The term “concussion” translated from Latin means “bruise.” A more precise definition of concussion is: general damage to the human body due to a sudden strong mechanical impact (water, sound from an air wave, impact with water or ground, and so on), which is not always accompanied by damage to tissues and organs. This phenomenon is characterized by loss of consciousness from short periods of time to a long coma. Characteristic symptoms of concussion are amnesia, dizziness, loss of consciousness, headaches, hearing and vision impairment. After a severe concussion, a person may lose hearing and vision, as well as fall into a prolonged coma with impaired body functions. As a rule, the type of pathology depends on the damaged organ: brain contusion, eye contusion, etc.
The consequences of concussion can be varied: from temporary loss of vision, hearing and speech with further partial or full recovery to severe mental disorders.
Causes and risk factors
Concussion can have several causes. The conditions for the appearance of pathology in everyday life, at work and on the battlefield differ significantly from each other, so approaches to diagnosis and treatment will differ from each other.
Explosion is one of the common causes of concussion
Table: causes of contusion in different conditions
| Military reasons | Production reasons | Household reasons |
| Use of firearms | Powerful vibrations of various equipment | Gas cylinder explosion |
| Military grenade explosion | Explosions of flammable substances in workshops | Fall from a great height |
| Prolonged stay in military equipment while it is moving | Pressure drops when diving to depth | Sudden change in atmospheric pressure |
| Violation of safety regulations during military operations | Collapse of sand or rocks | Physical and mechanical impact on the body (accident) |
| Depressurization of a submarine or aircraft | Excessive noise levels and harsh sounds in production | Strong impact on the water surface |
Table: causes of contusion damage to individual organs
| Brain | Auditory and vestibular apparatus | Visual apparatus | Spinal column |
| Traumatic brain injury | A sharp blow to the ears | Impact with force that deforms the eyeball | Traumatic damage to the bones of the spine |
| Infectious and inflammatory processes in brain tissue, leading to its enlargement | Mechanical rupture of the eardrum | Compression of the eyeballs | Infectious processes in the bones of the spine (syphilis, tuberculosis) |
| Dropsy of the brain | Accumulation of fluid in the middle ear cavity | A sharp increase in intraocular pressure | Changes in atmospheric pressure |
| Violation of the biological and chemical composition of cerebrospinal fluid | Infectious and inflammatory processes in the sinuses of the skull | Impaired blood supply to the eyeball and optic nerve | Bone compression and deformation |
Risk factors
Like any traumatic injury, concussion has certain risk factors. By reducing their number, the possibility of pathology occurring is minimized. But unfortunately, most of them cannot be completely eliminated.
Main risk factors:
- engaging in dangerous sports;
- work in physical and chemical production;
- work related to the effects of vibration on the body;
- long stay in the zone of radiation contamination;
- work with high-power radiation;
- violation of safety regulations when handling weapons;
- violation of the rules of movement in military transport;
- staying in the blast wave zone;
- close proximity to a military training ground where weapons are tested.
Bottom line
An eye contusion is a serious injury that can lead to critical vision loss. Therefore, immediately after providing first aid, the victim must be checked by a doctor (traumatologist, ophthalmologist), undergo the required tests and complete the course of therapy to the end. An untreated disease is dangerous for the development of complications that are worse than the disease itself.
Sources used:
- Stratton GM Vision without inversion of the retinal image (English) // Psychological Review (English) Russian. : journal. — 1897.
- Eye diseases. Fundamentals of ophthalmology / Edited by Professor V. G. Kopaeva. — M.: OJSC “Publishing House “Medicine”, 2012.
- D. Hubel. Structure of the eye, brain, vision. — ed. A. L. Byzova. - M.: Mir, 1990.
- Department of Ophthalmology - University of Colorado
Eye contusion
There are two types of eye contusions:
- Direct - a blow to the eyeball with a large object, for example, a ball, a fist, a sliver when chopping wood;
- Indirect – concussion of the torso during a fall.
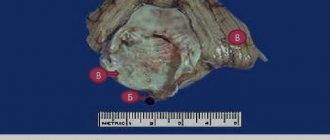
The degree of damage is affected by the force and direction of the impact, the mass and speed of the traumatic object. As a result, after a contusion, a slight hemorrhage may occur in the thickness of the eye, and with severe injuries there is a high risk of rupture and destruction of the eyeball.
A strong blow to the eye leads to the fact that all the structures of the organ are displaced back. The eyeball itself is a closed structure that is filled with incompressible liquid content. Such displacement during contusion provokes identical stretching of the fibrous capsule of the eye in width.
What should you do if someone suffers such damage?
Help for a person who has been shell-shocked must be provided taking into account the fact that he is unconscious. He is completely helpless. Therefore, if, for example, he fell face-first into a puddle, he could easily choke. And if there is a spark on the clothes, it can burn.
If the degree is not severe, then consciousness will return quickly enough , and the only help in this case will be to make sure that he breathes well. It is important to check for bleeding and also call an ambulance quickly. There is nothing more you can do to help.
Now you know what to do first if someone is injured and concussed as a side effect of this disaster.
Healing Methods
Treatment of contusion in a medical facility involves a set of measures:
- Drug therapy. The attending physician - a neurologist or traumatologist - prescribes medications depending on the type and severity of the injury. The main efforts are aimed at normalizing water balance, eliminating pain, suppressing the gag reflex, solving neurological problems, and fighting inflammation.
- Surgical intervention. The operation is indicated to normalize intracranial pressure, in case of hemorrhages, or violation of the integrity of the skull. In these cases, the patient cannot be treated only with conservative methods.
- Psychotherapeutic sessions. Elimination of neurasthenic manifestations, depression, pathological fears.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at restoring motor skills.
- Speech therapy exercises to help cope with the absence or defects of speech.
During rehabilitation, the patient is recommended massage, sanatorium treatment, and soothing baths. Family support, a favorable microclimate at work, and the absence of noise and turmoil are very important at this time. The participation of family and friends is the most important condition for successful recovery.
To clarify the diagnosis of a possible brain contusion, the doctor:
- Finds out the causes of injury.
- Collects anamnesis.
- Interviews witnesses to the incident (if the patient is unconscious).
- Conducts a general examination and evaluates the functioning of important organs and systems.
These actions are carried out at the scene of injury or after the person is transported to the hospital.
In the future, the following diagnostic methods are used:
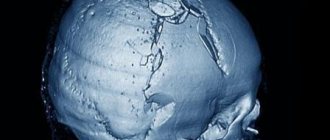
- X-ray examination reveals violations of the integrity of the bones of the skull (severe head injury is a mandatory indication for this examination).
- Electroencephalography, which allows you to study the brain by recording its bioelectrical activity.
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging will help to accurately determine the severity and location of injuries received, even in the deep structures of the brain.
Having established the extent of the damage and identified possible hemorrhage, the specialist prescribes appropriate treatment. It should be noted that during the period of therapy and rehabilitation, the patient will have to be periodically examined so that the recovery process can be monitored over time.
The examination is carried out using instrumental methods - CT, MRI, EEG. Additionally, blood tests and lumbar puncture tests are performed. The degree of neurological impairment is determined using special tests. Level of disturbance of consciousness – according to the Glasgow scale.
What other outcomes are there?
We can talk forever about what concussion leads to. If the brain is affected, then the person may be bothered by headaches, intolerance to sounds, sudden changes in light, and stuttering. Psychological disorders also often occur here.
If a person receives a second degree contusion, complications may include disruptions in the functioning of the heart muscle of the respiratory system. When suffering from a severe form of the disease, it is important to provide the necessary treatment in a timely manner . Otherwise, death may occur.
Regardless of the degree of the disease, contusion is the presence of a large number of fractures and cracks, as well as concussions. When examining for the presence of disorders, it is important to pay attention to the kidneys, liver, and spleen.
If we talk about preventive measures that are aimed at preventing illness, doctors strongly recommend paying attention to the rules of personal safety. You should avoid places where you can get such severe injuries.
In wartime, it is not so difficult to protect yourself from shell shock. In any case, if the first symptoms appear, you can visit a doctor and get examined.
Read more about contusion of the eye and human ENT organs in separate articles.
Consequences
Most often, contusion develops when affected by the air shock wave of a powerful explosion, when mechanical trauma is necessarily combined with barotrauma and vibration trauma, as well as with acoustic trauma, although the significance of the latter is small. The terms “blast injury” and “air concussion” are often, and not without reason, used as synonyms for the term “concussion”. However, concussion occurs not only from the action of an air, but also a water shock wave during an underwater explosion, and sometimes without connection with any explosion, as a result of only a mechanical impact, more or less uniformly injuring a significant surface of the body. Thus, a concussion can cause a fall flat into the water from a considerable height, an impact with large masses of loose bodies - sand, small stones, for example, during landslides, if the victim is carried away by the flow of crumbling soil. But in these cases, important components, especially hearing impairment, may disappear from the typical picture of concussion, while with a blast injury, concussion syndrome develops in full (disorders of consciousness, hearing, speech, central nervous system, manifested to varying degrees) according to the severity of the injury .
On this topic ▼
Explosion
Effects of the shock wave and damaging factors
The pathogenesis of contusion is based on extreme inhibition of the central nervous system (CNS), which occurs in response to extremely strong irritation. In addition, a number of manifestations are due to changes in the hearing system, in the paranasal sinuses; these changes are caused mainly by barotrauma. The disorders typical of general contusion are often accompanied by additional ones caused by local mechanical damage to tissues and organs. In case of blast injury, these injuries are usually divided into primary, caused by the shock wave itself, secondary, caused by stones, logs and other secondary projectiles, and tertiary, occurring in the victim thrown back by the explosion when hitting the ground, wall, etc.
Primary damage may include bruises on the surface of the body facing the direction of the explosion; they manifest themselves as bruising and the formation of blisters on the skin. Severe, even fatal, primary injuries to internal organs are common with water shock wave injuries and are less likely with air concussion. The exception is traumatic brain injury. Concussion syndrome is often accompanied by disorders caused by primary traumatic brain injury - cerebral contusion, cerebral compression and concussion. The latter, apparently, is observed most often, although the symptoms of a concussion cannot always be isolated from the general picture of the syndrome.
Secondary and tertiary injuries vary from mild (bruises, abrasions) to the most severe, such as rupture of internal organs, crushing of a limb, fracture of the spine, etc. Long-term compression of large muscle masses with the subsequent development of traumatic toxicosis is also possible.
The likelihood of local damage during a blast injury depends on the power of the shock wave and the characteristics of the terrain where the victim was located. The highest frequency of secondary and tertiary mechanical damage can be achieved during concussion caused by a nuclear explosion in a large populated area. During a nuclear explosion, combinations of contusions with thermal and radiation injuries (combined injuries) may occur.
Hearing-speech disorders
Hearing-speech disorders, so typical of concussion, are divided into two groups. The first group includes hearing impairments associated with barotraumatic changes in the peripheral part of the auditory organ - destructive or dislocation. The latter (displacement of the otolith membrane, individual sections of the organ of Corti) usually do not cause long-term consequences. Ruptures of the tympanic membrane, destruction of the formations of the middle and inner ear, hemorrhages in their cavity with subsequent degenerative atrophy of the spiral (Corti) organ, spiral ganglion, and nerve fibers lead (especially with the development of infectious complications) to long-term, sometimes persistent deafness or hearing loss.
The second group includes hearing disorders of central origin, caused by dysfunction of the brain. With acoustic trauma, deafness occurs as a result of inhibition of the auditory center under the influence of super-strong sound stimulation. The organic nature of functional disorders of the central nervous system that caused deafness is indicated in some cases by increased pressure and impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, leading to asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain (according to contrast encephalography), etc.
Speech disorders
Speech disorders without deafness are rare and short-lived; Deafness without mutism usually does not last long either. With surdomutism, hearing is usually restored much later than speech (several weeks after the concussion). To judge the duration of hearing loss, it is important to differentiate deafness caused by changes in the peripheral part of the auditory analyzer from deafness associated with a disorder in the function of the auditory centers, because with the latter, hearing can quickly improve and even return completely to normal without any consequences. After acoustic trauma, sometimes there remains a reduced perception of only the highest tones. Uniform bilateral hearing loss and the absence or insignificance of changes detected by otoscopy indicate a central origin of the disorders. Obvious asymmetry of hearing impairment indicates peripheral damage, which is consistent with the otoscopic picture. Long-term speech disturbances with rapidly recovering hearing indicate compression or contusion of the brain in the area of the motor center of speech. General contusion, not accompanied by concomitant local injuries, is recognized without difficulty on the basis of the wedge, manifestations, first of all, disturbances of consciousness.
Simultaneous impairment of hearing and speech (surdomutism), and even more so only speech (mutism), is mainly of psychogenic origin; Local damage to the larynx, nose and paranasal sinuses leads to changes in speech (aphonia, hoarseness, nasal sound), which is not typical for general contusion. In some cases, auditory-speech disorders have a mixed (peripheral and central) origin, and prolonged surdomutism, as a rule, is of hysterical origin.
Internal organ injuries
Recognizing trauma to internal organs is difficult, because the picture of severe general contusion masks the symptoms. Of the brain injuries, compression of the brain by an intracranial hematoma is especially important, the most demonstrative sign of which is a secondary (after the “lucid interval”) loss of consciousness, often preceded by an increase in headaches and drowsiness.
Brain damage due to explosion in war
Nowadays you can often find such consequences:
- Increased sweating.
- Epilepsy seizures.
- Hysterical attacks.
- Dizziness with concussion.
Dizziness
It can be observed at different stages of the disease. Often the cause of dizziness is a concussion. A sudden fall or beeping sound may cause injury.
Loud noise intolerance
The main reason for intolerance to loud sounds is acoustic trauma to the ear due to contusion. Factors and circumstances of such intolerance may be different :
- Shot from a weapon.
- Powerful explosion.
- Loud music.
- Shout.
And this is not the entire list of reasons that can disrupt the functioning of the hearing aid. Regardless of what factor affects the hearing organs, contusion can begin if the noise level is above 160 dB.
Tachycardia
Tachycardia is another consequence of contusion. It can begin with a heart bruise. Characteristic symptoms are severe shortness of breath and pain in the heart area.
Consequences for the psyche
Of particular danger are:
If you can somehow come to terms with the first consequences of a concussion for the psyche and muffle them, then epilepsy can begin at any time and in any place. Even simple external factors can indicate the onset of epilepsy.
Degrees
- Mild degree (first) . In this case, the damage is minor and the symptoms are not too pronounced. This degree of contusion has no negative consequences and does not require special treatment.
- Average degree (second). The patient may lose consciousness for a while. He may experience diarrhea and vomiting. Often there is some lethargy, aggression, problems with heartbeat and breathing. The functioning of the brain is impaired, so all functions slow down.
- Severe degree (third). In this case, the patient may not regain consciousness for up to 3 weeks. Sometimes a patient can die if first aid is not given and taken to the hospital.
Diagnosis of the condition
To distinguish a concussion from a regular bruise, concussion or shock, it is necessary to carry out a wide range of diagnostic measures. Since it is not possible to interview the patient at first after the injury, a brief life history is collected from his closest relatives or friends, and the circumstances of the injury and the first medical measures taken are collected from eyewitnesses of the incident.
After the patient returns to consciousness, the doctor collects complaints and checks the organs of vision, hearing, smell and the patient’s ability to move his limbs. Based on the data obtained, a preliminary diagnosis is made.
Conversation with the patient is an important stage in collecting anamnesis.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
To establish a final diagnosis, specialists resort to modern research methods. They allow us to clarify the severity of the lesion and suggest possible outcomes.
The main methods of instrumental examination are:
- X-ray examination: will determine whether the integrity of the bones (skull, limbs, spine) has been compromised;
- Ultrasound diagnostics: will show the presence or absence of hematomas and soft tissue damage;
- electroencephalography: is a recording of the bioelectric potentials of the brain, with its help you can track the decrease and increase in the activity of a particular segment, which will allow you to find out the location of the damage;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging: will allow you to differentiate a concussion from a bruise, fracture or concussion;
- visual acuity examination and intraocular pressure measurement: will help make a diagnosis of visual contusion;
- hardware diagnostics of hearing acuity using audiometry: will show the degree of damage to the hearing organs;
- static and dynamic functional tests: will allow you to determine damage to the balance organs;
- microscopic examination of the cellular composition of the cerebrospinal fluid using a puncture: will make it possible to diagnose a spinal cord contusion.
Treatment
Victims need rest; for moderate to severe concussions, strict bed rest for 1-3 weeks. Sedatives (bromides) and hypnotics (phenobarbital) are prescribed in the usual dosage; according to indications, drugs that stimulate respiration and cardiac activity are prescribed. In case of severe contusion, especially with the likelihood of a traumatic brain injury, a spinal puncture is indicated, always with measuring the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid and determining the content of protein and formed elements in it. For liquor hypertension, repeated punctures and dehydration therapy are needed; for hypotension, drip infusions of a 5% glucose solution are needed. At the end of the acute period, vitamins C, B1, B12, antipsychotic drugs (aminazine for 2-3 weeks), insulin (4-10 units 2 times a day) with oral glucose are prescribed. Warm baths or showers are recommended. In the future, with a long-term post-concussion psychasthenic state, a dosed workload, periodic sanatorium treatment, observation by a neuropsychiatrist, and complete abstinence from alcohol are necessary. Treatment of surdomutism and mutism should begin as early as possible, before the patient develops a consciousness of his own inferiority. Psychotherapy is of great importance - a thorough, systematically repeated examination of the ENT organs, creating the appearance of vigorous treatment. Treatment of persistent post-concussion deafness of organic origin. Persistent speech disorders require speech therapy treatment.
In case of musculoskeletal injuries accompanying contusion, treatment is carried out according to general rules. The appearance or increase of focal symptoms, changes in breathing indicate compression of the brain and require emergency craniotomy, which, if possible, should be preceded by an angiographic examination of the brain.
Signs of abdominal bleeding or peritoneal irritation prompt laparotomy.