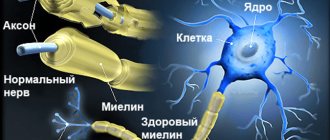
A stroke, formerly called apoplexy or cerebral stroke, is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation. Blood does not enter the brain cells, they stop receiving oxygen and begin to die.
During a stroke, a person's abilities that are controlled by the affected area of the brain, including, for example, memory and muscle control, are lost.
A stroke can happen to anyone, anywhere, at any time, which is why it is important to be educated about the signs of a stroke and know what to do.
Types and classification
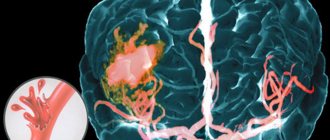
A major stroke occurs when large arteries are damaged, including the carotid arteries - they take part in the blood supply to the cerebral hemispheres. As a result of their blockage or rupture, the power supply to one or even two hemispheres may completely stop. This leads to a sharp deterioration in nervous activity, and in the absence of medical assistance within the first few hours, to death. It is important to determine the type of stroke and its causes - these factors influence the selection of further treatment and rehabilitation after a stroke.
Ischemic major stroke
Ischemic stroke occurs in 80% of patients. Its main reason is the deterioration of blood conductivity through the vessels, while their walls remain undamaged. Ischemia is oxygen starvation of tissues, which is especially dangerous for the brain. This type of stroke can occur suddenly or develop gradually, against the background of the main predisposing factors:
- blockage of a vessel by a thrombus, including atherosclerosis and plaque formation;
- vascular spasm, as a result of which blood cannot flow freely to the brain tissues;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure - in such conditions, a small amount of oxygen-enriched blood reaches the nervous tissues.
With an ischemic stroke, there is still a chance of full recovery. If the walls of the vessel remain intact, in the first few hours all possible measures should be taken to restore blood circulation.
Extensive hemorrhagic stroke
A hemorrhagic stroke is a stroke that occurs when an artery ruptures. Its second name is non-traumatic cerebral hemorrhage. This is a dangerous phenomenon that can be fatal even if emergency care is provided in a timely manner. An extensive hematoma deprives brain tissue of the ability to receive and transmit nerve impulses, which can result not only in deterioration of memory, attention, skills and reflexes, but also coma and complete suppression of nervous activity.
There are several types of hemorrhagic stroke, which differ in the location of the hematoma and the degree of danger for the patient.
- Intracerebral hemorrhage is the most common type. Blood enters the brain matter and damages nerve cells that are responsible for various skills and functions in the human body. Risks to the patient's life are present, but they are minimal compared to other types of hemorrhagic stroke. The main causes are hypertension (high blood pressure), atherosclerosis and thrombosis. P
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage is a pathological condition in which blood enters the subarachnoid space, between the membranes of the brain. It often occurs spontaneously and can be fatal, even with prompt medical attention. Among the causes of subarachnoid hemorrhage, in addition to hypertensive crisis, are smoking, excess weight and alcohol abuse - all these factors lead to weakness of the vascular walls.
The danger of hemorrhagic stroke is that not every patient is able to fully restore lost skills. Even if all the doctor’s recommendations are followed, the nerve tissues undergo necrosis and cannot perform the function of transmitting nerve impulses.
Brainstem stroke
Both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes can be located in the brainstem center. Here are vital centers that are involved in the regulation of breathing, swallowing, and heart rate. If blood enters this area, it can be instantly fatal due to the cessation of breathing and heartbeat.
Early and late diagnosis of the disease
The early detection of circulatory disorders in the brain structures has a great influence on the final result of rehabilitation. If this is successful, the doctor first assesses the patient’s condition using the following indicators:
- The number of points is determined using a special stroke scale.
- The time from the onset of the disease is recorded.
The patient is examined using MRI, determining the volume of tissue affected by the disease. After this, the patient is diagnosed and the prognosis for rehabilitation is considered. In fact, this is an attempt to predict what may happen to a patient in the first month after a stroke.
The sum of points on the disease scale allows doctors to predict what will happen to the patient after another stroke. The patient's chances of recovery increase sharply if he is under 40 years old and has a spouse. A low (compared to other patients) body temperature during the acute stage of the disease can give a chance for successful rehabilitation.
Read also: First aid for stroke game
Rehabilitation conditions improve if, in the first 7 days after a stroke, a person experiences positive dynamics, indicating some improvement in the patient’s condition. Such patients quickly restore speech skills and motor functions.
When diagnosing a stroke in a person late (it is carried out 30 days after the onset of the disease), doctors assess the condition and the chances of recovery based on factors such as:
- Manifestations of impaired motor function, speech disorder (at the same time, vision damage is possible), a drop in the patient’s mood, a change in his behavior.
- A person who has suffered a stroke experiences difficulties with self-care and movement, and cannot go to the store or drive a car on his own.
- After the third apoplexy, most patients cannot work in the same place.
After taking into account all these factors, doctors make a prognosis for the recovery of a particular patient after a stroke. If treatment is possible, the patient is prescribed the appropriate drug. Full recovery occurs in only 12-15% of the total number of patients with stroke.
An unfavorable outcome occurs when the patient has impaired perception and consciousness, persistent paralysis of the limbs, and signs of urinary incontinence.
Causes and risk factors
A major stroke can happen suddenly, but in some cases symptoms worsen over several hours. An attack can occur in any person, regardless of gender and age. However, there are a number of predisposing factors that reduce the strength and elasticity of the vascular walls, thereby increasing the likelihood of developing a stroke. These include:
- old age (over 50 years) - over time it is worth paying more attention to proper rest, proper nutrition and physical activity;
- chronic hypertension - patients are advised to monitor their well-being and regularly measure blood pressure;
- any heart disease - if it worsens, there is a risk of increased or decreased pressure, deterioration in the quality of vascular walls, various types of arrhythmia (regular examinations are required);
- ischemic attacks - often occur as precursors of a stroke or heart attack;
- type and schedule of work, including high levels of nervous tension, night shifts and hazardous working conditions;
- bad habits - smoking reduces the strength and elasticity of blood vessels, causing surges in blood pressure;
- overweight;
- vascular diseases, including stenosis (narrowing) of the arteries that supply the brain;
- hereditary predisposition - a history of stroke in relatives.
To reduce the likelihood of a major stroke, doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute recommend undergoing regular examinations for any pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, as well as in old age. It is also important to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, choose proper nutrition and perform light physical activity. Fatty foods of animal origin are the main source of cholesterol. It accumulates on the vascular walls and can form plaques that narrow the lumen of the arteries.
Another reason for major strokes and complications after them is the lack of early diagnosis and timely treatment. The most effective period during which it is important to see a doctor is the first two hours. The Clinical Brain Institute has the necessary equipment, and specialists have extensive experience in treating strokes of any type, which guarantees maximum chances for a successful recovery.
Prevention of strokes
You can take care of yourself now by changing your daily habits and consulting with your doctor based on the results of a comprehensive examination.
Below are a number of simple rules that will help prevent over half of all cases of ischemic stroke:
- get into the habit of daily walks for 40 minutes (this is the best remedy for stress relief, good sleep, and also gymnastics for blood vessels)
- establish a healthy diet (more vegetables in any form, potatoes don’t count; try organizing vegetable days - it’s not only satisfying, but also very healthy);
- Schedule time in your schedule for live communication with dear and interesting people;
- Go to bed no later than midnight, use blackout curtains in the bedroom and turn off all gadgets. This is a prerequisite for the production of sufficient levels of melatonin, a hormone that lowers blood pressure, body temperature and blood glucose levels, and also promotes good deep sleep.
- give up bad habits;
- pay attention to the annual preventive examination, especially after 40 years (everyone should know the level of their blood pressure, sugar and lipids in the blood. Take advantage of the social discount for your elderly relatives);
- follow the therapy prescribed by the doctor;
- Practice positive thinking and relaxation techniques.
And remember: exercise is one of the key healthy habits for stroke prevention!
Compliance with all of the above rules reduces the risk of stroke by 80% in both men and women.
Clinical picture
A major stroke occurs with damage to a large area of the brain. The clinical picture is pronounced, and the damage poses a danger to the patient’s life. It is important to seek emergency help if the victim exhibits the following symptoms:
- a sharp decrease in hearing and vision, impaired coordination of movements, inability to concentrate;
- acute headache, dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- redness of the skin and mucous membranes or their pallor;
- decreased skin sensitivity, often on one side of the face or torso, muscle paralysis;
- the appearance of memory lapses;
- fainting.
With a major stroke, there is still a risk of developing coma. This is a condition in which the victim does not respond to any external stimuli, but his breathing and heartbeat continue. The coma can last for a long time, and the chances of further recovery depend on this.
What conditions are necessary for a favorable prognosis?
Patients who were admitted to hospital on time survive. This should happen within 2-5 hours after the third stroke.
The chances of rehabilitation increase sharply if the person is young or the patient does not have concomitant diseases. The prognosis is more favorable for women than for men.
The chance of recovery decreases sharply if a person has been diagnosed with mental disorders. The prognosis will be favorable for people who have had a third apoplexy in the absence of severe neurological symptoms.
When a patient's movements in his arms and legs are restored within 90 days after paralysis and paresis, in some cases doctors are able to completely rehabilitate the health of such a patient. After 6-7 months, 50% of people with such symptoms can switch to full self-care. 30% of patients still need outside care.
If a person who has suffered a third apoplexy is lonely, then he has less chance of recovery than patients living in families.
Test for rapid diagnosis of major stroke
At home, you can identify the first signs of cerebrovascular accident and prevent the development of a major stroke. They can appear several hours before the attack, and it is important to distinguish them from the normal state. The patient may not understand the danger of what is happening and may be in good health, so primary diagnosis is the task of those around him. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain offer to familiarize yourself with simple tests that should be performed immediately if you suspect a stroke - they will help you seek medical help early and increase your chances of a full recovery.
- The first way to detect a stroke is to ask the person to smile. When cerebral circulation is impaired, one of the corners of the mouth remains drooping.
- The second way is to raise both arms in front of you and hold them for a few seconds. If normally this exercise does not cause difficulties, then during a stroke one arm either does not rise or immediately falls down.
- The third way is to ask to repeat a simple sentence. The person's speech may become unintelligible. You can also ask simple questions about the location of the victim, his name and date - he will not be able to give a clear answer to them.
- The fourth way is to direct the light source into the eyes. During a stroke, one of the pupils does not respond to light, while the other will constrict and then dilate in less intense light.
It is important to understand that not all the first signs of a stroke may appear in one person. If at least one of the points coincides, it is important to seek emergency medical help. At an early stage, there is a possibility of completely preserving brain functions and not losing nerve connections.
Ischemic cerebral stroke: prognosis and consequences
Cerebral stroke, or “brain stroke,” is the number two “killer” in the structure of overall mortality worldwide: 25% of men and 39% of women die due to it.
More often, in four cases out of five, it is ischemic in nature, that is, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted due to blockage of the arteries by a thrombus or embolus.
Read also: Stroke and stress
The brain is such a delicate and demanding structure of the body that with a weight of 2% of body weight, it consumes 1/5 of the volume of incoming oxygen and 17% of all glucose. Even a short-term disruption of the blood supply to a small area of the brain does not go away without leaving a trace. If ischemia continues for more than 5 minutes, irreversible changes in the cerebral cortex occur. When the focus is localized in the midbrain, the cells die within 10 minutes of ischemia, and in the medulla oblongata - within 25 minutes.
What are the consequences and prognosis of ischemic cerebral stroke - read in this article.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
Treatment tactics depend on the type of major stroke, the patient’s age, concomitant diseases and other factors. With the hemorrhagic type, it is important to eliminate the source of bleeding, and some patients may require surgery to remove the hematoma or aneurysm. For ischemic stroke, therapy is carried out in several directions:
- correction of breathing and heartbeat;
- elimination and prevention of brain swelling;
- thinning the blood and preventing the formation of blood clots;
- symptomatic treatment aimed at relieving seizures, fever and other clinical signs.
The Clinical Institute of the Brain has all the necessary conditions for the treatment and rehabilitation of patients with strokes. At the first stage, all procedures must be carried out in a hospital, under round-the-clock supervision of doctors. In addition, in the first weeks the likelihood of a second attack is increased, and it is important not to miss its first symptoms. After complete stabilization, treatment continues at home, with mandatory examinations and constant monitoring of the patient’s condition.
Predisposing factors to the development of stroke
Stroke prevention is an important component of a person’s healthy lifestyle.
Risk factors for stroke:
- unstable hypertension with significant pressure drops;
- atrial fibrillation, as one of the heart rhythm disorders;
- diabetes;
- inhalation of tobacco smoke (active and passive smokers);
- alcohol consumption (more than 50 g of strong alcohol per day, 200 g of wine or half a liter of beer);
- abdominal obesity (waist circumference over 88 cm in women or 102 cm in men);
- salt consumption more than 5 g per day (teaspoon);
- frequent stress and psycho-emotional overload;
- physical inactivity.
If at least one of these points is present in your life or the life of a person close to you, you need to think about stroke prevention now. An examination and consultation with a specialist at our multidisciplinary center will help you assess the actual risk of developing the disease. Qualified doctors who have been trained in leading Russian and European clinics and are constantly improving their qualifications work here. The annual medical care program at the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia will allow you to be completely confident in the health of yourself and your loved ones!
Recovery after a major stroke
An important stage is the restoration of skills lost after a stroke. These can include the simplest functions, including speech, writing, and self-service in everyday life. A comprehensive program may include several stages:
- motor rehabilitation, development of damaged limbs, development of fine motor skills;
- speech, including regular classes with a speech therapist;
- physiotherapy is a set of techniques to improve blood circulation and improve brain nutrition.
The Clinical Brain Institute offers individual treatment and recovery programs after a major stroke. Here you have the opportunity to undergo a full examination and rehabilitation in a hospital setting, and then undergo examinations and attend useful procedures (physical therapy, hardware treatment, electrical and magnetic stimulation). A neuropsychologist, speech therapist, massage and physical education specialists work at the Clinical Institute of the Brain. However, exercises at home also play an important role in rehabilitation and should be performed by the patient independently.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 11 votes
Share article on social networks
Disease prognosis
We should talk about three outcomes of stroke: recovery, disability and mortality, both of which can be considered favorable. Within a month after an ischemic stroke, every third or fourth patient dies. By the end of the first year, mortality increases to 50% in rural areas and 40% in large cities.
Stroke is the first cause of permanent disability in the structure of disability in Russia. Only one in five patients who have suffered a cerebrovascular accident can return to work, and no more than 10% recover completely.
Among those who survive, half of people have another episode within five years.
The fate of a particular patient depends on the location and size of the ischemic focus, the condition of the cerebral vascular anastomoses and concomitant pathology. It is difficult to make an individual forecast even after the most detailed examination. If the stroke zone is localized in the area of the pyramidal tract, motor disorders will be more pronounced, if speech disorders are observed in the cortical speech areas of Brocca and Wernicke.
However, there are general trends that have statistical significance. For example, it is known that certain factors worsen the prognosis:
- Location. It is known that urban residents suffer from stroke much more often than rural residents: the incidence of the disease is 3 and 1.9 cases per 1000 population, respectively. However, the mortality rate from stroke in the region is higher than in the city, which emphasizes the role of timely provision of qualified medical care.
- Repeated strokes. In 3/4 of cases, stroke develops primarily, in 25% - secondary. Quite accurate risk assessment scales have been developed to predict secondary stroke, but the prognosis is much more difficult.
- Elderly age. In half of the cases, the disease develops at the age of 70 years or older; the mortality rate in such patients is also significantly higher than in the general population. The prognosis for recovery of speech and complex movements is also usually much worse.
- Personality changes. With any stroke, cognitive and emotional-volitional disorders occur. By the degree of their severity and the speed of reverse development, one can also judge the prognosis of the disease.
The positive outcome of the disease is influenced by factors such as earlier provision of medical care, early activation and initiation of rehabilitation measures, as well as spontaneous restoration of lost functions, both speech and motor.
For a more accurate forecast, individual risk assessment scales have been developed. Unfortunately, they are not able to predict the first episode of stroke. The most common cause of ischemia is cerebral artery embolism. It is almost impossible to prevent the detachment of a plaque or blood clot and blockage of a vessel using medication, as well as to predict at what point this will happen.
Methods for assessing total risk factors show good results in terms of preventing secondary episodes. A fairly accurate prediction of stroke is provided by the AVSD scale in patients who have already suffered transient ischemic attacks (TIA). It includes criteria such as age, blood pressure, clinical symptoms and their duration, as well as the presence or absence of diabetes mellitus.
Programs:
Assessment of rehabilitation potential
Movement restoration
Rehabilitation after stroke
Restoration of cognitive functions
Early (resuscitation) rehabilitation
How to provide first aid for a stroke
There is a clear algorithm for providing first aid to a person suffering from a stroke :
- Call a medical team . To do this, you need to dial 103 from a landline phone. If you happen to have a smartphone at hand, then the call is made to the single number 112. The doctor must immediately be informed that the person is unwell and there is a suspicion of a stroke.
- The victim must be laid on a flat surface so that his head is higher than his body. They take off his glasses and remove his lenses. If possible, you need to help him get removable dentures.
- If there is no consciousness, then you need to open the patient’s mouth slightly and turn his head to the side . This is done to prevent aspiration of vomit. It is imperative to listen to the patient’s breathing.
- For better access to fresh air, it is recommended to open a window or vent..
- Before the arrival of the medical team, it is necessary to prepare documents, if any..
Doctors need to be informed about the person’s illnesses, as well as what medications he is taking. It is prohibited to give the victim any medications. Medication correction should be carried out by emergency physicians. You should not try to give water or food to a person. This may make the situation worse.
If the patient falls and has an epileptic attack, there is no need to unclench his teeth or try to hold him. It is necessary to protect the victim from injury. To do this, place a soft object, such as a pillow, under his head. If a stroke with an epileptic attack happened on the street, then you can use a jacket or other suitable thing. Foam flowing from the mouth is wiped away with a cloth. The head should be elevated at all times.
There is no need to try to bring a person to his senses with ammonia. Until the end of the attack, it should not be moved from place to place.
If breathing stops, resuscitation measures must be started immediately. To do this, perform a heart massage and breathe mouth to mouth or mouth to nose.
How to provide first aid for a stroke
There is a clear algorithm for providing first aid to a person suffering from a stroke :
- Call a medical team . To do this, you need to dial 103 from a landline phone. If you happen to have a smartphone at hand, then the call is made to the single number 112. The doctor must immediately be informed that the person is unwell and there is a suspicion of a stroke.
- The victim must be laid on a flat surface so that his head is higher than his body. They take off his glasses and remove his lenses. If possible, you need to help him get removable dentures.
- If there is no consciousness, then you need to open the patient’s mouth slightly and turn his head to the side . This is done to prevent aspiration of vomit. It is imperative to listen to the patient’s breathing.
- For better access to fresh air, it is recommended to open a window or vent..
- Before the arrival of the medical team, it is necessary to prepare documents, if any..
Doctors need to be informed about the person’s illnesses, as well as what medications he is taking. It is prohibited to give the victim any medications. Medication correction should be carried out by emergency physicians. You should not try to give water or food to a person. This may make the situation worse.
If the patient falls and has an epileptic attack, there is no need to unclench his teeth or try to hold him. It is necessary to protect the victim from injury. To do this, place a soft object, such as a pillow, under his head. If a stroke with an epileptic attack happened on the street, then you can use a jacket or other suitable thing. Foam flowing from the mouth is wiped away with a cloth. The head should be elevated at all times.
There is no need to try to bring a person to his senses with ammonia. Until the end of the attack, it should not be moved from place to place.
If breathing stops, resuscitation measures must be started immediately. To do this, perform a heart massage and breathe mouth to mouth or mouth to nose.