Leptospirosis is a severe infection in half of the cases and is found in all countries, except in the North and South Poles. People get sick especially often in tropical countries, from where tourists carry the pathogen around the world. The migration of infection is facilitated by the growing popularity of water sports. Leptospirosis affects more than a hundred species of wild and domestic animals - the main source of human disease.
Our expert in this field:
Nagibina Margarita Vasilievna
Infectious disease doctor, doctor of medical sciences, professor
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Causes of infection
At the Medica24 international clinic, the entire range of therapeutic and rehabilitation measures is performed at a guaranteed high professional level, which reduces recovery time.
The causative agents of the infection are spirochetes, there are more than 250 variants of them. Spirochetes produce toxins and enzymes; these substances destroy cells and disrupt the structure of the blood. Spirochetes are delicate, but can live up to 3 months in water and soil, and a month on food.
Spirochetes are carried in the urine by rodents and animals. A person becomes infected by consuming food and water that contains the pathogen through animal urine. Livestock gets leptospirosis, and dogs get it too, passing the spirochete to their owner. Human susceptibility to infection is very high. The disease is almost never transmitted from person to person.
Leptospirosis follows a seasonal pattern - in summer the incidence of the disease increases, but you can get infected from an animal at any time. In recent years, the main contingent of Russian patients are young men who are fond of water sports.
The international clinic Medica24 has everything necessary for the early detection of pathogens of infectious diseases and diagnosis of pathological changes, which allows you to make the correct diagnosis and begin therapy as soon as possible.
Treatment with folk remedies
Since leptospirosis is a serious disease that requires urgent medical attention, in this case you should not hesitate and self-medicate. The use of folk remedies for leptospirosis is possible only as an auxiliary treatment, but in no case as the main therapy. It is advisable to use folk remedies during the recovery period - to restore the body and maintain the functioning of internal organs. The following means can be used:
- Fresh apple juice with honey - drink with 1 tsp. It is recommended to drink honey every day on an empty stomach.
- Beetroot and carrot juice - freshly squeezed vegetable juices should be diluted in half with water and drunk a third of a glass on an empty stomach.
- Potato juice – it should be drunk fresh. Drink half a glass half an hour before meals.
- Tomato juice with cabbage brine - it is recommended to mix them in equal proportions and drink throughout the day.
- Herbal tea - you can prepare it from chamomile, oregano, mint, lemon balm and other herbs with a general strengthening effect.
- Lemon with garlic – mix the juice of 1 lemon and 1 head of garlic. Drink half a teaspoon after meals.
Symptoms of leptospirosis in humans
Leptospirosis goes through four periods, their duration is variable, lasting a total of 4-6 weeks.
The incubation period from infection to the first symptoms of leptospirosis lasts from two days to a month, more often – one to two weeks. It is impossible to find the site of entry of the pathogen; the spirochete passes “through” the skin and is carried throughout the body by blood.
The period of onset of the illness is no more than a week, the onset is so acute that the patient can name the hour when he fell ill. Severe intoxication with high fever, muscle and headaches, nausea and palpitations is caused by the production of toxins by spirochetes. Severe pain in the calves and lower back, aggravated by movement, is typical. The appearance is specific: a red and puffy face, herpes rashes on the lips and nose, the eyes are also red due to dilated blood vessels.
List of sources
- Avdeeva M.G. Leptospirosis as a disease with a prolonged complicated course (immunopathogenesis, diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, rehabilitation): abstract of thesis. Dr. med. Sci. - M., 1997. - 32 p.
- Avdeeva M.G. Causes of lethal outcomes of leptospirosis / M.G. Avdeeva // Epidemiology and infectious patients. – 2003. – No. 6. – P. 30–33.
- Leptospirosis / [V.I. Luchshev, V.V. Lebedev, S.N. Zharov, S.V. Burova] // Russian Medical Journal. – 2009. – No. 4. – P. 47–49.
- Stoyanova N.A. Current problems of leptospirosis in infectious pathology of people // Sat. report/Biol. scientific-practical .-SPb., 1996.-Issue 2.-P.5-10.
Symptoms at the height of the disease
The peak period of leptospirosis lasts up to two weeks, the pathogen is “located” in the internal organs, which leads to disruption of their function, and multiple organ failure develops. The entire period is high temperature, which ends with a sharp decrease almost within a few hours upon recovery.
Liver cells are damaged and jaundice develops. The larger part of the organ is affected, the brighter the color. The kidneys are always affected, leading to renal failure. Capillaries are damaged, which leads to hemorrhages and bleeding in the organs and nose. Hemorrhagic syndrome and hepatic-renal failure can lead to death.
By the end of the second week of the peak, a bacterial infection may occur with the development of bacterial inflammation in the organs and even sepsis.
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Pathogenesis
As a rule, the infection enters the body through wounds, mucous membranes, the gastrointestinal tract, and the genitourinary system. You can become infected through soil, water, and food. The incubation period in most cases lasts from 4 days to 2 weeks. However, sometimes it can last for a month. Most often, infections occur in late summer and autumn.
After infection, several phases of disease development are determined. In the first phase, the causative agents of the disease penetrate into the blood through the affected mucous membranes and skin, after which the leptospires invade the kidneys, liver, spleen, and adrenal glands, where they actively reproduce. This is the incubation period of the disease.
This is followed by a phase of generalized infection . During this period, repeated leptospiremia occurs, after which the pathogen enters the liver, kidneys, adrenal glands, and membranes of the brain. During this period of the disease (initial), Leptospira parasitizes on the surface of cells.
In the toxinemia , the disease progresses. The endothelium of the capillaries is damaged, as a result of which their penetration increases. Hemorrhagic syndrome develops , the kidneys, liver, and adrenal glands are affected.
During the formation phase of the non-sterile stage of immunity, antibodies appear in the blood, and the process gradually begins to fade.
In the sterile stage of immunity, humoral immunity is combined with local organ and tissue immunity. At this stage, the healing process occurs.
However, there are several varieties of the pathogen, so immunity to one type does not provide protection against other varieties.
When does recovery begin?
By the end of the fourth to sixth week, from the appearance of the first signs of infection, recovery begins with a gradual fading of symptoms - a period of convalescence. But full recovery will not happen soon; weakness remains for a very long time.
In half of patients, recurrent infections are possible because the spirochetes take refuge inside the kidneys. The return is manifested by an attack of high fever with muscle and headaches, a red face with bloody eyes, that is, symptoms of the onset of the disease, but a little milder and disappear in just a few days.
Dispensary observation
Dispensary observation of those who have had leptospirosis is carried out by infectious disease specialists at clinics. The period of clinical observation is at least 6 months. Inspections are carried out once a month. In the 1st month after the illness, patients are subject to mandatory clinical examination by an ophthalmologist, neurologist and therapist. In subsequent months, specialized specialists are involved in the profile of clinical manifestations. Control general blood and urine tests, and in those who have had the icteric form of the disease, a biochemical blood test are done every month for the first 2 months, then depending on the results of the examination.
Criteria for removal from dispensary registration: clinical recovery, normalization of laboratory parameters. In case of persistent residual effects, those who have recovered from the disease are transferred under the supervision of specialists (ophthalmologist, neurologist, nephrologist, etc.) for at least 2 years.
Diagnosis of the disease
The general blood test shows a very high level of leukocytes, many band neutrophils, and a very high ESR. Urinalysis with large deviations. Biochemical blood test showed high bilirubin, AST and ALT, creatine phosphokinase.
The diagnosis is made by a characteristic clinical picture and identification of the pathogen in biological fluid - blood or urine. The infection is also looked for in contact pets. The recognized diagnostic standard is the microagglutination test or PMA of Leptospira.
Epidemiology
Leptospirosis is the most common zoonotic disease in the world. The infection is registered on all continents of the Earth except Antarctica. A high incidence rate is observed in tropical countries, the maximum level is recorded in regions with a developed river network, frequent floods, and in places with a high density of farm animals. The disease is of an occupational nature - agricultural workers and livestock breeders are most often affected. Both sporadic and epidemic outbreaks are recorded. There is a pronounced seasonality - leptospirosis is most often recorded in the summer-autumn season. Foci of infection form both in nature (natural foci) and in cities (anthropurgic foci).
Leptospira enters the human and animal body through the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, oral cavity, eyes, genital tract, and damaged areas of the skin.
- In humans, pathogenic species of bacteria cause leptospirosis jaundice (Vasiliev-Weil disease) and the anicteric form (water fever).
- In animals, there is a generalization of the infectious process with damage to the kidneys and liver. In pigs, sheep, cattle and horses, Leptospira causes abortion, stillbirth and mastitis during lactation.
- In dogs, the disease can have an acute course, often with fatal jaundice, or less often - a subacute or chronic course.
Reservoir and source of infection
The reservoir and source of infection are more than 80 species of wild and domestic animals, which spread the infection through feces, urine, semen, milk, bronchial mucus and genital discharge, contaminating soil, water, food and environmental items. A sick person is not a source of infection.
- The main natural reservoir of infection is small mammals, mainly rodents - wood mice, gray voles, water rats, shrews and rats.
- The reservoir of the second group is domestic animals - cattle, pigs, sheep, goats, horses and dogs.
- The reservoir and distributors of infection are caged fur-bearing animals - arctic foxes, nutria, foxes, etc.
Carriage of Leptospira has been recorded in more than 100 species of mammals and 6 species of birds. In cattle, the period of leptosironism is up to 6 months, in small cattle - up to 9 months, pigs - up to 2 years, cats and dogs - up to 3 years. Rodents and pigs are lifelong carriers of the infection.
Rice. 6. The main natural reservoir of infection in nature is rodents.
Transmission factors
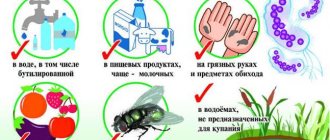
Transmission factors for leptospirosis are contaminated water (which is the main one) and contaminated food products. Sick animals infect pastures, water, feed, bedding, etc. Ponds, swamps, slow-flowing rivers, never-drying puddles and wet soil pose a danger.
Pathways of transmission of pathogens
Waterway. Water transmission is the main route of infection. Infection occurs when drinking water from open reservoirs, as well as using it for household purposes. Cases of the disease have been reported from ingestion of water while swimming in contaminated bodies of water.
Contact path. Cases of human infection during land reclamation and agricultural work have been recorded. Leptospira can enter the human body through contact (through microtraumas of the skin, often on the legs) when caring for sick animals, slaughtering livestock and cutting meat.
Food route. Pathogens are also transmitted through contaminated food, including milk.
Foci of infection
There are 3 types of foci of leptospirosis: natural, anthropurgic (household) and mixed.
Natural hotbeds
Natural foci of infection are located in forest zones, forest-steppe and forest-tundra, often in lowlands, reed thickets, and wetlands. Their
are formed by sick wild animals, most often moisture-loving small rodents and insectivores: wood mice, voles, water rats, shrews, rats, hamsters and hedgehogs, the infection in which occurs in a chronic form with intense and prolonged leptospira excretion, which lasts for months and even years.
In natural foci, human infection occurs mainly during agricultural work after river floods and heavy rains. Epidemic outbreaks involving hundreds and even thousands of people are often recorded. Leptospirosis is not recorded in areas with high acidity of water or high content of mineral salts in it.
Anthropurgic foci
Up to 95% of cases of the disease are associated with human infection from farm animals, which occurs in rural areas and cities at enterprises for processing animal raw materials. A special role is given to rodents and dogs. The share of cases of infection from dogs in Moscow and St. Petersburg accounts for up to 70% of all cases of the disease. In cities, gray and black rats often suffer from leptospirosis. The peak incidence occurs during the swimming season. Children and adolescents often get sick. In anthropurgic foci in rural areas, people employed in agriculture are more likely to get sick, since infection occurs especially easily and intensively. Water transmission is the main route of infection. Fur farm personnel are exposed to a certain risk of infection.
Rice. 7. In cities, dogs, gray and black rats often suffer from leptospirosis. The photo on the right is a sick animal.
Disease groups and risk factors
The following are at a certain risk of contracting leptospirosis:
- Livestock breeders.
- Agricultural workers.
- Workers in slaughterhouses and meat processing plants.
- Veterinarians and pest control specialists.
- Fur farm staff.
- Persons involved in water sports.
- Dog kennel employees and their owners.
- Dog handlers.
- Laboratory workers who work with rodents and pure cultures of pathogens.
Risk factors for leptospirosis:
- Participation of people in agricultural work: mowing water meadows, cultivating rice, flax and other irrigated crops, harvesting hay.
- Participation in water reclamation works.
- Work in garden plots.
- Hunting and fishing.
- Hiking trips.
- Swimming in natural reservoirs.
- Using water from unverified sources.
- Using food without proper heat treatment.
- Inappropriate organization of watering for farm animals.
Seasonality
The incidence of leptospirosis has a pronounced seasonality. The maximum number of cases occurs in the summer-autumn season (the peak occurs in August).
Rice. 8. Microphotograph of a bacterium.
Treatment and prevention of leptospirosis
Due to the high probability of multiple organ failure, even with a mild course, the patient must be hospitalized. They are treated with penicillin and, of course, against the background of active intravenous symptomatic therapy.
There is a vaccine, it is well tolerated, but vaccinations are done according to indications during an outbreak or in a natural source of infection. Repeated vaccination is done after a year. Dogs must be vaccinated. In case of contact with an infected animal, antibiotics are prescribed.
You can learn how to speed up recovery and ensure the fastest possible recovery from an infectious disease specialist at the international clinic Medica24, who has completed training and internship in the best centers in the country. Contact the Center for Infectious Diseases by phone 24 hours a day +7 (495) 230-00-01
The material was prepared by an infectious disease specialist at the international clinic Medica24, Doctor of Medical Sciences Margarita Vasilievna Nagibina.
Diet
Diet 5th table
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 14 days
- Duration: from 3 months or more
- Cost of products: 1200 - 1350 rubles per week
Diet 7 table
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after a week
- Terms: 1 month or more
- Cost of products: 1200-1300 rubles per week
In order for the treatment to be as effective as possible, the patient is recommended to adhere to the Table No. 5 , which has a beneficial effect on the liver. In case of kidney damage, it is recommended to follow the diet Table No. 7 .
The patient's diet should contain the following products:
- Fresh vegetable and fruit juices, compotes, rosehip decoction.
- Pumpkin, carrots.
- Oatmeal, buckwheat.
- Honey.
- Lean meat and fish.
- Vegetable soups.
- Egg white, one egg per day is allowed.
- Low-fat cottage cheese, yogurt
- Stale bread, oatmeal cookies.
The following should be excluded from the diet:
- Meat of young animals, fatty meat.
- Mushrooms.
- Fatty fish.
- Legumes.
- Salty foods.
- Alcohol.
- Canned food, smoked meats.
- Soda.