Hemorrhagic stroke is a serious disease that requires immediate medical attention. One of the tasks of the “Special Medical Assistance” advisory service in Moscow is to provide all stages of treatment for hemorrhagic stroke, including surgical treatment.
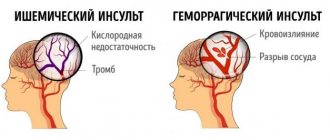
A hemorrhagic stroke is a bleeding in the brain, most often caused by high blood pressure. Unfortunately, about half of all cases of this disease in the acute period end in death, and more than 2/3 of survivors become disabled. The outcome depends primarily on the timeliness of medical care.
Modern surgical treatment for hemorrhagic stroke
Only in specialized centers is it possible to conduct a thorough diagnosis and adequate surgical or therapeutic treatment of hemorrhagic acute stroke. However, most often a free ambulance will take the victim to the nearest city hospital, where first aid will be provided, limited by the capabilities of the institution. And surgical treatment of stroke, unfortunately, can not be performed in all hospitals.
Therefore, relatives of patients are increasingly turning to specialized advisory services that can provide:
- safe transportation;
- rapid hospitalization;
- expert monitoring of victims in intensive care units and departments of medical institutions.
Only in highly qualified centers will they conduct the necessary research, assess all the risks, and then choose the necessary treatment tactics.
Another important point that affects the patient’s further capacity is rehabilitation and care after surgical treatment of hemorrhagic stroke. The success of postoperative therapy largely depends on the experience of specialists and the availability of modern equipment.
No problem with a vascular surgeon
Duplex scanning is an absolutely safe ultrasound examination of the arteries, which accurately determines whether there is damage to the vessel and to what extent it is expressed. The study is carried out using expensive equipment within a few minutes and immediately after the end of the study you are given a conclusion about the condition of your blood vessels.
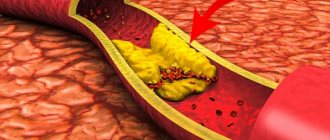
If an ultrasound examination reveals stenosis (narrowing) of the carotid artery, you need to see a vascular surgeon. It is the vascular surgeon who can determine further treatment tactics: if the narrowing is still insignificant, drug correction of blood circulation in the brain is possible, or correction of blood cholesterol levels and blood pressure is necessary. Of course, it is additionally necessary to change your lifestyle and give up bad habits. But if the narrowing of the vessel significantly limits the flow of blood to the brain, then medication is not enough - you need to have surgery. A timely operation greatly (and this has been repeatedly proven by large studies conducted both in Russia and around the world) significantly reduces the risk of developing a stroke. The technique of such operations has long been developed and is performed, including by our surgeons: under anesthesia, an incision is made in the neck, the carotid artery is isolated, the carotid artery is cut and a dangerous plaque is removed from its lumen, then the artery is sutured. The hospitalization period is approximately 5-8 days. Like any operation, such an intervention has its complications, and it is performed under general anesthesia, which is simply contraindicated for many, especially elderly patients and with concomitant cardiac pathology. But if a dangerous narrowing of the vessel is found and surgery is indicated, there is nothing left - the consequences of an inevitable stroke are much more serious than the risk of surgery.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs in a person due to a number of disorders (this can also include the consequence of a traumatic blow). One of the reasons why cerebral circulation may be impaired is pathological diseases: vasculitis, arterial hypertension, vascular abnormalities that were detected from birth, hypertension. Also, bleeding in the brain occurs due to poor blood clotting. The cause of violations may be the use of amphetamine and cocaine.
During a hemorrhagic stroke, a person feels unwell. Symptoms appear in various forms:
- balance problems;
- severe headache;
- nausea;
- perception is disrupted;
- Pain in the eyes;
- cardiopalmus;
- noise in ears;
- paralysis of the muscles of the face, arms, legs.
The consequence of all alarming symptoms is the rupture of intracerebral vessels under the influence of high blood pressure.
Why is this condition dangerous? What are the possible consequences of a stroke?
More than 2/3 of surviving patients become disabled. Various complications may develop:
- Partial (paresis) or complete (paralysis) loss of movement in certain muscle groups. Disorders can be expressed in varying degrees: from gait disorder to paralysis of the right or left half of the body. Some patients experience swallowing and speech disorders.
- Sensitivity disturbance and discomfort. When sensitivity is lost in certain parts of the body, discomfort, pain, and tingling may occur.
- Disorders in the cognitive sphere. Many patients experience deteriorating memory and thinking.
- Changes in behavior and disturbances in the emotional sphere. A person may become withdrawn, apathetic, and it becomes more difficult for him to control his emotions.
Serious brain damage can lead to the death of the patient.
Treatment approaches
The patient requires urgent hospitalization and medical care. After normalization of health, it is necessary to undergo in-depth diagnostics (computed tomography and MRI, cerebrospinal fluid sampling). After consultation with a neurosurgeon, treatment is prescribed.
There are two treatment options for the disease:
- Conservative. The neurologist prescribes treatment, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body and the diagnostic results. Conservative treatment consists of taking medications. The patient is prescribed drugs to regulate intracranial pressure and cerebral edema, antispasmodics, antihypertensive drugs, calcium antagonists. Intensive use of medications is necessary in the acute stage of hemorrhagic stroke. The patient also needs to be observed by a doctor to diagnose a decrease in cerebral edema.
- Surgical treatment of hemorrhagic stroke. Before performing an operation, doctors must exclude contraindications, stabilize the patient’s condition, and study the results of neuroimaging in detail. Surgical treatment of stroke cannot be avoided if a hemorrhage of medium or large volume occurs. Specialists choose the type of intervention.
From miracle to reality one puncture
Angioplasty and stenting of arteries
- Cost: 100,000 - 250,000 rubles.
- Duration: 40 minutes
- Hospitalization: 1-2 days in hospital
More details
There is now an alternative to open carotid artery surgery!
All over the world, including in our Clinic, another type of operation has long been actively used: no incisions, no anesthesia, hospital stay is only 2-3 days, after which the person is fully functional! This intervention is called balloon angioplasty and stenting of the carotid artery, it is carried out as follows: through a puncture of the artery in the groin, a balloon is inserted into the area of narrowing of the carotid artery and inflated under high pressure, crushing the atherosclerotic plaque, thereby freeing the artery for blood flow. A special frame, a stent, is installed in the area of the removed plaque, which prevents re-narrowing of the artery in this place. Considering that no incisions are made, there is no general anesthesia - such an operation is possible for any category of patients and the hospitalization period is only a couple of days. Fantastic? No. This procedure is possible and successfully performed by specialists in our department on almost any human artery, saving patients from angina, heart attack, gangrene, increased “renal” pressure and other dangerous manifestations of atherosclerosis. A similar intervention is performed for pathological dilations of arteries - aneurysms, which are dangerous due to their sudden rupture. According to various studies conducted here and abroad, angioplasty is not only an alternative to open surgery on the arteries, but is also significantly superior to them in a number of indicators. The only disadvantage of such an operation is its relative high cost. But when there is no health, then why money? Remember: diseases are much easier and cheaper to prevent than to treat their consequences later. Come - we will help you!
Indications and contraindications for surgical treatment of stroke
Not all cases of the disease require aggressive tactics and surgical intervention. Examination by specialists and data from instrumental diagnostic methods allow an adequate assessment of the patient’s general condition.
Contraindications to surgical treatment of stroke are:
- severe concomitant diseases;
- old age over 65-70 years;
- large volume of hematoma;
- depressed consciousness - coma.
Depending on the indications, our consultants will be able to select the best specialized hospital for the victim.
Types of surgery
Neurosurgeons distinguish several methods by which a hematoma can be removed:
- Direct surgery. The hematoma is removed by encephalotomy, then careful hemostasis is performed. When suturing, microsurgical techniques are usually used.
- Puncture-aspiration method. Fibrinolytics are administered. This method is effective if the hemorrhage is of medium size and the patient is in a stable condition.
- Endoscopic method. Modern method of surgical treatment. During surgery, endoscopic technology is always used. Using an endoscope, they penetrate into the hematoma cavity, after which a set of specific manipulations is carried out. Surgical treatment of hemorrhagic stroke is excluded in case of unstable hemodynamics.
After surgery, the patient should remain under observation. The rehabilitation period is long and difficult, can last up to two months. Special conditions are required for the patient’s recovery (a set of procedures in a rehabilitation center).
What can be done to identify symptoms of a stroke in a patient?
Some simple tests can help identify additional signs of stroke:
- Ask the patient to raise their hands. The arm on the affected side does not rise at all, or rises lower than the healthy one.
- Ask the patient to smile. One part of the face “smiles”, the other remains downcast.
- Ask the patient to stick out his tongue. The tongue deviates to the side.
- Ask the patient to bare his teeth. One half of the mouth is grinning, the other is closed.
- Ask the patient to frown. One eyebrow frowns more than the other, and asymmetry is noticeable.
- Ask the patient to repeat a phrase. The patient's speech is slurred and does not sound as usual.
If you notice any of these symptoms, there is a risk that the person is having a stroke. Call an ambulance immediately. Until the doctor arrives, the patient must not be left alone; he must be constantly under supervision - his condition may worsen at any time.
For relatives and people who are nearby, it is very important to quickly understand what happened to the person and immediately call an ambulance. In English-speaking countries, doctors recommend using the abbreviation FAST (if you read it by letter, you get a word that is translated into Russian as “fast”), which makes it easy to remember what needs to be done:
- F – face drooping: “lowering of the face.” When a person tries to smile, it can only be done with one half of the mouth, while the other remains lowered.
- A – arm weakness: “weakness in the arm.” When you try to raise your arms up, one of them does not rise at all, or rises worse, less than on the healthy side.
- S - speech difficulty: “difficulty with speech.” It is difficult for a person to understand someone else’s speech, to repeat phrases, he speaks indistinctly, his tongue becomes slurred.
- T – time: “time”. It's important to act quickly. If one of these signs occurs, you should immediately call an ambulance.