Diabetic polyneuropathy is a common complication of diabetes mellitus. According to research, it is believed that up to a quarter of patients with this diagnosis suffer from clinically significant manifestations of the pathology. And in an asymptomatic form, the disease is detected in almost all patients with diabetes. Manifestations of polyneuropathy are quite characteristic and are expressed in the form of pain in the feet, legs, paresthesia, night cramps, and sensitivity disorders. Few people realize what diabetic polyneuropathy means, but if you consult a doctor too late, the disease can result in the appearance of skin ulcers on the feet, which can lead to the development of gangrene.
What is diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy
is a combination of syndromes affecting various parts of the peripheral and autonomic nervous system, which occurs against the background of metabolic disorders in diabetes mellitus and complicates its course.
According to statistics, being one of the most common and serious complications of diabetes, various forms of diabetic neuropathy are diagnosed in almost half of all patients with diabetes.
Diabetic neuropathy is characterized by signs of impaired conduction of nerve impulses, sensitivity, as well as various disorders of the somatic and autonomic nervous systems that arose when other causes and factors of nervous system dysfunction (trauma, infections, etc.) were excluded. The clinical manifestations of the disease are very diverse, so most doctors with a narrow specialization encounter diabetic neuropathy - neurologists, urologists, endocrinologists, gastroenterologists, dermatologists, etc.
Causes and mechanisms of development of diabetic neuropathy
The main cause of diabetic neuropathy is chronically elevated blood glucose levels.
, ultimately leading to changes in the structure and functioning of nerve cells.
Due to impaired carbohydrate metabolism in diabetes mellitus, patients develop microangiopathies
- pathological changes in the vessels of the microvasculature, due to which the normal blood supply to the nerves is disrupted. As a result of multiple metabolic disorders, swelling of the nervous tissue develops, all metabolic processes in the nerve fibers are disrupted, the conduction of nerve impulses deteriorates, the antioxidant system is inhibited, leading to the accumulation of free radicals that have a detrimental effect on nerve cells, the production of autoimmune complexes begins, which ultimately can lead to atrophy of nerve fibers.
There are a number of factors that increase the risk of developing diabetic neuropathy:
- old age;
- long history of diabetes mellitus;
— decompression phase;
- increased blood pressure;
- overweight and obesity;
- smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages.
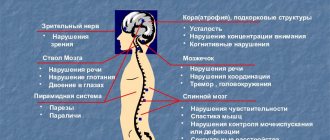
Diabetic neuropathy - symptoms, syndromes, types
Diabetic neuropathy is classified in several ways. A number of authors distinguish four main types of diabetic neuropathy:
— peripheral neuropathy
- one of the most common types, in which there is damage to the nerve fibers of the extremities, and the lower extremities are affected more often;
— autonomic neuropathy
- in which the functioning of many internal organs is disrupted - the heart, stomach, intestines, and sexual dysfunction develops;
— proximal neuropathy
- characterized by severe pain in the thighs, buttocks and hip joints;
— focal neuropathy
- in which local damage to individual nerve fibers occurs.
There is a classification of diabetic neuropathy, which is based on the principle of identifying syndromes with characteristic clinical manifestations and course. According to it, diffuse neuropathy
(affecting all nerve fibers) and
focal neuropathy
(affecting certain areas of the human body).
The prevalence of diffuse neuropathy is much higher, it progresses rapidly and is often asymptomatic. It includes autonomic diabetic neuropathy
and
distal symmetric sensorimotor diabetic polyneuropathy
.
Focal neuropathy is less common and occurs acutely, losing its clinical manifestations over time. It includes cranial neuropathy, radiculopathy, plexopathy, mononeuropathy.
Dynamics of manifestations
In patients suffering from sensory polyneuropathy of the lower extremities, positive sensory symptoms (burning sensations and other paresthesias) first appear in the feet, most often in the fingertips. Over time, negative sensory symptoms (numbness and decreased sensitivity) appear. As shorter and shorter nerve fibers are affected, they gradually spread proximally (to the lower leg and thigh).
After the symptoms in the legs rise to the middle of the legs, a violation of superficial sensitivity appears in the arms. This leads to the classic "socks and gloves" look. If the sensitivity disorder has risen to the middle of the thigh on the legs and to the level of the elbow on the arms, you can expect the appearance of an area of reduced sensitivity in the lower part of the anterior abdomen. It is caused by damage to the longest trunk nerves and has the shape of an irregular semicircle with the apex directed towards the sternum. In contrast to the level of damage in diseases of the spinal cord, sensory disturbances in sensory polyneuropathy are detected only on the anterior surface of the body and are absent on the back. Their upper border is curved rather than horizontal.
With porphyritic polyneuropathy, sensory disturbances are not detected on the feet and hands. And in the proximal parts of the limbs and on the trunk. If deep sensitivity fibers are involved in the pathological process, sensitive ataxia develops - a disorder of sensory perception of pressure, vibration and body position in space. It leads to incoordination and movement disorders. It manifests itself as a disorder of coordination and gait, decreased tone of skeletal muscles and distal limbs. Patients experience constant worm-like hyperkinesis of the upper extremities (slow movements of the fingers) with outstretched arms, which intensify with closed eyes.
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral diabetic neuropathy occurs predominantly in the lower extremities and is characterized by burning and painful sensations in the legs, often occurring at night, a feeling of sudden heat or cold, and pins and needles in the legs. Patients are very sensitive to touch, sometimes it is even painful. Deformations of the muscles of the limbs may be observed. Any damage. violating the integrity of the skin of the extremities become wounds that do not heal over a long period.
Autonomic neuropathy
Autonomic diabetic neuropathy is characterized by damage to the autonomic nervous system, which controls and coordinates the functioning of internal organs. In this case, violations of most organs and systems may be observed.
In particular, when the nerve fibers responsible for the functioning of the digestive system are damaged, patients complain of nausea, heartburn, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach even with a small amount of food consumed, flatulence, diarrhea or constipation. These symptoms may indicate the development of gastroparesis, a dysfunction of the stomach. At the same time, there is a slowdown in the evacuation of food from the stomach to the intestines. If the process involves the nerves that control the small intestine, nocturnal diarrhea develops.
If the nerve fibers responsible for the functioning of the genitourinary system are damaged, bladder paresis may develop, while urine is not evacuated from the bladder in a timely manner due to the lack of urge to urinate, thereby increasing the risk of a genitourinary tract infection. Patients complain of frequent, infrequent or involuntary urination.
In addition, due to the negative impact on the nerves responsible for the occurrence and maintenance of an erection in men during sexual arousal, autonomic neuropathy can lead to erectile dysfunction while maintaining sexual desire in the patient. Female patients may complain of decreased arousal and excessive dryness in the vagina, which occurs due to a decrease in the amount of vaginal secretion during sexual intercourse.
With autonomic neuropathy due to damage to the cardiovascular system, symptoms such as dizziness and causeless loss of consciousness, increased heart rate, painless angina, etc. may occur.
On the skin side, patients note excessive dryness of the extremities, profuse sweating or its complete absence.
Other problems
- Gastrointestinal problems
, especially mild symptoms of gastroparesis: mild intestinal upset, flatulence, nausea, vomiting. A light low-fat diet, limiting the consumption of fats and cell foods is necessary. If the symptoms are more severe, the endocrinologist will prescribe antibiotics, drugs that improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, agents that reduce stomach acid, and other medications. - Dizziness and weakness
. The patient should avoid sudden movements - fast walking and lifting heavy objects. With low blood pressure, wearing special elastic socks and stockings, salty foods and taking hormones can improve the condition. For high blood pressure, special medications are needed. In case of muscle weakness and coordination problems, physiological procedures are also used. - Urinary tract infections
. Such diseases are treated with antibiotics. To prevent urinary tract infections, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids. If a person has urinary incontinence, they should try to go to the toilet at regular intervals, such as every three hours. - Erectile disfunction.
Men first need to rule out hormonal dysfunction by taking hormone tests. If hormones are normal, treatment for nephropathy is required. Erectile dysfunction caused by neuropathy can be treated with several methods that involve increasing blood flow to the penis. Local medications, procedures, vacuum devices, and implants are also used. - Dryness of the genital tract.
In women, neuropathy can cause vaginal dryness. In this case, vaginal lubricants are recommended.
Focal neuropathy
This type of neuropathy usually occurs suddenly, affecting the nerve fibers of the head, torso, and limbs. It is characterized by pain of varying strength and muscle weakness. In addition to these signs, Bell's palsy, which affects one side of the face, double vision, and pain in the chest or abdomen, which is often mistaken for a heart attack or appendicitis, may occur.
If one or a complex of the above symptoms are detected, patients suffering from diabetes should consult a specialist for differential diagnosis of diabetic neuropathy with other diseases with similar symptoms, such as alcoholic neuropathy, neuropathy that occurs while taking neurotoxic drugs or exposure to toxic chemicals (solvents, heavy metal compounds, etc.).
Recommendations for foot care for diabetic nephropathy
- Wash your feet daily with warm (not hot) water and mild soap.
- Dry your ankles with a soft towel, leaving space between your toes.
- Check your feet every day for redness, sores, swelling, or fluid-filled blisters. Use a mirror to examine the back of your legs.
- Wet your feet with a special lotion, but do not apply moisturizer between your toes.
- Get rid of dry, dead skin. After swimming or showering, gently rub your heels with a pumice stone. Trim your nails promptly.
- Don't go barefoot. Wear thick, soft socks.
- Choose the right shoes—loose, well-fitted shoes that allow you to move your toes. For the first few days, wear your new shoes for an hour a day so that they take the desired shape and do not rub your feet later.
- Before getting dressed, check the inside of the shoes well - they should not be damaged, they should not have rough seams or other areas that could damage the foot and ankle.
Feet in socks
Feet care
Don't ignore even minor foot problems. Contact your endocrinologist for any abnormalities, including scratching and scratching.
A set of methods for diagnosing diabetic neuropathy
The list of diagnostic methods for diabetic neuropathy is directly related to the form of neuropathy the patient presented with. Therefore, at the initial consultation, anamnesis and complaints are carefully collected, based on which the endocrinologist or diabetologist involves other specialists in the study.
All patients need to determine the level of sugar, insulin and glycosylated hemoglobin in the blood; examination of the legs is mandatory to identify wounds, trophic ulcers, fungal infections, calluses, etc.
Neurological examination of patients with diabetic neuropathy includes electromyography and electroneurography, assessment of reflexes and the level of perception of all senses.
If there are symptoms of damage to the digestive tract, it would not be superfluous to do an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, radiography of the stomach, and esophagogastroduodenoscopy. If the patient has complaints from the genitourinary system, it is necessary to conduct a general urine test, ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder with determination of residual urine volume, cystoscopy and urography.
Other studies
The doctor may also consider other tests necessary:
- Electromyography
– to determine the type and extent of nerve damage. A special device sends an electrical current to the nerve, and the electromyogram shows how the muscles respond to the electrical impulses delivered through the nerves; - Heart rate variability
. The doctor must know how the heart reacts to deep breathing, exercise, blood pressure and other changes; - Ultrasound examination of the pelvis and other systems
. Using ultrasound, the structural state of organs and some functions are assessed. For example, how the bladder works.
Electromyography
Pelvic ultrasound
How to treat diabetic neuropathy
In the treatment of diabetic neuropathy, consistency and phasing are important. Since the disease is concomitant with the main one - diabetes mellitus of the first and second types, first of all it is necessary to transfer diabetes mellitus to the stage of compensation. Correction of blood glucose levels is carried out by an endocrinologist or diabetologist by prescribing insulin or antidiabetic drugs. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is necessary. In addition, for complex treatment of the patient, a special diet must be developed and a physical activity regimen must be determined. If the patient is obese, it is necessary to develop a program to reduce excess weight. Monitoring blood pressure levels is no less important.
Symptomatic treatment depends on the type of diabetic neuropathy and consists of taking B vitamins that have a neurotropic effect, antioxidants, magnesium and zinc. When diabetic neuropathy is accompanied by severe pain, they resort to prescribing painkillers and anticonvulsants.
Specialists widely use physiotherapeutic methods of treatment in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy of the legs, such as electrical nerve stimulation, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, acupuncture, and physical therapy. Patients with predominant lesions of the feet are recommended to carefully care for the feet, moisturize them and wear comfortable shoes to prevent the formation of calluses and corns.
Pain management
Many painkillers help relieve the pain of nephropathy. For severe pain, a combination of several medications is prescribed. Antidepressants, anticonvulsants, opioids and other medications are used for this purpose, although they all have side effects. Some of the painkillers are not recommended for older people and people with heart disease. As for over-the-counter pain relievers (paracetamol, ibuprofen), some experts advise patients not to take them because they are not enough to relieve neuropathic pain, but they have serious side effects.
Painkillers
External remedies are also used to relieve pain, especially effective for use on the ankles. The doctor may prescribe a cream containing capsaicin, lidocaine, nitrate spray, etc. In some patients, the condition is alleviated by alpha-lipolic acid, endotracheal oil and other means.
For patients with increased sensitivity to the feet and touching, for example, a blanket, a special device is used - a frame that holds the blanket in the air.
Some patients relieve pain with acupuncture, bio-communication, and physical therapy. But the effects of electrical stimulation on nerve pain, magnetic therapy, laser therapy and phototherapy have not yet been studied.
Prevention and Treatment – Differences in Effectiveness
The likelihood of developing and the severity of complications of diabetes mellitus directly depends on the fullness of compensation for carbohydrate metabolism, as well as on the implementation of a set of preventive measures. Every patient with diabetes should undergo a course of vascular therapy at least once every 6 months, aimed at preventing the development of complications, including diabetic neuropathy.
Unfortunately, it is often quite difficult to convince patients with diabetes mellitus of the need for preventive courses of treatment, since in the initial stages of the disease nothing bothers patients, and the person usually ignores elevated glucose levels altogether. At the same time, the effectiveness of treatment measures directly depends on how early they are started and how regularly they are carried out.
After complications become visible to the naked eye (at this point the quality of life of patients begins to rapidly decline), almost all patients begin to undergo active treatment. Unfortunately, in the later stages of the disease, the effectiveness of vascular therapy is no longer as high as at the beginning of the disease. Therefore, it should be recognized as absolutely proven that the prevention of the development of neuropathy and other complications of diabetes mellitus should begin immediately after diabetes is diagnosed and continue throughout the entire period of its treatment.
In diabetes, the condition of the legs is primarily monitored
In nephropathy, the ankles are the first to be damaged. A diabetic should have their ankle checked at least once a year, and even more often if peripheral neuropathy is diagnosed.
A thorough ankle examination involves examining the skin, muscles, bones, circulation and sensation. Sensitivity is studied using a special brush or light pressure with a sharp object. Loss of sensation increases the risk of ankle sprains and ulcers, which can be difficult to treat if you have diabetes.
If necessary, the patient's legs perceive temperature and vibration are checked.