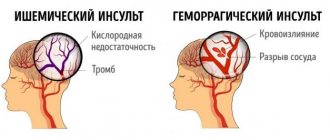
Hemorrhagic stroke is a rupture of cerebral vessels and hemorrhage in brain tissue. Depending on the localization and extent of the process, the prognosis of the disease is determined. Hemorrhagic stroke occurs less frequently than ischemic stroke, but the prognosis of the disease is more unfavorable.
The Yusupov Hospital treats patients with strokes and provides emergency care with the patient being transported to the intensive care unit. In the hospital, the patient will be examined using innovative equipment and will receive effective treatment using minimally invasive neurosurgery methods, the latest developments in the field of stroke treatment, and modern medications. The hospital provides comfortable rooms, dietary meals, and doctors create an individual treatment and rehabilitation program.
Types of hemorrhagic stroke
The effectiveness of stroke treatment depends on timely medical care. In hemorrhagic stroke, symptoms depend on the location of the injury. There are several types of hemorrhagic stroke:
- Intraventricular stroke - characterized by rupture of blood vessels and breakthrough of blood into the ventricles of the brain. The brain tissue becomes saturated with blood or hematomas form in the ventricles of the brain. Such a stroke most often ends in the death of the patient on the 2nd or 3rd day.
- Parenchymal stroke - hemorrhage occurs in the substance of the brain, a hematoma can form or the nerve tissues of the brain become saturated with blood, as a result of such a stroke a severe neurological deficit is formed.
- Subarachnoid stroke - hemorrhage occurs in the cavity between the arachnoid and pia mater of the brain.
- Mixed hemorrhages - bleeding is accompanied by changes that are characteristic of different types of strokes.
Diagnostic methods
In the acute phase of a hemorrhagic stroke, the patient must be urgently examined to preliminarily determine the prognosis and select treatment tactics. The condition is complicated by the following factors:
- extensive hematoma in the brain tissue, which occupies an area of 7 square cm or more;
- large intraventricular hematomas - more than 2 square cm;
- high blood pressure;
- elderly age of the patient;
- any chronic diseases;
- presence of dislocation syndromes.
Dislocation syndromes are signs of an increase in the volume of the brain with a subsequent change in its localization in the skull. Using these symptoms, you can determine in which area the main pathological focus is located, as well as predict the chances of recovery. The primary diagnosis of strokes is based on the clinical picture, so dislocation syndromes play an important diagnostic role. In total, there are 9 options for how the brain matter can shift. However, when diagnosing strokes, 2 of them are most important.
Causes
Hemorrhagic stroke is poorly diagnosed, although the causes and mechanism of its development are well studied. Various factors can provoke the development of hemorrhoidal stroke:
- Hypertension, arterial hypertension.
- Vascular aneurysm.
- Long-term use of anticoagulants.
- Diseases of the brain, spinal cord, cardiovascular system, diabetes.
- Congenital vascular defects.
- Blood diseases.
- Systemic diseases.
- Kidney and liver diseases.
- Alcoholism, drug addiction, tobacco addiction.
- Obesity.
- Stress.
- Hard physical labor.
- Hereditary predisposition.
A persistent increase in blood pressure leads to the formation of fibrinoid-hyaline necrosis of the walls of arterial vessels and can cause rupture of the walls of the aneurysm and the development of bleeding. The hematoma compresses the surrounding brain tissue, causing brain swelling. Blood from ruptured vessels can permeate the nerve tissue of the brain or, under pressure, break into the ventricles of the brain, the subarachnoid space.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is accompanied by severe headache, vomiting, convulsions may begin, consciousness is impaired, Terson syndrome is observed, and meningeal symptoms appear. Parenchymal stroke is characterized by unexpectedly occurring severe headache, pallor or redness of the face, asymmetry of facial features, impaired coordination of movement, impaired respiratory function, and agitation. Ventricular stroke, the most severe form of the disease, is characterized by rapid deterioration of the patient's condition; bloody vomiting, loss of consciousness, fever, convulsions, and coma may occur. Ventricular stroke most often leads to the death of the patient. In most cases, hemorrhagic stroke occurs during the daytime, and the patient suddenly loses consciousness.
At the first examination, doctors note a change in complexion, high blood pressure, impaired respiratory function, slow pulse, decreased muscle tone, and tendon reflexes. Such symptoms are characteristic of the first hours after a stroke, then an increase in muscle tone and tendon reflexes occurs, the function of the pelvic organs is disrupted, the condition worsens, and the patient may fall into a coma.
Make an appointment
Difference between hemorrhagic stroke and ischemic stroke
Strokes are characterized by the same symptoms, but have different causes of pathology. Hemorrhagic stroke has a more unfavorable prognosis and is characterized by the development of various severe disorders. In ischemic stroke, a favorable prognosis depends on the degree of brain damage. All types of strokes are characterized by the following disorders:
- Loss of speech.
- Paralysis of the body and limbs.
- Impaired sensitivity.
- Visual impairment or complete loss.
- Loss of coordination.
- Partial or complete hearing loss.
- Disorder of the function of the cerebral cortex.
- High blood pressure.
The consequences of a stroke depend on the location and extent of the brain lesion. Hemorrhagic stroke begins acutely, the disease progresses rapidly, and coma may develop within the first minutes or several hours. With hemorrhagic stroke, symptoms appear earlier than with ischemic stroke, they are more pronounced.
How to determine if you have a stroke?
Manifestations of the disease can be different, they depend on exactly where the vessel ruptured, where the blood accumulated and how the hematoma is located inside the tissue. It can exert different pressure on areas of the brain responsible for individual capabilities of the body, which causes variability in the signs of the disease.
Rupture usually occurs instantly, but the severity of the condition may worsen as a hematoma forms. In this case, one or several symptoms can be observed over time:
- My head suddenly started to hurt;
- dizziness occurred;
- the person lost consciousness;
- general weakness of the body;
- presence of nausea, vomiting;
- the pulse becomes uneven;
- convulsions may occur;
- difficulty breathing;
- the skin turns red.
If individual symptoms were noticed or the person’s general condition worsened, he should be urgently taken to the hospital.
Treatment after a stroke
A patient with a hemorrhagic stroke should receive first aid. The patient is placed on the bed, clothes are unbuttoned to make breathing easier, and a window is opened to allow fresh air to enter. The patient's head should be higher than the body level. The patient should measure blood pressure and pulse, monitor breathing in case of loss of consciousness and, if necessary, carry out resuscitation measures. The main task of doctors in case of hemorrhagic stroke is to stop bleeding, maintain respiratory function, the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and relieve cerebral edema.
In case of extensive hemorrhage in the brain, neurosurgical microtechnical operations are used - the hematoma is removed in order to reduce the pressure on the brain tissue and prevent the development of cerebral edema. Surgery for hemorrhagic stroke is performed strictly according to indications. Painkillers are prescribed to reduce headaches. If the cause of a hemorrhagic stroke was an aneurysm, doctors perform an operation and prescribe hemostatic drugs to stop the bleeding. Often, subarachnoid stroke is accompanied by vasoconstriction (secondary vasospasm) and the development of ischemic stroke. In this case, calcium channel blockers are prescribed to prevent narrowing and spasm of blood vessels.
Consequences
The consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke can bother the patient for the rest of his life. Depending on the severity of the disorders, recovery occurs; the most severe condition is in patients with extensive hemorrhagic stroke. Depending on which hemisphere of the brain is affected, the consequences of cerebral hemorrhage are observed. Hemorrhagic stroke of the right hemisphere of the brain:
- Partial or complete loss of vision.
- Disorders of urination and defecation.
- Paresis or paralysis of the body, decreased sensitivity of the left half of the body.
- Development of mental disorders.
A stroke to the left hemisphere of the brain causes paralysis on the right side of the body. When hemorrhage occurs in the area of the brain stem or cerebellum, loss of sensitivity occurs, the patient cannot swallow or speak, partial or complete loss of hearing in the right ear occurs, vision is impaired, coordination of movements is impaired, the patient cannot make unilateral or bilateral voluntary movements. Often the consequence of a hemorrhagic stroke is dementia (dementia), which develops gradually.
Rehabilitation of hemorrhagic stroke
Rehabilitation of the patient in the first 6-12 months consists of maintaining his vital functions and restoring lost abilities. During this period, when the patient has lost motor functions, the risk of bedsores and congestion increases. The patient is turned several times a day, the position of the body is changed, hygienic procedures are carried out, massage is carried out, the instructor engages in physical therapy exercises with the patient. During this period of time, the patient’s condition is monitored by several doctors - a therapist, a neurologist, a cardiologist and a psychologist. Rehabilitation measures are aimed at improving the patient’s quality of life and restoring lost functions.
Restoration of motor functions
At the “New Hospital” in Yekaterinburg, rehabilitation specialists, neurologists and physical therapy doctors are involved in the restoration of motor functions. The tasks in this case are:
- stimulation of muscle activity;
- muscle strengthening;
- massage;
- stimulation of coordination between the brain and organs of the musculoskeletal system.
In this case, the main thing is to create a safe environment for the patient. To achieve the goal, special products for rehabilitation after a stroke are used (canes, walkers, exercise equipment, etc.).
Forecast
The prognosis for hemorrhagic stroke depends on the severity of brain damage and the time of seeking first aid. If the stroke was not extensive and did not affect the vital centers of the brain, timely assistance was provided - there is a chance to return to normal life. It is impossible to predict the patient’s life expectancy - the prognosis depends on many factors:
- Patient's age.
- Severity of brain damage.
- Concomitant diseases.
According to statistics, more than 30% of patients die within a few weeks after a stroke, more than half of patients die within a year, and more than 60% of patients become disabled. No more than 20% of patients can recover completely within a few years.
Effective rehabilitation programs have been developed and tested at the Yusupov Hospital. The recovery process after a hemorrhagic stroke is unpredictable, lengthy and difficult. You can get advice on the treatment and rehabilitation of a patient by calling the hospital.
Make an appointment
Comprehensive program “Rehabilitation+”
This stroke rehabilitation program aims to return patients to as full a life as possible.
The main task of the specialists at the “New Hospital” is a separate approach to each patient. We use maximum opportunities to restore lost skills:
- restoration of vision;
- motor activity (recovery of arms and rehabilitation of legs after a stroke, fine motor skills);
- speech restoration;
- learning to tie shoelaces, wash dishes, etc.;
- restoration of driving skills.
As part of the program, our specialists try to restore not only the basic skills that were lost. We try to return the patient to a full life, focusing on the tasks that are necessary for a specific person.