotherapists and neurologists.
Certain types of lability
Type 1. Intelligent
There is also intellectual lability, which is distinguished by the fact that it is a positive characteristic of the nervous system. Here, the high speed of excitation processes plays into a person’s hands: he instantly reacts to the task assigned to him, quickly and accurately solves it, and immediately switches to another task. Such multifunctionality, according to experts, in the modern world with its frantic rhythm is much more in demand and useful than IQ level.
Example. A person with high intellectual lability takes the subway in the morning. From the outside it may seem that he is not doing anything special. In fact he:
- monitors the movement of the electric train so as not to miss its stop, and evaluates the surroundings (when to stand up and give way);
- listening to music;
- plans his day in his thoughts: what he will do at work first, and what things can wait;
- scrolls through social media feeds to keep up with the latest events;
- communicates with several people at once in different messengers.
And all this at the same time!
On the subject: Tests to determine intellectual lability
Type 2. Social
An insufficiently described type, about which there is no established and unambiguous opinion in psychology. Some believe that this is a consequence of emotional instability, and therefore bears its imprints. That is, a socially labile person cannot build strong and long-term relationships (neither family nor friendly), since not everyone can tolerate his mood swings.
However, another group of psychologists believes that social lability should be viewed in a completely different way - positive. A person who has it can easily make acquaintances. And if on a personal level this is not a virtue, then in networking it is simply an invaluable quality.
The main causes of the pathological process
It is worth specifying the mechanisms. It is important to know the reasons in order to, on the one hand, develop a competent prevention strategy. On the other hand, it helps to cope with an existing disease.
- Being male
Statistics show that boys are more prone to developing a pathological process compared to girls. Apparently, this is due to the later development of speech motor functions. Girls, due to their early development, bear less risk. Although there is still a possibility of a pathological process. The ratio, according to various estimates, is 3:1 in favor of males. There are some discrepancies in these figures: some point to larger figures and proportions.
- Lability of the nervous system
Or, to put it simply, increased mobility of the central nervous system. Higher activity is characterized by instability. Objectively, a labile nervous system is manifested by sudden changes in mood. This is noticeable almost from the cradle. Now the child is smiling, and a second later he is crying and capricious. To some extent, all children are prone to this behavior. Therefore, it is quite difficult to determine the type of nervous system before reaching 3-5 years of age. Diagnosis can be complicated.
- Psychotrauma
Psychotraumatic situations increase the likelihood of a pathological condition several times. This can include anything: the absence of a mother during a vital period, punishment, violence and other factors. Such causes of stuttering are not corrected at all. All that remains is to deal with the consequences. According to medical practice, this is possible with varying degrees of success. We need a good, qualified speech pathologist.
- Left-handedness
Lefties are not much different from other people. But at a fundamental level, changing the “roles” of brain structures leads to pronounced disharmony in the interaction of the hemispheres. The result is an insufficiently uniform redistribution of the nerve impulse. A person who stutters is not necessarily left-handed. But in almost 30-40% of cases, a left-handed person is a person with a stutter. Although latent, “dormant” forms of the disorder are also possible, waiting in the wings.
- Late onset of speech
In the first few years of life, the correct patterns of distribution of load on the brain and stimulation of the speech apparatus are formed. Gradually, movements and articulatory positions become automatisms, a person accepts them without the participation of consciousness and volitional effort. The pathological process begins if in the first three years of life the child has not mastered basic speech skills. The further you go, the higher the likelihood of an anomalous condition. And the more difficult it will be to correct in the future.
- Early development of speaking skills
We are talking about the development of incorrect articulatory positions. Children who begin to speak earlier than their peers (that is, by about one and a half to two years) do not have sufficient speaking experience. But they love to talk and communicate with parents. Haste is what leads to the pathological process.
- Aggravated medical history
It has already been mentioned earlier. Genetic predisposition, unfavorable heredity. The likelihood of developing a pathological process is initially higher than that of other people. All risks can be mitigated only if sufficient measures are taken to prevent the disorder.
- Insulation
In this case, we are talking about a variant of mental trauma. The young patient should have a sufficient number of social contacts. The matter cannot be limited to parents. You need to communicate with peers. This allows you to develop social skills and provide sufficient speech experience. The situation is even worse if the parents themselves and adult relatives do not want to listen to the child and are busy with their own affairs. On the one hand, a strong stressful situation arises. On the other hand, there is not enough speaking practice to develop articulation skills and train the speech apparatus.
- Strictness in education
Provokes increased stimulation of the central nervous system. Excessively strict, authoritarian parents (especially toxic mothers) who put pressure on their children provoke psychological trauma. Being under constant tension, the central nervous system of the young patient cannot cope with such an overwhelming load. Stuttering begins in the first few years of life. But it can develop later. Strictness, an imperative approach to education becomes the very trigger, the trigger mechanism for the development of the disorder.
- Organic and structural brain lesions
Tumors, inflammatory processes, congenital anomalies and anatomical changes. The number of possible states goes into dozens. It is necessary to identify the specific cause and eliminate it. This will be the first step towards correcting speech function.
- Speech apparatus defects
The psychosomatics of stuttering is a complex of processes. Some relate to the functioning of the brain and psyche. The second are organic disorders. But this is not always what happens. Sometimes it’s all due to a banal inability to pronounce sounds normally. For example, with uneven development of the jaws, facial asymmetry, short frenulum of the tongue, congenital malformations. There is a purely physical violation taking place here. Anatomical anomaly. It needs to be eliminated faster. Because then it will be difficult to retrain the child in a healthy way.
- General health
Mental and somatic diseases themselves increase the likelihood of developing a pathological process. But they still do not guarantee that the child will stutter. It all depends on compensatory factors: social environment, medical care.
- Learning several languages at once
Bilinguals are more likely to develop stuttering due to accelerated development of the speech cortex. Simply put, the child’s body and brain simply cannot keep up with his social activity. Therefore, scientists and speech therapists strongly advise against learning two languages with a child at once. Even if these are the sociocultural and ethnic needs of the parents. You need to wait for the right moment. At least wait out the first 5-6 years of life.
- Birth injuries
They occur quite often. Mainly caused by an iatrogenic factor (actions of a doctor, obstetrician, paramedics).
- Excessive fatigue
Especially in the early years, when the central nervous system is just developing and cannot yet withstand the stress that adults experience. This happens especially often when there is an excess of impressions. For example, when a child goes to kindergarten. Stuttering can manifest itself in the first grade due to a sharp increase in workload. The child's condition must be carefully monitored. If anything happens, correct it, as they say, “on the shore.”
The mechanisms of stuttering and the causes of pathology in children of preschool and school age are approximately the same.
Does stuttering develop in older patients?
Yes, adults are also at increased risk. What are the reasons for the development of the pathological process:
- Severe stressful situations. Psychotraumatic cases. Typically, this is not true stuttering. Therefore, with sufficient work with a psychotherapist, you can cope with the disorder and eliminate it without a trace.
- Brain disorders. For example, aging processes, dementia, pre-dementia. This also includes sclerotic changes in patients of any age.
In adult patients, stuttering develops extremely rarely. The reasons for this are always pathological.
Causes
Since lability is a borderline phenomenon that concerns both the psyche and physiology, the factors that provoke its appearance lie precisely in these planes.
Physiological (vegetative)
- Buerger's disease;
- hormonal dysfunction;
- deficiency of nutrients necessary for the normal functioning of the nervous system;
- intoxication (medicine, narcotic, alcohol, toxic chemicals);
- unstable pressure, its constant jumps;
- complications during or after pregnancy and childbirth;
- suffered a stroke or heart attack;
- consequences of unsuccessful anesthesia;
- brain cancer, traumatic brain injury;
- thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism;
- severe neuroinfections: meningitis, encephalitis, myelitis, polio, tetanus, HIV infection, cerebral malaria, etc.;
- epilepsy.
Vegetative lability often develops against the background of diseases such as:
- Crohn's disease;
- diabetes;
- kyphoscoliosis;
- lupus erythematosus;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- cancer in the last stages;
- ulcer.
Psychological
- Distress;
- spoiled;
- lack of education (from childhood a person is not taught to control himself, and over time his inhibitory synapses weaken to such an extent that later, even if he wants to stop expressing his emotions, he will not be able to do this);
- psychotrauma;
- attention deficit hyperactivity disorder;
- excessive emotional stress.
Intellectual lability, according to experts, is determined to a large extent by heredity. Some even believe that for this reason it cannot be corrected, since it is laid down at the genetic level. However, training and the constant development of memory and attention lead to increased performance, which refutes this point of view.
Symptoms
As already mentioned, if a person’s nervous system is labile, this will manifest itself at different levels. The clinical picture is usually visible to the naked eye. In response to an external challenge, the autonomic nervous system activates the body's systems as a defensive reaction. Since inhibitory impulses do not have time to stop the exciting wave, this is instantly indicated at the physiological level.
At the same time, approximately the same thing happens at the mental level. The central nervous system sends the brain a task to cope with the situation that has arisen. It responds with a powerful reaction that the inhibitory synapses do not have time to stop. The result is an emotional explosion.
Sometimes this occurs in a single complex, sometimes vegetative symptoms predominate over mental symptoms (or vice versa). The clinical picture may be as follows.
Psycho-emotional signs
A labile psyche can react to a stressful situation in the following way:
- hot temper, impulsiveness;
- loud, uncontrollable, hysterical laughter;
- hysterical fits;
- rash actions;
- irritability, anger, aggression;
- a sharp change in mood;
- speech dysfunction (stuttering, for example);
- tears, tearfulness, moodiness;
- spontaneous, unexpected reactions;
- excessive emotionality.
In the long term, frequent breakdowns lead to insomnia, neurotic phobias and panic attacks. At the time of a problematic situation, everything can end even worse: being unable to control their own emotions, a person becomes dangerous to others and to himself (suicide is possible).
Such conditions must be differentiated from mental disorders. The main difference is mood lability. That is, outside of such situations a person is completely adequate. And almost always - intertwined with a physiological symptom complex.
Physiological signs
If a person is labile, in response to a stressful situation, along with emotions, he will feel how his body includes defensive reactions that may be completely unnecessary:
- the pressure either jumps sharply or drops just as quickly;
- the ground disappears from under your feet due to dizziness and spots before your eyes;
- tremor or numbness of the limbs may begin;
- there is tachycardia to the point of ringing in the ears, it seems that the heart is about to jump out of the chest;
- lack of air is detected;
- sweating increases (perspiration appears on the forehead, armpits become wet, palms become wet);
- sensitivity increases: sounds hit the ears, light blinds the eyes, a barely noticeable touch causes pain;
- severe migraine develops;
- auditory hallucinations are heard.
Moreover, outside of such situations, a person is absolutely healthy. As soon as the autonomic nervous system is convinced that there is no danger, the excitatory synapses subside, and in literally 5 minutes the state returns to normal, as if nothing had happened. Too frequent such attacks can lead to decreased libido, irritable bowel syndrome, weakened immunity, cystalgia and other serious diseases.
Symptoms of the pathological process
The clinical picture depends on the individual case. But in general, the same manifestations are always present. Plus or minus. Among them:
- Breathing disorders
Inhalations become frequent. The reason is that a person takes in a lot of air. This has to be done because the person who stutters has a huge consumption of air. This is due to the peculiarities of pronunciation. Inhalation is usually noisy. Gradually, a person begins to pronounce speech structures both while exhaling and inhaling. This is a kind of compensatory mechanism to correct a functional problem.
- Hoarseness of voice, wheezing
The reason is that the glottis sharply spasms. This occurs especially often in the tonic variety of the pathological process. Hoarseness is observed as a temporary phenomenon. As soon as the tone of the local muscles is restored, the voice also returns to normal. Changes are observed in the acute period.
- Looping on the same sound
Occurs in clonic form of stuttering. A person repeats the same sound. Usually - consonant. He cannot switch to another, no matter how much he wants, because repeated contraction of the same group of articulatory muscles develops. Then the condition disappears, then it recovers again. And so on in a circle.
- Abrupt stop in the speaking process
Develops against the background of the tonic form of the pathological condition. There is a sharp spasm of facial muscles, structures of the tongue, cheeks, lips, and palate. All tissues and organs that are involved in speech. The articulatory apparatus “jams.” It remains to wait for the symptom to resolve itself. Then everything fades away. And then it repeats again.
- Objectively, disturbances of normal articulation are noted
Only a qualified speech therapist can detect this symptom. It is impossible to detect the problem on your own.
- Shyness, timidity
As a consequence of the public, social component of stuttering. The person becomes fearful, afraid to communicate, and avoids people. This can go on indefinitely. In the absence of treatment, it very soon results in reclusion.
- Phobias. It comes to the point of being afraid to speak due to a pronounced defect.
- Tendency to social isolation
Inability to communicate even with a strong desire. A person tries to isolate himself from the world, is not confident in himself, is afraid of society and people. This condition needs to be treated as quickly as possible. A psychotherapist will help.
- Embedding extra sounds into words and sentences
This is the so-called embolophrasia. What degree of stuttering is associated with embolophrasia? It develops as a compensatory mechanism, starting from the second stage of the pathological process. A person composes extra sounds as passing structures. To make it easier to move from one articulatory position to another.
Stuttering is accompanied by typical symptoms. It is impossible not to notice him.
Diagnostics
Often people with nervous system lability are referred by their loved ones either to a psychologist (psychotherapist) or simply to a doctor. This is not surprising, because emotional outbursts and the physiology that manifests itself in such situations can frighten anyone. Mental disorders or hidden illnesses are usually suspected.
At the appointment, it is not enough for a specialist to collect anamnesis through a conversation with the patient. He must study the disease chart to see that he does not have any chronic or hereditary abnormalities. After this, the person is observed for 2-3 months to find out how stable his explosive reactions are and how often they manifest themselves.
When it turns out that all this happens spontaneously and not systematically, a diagnosis is assumed (organic emotionally labile asthenic disorder). It is confirmed using diagnostic methods such as:
- analysis of cardiovascular reflexes;
- urine, blood, and hormone tests;
- testing;
- Doppler ultrasound;
- electrocardiography;
- electroencephalography.
Lability must be confirmed by various specialists, as it affects both the psyche and the functioning of the body. A single team (ideally) of a cardiologist, psychologist, neurologist, psychiatrist, psychotherapist and endocrinologist works on its diagnosis and correction.
How can you help a patient?
To save the patient from the disease, it is necessary first to confirm the presence of lability. To do this, you should contact a highly specialized specialist, who will first of all conduct a conversation with the patient, collect anamnesis and prescribe a number of diagnostic measures. In such a situation, self-medication can lead to serious consequences, which will then be extremely difficult, and sometimes impossible, to cope with even for an experienced doctor.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the specialist will prescribe medication to the patient. It is worth noting that for each case, medications are selected individually. During the course of drug treatment, the patient will need to visit a psychologist. This specialist will monitor his condition and, if necessary, adjust both the dosage of medications and his behavior and emotional state.
Treatment
Eliminating the lability of the nervous system is an extremely difficult task, since it affects the processes of excitation and inhibition, which are difficult to correct.
The first goal of treatment is to eliminate possible causes. If it is an incurable chronic disease or a hereditary factor, medicine is powerless to do anything. Only psychologists and psychotherapists will help here. They cannot eliminate attacks, but they teach people how to deal with them on the spot. As soon as a person feels a crisis approaching, he will know what to do:
- drink a glass of cold water in small sips;
- take a deep breath and hold your breath;
- go out into the fresh air;
- wash;
- get away from people;
- urgently switch to another problem, etc.
Sometimes the cause can be eliminated (by treating the disease, avoiding emotional stress) - and then the lability gradually disappears.
Tranquilizers, antidepressants and other sedatives are prescribed as drug treatment.
Lability is a polysemantic and ambiguous concept in psychology and medicine.
Experts have yet to figure out the mechanism of its development and the degree of danger to human health. You may also be interested in:
Lability
(from Latin labilis “sliding, unstable”) in physiology - functional mobility, the speed of elementary cycles of excitation in nervous and muscle tissues. The concept of “lability” was introduced by the Russian physiologist N. E. Vvedensky (1886), who considered the measure of lability to be the highest frequency of tissue irritation reproduced by it without rhythm transformation. Lability reflects the time during which the tissue restores its functionality after the next cycle of excitation. The processes of nerve cells - axons - are characterized by the greatest lability, capable of reproducing up to 500-1000 impulses per 1 s; the central and peripheral places of contact - synapses - are less labile (for example, a motor nerve ending can transmit no more than 100-150 excitations per 1 s to the skeletal muscle). Inhibition of the vital activity of tissues and cells (for example, cold, drugs) reduces lability, since this slows down the recovery processes and lengthens the refractory period. Lability is a variable value. Thus, in the heart, under the influence of frequent irritations, the refractory period is shortened, and consequently, lability increases. This phenomenon underlies the so-called. mastering rhythm. The doctrine of lability is important for understanding the mechanisms of nervous activity, the work of nerve centers and analyzers, both normally and in various painful abnormalities.
In biology and medicine, the term “ lability”
"denote mobility, instability, variability: for example, the psyche, physiological state, pulse, body temperature, etc.
Blood pressure lability
Another expression found in medicine. It is characterized by a permanent or temporary manifestation of either an increase or decrease in blood pressure. Such jumps can manifest themselves through headaches in the back of the head, “floaters” and double vision, sleep disturbance, decreased attention and memory, numbness of the limbs, as causeless excitability and irritability. You need to pay attention to these symptoms and also try to determine the cause of their occurrence. You need to measure your blood pressure twice a day for about two weeks and try to change your lifestyle - diet, sleep patterns, spend more time in the fresh air, pay attention to sports, reduce physical and psycho-emotional stress.
see also
This page was last edited on 15 February 2021 at 07:42.
Emotional lability is a transient process of mental etiology, characterized by rapid changes in a person’s mood. Since labilis is translated from Greek as instability.
What is lability in psychiatry? This is a pathological condition that serves as an impetus for triggering the development of deviations, when in psychology it is a feature of the central nervous system that determines a specific type of temperament, and in physiology it is only the speed of responsiveness of tissue cells to present stimuli.
Content
Complications of the disorder
Possible consequences include:
- Difficulties in communication.
- Problems in personal life and professional activities.
- Difficulties in finding a job, getting an education.
- General delay in intellectual and emotional development.
- Development of an inferiority complex.
- Formation of strong and difficult to eliminate phobias. This is also possible.
And this is only part of the complications. Therefore, it is worth starting treatment as early as possible.
Causes
In a situation where such a concept as lability is understood in a psychological sense, it should be noted that this is the individuality of the nervous system of a particular person, innate in nature and characteristic of a person with a choleric temperament.
It’s common for him to “swing” with his mood. As a rule, even the slightest irritant can cause uncontrolled behavior . This factor may cause problems of physiological and mental origin in the future.
An emotional labile state, if we consider it as a disease that needs treatment, then it must be understood as a set of physiological and mental symptoms.
The reasons for the formation of such a state are considered to be both the somatic part of the body and the mental component.
Physiological reasons include:
- Oncological diseases of the brain.
- Vascular pathologies.
- Brain diseases.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Hypotension or hypertension.
An emotionally labile person is a patient with somatic abnormalities. This disease is detected through changes in the body that occur as a result of hormonal changes or due to age. Therefore, lability (weakness) is characteristic of people of the older generation.
In a situation where there is asthenic syndrome, which is directly connected with weakness, it can be defined both as a basis and as a consequence.
As a rule, asthenic syndrome (mental disorder) together with emotional instability often causes anxiety and depression.
The mental part of a negative state usually includes attention deficit, negative parenting and influence on the child. Often, a labile emotional state manifests itself against the background of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Psychotraumatic conditions often become auxiliary causes of lability at different ages.
Often, a person with suicidal tendencies or after an unsuccessful suicide attempt, as well as with neurotic deviations, can suffer from weakness.
As a rule, neuroses or psychological diseases accompanied by a deficit in the control of emotions are considered a sign or basis for a negative change in condition.
In addition, an important factor in the formation of emotional lability is the lack of vitamins and microelements in the human body.
Symptoms of the pathological condition
The main labile symptom is an instant change in mood regarding someone or something. At the same time, tears easily give way to incomprehensible laughter, and complacency turns into obvious aggression.
At the same time, emotional lability can be expressed in outbursts of affective genesis. People with such a pathology cannot be responsible for their actions, and the basic instinct of self-preservation is dulled. Because of what, such individuals are capable of rash actions.
Labile emotional deviation of an organic nature is mainly associated with the presence of a feeling of being moved against the background of a tearful state.
On the physiological side, in addition to the exacerbation of vegetative abnormalities, for people with emotional lability, a short-term (vasovagal) loss of consciousness may occur, which is present under the influence of emotional manifestations, in which the blood vessels instantly dilate, but there is a significant slowdown in the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle.
But the pathogenicity of emotional lability can manifest itself in weakness of an impulsive and borderline nature.
Labile impulsive weakness is characterized by negative manifestations.
Symptoms of this pathology are:
- Dysphoria (gloominess).
- Irritability.
- Touchiness.
- Vengefulness.
- Pathological stubbornness.
Due to the presence of such signs, it is difficult for a person to work or study in a team, and it is also problematic for him to create and maintain family relationships.
In addition, a person with an impulsive nature of labile pathology does not find life easy, which is why affective outbursts often occur. An aggressive state can be concentrated inside oneself, leading to self-destruction, or into the environment, resulting in antisocial behavior.
Borderline weakness is caused by impressionability, helplessness in difficult situations, fluctuations between interests, intense emotional behavior, emotional and physical exhaustion, loss of time in one work process and neglect of parental instructions in childhood.
Drug therapy
The basis of drug treatment is the use of drugs to eliminate the physiological basis of the disease, which serves as a provocateur of deviations of emotional significance.
Based on the pathology present, the doctor may prescribe:
- Tranquilizers (anxiety and panic attacks).
- Antipsychotics in combination with herbal teas (sleep problems).
- Antidepressants (depression).
In a situation where it is not possible to get rid of the pathology, the patient is prescribed drugs that work as a stopper against the further development of the disease.
Psychotherapeutic correction
Such an edit serves as a diagnostic method that determines the presence of fears or the psychological factor of lability. This type of therapy ensures the elimination of difficulties by analyzing them, feelings of anxiety, and the process of resistance to stressful situations with deviations in self-perception.
In addition, work is underway to establish control over the patient’s own aggressive temperament. If there are problems of a social nature with communication traits, then training is often carried out.
It is important that not only medical workers perform their duties efficiently, but also the family of a person with weakness (emotional lability) must learn how to correctly respond to frequent mood swings.
The term “emotional lability” in psychiatry means a pathological violation of the stability of emotional status. This state is characterized by regular fluctuations in emotional tone and high mobility of the emotional-volitional sphere. With emotional lability, an individual experiences a rapid replacement of some experiences with other feelings. The mood background is extremely unstable. A person’s disposition of spirit changes depending on the situation and depends on insignificant details of reality.
With emotional lability, changes in environmental conditions or one’s own well-being lead to instant, very violent and vivid reactions. A person with this disorder responds equally sharply to the influence of both positive and negative factors. An individual can easily and quickly develop states of emotion, sentimentality, and excessive tenderness, accompanied by causeless tearfulness. Over time, a person may demonstrate traits of hostility, anger, and aggressiveness. At the same time, the presented stimulus does not always cause adequate reaction situations. For example, being offended by your interlocutor can cause inappropriate fits of hysterical laughter. Or, having received good news, a person will begin to sob violently.
A distinctive characteristic of emotional lability is the regular alternation of short-term emotional states. In contrast to such mood swings, another condition has been described - emotional rigidity, also called “emotional flatness”. This disorder is characterized by minimal expression or complete absence of emotions.
Treatment methods for stuttering or how to cope with the pathological process
There are several ways to effectively treat stuttering. The task is to synchronize the speech centers and articulatory apparatus. The methods are divided depending on the age of the patients.
Preschoolers
There are several techniques that help get rid of stuttering. The most effective are the following:
- Vygodskaya's technique. Designed for several months of intensive work. In a relaxed atmosphere, the doctor creates game situations. Due to this, the child develops special speech skills and does not worry. Can move at his own pace. There is no pressure, which has a beneficial effect on the result. Treatment of logoneurosis includes 36 sessions on average.
- Smirnov's method. The complex is suitable for preschool children. Based on the correction of speech skills and personal qualities. Designed for a full year of correction. Classes take place every day for 15-30 minutes.
- Silivestrov's technique. The course lasts 4 months. Classes are structured according to the principle of simple to complex. Therapy takes place in three stages. Each one is more difficult than the previous one. At the final stage, the result is consolidated.
Corrective work for stuttering begins at approximately 2-3 years of age. Previously it does not make sense, since transient forms of the pathological process are possible.
Adolescent and adult patients
Is it possible to cure stuttering in adults and teenagers? Yes, it is quite. But the methods used are completely different.
- Inpatient treatment according to Shklovsky. This is a whole complex of therapeutic activities. The intensive course lasts several months. Plus or minus. The person is under the supervision of a neurologist, psychotherapist and speech pathologist. Receives high-quality correction, after which he gets rid of stuttering.
- According to Harutyunyan. The person is in the hospital for approximately 30 days. Then another 30 sessions of therapy take place on an outpatient basis with a break of a week between every 5-7 sessions. The result is permanent. It is possible to consolidate it due to a longer and less intense effect.
There are other ways. These are especially widespread in Russia, Ukraine and the countries of the former Soviet Union. They are relatively simple and inexpensive. The main disadvantage when treating older patients is the risk of recurrence of the pathological process. Speech therapy measures for stuttering relapse will be approximately the same: speech practice, motivation, psychotherapy, breathing exercises.
Gradually, innovative treatment methods are being introduced into speech therapy practice. For example:
- Hypnosis. Psychotherapeutic instillation of an attitude of complete calm and control over speech. It helps if the person is suggestible enough and the therapist has enough experience.
- Speech prosthetics. The technique is based on the synthesis of the patient's voice. First, the person says a phrase. Then it is processed. The correct version is sent to the patient. A person listens to it and assimilates it as it should. This stimulates the speech centers and has a beneficial effect on the condition of the stuttering patient.
Getting rid of stuttering on your own is quite difficult. In addition, you can instill additional negative habits. It is recommended to consult a doctor first. Exercises for stuttering that your doctor prescribes can be done at home. You should not engage in amateur activities. It will only get worse.
Emotional lability: reasons
A pathological state of the psyche - emotional lability - is determined in various somatic, neurological and mental disorders. Instability of emotional status is a typical symptom:
- benign and malignant formations of the brain and adjacent formations;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- dyscirculatory encephalopathy;
- arterial hypertension and hypotension (hypertension and hypotension);
- asthenic syndrome;
- affective (depressive) states;
- disruption of the activity of the limbic-reticular complex structures;
- pathologies of the endocrine system.
The cause of emotional lability can be chronic stressful conditions or intense mental trauma. The basis for the development of this condition is an affectively labile (cyclothymic) temperament. Mood swings are often found in people with a hysterical character (demonstrative personalities). In this situation, the foundation for mood swings is congenital mental weakness and instability of hysterical drives, which is combined with an obsessive desire to be the center of attention.
Often, emotional lability starts after illnesses of a viral or bacterial nature, with vitamin deficiency, in particular, with a deficiency of B vitamins. A typical provocateur of mood swings is serotonin syndrome: a failure in the exchange of neurotransmitters that regulate the emotional sphere.
Ways to prevent the disorder
There are quite a lot of prevention methods. Among them are:
- Gentle parenting style. Minimum of rudeness and swearing.
- Dosing of information. There is no need to overload the child's brain.
- Correct sleep and wakefulness.
- High-quality, varied food. Vitaminized diet.
- Avoiding situations that may provoke fear in a child.
- Sufficient amount of communication. Speech practice should be constant.
- Refusal to learn two languages at once. Wait until you grow up.
- Reading books, fairy tales.
- Socialization of the child. He should not sit at home, be left to his own devices. A sufficient number of contacts with peers is the key to successful development of personality and emotional sphere.
- Creating a calm environment at home.
Emotional lability: symptoms
The main characteristics of this pathological condition are unreasonable mood swings, impulsiveness and spontaneity of actions, the inability to control one’s own behavior, and the inability to foresee the consequences of one’s actions. A change in emotional state occurs for insignificant reasons or even in the absence of objective reasons. Demonstration of emotions can reach the size of affective outbursts, when the demonstrated reaction significantly exceeds the strength of the presented stimulus.
A person with emotional instability may experience an angry-sad mood for no reason, combined with violent outbursts of aggression. After a short period, dysphoria may be replaced by the opposite phenomena - high spirits, a feeling of lightness with characteristic psychomotor agitation.
Emotional lability is adjacent to excessive impressionability, suspiciousness and vulnerability of the individual. Such a person reacts extremely painfully to criticism addressed to him and is particularly suspicious.
A person with emotional lability easily becomes a victim of addictions. The lack of a strong inner core, the lack of clear life guidelines leads an unstable personality into the ranks of chronic alcoholics and drug addicts. The inability to control emotions often rewards with uncontrollable passion in various areas. An emotionally labile person can become an avid casino visitor, embark on countless love affairs, and become addicted to computer games.
With mood lability, a person can go from one extreme to another. Today he will swear eternal love to his chosen one, and tomorrow he will simply file for divorce. An emotionally unstable person, driven by immediate desires, often changes jobs or leaves school.
Emotional lability: methods of overcoming
In most cases, it is possible to eliminate emotional lability in a person. In the absence of pronounced and persistent personality changes, it is possible to overcome this condition with the help of psychotherapeutic techniques, auto-training and hypnosis techniques. The main task of the doctor is to establish the true causes of the anomaly, confirm or exclude organic lesions, and eliminate triggers.
The emphasis in correcting emotional lability is on cognitive behavioral therapy techniques. During sessions, the psychotherapist teaches the client ways to control their emotions and relaxation methods. In severe situations, pharmacological drugs are used in the treatment of emotional lability: sedatives of plant origin, benzodiazepine tranquilizers, anxiolytics, antidepressants.
Emotional lability usually means a state of the human nervous system, which is characterized by high excitability, apathy, and depression. It arises as a result of life's difficulties. The condition can be both short-term and permanent. It can occur in any person, regardless of gender and age. Psychology notes that the main factor for people with this pathology is the support of family and friends. If an organic emotionally labile disorder is detected, it is necessary to begin treatment as quickly as possible.
1 Types and characteristics
Lability is a definition used to denote mobility, including mental state. The following types are distinguished:
- intellectual - the ability and ability to reactively switch from solving one problem to another;
- vegetative - the presence of an unstable nervous system;
- affective - variable mood;
- psycho-emotional, or emotional - a variety of emotions;
- mental - personality disorder.
Emotional lability is similar to asthenic syndrome. The disease manifests itself with one or more symptoms. Knowing them will help you recognize the problem in time and begin solving it.
The most common symptoms of emotional lability are:
- 1. Constant mood changes. A person who is in this state falls either into joy or into apathy, and finds himself on the verge of a nervous breakdown. This also affects those close to him.
- 2. Hot temper and aggressiveness. Trying to get rid of some problem, a person experiencing emotional lability usually lashes out at others.
- 3. Excessive enthusiasm. To get distracted, a person begins to look for something to do.
Patients suffering from this disorder may experience brief periods of fainting.
If the disease does not progress, it smooths out over the years. For example, in women this occurs due to hormonal changes in the body after childbirth.
We recommend Alzheimer's disease - symptoms, stages, causes and treatment methods2 Causes of occurrence
Emotional lability can arise for a number of reasons. The most common ones are:
- constant stress, psychological trauma, lack of attention;
- hormonal imbalances in the body;
- physical ailments, vitamin deficiency.
Prolonged emotional turmoil leads to the fact that people stop trusting not only others, but also themselves. A person begins to become disillusioned with his life and refuses to strive for better.
A labile psyche can be temporary during a period of hormonal disruptions. Before menstruation, many girls and women notice emotional instability.
Tumors, hypertension, and concussion can provoke this disease. It is also often preceded by a lack of microelements and vitamins in the body.
A stable, labile psyche in children can lead to nervous exhaustion. This condition develops due to emotional overstrain caused by indulgence in whims or constant punishment.
3 Treatment and prevention
If emotional lability is detected, it is necessary to immediately begin its treatment, which includes psychotherapy or special medications.
If it is caused by other diseases, they must be eliminated.
Diagnosis is carried out by studying the anamnesis and based on the patient’s complaints. Instrumental examination and additional tests may be prescribed.
In pediatric therapy, it is necessary to develop an individual treatment plan and constantly monitor the patient’s health. At this age, experts prescribe herbal medications with a slight sedative effect. These include herbal syrups, valerian or motherwort.
Therapy for an adult begins with a complete diagnosis. The specialist finds the cause of the condition and eliminates it.
For emotional lability, the attending physician prescribes antidepressants, nootropics, strengthening therapy and sedatives.
The method for preventing this condition is as follows:
- 1. You must try to avoid conflicts or resolve them as quickly as possible, without accumulating anger and irritation.
- 2. You need to try to keep your emotions and thinking under control and eliminate all problems before they begin to turn into illness.
- 3. Physical and mental activity, daily routine and sleep patterns should be properly organized.
Potent drugs should only be prescribed by a medical specialist. If you have panic attacks or causeless anxiety, you should consult a psychiatrist.
Sources used:
- https://ponervam.ru/labilnost.html
- https://wiki2.org/ru/lability
- https://psiho.guru/populyarnye-voprosy/chto-takoe/chto-takoe-emocionalnaya-labilnost.html
- https://depressia.info/emotsionalnaya-labilnost/
- https://neurofob.com/mental-behavioural/organic/labilnost-eto.html
Mechanisms of development of stuttering
If we talk about the pathogenesis of the disorder, it develops according to this scenario.
- Two main structures are responsible for normal speech, the function of speaking, and constructing phrases. The first is located in the temporal region. This is the so-called Wernicke's zone. It regulates the perception of others and the reconstruction of one’s own internal speech. The second structure is Broca's center. Located in the frontal lobe. Responsible for the formation of speech, the logic of statements and other fundamental features. During stuttering, it is Broca's area that is affected. She becomes hyperexcited. Excessively intense signals are transmitted to those areas of the brain that regulate the motor activity of facial and articulatory structures: palate, tongue, lips.
- After transmitting the signal to the motor centers, they also become overexcited. They transmit impulses to the muscles themselves. The final phase of the pathological process develops.
- The facial muscles themselves, the muscles of the palate, tongue, and lips, begin to move chaotically.
As a result, a person begins to lengthen sounds and repeat them several times. The pace and rhythm of speech becomes unstable. Basically, difficulties arise with consonant sounds.
This is the basis of pathogenesis. As for specific mechanisms, there may be several of them. And in the same patient. To summarize the factors causing the problem:
Social mechanism
As a rule, in isolated form it does not provoke stuttering. This mechanism concerns the characteristics of the sphere, the environment in which the child grows up. As a rule, the most destructive influence is exerted by stressful situations, constant swearing, conflicts, and punishment. And the authoritarian-imperative type of education in general. This is harmful not only for the behavioral component, but also for the psyche in general. Including in such an aspect as the development of the speech function of a young patient.
Organic brain disorders
A pathological process of this kind can be anything. From hypoxia due to birth problems to past infectious diseases such as encephalitis, meningitis. This also includes tumor processes and injuries. It is interesting that epilepsy sometimes provokes stuttering. And not necessarily the classic form with convulsions and seizures. There are also milder forms of the disease. Often these pathologies go hand in hand, this must be taken into account when examining and consulting a doctor.
Organic disorders of the functional activity of the articulatory apparatus
For example, congenital disorders of the structure of the speech apparatus. Defects such as cleft lip, cleft palate, even if they were eliminated at a very early age. And if there is a delay in treating the disease, the risks increase many times over. There are also less noticeable problems: a short frenulum of the tongue, minor structural changes in the bones of the skull, jaws, and so on. You need to figure it out on the spot.
Features of the central nervous system
The excitability of cerebral structures is different for everyone. This is why some people are more prone to stuttering than others. Features of higher nervous activity are manifested within the framework of temperament and accentuation. Therefore, it is quite easy to predict in advance what the likelihood of a violation is for a particular person. If the risks are significant, it is strongly recommended to adhere to the rules of prevention (prevention will be discussed later).
Genetic factors
Oddly enough, stuttering has a clearly defined hereditary component. This is not a 100% guarantee that pathology will definitely develop. But there really are such risks. If the father, mother or older relatives in the ascending line suffer from stuttering, the likelihood increases several times. Prevention rules must be strictly followed. To a somewhat lesser extent, risks are present when a relative of the lateral branch is sick. For example, brother or sister. But it is still worth paying a certain amount of attention to the condition. Is stuttering inherited? Strictly speaking, no. But the risks are passed on from parents to children.
None of these mechanisms provokes a pathological process on its own. Even in the complex there is no talk of guaranteeing the development of stuttering. These are just predisposing factors. The likelihood of illness increases. Next, a trigger, a trigger mechanism, is enough.
Simply put, the disease has two aspects: the patient is predisposed to the disorder. Under certain conditions, it may or may not be updated.
As mentioned, factors often occur several at once. For example, personality traits plus socially determined mechanisms. It is important to provide the speech therapist or speech pathologist with all information that is somehow relevant to the situation. This will help to collect a truly complete history and develop an effective strategy for treating the pathological process.