Pathogenesis
The causes of the onset and development of the disease include multiple factors. These include:
- disruption of lipid (fat) metabolism;
- excess cholesterol in the blood (this condition has its own reasons);
- slow elimination of cholesterol;
- persistent increase in blood pressure for a long time;
- genetic predisposition;
- increased blood viscosity;
- diabetes mellitus (therapy is carried out by an endocrinologist);
- weakness of the vascular wall;
- general condition of the body;
- diseases of unspecified genesis (origin).
The group of those at risk of cerebral atherosclerosis includes:
- smoking and alcohol abusers;
- obese;
- leading a sedentary lifestyle;
- having frequent or prolonged experiences, stress. (Consultation with a psychologist will help to cope with the problem)
Physical education and exercise for cerebral atherosclerosis
Physical education for cerebral atherosclerosis is aimed at reducing the level of “bad” cholesterol in the blood, increasing the elasticity of the endothelium (the inner layer of the surface of blood vessels), and improving metabolism. Physical activity for atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries and brain should not cause a sharp increase in arterial (upper) pressure, which can provoke tearing or destruction of a cholesterol plaque, the formation of a blood clot (thrombus) and cause a stroke.
The safest and most accessible for atherosclerosis of the vessels of the heart and brain are the following physical exercises: walking, including Scandinavian (Swedish), swimming, gymnastics (including with small weights - kettlebells weighing 1 - 2 kg). Daily physical activity lasting from 30 to 120 minutes is recommended, depending on your well-being and general health.
Sports for cerebral atherosclerosis are also allowed, but preference should be given to calm sports, such as race walking or swimming. Exercise can only be recommended after a medical examination, including a stress test.
Therapeutic exercise for cerebral atherosclerosis
Depending on the level of development of the disease (the degree of narrowing of blood vessels and the number and size of atherosclerotic deposits in the vessels of the head and neck), even strength exercises - resistance exercises - may be included in the exercise therapy (PT) program for cerebral atherosclerosis. This can be exercise therapy with weights (dumbbells, kettlebells) or an expander.
Therapeutic exercise for atherosclerosis of the blood vessels of the heart and brain aims to improve the lipid profile of the blood (reducing the level of “bad” cholesterol and increasing the content of good cholesterol - HDL), reducing the amount of triglycerides in the blood, increasing the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels.
What happens in the vessels?
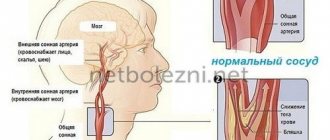
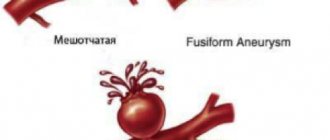
As a result of a failure in lipid (fat) metabolism in the body, cholesterol begins to be deposited on the vascular wall, gradually increasing and forming atherosclerotic or lipid plaques. Over time, they become larger and clog the channel, slowing down the normal flow of blood, and with it delaying the supply of oxygen to all parts of the brain.
Next, loose and then dense blood clots form in the vessels of the brain tissue, which accumulate near the nodes where the lateral branches depart from the arteries and in the cerebral cortex.
The main and middle arteries are at risk of overgrowing with thrombotic plaques. Thrombosis results in cysts, scars, and areas of dead cells (necrosis).
When nerve cells suffering from a lack of oxygen are destroyed, mental activity is disrupted.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis of neck vessels
The first manifestations of the disease can occur at an early age. They are expressed in the appearance of lipid stains in the vessels, from which atherosclerotic plaques subsequently develop. In the early stages of atherosclerosis, plaques do not interfere with blood flow in any way and the disease does not manifest itself clinically. Over time, atherosclerotic plaques narrow the lumen of blood vessels, which causes circulatory problems. The occurrence of atherosclerotic stenosis leads to a stable deterioration in blood flow.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis depend on the location of the process. Signs of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the head are transient ischemic attacks or stroke. With atherosclerotic narrowing of the coronary arteries, myocardial ischemia occurs, manifested by an attack of angina. Atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels of the heart in the elderly leads to myocardial infarction or sudden death. However, even complete occlusion (blockage) of an artery with plaque does not always result in a heart attack. Repeated ischemia may promote the development of collateral circulation, which mitigates the effects of occlusion.
Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities causes ischemia and the development of intermittent claudication. The atherosclerotic process in the renal arteries leads to the development of persistent arterial hypertension. Damage to the mesenteric arteries is manifested by symptoms of intestinal ischemia.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis of neck vessels:
- headache;
- memory impairment;
- periodic dizziness;
- emotional lability;
- visual impairment;
- speech problems.
In the later stages, small tears appear on the surface of the plaques, platelet adhesion is observed, and blood clots form, which can completely block the lumen of the vessel, leading to myocardial infarction or stroke.
Symptoms at different stages of the disease
The disease manifests itself in constantly developing brain failure, chronic circulatory disorders in the vessels, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
The main external signs of developing dystrophy and necrosis of brain cells are disturbances in the human psyche and mental activity, paresis, paralysis, urinary or fecal incontinence.
In this case, three base periods are distinguished.
First stage
Its signs are:
- weakness, fatigue;
- problems with remembering information;
- noise, ringing in the ears;
- dizziness, lightheadedness (for other causes of dizziness, read here);
- feeling of constriction, dull pressure in the head,
- sensation of “goosebumps” on the skin, numbness;
- “flies” before the eyes;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- flushes of heat and sweat on the face;
- increased cholesterol (cholesterol levels are described here).
During the development of atherosclerosis it is characteristic:
- memory impairment (especially for numbers, names, dates);
- decreased performance;
- problems with switching attention to different thoughts and activities;
- neurotic manifestations;
- low mood, pessimism;
- lack of desire to do anything;
- inhibition of reactions and thoughts;
- unmotivated tearfulness, touchiness, and for some, euphoria for no reason.
Period of progression and clear clinical symptoms
Signs may be:
- trembling hands, unsteadiness of gait, unintelligibility of speech;
- problems with coordination, slow pace (motor skills);
- anxiety, suspicion, the emergence of fears (stalking, spying, theft, death at the hands of relatives and neighbors);
- preoccupation with imaginary diseases;
- soreness while eating;
- intense constant headache;
- nightmares;
- complaints of strange sensations - tingling in the legs, “burning in the back of the head.”
Manifestations of psychopathic states:
- short temper, irritability, malice, hysterical reactions with exacerbations;
- development of stinginess, pettiness, constant grumpiness, sloppiness;
- obsessive thoughts (fixed ideas) about money, dangers, thieves;
- interests are narrowed to physiological needs for food and sleep.
This phase is characterized by anxiety-delusional, depressive syndromes, degenerative changes in brain tissue (atherosclerotic encephalopathy). If you have symptoms, seek help from a psychologist.
Period of dementia (dementia)
Among the signs are the following:
- temporary memory loss, deterioration in thinking ability;
- trembling of the head and hands;
- narrowing, tortuosity of the vessels of the fundus;
- increased pulse in the arteries of the neck (even with normal pressure);
- impaired memory of present events;
- problems with self-service (gas, iron, electricity, water turned on);
- violations of hygiene (during defecation, urination);
- disorientation in time and location.
At this stage, a person is practically unable to do without help, care, and constant supervision.
At this stage, an acute circulatory disorder in the cerebral vessels may occur in the form of strokes:
- Ischemic occurs due to blockage of blood vessels by a thrombotic substance. Oxygen does not reach the brain, cells begin to die. There is trembling and changes in the shape of the pupils, sensory disturbances, movements in the limbs, disturbances in speech, swallowing, vision, asymmetry on the face, a constricting headache with dizziness.
- Hemorrhagic stroke occurs less frequently, but its development is more rapid. In this case, the vessel does not close, but bursts, and blood flows out of it into the brain tissue. There are 2 areas of damage - a bloodless area and brain tissue, compressed by the resulting hematoma.
The complexity and danger of the last two stages of the disease is that it is very difficult to accurately determine the type of stroke in a patient based on the signs.
Diagnosis of cerebral atherosclerosis
Suspicion of this disease arises when examining the patient based on characteristic symptoms in accordance with the stage of the disease and his age.
A refined diagnosis is made based on the results:
- duplex ultrasound examination of extracranial vessels (assessment of their condition, absence or presence of narrowings, lipid plaques, blood clots);
- transcranial Dopplerography (analysis of the condition of intracranial arteries);
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- angiography of veins and arteries.
Treatment
Therapy involves the use of medication (conservative) and surgical techniques.
Surgery
If an ultrasound reveals more than 70% reduction in the diameter of a cerebral artery, the question arises about the need for surgical treatment of the damaged vessel. The most commonly used method is carotid endarterectomy. During the procedure, the vessel is dissected at the site of the blood clot, which is removed, and the integrity of the vessel is restored using sutures.
Other methods are endovascular operations, stenting.
Drug treatment
It is prescribed only by a doctor, taking into account contraindications, medical history and based on the results of studies and tests.
Therapy for cerebral atherosclerosis is aimed at:
- harmonization and restoration of lipid metabolism;
- lowering cholesterol levels (find out the norm from the table);
- elimination of metabolic disorders;
- treatment of concomitant diseases.
To solve these problems, several groups of medications are prescribed:
Statins are an active group of drugs that block cholesterol synthesis in the body, reduce its amount and prevent the formation of plaques. These drugs are Lovastatin, Mevacor, Fluvastin, Mekafor, Simvastatin, Pravastatin.
Means for improving microcirculation , dilating blood vessels, relieving spasms and at the same time preventing platelets from aggregating (sticking together) into clots:
- "Actovegin", "Cavinton", "Curantil".
- “Parmidin”, “Anginin”, “Aspirin” restore blood flow in small vessels, reduce the permeability of the walls, suppress the adhesion of platelets into clots, stimulate the resorption of blood clots, and prevent the deposition of fats and cholesterol on the vascular wall.
Vasodilators:
- “Nicotinic acid”, Nikoshpan” - expand small capillaries, strengthen the cells of the arterial wall, and effectively help reduce cholesterol concentrations. From simple standard means - “Papaverine”, “Eufillin”.
- Among the more progressive medications: Isoptin, Lomir, Amlodipine, Diazem. Cinnarizine and Nimodipine are suitable for long-term use.
- Medicines containing the alkaloid of the periwinkle plant - Vinpocetine (Cavinton, Bravinton) allow you to dilate blood vessels and stimulate metabolism.
- Dietary supplements based on the Gingko Biloba plant are good at relieving vasospasm, stimulating the work of brain cells, and reducing blood viscosity. Taking Gingium, Tanakan, Ginkor Fort is not combined with medications containing aspirin (Trombass, Cardio-magnyl) due to the risk of a serious increase in blood flow and bleeding.
Nootropic drugs activate the process of energy exchange in brain cells, improve memory, mental activity, cerebral circulation and cell resistance to oxygen deficiency.
They treat problems of mental disorders, senile dementia: Piracetam, Nootropil, Bemitil, Cerebrolysin, Aminalon, Sermion (nicergoline), Meclofenoxate, Phezam, Biotredin, Vinpocetine.
Medicines that activate energy metabolism and remove lipids - Lipostabil, Omacor, Eikonol, Thioctic acid.
Medicines to prevent the formation of blood clots when blood viscosity increases and the content of prothrombin in it increases - “Trental”, “Aspirin-cardio”, “TrombASS”, “Pentoxifylline”, “Cardiomagnyl”.
Doctor's advice
There are risk factors for developing stroke and heart attack in the next 5 years that have long been studied and taken into account, called the “SCORE Scale”, in which the higher the cholesterol, the greater the risk. Accordingly, cerebral atherosclerosis increases the risk of sudden cardiovascular accidents. In the first place in the treatment regimen are statins - drugs that lower cholesterol and help reduce the volume of plaques.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
Additional tools:
Fibrates – suppress the formation of fats and total cholesterol: “Clofibrate”, “Gemfibrozil”, “Fenofibrate”, “Atromid”, “Bezafibrate”, “Atromidine”.
Fibrates currently cause much controversy in the treatment of cerebral atherosclerosis. When used uncontrolled, fibrates are dangerous, so the dosage regimen and therapy regimen are agreed upon with a cardiologist.
“Nicotinic acid” and “Enduracin” are recommended in cases where atherosclerosis is associated with an increased amount of high-density cholesterol. They dilate blood vessels, but cause a rush of blood to the skin, so their use should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Hypocholesterolemic drugs - Neomycin, Guarem, Colestipol, Probucol, Lipostabil, Eikonol, Benzaflavin - reduce cholesterol, stabilize metabolism, and suppress the formation of blood clots.
In addition to the main treatment medications, it is advisable to take:
- Antioxidants that suppress oxidation processes: Mexidol, vitamins A, E, Aevit, P (strengthen the walls and increase the density and elasticity of blood vessels), microelements - potassium, silicon, selenium, vitamin C, which prevents the formation of fat deposits on the walls of arteries , group B improves the functioning of nerve cells. The use of Ascorutin (vitamin C plus rutin) requires monitoring the level of blood viscosity.
- For neurological manifestations and depression, antidepressants are used: Paxil, Azafen, Amitriptyline.
- When phobias, panic attacks, or severe anxiety appear, tranquilizers are prescribed: Alprazolam, Diazepam, Atarax, Phenazepam.
- If sleep is disturbed, sleeping pills and antidepressants (Donormil, Nitrazepam) are prescribed.
- For headaches and myalgia, the use of drugs that relieve pain and spasms is indicated: “Spazgan”, “Spazmalgon”, “Pentalgin”.
Among the more progressive medications: Isoptin, Lomir, Amlodipine, Diazem. Cinnarizine and Nimodipine are suitable for long-term use. Nootropics are prescribed with caution for dementia, as well as in older people - they activate the nervous system, and thus, as a side effect, can cause hyperexcitability, irritability, and aggression.
Physiotherapy for cerebral atherosclerosis
Aimed at activating blood circulation in the brain and processes in nerve cells, increasing arterial tone, and improving adaptive capabilities. This:
- Electrophoresis with medications.
- Hydrotherapy using carbon dioxide, oxygen, iodine-bromine, sodium, radon baths.
- Electrosleep procedures to strengthen and restore the nervous system.
- Special therapeutic exercises to improve and stimulate proper motor skills, motor functions, and relieve muscle spasms.
Diet therapy
The main provisions of the diet for cerebral atherosclerosis:
- Salt per day up to 3 g.
- Meals are frequent, in small portions.
- The amount of fat is no more than 65 g per day, of which 72% is vegetable.
- The amount of protein is not limited. Animal protein prevents fatty liver and cholesterol deposits in blood vessels.
What you can do:
- lean veal, pork, beef, turkey, fish;
- eggs in the amount of 1 pc. per day: in the form of steamed, baked, soft-boiled omelettes; milk, low-fat cottage cheese, kefir, peas, beans, buckwheat, wheat, oatmeal;
- once a week a little caviar and tongue are allowed. 10-20 g per week of butter is allowed;
- sunflower, rapeseed, corn, cottonseed, olive seeds promote intestinal motility and remove excess cholesterol;
- seafood is very healthy (up to 6 times a week): fish, squid, shrimp, mussels, seaweed, kelp;
- vinaigrettes, salads from cucumbers, zucchini, cabbage, tomatoes, potatoes, pumpkin, soybeans, eggplant, pumpkin, dill;
- You can have low-fat sausage, ham, mild cheeses, dry cookies, marmalade, dried fruit candies, muesli.
What not to do:
- animal fats, offal products saturated with cholesterol, including liver, brains, kidneys are excluded;
- limit sweet dishes, fresh white bread, pure sugar, jam, honey, jams, cakes, buttery sweet cookies;
- Rich meat and mushroom soups, cream, ice cream, butter and custard creams, mayonnaise and sauces based on it, dark chocolate, strong coffee, tea, and alcohol are not recommended.
Folk remedies
In complex therapy of atherosclerosis, traditional methods are used with caution and after consultation with a doctor. They must be combined with medications
Among them:
- Collection for spasms of cerebral vessels, nervous tension. A collection is prepared from valerian root, cudweed, and St. John's wort in equal parts. Drink as an infusion.
- Honey and lemon juice are mixed equally with vegetable oil and taken a teaspoon in the morning (dangerous for allergies and gastritis).
- Drink 100 g of freshly squeezed potato juice for frequent headaches (harmful for stomach diseases).
- An alcohol tincture with garlic and lemon along with zest is known (extremely dangerous for gastritis, peptic ulcers, inflammation of the pancreas).
- Dill seeds (teaspoon), brewed in a glass of boiling water. Drink as tea for headaches.
Despite the fact that atherosclerosis occupies only the walls of blood vessels, the consequences for the brain, the entire body, psyche and intellect are devastating. A person gradually loses his personal qualities and turns into a thoughtless organism that requires constant care and regular feeding.
To prevent such an existence, you should pay attention to the very first signs of the disease, do all the necessary examinations and take timely the whole range of measures aimed at recovery.
How to recognize and how to treat cerebral atherosclerosis, watch the video:
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://www.angiolsurgery.org/recommendations/2013/recommendations_brachiocephalic.pdf
Rate how helpful this article was
4.5 10 people voted, average rating 4.5
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Treatment of cholesterol plaques in brain vessels
Treatment of cholesterol plaques in the vessels of the brain is more effective the earlier it is started. The problem is that in the early stages, even if symptoms appear, rarely do patients see a doctor. Thus, all of these symptoms may disappear after normal rest, prolonged (sufficient) sleep, or even simple physical activity (such as walking), when blood flow improves. The patient does not pay attention to the symptoms, since they themselves have passed.
See also:
How to treat if you have high blood cholesterol
How to treat cholesterol plaques
Medicine that dissolves plaques
What to do if you have high blood cholesterol
Treatment of cholesterol plaques in the vessels of the brain is aimed at reducing the level of cholesterol in the blood, for which methods of extracorporeal hemocorrection (blood sampling, purification of cholesterol and “returning” it to its place), drug treatment (statins or drugs based on nicotinic acid, drugs for treatment of vascular atherosclerosis). The medications do not destroy cholesterol plaques in the blood vessels of the brain; they only reduce and normalize high levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood. Sometimes statins can be discontinued, but often they are taken for life.
Treatment with medications is always complemented by diets against cholesterol plaques in the blood vessels of the brain. As part of a diet with high cholesterol levels in the blood, fatty foods and foods with high cholesterol levels are excluded. It is recommended to eat as much plant foods as possible (soluble and insoluble fiber effectively cleanse the blood of LDL). Omega-3 and omega-6 unsaturated fatty acids (fish oil, but also found in flaxseed oil, nuts) are effective against LDL.
Neither diet, nor medications, nor dietary supplements for high cholesterol will help destroy cholesterol plaques - unfortunately, there are no drugs against atherosclerotic deposits. However, diet and drug treatment will help slow down the formation of new atherosclerotic deposits and reduce the risk of stroke.
How to remove cholesterol plaques in the head?
Unfortunately, it is impossible to remove atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels (arteries and veins) of the head. Procedures such as stenting or bypass surgery, or even laser angioplasty, can be applied to the neck, arms, legs, and even the heart (in the coronary vessels), but they are not possible in the brain. You can relieve symptoms and prevent the development of the disease by treating atherosclerosis with nutrition, taking statins, and through exercise.