Classification of neurons
Nerve cells are diverse as such, so neurons can be classified based on their different parameters and attributes, namely:
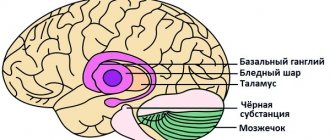
- Body shape. In different parts of the brain there are neurocytes of different soma shapes: stellate;
- fusiform;
- pyramidal (Betz cells).
- unipolar: have one process;
- axo-somatic. In this case, the axon contacts the soma of the neighboring cell of the nervous tissue;
Types of neurons
In order to carry out conscious movements, it is necessary that the impulse formed in the motor convolutions of the brain can reach the necessary muscles. Thus, the following types of neurons are distinguished: central motor neuron and peripheral motor neuron.
The first type of nerve cells originates from the anterior central gyrus, located in front of the largest groove of the brain - Roland's groove, namely from Betz's pyramidal cells. Next, the axons of the central neuron deepen into the hemispheres and pass through the internal capsule of the brain.
Peripheral motor neurocytes are formed by motor neurons of the anterior horns of the spinal cord. Their axons reach various formations, such as plexuses, spinal nerve clusters, and, most importantly, the performing muscles.
Functions of nerve tissue cells
Neurons that are located in the brain are a kind of knowledge base, theoretically capable of accommodating and storing the entire amount of information accumulated by humanity over thousands of years. The brain remembers absolutely all information received during life regarding interaction with the external environment and processes occurring in the human body. At the same time, a person cannot voluntarily extract from the depths of memory all the data that is stored in the brain matter. Functions of neurons:
- Reception (reception) of impulses. Cells of nervous tissue receive certain signals coming, for example, from sensory organs (light, temperature, olfactory, tactile influences) or other cells.
- Control of physiological processes through excitation or inhibition. Receiving a signal, a section of a nerve tissue cell reacts by transitioning to an excited or inhibited state.
- Transfer of excitation. Signals in a state of excitation are transmitted from one part of the nerve cell to another part of its process. In this way, the transmitted signal can cover a distance of 1.5 m (for example, from the medulla oblongata to the distal parts of the legs).
- Impulse conduction. Signals are transmitted from one nerve cell to another or to effector (executive) organs, the activity of which is regulated by reflexes - the body's responses to stimuli. Effectors include skeletal and smooth muscles, endocrine and exocrine glands.
Damage to nerve cells causes them to lose their ability to conduct electrical impulses and communicate with each other. Disruption of information exchange processes in neuronal structures provokes malfunctions in the functioning of the whole organism. A person loses the ability to perform movements, speak and perceive speech, feel, remember, and think.
Is it possible to improve brain function?
As with any other organ, the condition of the brain directly depends on a person’s diet and activity. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can actually improve its functioning.
Effect of diet
Poor nutrition can worsen a person’s health and cause the development of heart disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. And these diseases, in turn, increase the risk of dementia.
To improve brain health, you should include the following foods in your diet:
- dark-skinned plant foods (such as blueberries, broccoli, spinach), as they contain a lot of vitamin E, and red peppers and sweet potatoes are rich in beta-carotene, both of which are extremely beneficial for the brain;
- fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel) are excellent sources of Omega-3 fatty acids, which improve cognitive function;
- walnuts, pecans (antioxidants contained in nuts also have a beneficial effect on brain health).
Physical activity
The role of physical activity in maintaining brain health cannot be underestimated. It is enough to devote at least 30 minutes to active walking every day to reduce the risk of deterioration in brain function. Swimming, jogging, and cycling are also beneficial.
Mental training
The brain works on the principle of muscles: the more actively it is used, the better it performs its functions. Therefore, you should not ignore special mental training to maintain organ health. By the way, according to one scientific experiment, people who are passionate about logical tasks are 29% less likely to develop dementia [5].
Other common myths
Besides the 10% myth, there are many other misconceptions about the human brain. But most of them already have a scientific refutation.
Left and right hemisphere
Many people have probably heard that creative people have a dominant right hemisphere, while people with a logical type of thinking have a dominant left hemisphere. However, recent research shows that all this is nothing more than a myth. If a person is healthy, both hemispheres are equally developed [6]. The truth is that the hemispheres are actually responsible for performing different types of tasks. Thus, the left controls speech, and the right controls emotions [7].
Effect of alcohol
Long-term alcohol abuse can cause a number of health problems, including problems with the brain. However, it cannot be said that each serving of alcohol kills part of the brain cells - this is a misconception. The damage process is quite complex. For example, it has been proven that if a woman abuses alcohol during pregnancy, there is a high risk that the baby will be born with fetal alcohol syndrome. In people with this disease, the brain is smaller than normal and contains fewer cells. Such children will experience learning difficulties in the future and may have other disabilities.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Subliminal messages
There are many misconceptions about so-called subliminal messages and their influence on the human brain. Scientific research has confirmed that information received from the outside during sleep in the form of recorded sounds can cause a certain emotional reaction in a person [8]. But using this method to study foreign languages or other disciplines, as some believe, is inappropriate. Scientific experiments show that this method will help you remember previously known information, but it is impossible to learn new things in this way.
Convolutions
The relief of the human brain consists of grooves and convolutions. There is an opinion that every time a person learns something new, a new convolution is formed on the surface of the organ. But this is a misconception. Convolutions are formed before birth and continue to form in childhood.
How many neurons were there in the brain studied by scientists?
“We estimate that the brain, on average, consists of 86 billion neurons,” Herculano-Housell said. “No brain that has been studied has even close to 100 billion neurons.” Perhaps someone will consider the difference of 14 billion not so significant, but in fact it is a lot. Judge for yourself: a baboon's brain consists of 14 billion neurons. Half of a gorilla's brain contains the same number of neurons. So, in fact, the difference is quite impressive.
Thus, based on recent research, there are about 86 billion neurons in the human brain.
How many neurons are there in the brain of animals?
According to Herculano-Housell, the human brain is very similar to the brains of other primates, with one difference: we have many more brain cells, which require enormous amounts of energy to fuel and maintain.
According to experts, approximately 25% of all energy goes specifically to supporting these cells.
If we compare the number of neurons in the human brain and other representatives of the animal world, the difference looks simply huge. So how many neurons are there in the brains of other animals?
Fruit fly – 100 thousand neurons
Cockroach – 1 million neurons
Mouse – 75 million neurons
Cat – 1 billion neurons
Chimpanzee – 7 billion neurons
Elephant – 23 billion neurons
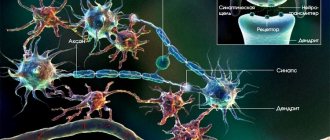
Interaction with neurotransmitters
Neurons of different locations communicate with each other using electrical impulses of a chemical nature. So, what is the basis of their education? There are so-called neurotransmitters (neurotransmitters) - complex chemical compounds. On the surface of the axon there is a nerve synapse - the contact surface. On one side there is a presynaptic cleft, and on the other there is a postsynaptic cleft. Between them there is a gap - this is the synapse. On the presynaptic part of the receptor there are sacs (vesicles) containing a certain amount of neurotransmitters (quanta).
When the impulse approaches the first part of the synapse, a complex biochemical cascade mechanism is initiated, as a result of which the sacs with mediators are opened, and quanta of mediator substances smoothly flow into the gap. At this stage, the impulse disappears and reappears only when the neurotransmitters reach the postsynaptic cleft. Then biochemical processes are activated again with the opening of the gates for mediators and those, acting on the smallest receptors, are converted into an electrical impulse that goes further into the depths of the nerve fibers.
Meanwhile, different groups of these same neurotransmitters are distinguished, namely:
- Inhibitory neurotransmitters are a group of substances that exert an inhibitory effect on excitation. These include: gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA);
- glycine.
- acetylcholine;