08 October 2021
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic endocrine disease that is caused by a deficiency of insulin produced. The following types of this disease are distinguished: type 1 diabetes (insulin dependent), type 2 diabetes (non-insulin dependent).
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic endocrine disease that is caused by a deficiency of insulin produced. The following types of this disease are distinguished: type 1 diabetes (insulin dependent), type 2 diabetes (non-insulin dependent). Type I occurs when there is insufficient production of insulin, and type II occurs when the body is unresponsive to insulin.
Type I diabetes occurs due to an absolute deficiency of insulin in the body against the background of a hereditary predisposition. Manifestation of the disease is possible after contact with certain viruses (rubella, mumps, hepatitis, mononucleosis), direct damage to pancreatic cells that produce insulin. This type of diabetes is often combined with other autoimmune diseases (glomerulonephritis, thyroiditis and others).
Type II diabetes develops as a result of a relative deficiency of insulin in the human body against the background of hereditary predisposition, poor nutrition, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, stress, long-term use of certain medications (diuretics, hormones, salicylates, cytostatics), and old age.
Can stress trigger diabetes?
Diabetes often occurs due to stress, poor nutrition and a sedentary lifestyle. In a stressful situation, all the body’s forces are concentrated on the changes taking place. This leads to suppression of the gastrointestinal tract, decreased sex drive and insulin release.
Under stress, a hyperglycemic state and insulin deficiency develop, as it reflexively inhibits basal insulin secretion and promotes the release of sugars.
Chronic stress can cause a decrease in blood glucose, so a person automatically tends to eat foods that can quickly increase sugar. Excessive indulgence in fatty and sugary foods results in weight gain. Against this background, insulin enters the blood in greater quantities than necessary. This negatively affects the condition of the pancreas and can provoke diabetes.
Another factor that proves the relationship between stress and diabetes is increased hormonal release, which provokes increased activity of the thyroid gland. If a person is constantly in a stressful situation, then his level of glucocorticosteroids increases. A complication in this case can be not only diabetes, but even a heart attack or stroke.
Stressful situations can lead to diabetes. In some cases, pathology is provoked by chronic stress, in others – one episode is enough.
What happens during stress
Having diabetes does not have any effect on the release of stress hormones during difficult life situations. Still under the influence of the tense state of the nervous system, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system gives a signal to the adrenal cortex to synthesize cortisol, and adrenaline and norepinephrine are still produced in large quantities. Together, they have the same effect on the body of a diabetic as on a healthy one, i.e. they increase the heart rate, provoke an increased need for glucose, release it from glycogen stores and lead to a desire to eat something sweet. In other words, stress leads to a sharp increase in blood sugar levels, which for a diabetic can result in very sad consequences, while a healthy person experiences a surge of strength as a result of a sharp increase in the energy reserves of cells.
In addition, stress can indirectly affect the condition of a patient with diabetes. The fact is that when experiencing negative emotions, a person tries to cope with this condition using the simplest and most accessible methods. Therefore, in such situations, he is often drawn to factors that aggravate the course of diabetes:
- drinking alcohol in large quantities;
- a decrease in the level of physical activity, the predominance of the desire to relax on the couch in front of the TV over the need to move to increase the sensitivity of tissues to insulin;
- violation of the diet and overeating (the desire to eat something sweet to make up for the apparent glucose deficiency can be irresistible);
- decreased control over blood sugar levels.
At the same time, critical blood glucose levels in diabetes can be reached very quickly, since the body is not able to absorb it in full. The consequence of this is an increase in the thickness and viscosity of the blood, which, in combination with tachycardia and high blood pressure, creates an increased load on the cardiovascular system and kidneys. Also, the result of maintaining high sugar levels can be other complications characteristic of hyperglycemia, including:
- ketoacidosis and ketoacidotic coma;
- diabetic macroangiopathy;
- diabetic nephropathy;
- diabetic encephalopathy;
- diabetic neuropathy;
- diabetic retinopathy;
- diabetic foot syndrome.
Therefore, during stressful situations, it is important not to succumb to weakness, but rather to strengthen control over the course of diabetes, strictly follow a diet, lead an active lifestyle and deal with stress using safer and more effective methods than alcohol, smoking and an apathetic state.
Ketoacidosis and ketoacidotic coma
Ketoacidosis is the most common complication of diabetes mellitus. It represents a serious disruption of the mechanisms regulating carbohydrate metabolism and can lead to the development of ketoacidotic coma and death. Stress causes a sharp rise in blood sugar levels, but the available amount of insulin is not enough to transport it into the cells.
When the permissible threshold is exceeded, glucose begins to be excreted from the body in the urine along with a large amount of liquid and electrolytes dissolved in it. Against this background, the blood thickens, but since the body needs energy to get out of a stressful situation and cannot get it from glucose, it begins to use fatty acids, which are metabolized in the liver. As a result of their chemical transformations, ketone bodies are formed, well known to everyone as acetone. This is the smell that can be felt from the patient’s mouth and from his urine.
This is accompanied by the appearance of characteristic symptoms:
- severe thirst accompanied by frequent urination with the excretion of large amounts of urine;
- dry skin, feeling of tightness, flaking, itching;
- rapidly increasing weakness, loss of performance, drowsiness;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea, vomiting;
- irritability;
- headache.
If emergency measures are not taken at this time to reduce sugar levels, the patient may lose consciousness, severe dehydration will occur, the severity of reflexes will be greatly reduced or absent, and coma will occur. In such situations, treatment is carried out in a hospital. Patients begin insulin therapy and are also prescribed drips to restore water and electrolyte balance. The sooner treatment is started, the higher the chance of avoiding complications. Death from ketoacidosis occurs in 5% of patients under 60 years of age and in 20% after this age.
Diabetic macroangiopathy
Diabetic macroangiopathy is also a complication of long-term diabetes if the endocrinologist’s recommendations regarding lifestyle and nutrition are not followed. With its development, atherosclerotic damage to the arteries occurs, which leads to angina pectoris, coronary heart disease, ischemic stroke or myocardial infarction.
Long-term hyperglycemia, especially in combination with high blood pressure in patients with abdominal obesity, which is observed against the background of the production of stress hormones, leads to thickening of arterial walls and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in them. Prolonged stress and depression, during which the patient ceases to control the course of diabetes, can lead to macroangiopathy progressing and leading to the formation of blood clots and blocking the lumen of the artery. The consequence of this will be the impossibility of blood passing through the vessel and severe tissue hypoxia in the affected area, which will provoke the complications of diabetic macroangiopathy listed above.
In this case, patients may not notice pronounced changes in their condition. Only sometimes there is numbness and coldness in the feet, swelling and pain in the leg muscles, and lameness. A sharp disruption of blood circulation can cause the development of trophic ulcers and gangrene. Treatment is selected individually depending on the type of diabetes mellitus, the degree of existing changes in the blood vessels and the presence of complications.
Diabetic nephropathy
This is a complication of diabetes, manifested by the occurrence of changes in the vessels of the kidneys, resulting in a decrease in their filtration capacity and the development of chronic renal failure. Typically, its development is preceded by the occurrence of diabetic macroangiopathy against the background of hyperglycemia and arterial hypertension.
The disease develops slowly, and the nature of its manifestations depends on the stage of pathological changes. Initially, there are no symptoms at all, but later, when performing a urine test, microalbuminuria can be detected, i.e., the excretion of a small amount of protein in urine. During physical activity and stressful situations, jumps in blood pressure are observed.
Gradually, the disease progresses, and pathological changes become irreversible. This leads to the development of nephrotic syndrome, which is accompanied by abundant excretion of protein in the urine, the appearance of edema, weakness, dry mouth and constant thirst, against the background of a small volume of urine, as well as headaches and aching in the lumbar region.
It is very important to diagnose developing diabetic nephropathy in time and take measures to stop this process. Therefore, you must not ignore follow-up examinations by an endocrinologist and tests, despite any difficulties in life. In such situations, patients are prescribed ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor antagonists, and a low-fat, salt-free diet. In later stages of development, the patient may require hemodialysis.
Diabetic encephalopathy
Diabetic encephalopathy is a complication of diabetes mellitus, in which brain damage occurs with the development of memory impairment, decreased intellectual abilities, and increased irritability. It is often accompanied by the occurrence of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Diabetic encephalopathy usually develops gradually against a background of hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis, and elevated blood pressure. As already mentioned, stress, especially severe stress, is precisely the triggering factor for the occurrence of such conditions. Often diabetic encephalopathy accompanies diabetic macroangiopathy and leads to:
- increased fatigue;
- anxiety, aggressiveness;
- problems with concentration;
- headaches.
Often the condition is complicated by a pathological fixation on the disease, which causes depression and further worsens the patient’s condition due to a new release of increased amounts of cortisol and adrenaline, an attack of hyperglycemia and arterial hypertension. If left untreated, patients may experience a progressive decline in intellectual abilities and dementia, as a result of which they are no longer able to independently control the course of diabetes.
Treatment is prescribed based on the patient's condition. First of all, it is aimed at restoring normal sugar levels, as well as improving cerebral circulation. Antihypertensive therapy and measures to normalize the psychological state may also be prescribed.
Diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is considered one of the most common complications, one of the causes of which is uncontrolled hyperglycemia. Obesity, high blood pressure and smoking increase the risk of its occurrence. The disease is characterized by damage to peripheral nerves, which leads to disruption of the conduction of nerve impulses, sensitivity disorders of individual parts of the body, as well as the addition of a wide variety of disorders of the somatic and autonomic nervous system.
Due to the fact that it can be accompanied by a huge number of disparate symptoms, it is quite difficult to recognize the development of diabetic neuropathy in a timely manner. It can lead to the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract from gastritis to cholelithiasis, fecal incontinence and fatty hepatosis, pathologies of the genitourinary system, etc.
When peripheral nerves are damaged, motor and sensory disorders may occur. Most often they affect the legs, which is accompanied by the appearance of:
- burning sensations;
- numbness;
- skin tingling;
- pain in toes and feet;
- muscle cramps;
- disturbances of sensitivity, both in the direction of its increase and depression.
When treating this complication, it is also necessary to maintain glucose levels within acceptable values, as well as normalize blood pressure and weight. To eliminate the consequences of nerve damage, long courses of treatment with B vitamins, antioxidants, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed.
Diabetic neuropathy can subsequently lead to the development of diabetic foot syndrome.
Diabetic retinopathy
This complication of diabetes mellitus is one of the types of angiopathy, which damages the blood vessels of the retina. It occurs against the background of long-term persistence of elevated sugar levels, arterial hypertension, obesity, chronic renal failure and is caused by increased permeability of the retinal capillaries, blocking of their lumen and the formation of neoplasms.
The main danger of diabetic retinopathy is the almost complete absence of symptoms, as vision deteriorates slowly. Patients may notice slight blurriness, blurred vision, or the appearance of floating spots. Initially, difficulties arise with reading or doing small work at close range, but later diabetic retinopathy threatens complete blindness.
Treatment of the disease is carried out through careful monitoring of glucose levels and the prescription of angioprotectors, antiplatelet agents and drugs to lower blood pressure. With pronounced progression of vision loss, laser coagulation of the retina is indicated.
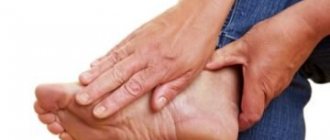
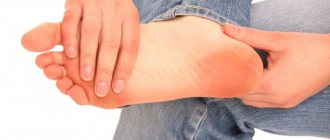
Diabetic foot syndrome
Damage to foot tissue due to diabetes mellitus occurs less frequently than other complications, but also occurs. It is characterized by the formation of cracks in the skin, ulcers with signs of tissue necrosis, areas of increased keratinization, as well as deformation of the feet, which together leads to pain in the legs. In advanced cases, diabetic foot syndrome can be complicated by gangrene. Treatment in such situations is quite complex, and sometimes surgery is required to excise dead tissue, followed by dressings, aggressive antibiotic therapy and laser therapy.
How it works?
It's all about the body's response to stress, which is called “fight or flight”. This reaction was first described by the American psychophysiologist Walter Cannon. It includes many aspects, but let's focus on one of them.
- Worry and anxiety cause the brain to release cortisol from the adrenal glands.
- The next stage is the production of sugar in the blood (glycogenesis), which leads to its increased content - hyperglycemia.
In this condition, the body's energy resources are released, and normally they are used for further enhanced muscle work.
It is natural for us to experience stress when faced with critical situations - this is a rational way to use the body's reserves. But what if anxiety and worry overwhelm you not just every day, but every few hours?
conclusions
Science has demonstrated the direct and indirect effects of long-term stress on the development of hypertension and diabetes. When prescribing an antihypertensive drug, the doctor is responsible for patients from the moment of diagnosis until treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to take into account individual risk and seek the most appropriate solution for each individual patient.
According to guidelines for the treatment of hypertension published by the European Society of Cardiology, the first and perhaps most important goal is to reduce blood pressure itself to the target value, that is, less than 140/90 mmHg. Art., And for patients with CD – less than 140/85 mm Hg.
The new guidelines state that all major antihypertensive drugs—diuretics, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers—are appropriate for the initiation and follow-up of hypertension. However, if the hypertension is refractory or the patient has a specific debilitating condition, such as stress or metabolic syndrome, other antihypertensive drugs, such as imidazoline receptor agonists such as rilmenidine, may be added.
Such drugs not only effectively control, but also reduce blood pressure variability. have a beneficial effect on metabolism, i.e. reduce insulin resistance, hyperactivity of the sympathetic nervous system, and heart rate.
It is important to understand that all drugs have side effects and contraindications, and therefore should be taken exclusively as prescribed by an endocrinologist.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Can stress trigger diabetes and why?
Under stress and emotional stress, there is an increased production of stress hormones: cortisol and adrenaline. The latter, in turn, cause an increase in blood glucose levels. This is due to the need for energy to overcome stress. In order to reduce blood sugar, compensation reactions must occur in the body, which are very weakened in people prone to diabetes.
Glucose is necessary to combat stress.
Negative health processes occur against the background of stress. The body is forced to mobilize all resources to overcome its influence. The main source of energy needed to overcome stress is glucose. As a result, the level of glucose and insulin in the blood will increase. It is enough to observe your body in various states yourself, measuring your sugar level with a regular glucometer. You can analyze how the glucose level will increase in a state of stress and how much the sugar level can rise, as well as how the indicator changes when using relaxation techniques.
Regular emotional shocks and elevated insulin levels lead to the pancreas being in a state of systematic “shock.” With associated factors, this condition significantly increases the risk of diabetes mellitus. Often systematic stress may be quite enough to trigger the mechanisms of disease development.
- Is diabetes transmitted through blood or saliva, inherited from parents?
Return to contents
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is manifested by hyperglycemia with blood glucose levels that exceed normal values, but do not reach diagnostic values for making a diagnosis of diabetes. Gestational diabetes is diagnosed during pregnancy. Women with this diagnosis have an increased risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth. They also have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. Most often, the diagnosis of gestational diabetes is made during prenatal screening; patients do not complain.
Decreased glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glycemia
Reduced glucose tolerance (PTH) and impaired fasting glucose (IFG) are intermediate conditions between normal and diabetes. People with PTH and IFN are at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes, but this may not happen.
How to deal with and control stress?
How to set yourself up in a positive way.
It is impossible to completely eradicate the risks of emotional turmoil in modern life, but minimizing the risk of emotional turmoil is quite possible. Methods for relieving stress are simple, and anyone can apply them in modern life.
Fact! A healthy and active lifestyle will help you overcome the effects of stress. The patient must learn to let go of problems rather than accumulate.
| How can a modern person deal with stress? | ||
| What do we have to do | Description | Characteristic photo |
| Breathe correctly! | The patient sits in a comfortable chair or lies down on a hard surface, closes his eyes, relaxes and takes a deep breath through his nose, then exhales through his mouth. It is worth performing the manipulation until the tension is completely relieved. The method is easy to use and helps to cope with difficult life situations. |
|
| Meditation | You can meditate alone by turning on some relaxing music. You can do this in silence, listening to your own breathing. This method is effective and helps increase stress resistance. | Meditation. |
| Simple physical activity | Sports will also help lift your mood; stress goes away along with body movements. Your favorite movements will be beneficial: gymnastics, stretching. We should not forget about the benefits of yoga for the human body. | The benefits of sports. |
| Music | Listening to calm, classical music or nature sounds can bring maximum benefit. | Listening to music will be beneficial. |
| Positive thoughts | The main problem of patients who regularly face stress in their daily lives is the inability to think positively. Any trouble in life can be turned in your favor if you put some effort into it. | Positive mood. |
| Cold and hot shower | A contrast shower is not just a hardening procedure that helps improve immunity. This method will allow you to relax and find a solution to the current situation, having previously eliminated anxiety. | Cold and hot shower. |
| Introspection | It is important to analyze your behavior in stressful situations and identify the true cause of anxiety. By eliminating the factor that provokes discomfort, you can cope with stress. | It is important to regularly analyze the situations that have occurred. |
| Hobbies you like | Unreasonable anxiety often occurs among people who have a lot of free time. It is important to find a hobby you like, it could be knitting, drawing, dancing. Any activity that brings satisfaction from the work done will be beneficial. | It is important to find a hobby that brings satisfaction. |
It is worth remembering that various forms of activity will help you better cope with any negative factors. Leading psychologists recommend combining several techniques, for example, meditation, active sports and drawing. In your free time from work, calm musical compositions will help you to abstract yourself from problems; it can even be pop music, if the patient likes it.
Diabetes and stress are closely related. In order to minimize the impact of negative factors, you need to provide your body with proper rest, including sleep at night.
What is the prognosis for treatment?
With proper and well-chosen treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
There are different types of insulin. Many children use insulin pump therapy. But it is important to know that much here depends not on the treatment, but on how the child and his parents perceive the diagnosis and how they treat it. They will have to learn a lot. The first thing is to streamline your diet
and lifestyle. Please note that the diet does not change completely, it just becomes correct. And this is not just eating chips, chocolates and sandwiches.
Secondly, in childhood diabetes mellitus, blood glucose control
. Children do this often: optimally 6–8 times a day. There are now many different means to control blood glucose. First of all, these are glucometers, when for each measurement of glucose in the blood the child needs to prick his finger. But now there are systems where a sensor is placed in children for two weeks (for example, in the shoulder area). And with a special device (scanner) you can determine blood glucose every minute by bringing this scanner to the sensor. And then you don’t need to prick your fingers 6–8 times a day.
Is a full life possible, and why will you have to give up forever? And our children live full lives
. Participate in various competitions and competitions. I would say, on the contrary, they are smarter and more capable than children without diabetes. Probably because they had to grow up earlier. Learn to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, and maintain a proper daily routine. They count bread units (this is the amount of carbohydrates) in order to correctly inject themselves with the required dose of insulin.
However, children with diabetes and their parents should be aware that they will be faced with the difficult question of choosing a profession. The fact is that some professions are contraindicated for diabetes:
- with heavy physical activity (miners);
- with significant neuropsychological stress (air traffic controllers, transport drivers);
- with irregular working hours, at night, with an unfavorable microclimate, with contact with toxic substances (chemical production).