General information about neurasthenia
The term “neurasthenia” is derived from two Latin roots and is translated as “weakness of the nerves.” The disease is often found in developed countries with an intense and stressful pace of life. It affects people aged 20 to 50 years. On average, every tenth adult notices certain symptoms of neurasthenia, and in women they are somewhat less common than in men.
The manifestations of the disease, at first glance, seem harmless; many are sure that the person cannot pull himself together and concentrate. In fact, the roots of the problem lie much deeper, and without the help of a doctor or at least a psychologist, it can be difficult to cope with it. Long-term neurasthenia significantly worsens the quality of life, depriving a person of the opportunity to enjoy anything, work effectively and feel confident and calm.
Make an appointment
Prevention of burnout syndrome
Prevention of emotional exhaustion syndrome will help prevent the development of extremely unpleasant symptoms, including apathy and depression. Psychologists recommend taking a number of fairly effective measures:
- Sports activities. This medicine is not only for physical diseases. Activity helps to cope with psychological problems. You don't have to go for a run or go to the gym in the morning. You can do some light exercise, do yoga, or learn meditation techniques.
- Complete rest. This is an excellent way to prevent emotional problems in people of any status, profession, age: teachers, educators, doctors and just parents. Rest does not necessarily mean sleep. A change of environment often helps, for example, a trip to another city. The main thing is to relax mentally, get new impressions, and recharge with positive emotions.
- Mode. Work and rest need to be planned. This way you can do everything you need to do without being distracted by useless activities.
- Psychological protection. The ability to protect yourself with an imaginary wall from unpleasant people will also help protect yourself from moral exhaustion. It will prevent stressful situations, provocations, and manipulation from others.
And, probably, the main preventive measure is maintaining harmony. You should not mix your personal life and work, or waste emotional resources discussing the problems of work colleagues or acquaintances. It is better to talk about abstract or constructive topics.
Reasons for development
The causes of neurasthenia are a variety of mental, somatic (related to the state of the body) and exogenous (external) factors. Most often the following problems act as a provoking factor:
- acute mental trauma or experience (death of relatives, divorce, etc.);
- exhaustion of the nervous system due to chronic multi-day stress (caring for a child or a seriously ill person, constant conflicts in the family, etc.);
- severe and/or long-term illness (oncology, infections, etc.);
- previous traumatic brain injuries, birth injuries, intracranial hypertension (act as predisposing factors);
- brain tumors, neuroinfections;
- alcohol and drug abuse;
- harmful working conditions (working with toxic substances, as well as regular mental or physical stress, overwork).
Any problem that knocks a person out of the usual rhythm of life can provoke the development of neurasthenia. If such situations are repeated regularly, the ability of the nervous system to adapt to changed conditions decreases, which provokes the development of pathology.
The impact of the problem on a person’s life
Many people suffer due to moral exhaustion. It manifests itself through various symptoms that disrupt a person’s life and reduce his productivity. Often, important relationships are destroyed due to emptiness.
Moral exhaustion in psychology is called nervous. But terminology has little effect on the essence of the processes that occur in the body during prolonged stress. It is not so important how many problems still have to be solved. Despite the mountains of work, it is necessary to give the body and mind timely rest. Otherwise, labor productivity and the ability to solve problems will continue to decline until it all results in chronic fatigue syndrome or psychosomatic illness.
Forms and symptoms
In the process of its development, neurasthenia goes through several phases, each of which has its own signs and distinctive features. In some cases, one of the phases exists in isolation, which makes it possible to distinguish it into a separate form of the disease. In the future, she can move on to the next or previous stage, or even pass completely.
Regardless of the phase, the patient may encounter problems characteristic of neurasthenia:
- increased heart rate;
- feeling of strong heartbeat;
- pressing or stabbing pain in the chest;
- increased blood pressure;
- paleness of the face or, conversely, redness;
- digestive problems: heartburn, belching, bloating, constipation or diarrhea;
- frequent urge to urinate under stress;
- decreased libido, sexual disorders (premature ejaculation, impotence, anorgasmia).
Each of these symptoms can appear alone or in combination with others.
Hypersthenic form (phase)
This form is manifested by excessive irritability and emotional instability. Any little thing can make a person angry: loud noise, extraneous conversation, a large crowd of people or a seeming lack of attention from others. As a result, the patient begins to scream, curse, or insult at the slightest provocation.
Performance in this phase suffers significantly due to severe inattention. The person does not feel tired, but it is very difficult for him to concentrate on the process. He collects his thoughts for a long time, and then is constantly distracted by some extraneous irritant. The vicious circle is repeated dozens and even hundreds of times during the day, which significantly affects the result, making the person even more nervous.
Characteristic symptoms of the hypersthenic phase are:
- sleep disorders: prolonged falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, nightmares;
- feeling tired and tired in the morning;
- drowsiness during the day;
- pressing headache like a helmet or a subjective feeling of heaviness in the head;
- decreased attention and memory;
- discomfort inside the body (in the area of the heart, stomach, intestines, etc.).
Irritable weakness
This is the second phase of neurasthenia, which develops if the provoking factors have not been eliminated. Outbursts of anger, rage and irritation continue to arise at the slightest provocation, but they quickly fade away, leaving behind complete mental exhaustion. Often the attack ends in apathy and tears.
The patient's ability to work continues to deteriorate. He hardly forces himself to start doing anything, but almost immediately stops due to severe fatigue and headache. Attempts to finish the task can be repeated several times throughout the day and, ultimately, exhaust the person. He feels immense weakness, fatigue and weakness to the point of complete exhaustion.
The phase of irritable weakness can develop independently. People with an explosive, emotional temperament (cholerics) or initially strong, self-confident and balanced people (phlegmatics) are most susceptible to it.
Hyposthenic form (phase)
With a consistent course of neurasthenia, this phase is the final one, but anxious and suspicious people can encounter it already in the early stages of the development of the disease. Hyposthenia is characterized by:
- constant physical and mental weakness;
- apathy;
- anhedonia (loss of the ability to enjoy life);
- emotional instability, tearfulness;
- lack of interests and hobbies;
- severe hypochondria.
In fact, a person becomes fixated on himself and his asthenic state, constantly looking for signs of various diseases. During this phase, the general symptoms described above often occur, which reinforce the patient's belief in poor health.
If the factor that caused the exacerbation of neurasthenia is eliminated, or the patient is prescribed effective therapy, the disease begins to recover, no matter what phase of development it is at. Repeated attacks are characterized by greater severity of symptoms, as well as an increase in the duration of recovery.
Signs of exhaustion: insomnia
One of the first signs of moral exhaustion is sleep disturbances. Due to stress, a person in this state cannot fall asleep even when very tired. But adequate sleep is vital. Therefore, for those who are faced with this problem, it is at least useful to properly prepare for rest every day. To do this, you can meditate and remember something pleasant.
Diagnostics
Neurologists, psychiatrists and psychotherapists can diagnose neurasthenia. To make a diagnosis they use the following methods:
- collection of complaints and medical history: the doctor finds out what exactly is bothering the patient, how long ago and against what background it started, under what circumstances it gets better or worse; special attention is paid to past illnesses or injuries, family and work environment, heredity, etc.;
- psychological assessment: during a conversation with a patient, the doctor pays attention to the emotional coloring and volume of speech, gestures, etc.; after the conversation, the person is asked to perform several tests that will help determine the level of anxiety, depression, asthenia, etc.
- general examination: blood and urine tests, ECG, hormone tests and other examinations are necessary if there are relevant complaints; So, for pain in the heart area, a cardiological examination will be required, and for digestive problems, a consultation with a gastroenterologist;
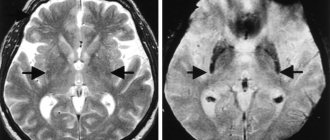
- exclusion of organic pathology of the nervous system: a thorough neurological examination, MRI or CT scan of the brain, ultrasound examination of the arteries of the head and neck and other examinations are performed to identify the possible cause of the patient’s painful condition.
It is important not only to diagnose neurasthenia, but also to distinguish it from a more severe and formidable pathology - depression. There are a number of fundamental differences between them:
- reason: neurasthenia always occurs as a reaction of the body to acute or chronic stress, overwork, etc.; depression often develops for no apparent reason;
- condition during the day: with neurasthenia, patients feel better in the morning, symptoms increase as fatigue increases; with depression in the evening, on the contrary, it becomes better;
- seasonal dependence: depression worsens in spring or autumn, while neurasthenia can occur with equal probability at any time of the year;
- response to treatment: when the cause is eliminated and treatment is prescribed, neurasthenia disappears completely, while depression often worsens again.
Asthenic manifestations
Feeling tired, dizzy, weak - all this indicates the need for physical rest. The body cannot withstand this amount of stress. If these signs are present, you need to think about self-healing.
Sometimes there is a pain syndrome, the origin of which is unknown. The person conducts specialized examinations, but doctors reveal nothing. The pain can be localized in the head, muscles, and abdomen. Chronic diseases can also worsen.
Treatment of neurasthenia
Treatment will be successful only if the factor that provoked the disease is eliminated. The patient is recommended:
- follow a daily routine, go to bed on time;
- get proper rest, avoid overwork and overexertion;
- change the environment if possible;
- eat right, avoid undereating or overeating;
- eliminate the use of alcohol, drugs, smoking;
- regularly walk in the fresh air, play sports at an amateur level.
A good effect is achieved using various types of psychotherapy. Sessions with a doctor help identify blocked traumas and experiences, cope with acute or chronic stress, and restore the depleted resource of the nervous system. In addition to working during the appointment, the specialist teaches the patient auto-training techniques that help stabilize the psyche.
Medications are prescribed depending on the phase of the disease:
- the hypersthenic phase requires the prescription of tranquilizers and sleeping pills, which help reduce the excitability of the nervous system and improve sleep;
- the hyposthenic form is a reason to prescribe tonics: caffeine, eleutherococcus, ginseng, etc.
Certain symptoms of neurasthenia can be corrected with the help of nootropics, angioprotectors, and B vitamins that improve the functioning of the central nervous system.
Non-drug methods of influence help increase the effectiveness of treatment:
- physiotherapy: electrosleep, various applications;
- restorative massage;
- acupuncture;
- various relaxing procedures (floating, aromatherapy, etc.).
Make an appointment
How to overcome burnout
How to deal with moral exhaustion syndrome? Treatment directly depends on the form of the “disease”. For example, the following measures will help get rid of a lung:
- reduce the load;
- share responsibility;
- set and achieve realistic goals;
- don’t panic if something goes wrong;
- realistically assess the possibilities.
Also, if possible, you should replace mental stress with physical activity, for example, by playing sports or just taking a walk. If you wish, you can relax in a sanatorium.
How to treat chronic exhaustion?
- You need to learn to say no. Don't take on extra work or responsibility. Let everyone fulfill their duties.
- Charge yourself with positive emotions. Walking with friends or going to the theater or museum will help here.
- Tell someone about your problems and together look for the right solution.
- Build relationships with colleagues.
- Communicate with self-confident people who are not prone to developing the syndrome.
- Find a pleasant hobby, do something new.
- Take short breaks during the working day.
- If your exhaustion is related to your job, you may need to change your job.
There is another way to fix the situation. You need to write down the reasons for your condition on a piece of paper. It is important to be as honest as possible. After that, think about possible ways to solve problems.
If necessary, psychologists recommend consulting a doctor. He will prescribe medications that will help you calm down and relax, at least for a short period of time.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
If stress and fatigue are the cause of loss of strength, the doctors at the Health Energy clinic will come to the rescue. First, we conduct a detailed examination that will help exclude other causes of pathological symptoms, and prescribe consultations with specialized specialists and tests necessary to assess the situation. Then you will be offered comprehensive treatment, which includes:
- individual selection of medications in accordance with the symptoms and characteristics of the body;
- modern psychotherapeutic techniques;
- physiotherapy, massage, physical therapy to stabilize the condition;
- organization of sanatorium-resort treatment.
Medicines
To prevent possible complications, it is important to identify the symptoms of nervous exhaustion in time. Treatment with drugs if a disorder is suspected is prescribed only by a doctor. Typically these are the following medications:
- Drugs that help dilate blood vessels, relieve migraines, and increase cerebral circulation. Usually these are analogues of Mexidol or Tanakan.
- Medicines that accelerate metabolism in brain tissue - Nootropil, Piracetam, Ceraxon.
- Calming agents – tincture of valerian, “Fitosedan”.
- If there are symptoms of depressive conditions, drugs from the antidepressant group or mild tranquilizers - Valium, Diazepam, Amitriptyline - are prescribed.
- Homeopathic remedies are also used - “Anakarium”, “Magnesia”, “Kali Phos”.
Treatment with drugs for nervous exhaustion is possible only as directed by a specialist. The listed medications have contraindications. Before using them, you should consult your doctor.
Our advantages
The multidisciplinary medical center offers each visitor services for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases. Our advantages include:
- the most popular areas of work: neurology, cardiology, surgery, gastroenterology, etc.;
- modern diagnostic equipment;
- all types of laboratory analyzes and tests;
- the most effective methods of treating various pathologies;
- individual approach to the selection of therapy;
- auxiliary treatment methods: physiotherapy, physical therapy, massage;
- comfortable day rooms;
- Appointment by appointment at a time convenient for the patient;
- affordable prices for all services.
Neurasthenia is a disease in which a person does not have the strength to pull himself together. Without qualified help and elimination of the traumatic factor, it will progress, increasingly depleting the nervous system. Help yourself get out of the vicious circle, sign up with Health Energy specialists.
The desire to quit everything
One of the clear signs of burnout is that a person no longer wants to take responsibility. He feels that there is a huge burden on his shoulders that he does not have the strength to carry.
A similar desire can periodically arise in a healthy person. But on the other hand, if apathy does not go away for a long time, it can lead to negative consequences. Therefore, it is necessary to take a break as soon as possible and get in shape.
Classification of neurotic disorders
Disorders are divided into 3 groups:
- hysterical;
- obsessive states;
- asthenic.
This classification of neurotic disorders is not similar to practice. It does not contain approved certain and most common pathologies. The differences lead to different ways of systematizing disorders.
Types of neurotic disorders
When making a diagnosis, doctors take into account the following types of neurotic disorders.
- Anxious-phobic. The main symptom is a sharp increase in anxiety and the appearance of obsessive fears. This group includes panic attacks, simple and complex phobias, and generalized anxiety disorder.
- Obsessive-compulsive. The main symptom is the appearance of obsessive ideas and actions.
- Asthenic disorders are characterized by asthenic syndrome.
- Somatoform. Clinically, they are similar to somatic ones, but do not imply a physical basis.
- Dissociative disorders imply disorders of motor function and sensations. Previously, this disease was classified as hysterical neuroses.
The sooner the patient seeks help, the more favorable the prognosis.
Forms of neurotic disorders
There are such forms of neurotic disorders.
- The most common is neurasthenia; it is divided into 3 stages. The first phase is characterized by irritability. Mental and physical abilities are not affected. The second stage is characterized by a decrease in working capacity, a person understands this. The third phase is manifested by lethargy, reluctance to do anything, and asthenic syndrome.
- Hysterical neurosis is the second form. The disease is caused by inappropriate behavior; the person is unpredictable and extremely irritable. There are signs such as seizures, paresis, vomiting, hypotension. The patient also complains of obsessive thoughts, a “lump” in the throat, and insomnia. During an attack, a person screams, lies on the floor, can get into a fight, or injure himself.
- The third form is depressive neurosis. It is characterized by symptoms such as insomnia, bad mood, loss of the ability to feel joyful emotions, a feeling of burden, and tearfulness. There are also disturbances in heart rhythm, stomach function, slow reaction to events, sexual dysfunction, and hypotension. The patient complains of despondency, sadness appears, and a feeling of uselessness.
- Obsessive states. With it, the patient is unable to control his thoughts and actions.
- Hypochondriacal neurosis - there is a fear of a circumstance from which a person cannot find a way out, or a fear of falling ill with an incurable pathology. The condition is complemented by hysteria and obsessions.
Each form requires an individual approach to therapy.
Neurotic disorders in adults
Neurotic disorders in adults have a reversible, relatively mild course, unlike psychoses. According to statistics, the problem is detected in 20% of the population. The causes include a disorder of brain activity responsible for human adaptation. Somatic and mental disturbances appear. Patients are rarely admitted to the hospital; conservative methods are usually successful.
Neurotic disorders in children
In children, the catalyst for the development of neurosis is delays in personality development. Against the background of separation from parents, stress, loss of a loved one, psychological trauma is possible. A child who experiences these situations becomes infantile or acquires neurosis.
Neurotic disorders in children: features of occurrence and course.
1. The age of 7-11 years is considered the affective stage of personality formation. If at this time the child encounters a traumatic factor, his development as a person may be delayed. In adulthood, such people experience emotional instability; a person cannot adequately assess the situation or think about the consequences. The only and beloved children acquire hysterical traits.
2. At the age of 11-14, a teenager learns to independently assess the situation, analyze, and plan his actions. There is a subsequent development of the affective component of the personality. If at this age a stressful situation arises, neuroses are possible in the future. Such teenagers outwardly look older than their peers and are more reasonable, but subconsciously, the synchronicity of personality development is disrupted.
Attention! The most important role in the successful growth of a child is played by the relationship with parents. Those who felt overprotected in childhood and were not allowed to make their own decisions become timid and unsure of themselves. It is in this category of people that neurotic disorders arise.
Nutrition
Vitamins and microelements are needed not only to maintain the body in optimal condition. They are extremely important for the effective functioning of neurons - brain cells. Therefore, during periods of exhaustion, it is important to eat large amounts of fruits and vegetables.
During prolonged nervous tension, nutrition must certainly include more proteins and fats of plant origin. It is useful to obtain proteins from dairy products containing bifidobacteria. Also good sources of proteins include fish, meat, and seafood.
Recommendations from psychologists: the need to give yourself the opportunity to rest
To cope with the symptoms of mental exhaustion, it is important to remember to get plenty of rest. Often workaholics suffering from this disorder justify themselves with the help of folk wisdom - “Time for work, time for fun.” Psychologists advise not to forget that if there is no fun, then you will not be able to complete the task. Either the strength will completely run out, or the body will become so exhausted that the person will get sick or “pay” with an anxious-depressive state. Therefore, rest and entertainment should not be perceived as something that interferes with work; rather, this pastime is the key to the successful performance of one’s duties.
It’s completely normal to be tired in the evenings and on weekends. Fatigue is an indicator of the need to rest. If signs of moral and physical exhaustion are detected, the best way to recuperate is a vacation. After great stress (for example, the threat of dismissal from work, serious family conflicts), it is recommended to rest for at least 10 days.