A common state of general mental helplessness, which manifests itself in the form of a severe decrease in memory, intelligence, will, and is also reflected in emotional instability and decreased ability to work, is usually called psychoorganic syndrome. Although this disorder can occur at any age, it is often diagnosed in older people, who already have a deteriorating ability to quickly adapt to constantly changing environmental conditions.
Content:
- Psychoorganic syndrome, causes
- Complaints and symptoms of organic psychosyndrome
- Psychoorganic syndrome, clinical variants
- Diagnosis of organic psychosyndrome
- Psychoorganic syndrome, treatment
- Psychotherapy
- Rehabilitation
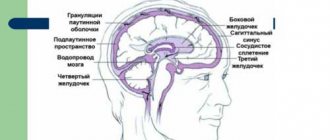
The human brain often suffers due to exposure to painful factors. As a result, the patient develops a pathological complex, called in medicine psychoorganic syndrome (PS, organic psychosyndrome). It is manifested by memory impairment, deterioration of intellectual capabilities, emotional disturbances and other mental disorders. Identified deviations must be treated with medication and psychotherapeutic methods in specialized clinics.
Danger to yourself and others
The social significance of the clinical picture is great. If at the asthenic stage patients can take care of themselves, and many are able to work, then with increasing severity of the disease they can first become dangerous for people around them (explosive, euphoric stage), and later for themselves (apathetic stage) due to pronounced apathy and helplessness.
Therefore, organic mental disorders require timely correction. If there is one or another option, you need to contact a psychiatrist.
All materials on the site are presented for informational purposes only, approved by certified physician Mikhail Vasiliev, diploma series 064834, in accordance with license No. LO-77-005297 dated September 17, 2012, by a certified specialist in the field of psychiatry, certificate number 0177241425770.
Psychoorganic syndrome, causes
A wide variety of pathologies can lead to the development of the disease.
Most often, doctors have to identify the following causative factors:
- Atrophic phenomena in the brain caused by senile processes.
- Atherosclerosis of blood vessels supplying brain tissue.
- Traumatic head injuries.
- Viral and bacterial infections affecting the central nervous system. Often specialists have to deal with meningitis and encephalitis.
- Tumor processes.
- Brain surgeries.
- Epilepsy.
- Diseases of the endocrine system – diabetes mellitus, damage to the thyroid gland.
- Cardiovascular pathology, strokes.
- Substance addiction.
Methods for treating insidious syndrome
Regardless of whether the disease has struck a teenager or an elderly person, close attention should be paid to quickly getting rid of the disease, which can significantly worsen the quality of life. By turning to experienced, highly qualified medical specialists, you can receive competent assistance that will allow you to once again experience the beauty of life. Doctors often prescribe antioxidants, vitamins and nootropics to improve mental performance. If aggressiveness is present, treatment will be supplemented with antipsychotic drugs.
Complaints and symptoms of organic psychosyndrome
The disease develops gradually. Minor manifestations become more obvious and are supplemented by new ones.
Patients are diagnosed with:
- Asthenic syndrome with weakness, emotional instability, headaches associated with weather changes, increased blood pressure, and attacks of tachycardia.
- A progressive decrease in the ability to concentrate.
- Absent-mindedness, inattention.
- Mental exhaustion and physical fatigue.
- Weakening of memory, loss of the ability to remember, forgetfulness, turning into amnesia.
- Confabulatory syndrome with distorted memories, fantasizing.
- Narrowing of intellect and usual range of interests. The patient loses the ability to isolate the main from the secondary.
- Dementia process.
- Impoverishment of speech.
- Loss of self-criticism, ethical distortions - a decrease in the ability to determine what is good and what is bad.
PS is characterized by Walter-Bühel's diagnostic triad:
- Increasing memory loss.
- Progressive intellectual impoverishment.
- Emotional and volitional deviations.
Main symptoms of the disease
Memory impairment. There is a significant decrease in the fixation type of memory. A person begins to have difficulty assimilating new information. Often forgets what he did a few minutes ago or cannot retell what he is doing at the current time. It is difficult for a person suffering from this syndrome to maintain the correct chronology of recent events. Other types of memory may also suffer.
Intellectual impairment. With such disorders, a person’s cognitive activity decreases and his range of interests narrows. He begins to operate with simpler judgments, cannot perceive the situation as a whole, logic and the separation of the particular from the general suffer. Lengthy discussions emerge. Thinking becomes rigid, that is, it is difficult for a person to change the plan of activity or switch to something new.
Changes also affect personality. A person becomes more rude, egocentrism increases, and people around him cause negativity and dissatisfaction. Often the patient does not have a critical attitude towards his condition.
Emotional disorders. Psychoorganic syndrome is characterized by neurosis-like disorders:
- various fears (phobias, nightmares);
- increased anxiety;
- excessive activity or lethargy;
- obsessing over one’s health and looking for serious illnesses;
- depression;
- bouts of aggressiveness.
A person's emotions become poorer. Indifference appears, which is sometimes interrupted by a violent emotional reaction. Sudden mood changes are possible.
Psychoorganic syndrome, clinical variants
Observations of patients enable attending physicians to identify the dominant type of disease course.
Several types of the disease are identified:
- Asthenic. Sick people lose the ability to engage in any type of activity. They complain of severe fatigue, physical weakness, irritability, lack of performance and low mood. They are concerned about hypersensitivity to sounds, colors, and smells.
- Explosive. Patients are overly excitable, overly receptive to any information, and aggressive. Any contradiction towards themselves provokes an angry response from them, often with elements of hysteria. To alleviate their condition, they often take alcohol. Over time, they develop pettiness, pickiness, the formation of overvalued ideas and paranoia.
- Euphoric. Patients are prone to repeated sudden mood swings throughout the day. Bouts of gaiety and carelessness quickly turn to aggressive agitation.
- Apathetic. In the clinical state, patients are dominated by indifference to the environment, indifference to life. Against the background of weakening memory and intellectual narrowing, dementia develops.
Neurological symptoms
Patients may also complain of the following manifestations of the syndrome:
- rhythmic tinnitus, varying in intensity;
- dizziness that occurs when changing body position;
- sensitivity disorders - a person may experience goosebumps, tingling and numbness in the limbs;
- morning headaches mainly in the back of the head;
- sleep disorders (shallow sleep with frequent awakenings, insomnia, daytime sleepiness);
- asthenia (severe fatigue, fatigue, lack of strength and energy);
- deterioration of health in conditions of stuffiness, noise and heat.
These symptoms are often accompanied by speech disorders (aphasia), movement disorders (paralysis) and agnosia (impaired recognition of various objects and phenomena of the surrounding world).
Diagnosis of organic psychosyndrome
Upon admission to the clinic for treatment, patients are offered a full range of studies.
The examination plan includes:
- Collection of data on the onset of the disease. In a difficult situation involving loved ones.
- Examination of appearance with physical methods (auscultation, palpation, percussion).
- Determination of neurological status.
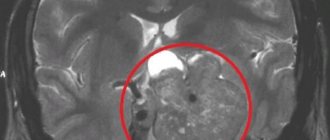
- Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics (ECG, CT and MRI).
In some cases, it is necessary to involve specialized specialists in identifying the cause of the disease: an infectious disease specialist, a traumatologist, a neurologist, an endocrinologist.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis is made on the basis of anamnesis and characteristic clinical manifestations. To identify the underlying disease that caused the development of psychoorganic syndrome, the patient may be referred for consultation to a neurologist, vascular surgeon, infectious disease specialist, venereologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist and other specialists. The list of additional studies is determined by changes in various organs and systems. Patients with suspected psychoorganic syndrome are referred for MRI of the brain, EEG and other studies.
Psychoorganic syndrome, treatment
After receiving all the examination data, it becomes clear which hospital requires care. When the causative factor is eliminated, mental disorders are removed in a psycho-neurological or drug treatment hospital.
To remove the symptoms of PS, drug treatment is used, including the use of:
- Groups of nootropics. These drugs play an important role in eliminating mnestic, intellectual and cognitive disorders. In order for them to give the desired effect, they must be prescribed for a long time and in large doses. Over time, patients experience a clear improvement under the influence of nootropic drugs.
- Neurotrophic agents with a protective effect. The metabolic and neuroprotective effect allows you to restore brain trophism and have a beneficial effect on all mental functions.
- Vitamins, especially group B, involved in the transmission of nerve impulses.
- Antioxidants that quickly remove toxic catabolites from cells.
- Sedative, eliminating emotional arousal and psychotic reactions.
- Tranquilizers that relieve fears.
As additional therapy, hormonal agents, anticonvulsants and others are used as indicated.
Treatment
Psychoorganic syndrome is treated differently, depending on the depth of the disorder. A severe syndrome requires more drastic measures and the use of more drugs, while a moderate psychoorganic syndrome has a more favorable prognosis.
Severe psychoorganic syndrome requires hospitalization measures. Hospitalization is required by psychoorganic symptoms, which manifest themselves as productive delusional and hallucinatory symptoms. Social helplessness is also an indication for hospitalization of the patient. Usually hospitalization is voluntary, but if a person becomes dangerous to himself or others, then it makes sense to solve the problem through the court.
To diagnose a psychoorganic syndrome and the causes that provoked this disorder, several different diagnostic procedures are necessary. To diagnose the syndrome itself, a consultation with a psychiatrist is enough, but to diagnose the root cause of the syndrome, it makes sense to undergo a CT scan and contact a neurologist.
Diagnosis is made in the presence of certain criteria, including damage to cognitive functions and perception disorders. The development of these disorders occurs against the background of mental pathologies.
Depending on the root cause of the pathology, relief will also be different. According to the etiotropic approach, antibiotics of various etiotropic effects, antiviral ones can be used, hormone therapy and detoxification therapy are often used. Symptomatic therapy is also necessary, especially in the presence of complications. Anticonvulsants, vascular and psychotropic medications are often used.
Nootropics are irreplaceable drugs that are used in cases of decreased intelligence to maintain a certain stable state, among them: Piracetam, Vinpocetine, Cinnarizine. Furosemide is indicated for the prevention of edema. There is often a need to use Valproate, Carbamazepine, Lamotrigine. Sometimes it makes sense to use antipsychotic drugs in severe general conditions: Clozapine, Thioridazine, Diazepam, Haloperidol, Trifluoperazine, Risperidone. Sometimes there are depressive symptoms, especially in the first stages, when criticism is preserved. Then you can use low doses of antidepressants: Saroten, Amitriptyline, Fluoxetine, Milnacepran, Paroxetine.
Group psychotherapy is used to improve the general condition of people with this syndrome. Moderate psychoorganic syndrome can allow the use of different types of psychotherapy, support groups and cognitive techniques have a particularly beneficial effect. Family psychotherapy will help teach relatives to deal with this disorder as they should, and to accept the problems of their loved one more adequately. Moderate psychoorganic syndrome can even be treated through individual psychotherapy.
Psychotherapy
Features of the treatment of psychoorganic syndrome involve a combination of drug treatment and psycho-rehabilitation methods.
Psychotherapy includes:
- Individual psychocorrection sessions.
- The use of waking suggestion and hypnotic influence.
- Cognitive-behavioral form of influence on the psyche.
- Art therapy.
- Family format of psychorehabilitation.
Particular importance is attached to physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, and physical therapy exercises. Acupuncture provides a good therapeutic effect, eliminating many neurological symptoms.
Forecast
To assess prognostic expectations, the cause of the pathology should be taken into account. In situations where we are talking about post-traumatic problems, conditions after removal of formations, doctors achieve stabilization and improvement of health. With organic processes in the brain, you can only slow down the progression of painful symptoms and improve the quality of life of patients, as well as alleviate the situation for people caring for them.
If you or your relatives have psycho-organic syndrome, try to contact us without delaying your decision for too long. We will find a way out of the situation for any variant of the disease and will do everything possible to achieve a positive result.
Rehabilitation
The majority of patients with psychoorganic syndrome belong to the senile age period. At this age, most patients require special care and supervision by staff. Therefore, special conditions are created for them in the clinic.
After completing the course of treatment, clients benefit from counseling and psychological support. With the help of rehabilitation specialists, people with loss of social skills are taught self-care techniques. If necessary, relatives can call a doctor at home.
The degree of recovery and the percentage of restoration of lost functions depends on the cause of the disease. The best prognosis is given by post-traumatic types of psychoorganic syndrome, since the causative factor can be eliminated quite quickly. Destructive processes in the brain occur in the form of progressive disorders, so treatment and rehabilitation can only achieve relief.
The text was checked by expert doctors: Head of the socio-psychological service of the Alkoklinik MC, psychologist Yu.P. Baranova, L.A. Serova, a psychiatrist-narcologist.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 798-30-80
Call! We work around the clock!
Causes
This disorder is formed due to organic lesions of the brain, which is why the progression of the pathology is very expressive. Psychoorganic syndrome is often formed under the influence of atrophic pathologies of the brain, and often develops with the progression of dementia. This disorder develops in Pick's disease, Alzheimer's dementia, Parkinson's dementia and Huntington's. Depending on the disorder and the type of underlying pathology, the psychoorganic syndrome progresses differently, and in Huntington and Parkinson's it is much slower.
Vascular damage to brain tissue also forms a disorder with psychoorganic syndrome. Cerebral atherosclerosis forms a psychoorganic syndrome with the course and progression of the pathology, especially if atherosclerotic lesions lead to brain catastrophes. Hypertension also affects the brain with subsequent development of psychoorganics. Psychoorganic syndrome is a disorder that develops with vascular dementia, that is, atherosclerosis itself and hypertension will not give psychoorganic symptoms until vascular dementia develops.
Infectious lesions localized in brain tissue can also affect brain tissue up to psychoorganic syndrome. The most dangerous infections are sexually transmitted infections with a long history, among them neurosyphilis, as a tertiary form of syphilis, which irreversibly affects the individual’s brain. AIDS, at its peak of symptomatic manifestations, also ends in psychoorganic syndrome. Not only these lesions lead to the described syndrome, encephalitis and meningitis of various etiologies also lead to it. Often herpetic encephalitis becomes the root cause of this disorder; it can also develop with influenza, rheumatoid vascular disease, or the herpes zoster virus, which causes chickenpox. In addition, such a lesion is possible during epidemics. mumps, scarlet fever and plasmodium falciparum.
Oncological processes localized in the brain, as well as metastatic parts in the brain, can provoke psychoorganic syndrome. Traumatic lesions that were of sufficient force can lead to a disorder with a similar syndrome. Epileptic lesions with the presence of convulsive seizures, and even with their equivalents, lead to this disease with a consistent course of the pathology. Each convulsive seizure destroys part of the brain neurons, which, as it progresses, leads to personality pathology with psychoorganic syndrome.
Intoxication poisonings that affect brain tissue also lead to PS. Drug addiction and poisoning with various kinds of neurotropic substances often become predictors of psychoorganism; this often happens when exposed to M-anticholinergics. In addition, somatic pathologies can lead to mental disorders, this is especially common with Cushingoid, hypothyroidism and Addison’s pathology.