Such an unpleasant problem as dizziness is familiar firsthand to people suffering from pressure changes, and it is especially common in women. Dizziness can occur as a result of either high or low blood pressure. Any deviation from normal blood pressure can lead to disastrous consequences, which is why it is so important to monitor personal indicators and not ignore the “signals” of the body. To determine how to help a patient, it is necessary to understand at what pressure the dizziness occurs - further actions will depend on this.
Features of dizziness in hypertension
It is not an increase in blood pressure that provokes dizziness, but sudden changes in data that confuse the brain. When you feel dizzy and your blood pressure rises, your organs stop receiving the volumes of oxygen necessary for normal functioning. This is what explains dizziness with pressure both in hypotensive patients and in patients with hypertension. At this time, the patient may feel very lethargic, headaches may begin, and signs of intoxication may appear. In addition, dizziness after high blood pressure is provoked by careless sudden movements.
Treatment methods for dizziness
Since dizziness is not an independent disease, treatment will depend on the cause that caused it. In some cases, due to the brain's ability to adapt to changes in the inner ear and use other mechanisms to maintain balance, dizziness goes away without treatment.
Audiologists at the MasterSlukhtm clinic recommend vestibular rehabilitation as one of the most effective methods for dizziness associated with dysfunction of the inner ear. This is one of the options for physical therapy, including a set of exercises that simulate the loads of the vestibular apparatus. Performing these exercises allows you to restore the normal functioning of the balance organ or cause a faster and more effective adaptation of the brain to disturbances by training other senses.
If dizziness is caused by infection or inflammation, drug therapy is used. Patients may also be recommended a diet that limits the amount of fluid consumed and foods that cause fluid retention in the body.
In cases where dizziness seriously impairs the patient's quality of life and performance, surgical treatment may be prescribed: transection of the vestibular nerve or destruction of the labyrinth. This leads to irreversible hearing impairment, but can significantly reduce the severity of vestibular disorders.
Dizziness with low blood pressure
Dizziness with low blood pressure can appear at any time, but most often before this, blood pressure drops below 100/60 mmHg. Art. This is a very dangerous condition that can provoke the development of serious diseases - ischemia and tissue hypoxia. They slow down the transmission of impulses and worsen the nervous system's response to external stimuli.
Low blood pressure and dizziness directly indicate hypotension, which must be treated rather than tolerated. Unfortunately, many do not attach serious importance to these symptoms, since the disease is mistakenly considered not life-threatening. Such negligent attitude towards one's health often leads to serious consequences. The most dangerous complication of this disease is brain atrophy. You can also find out about the presence of hypotension and low blood pressure by other symptoms:
- intoxication;
- throbbing pain in the occipital region;
- loss of consciousness;
- stuffy ears;
- trembling fingers;
- coldness of the extremities.
These symptoms do not necessarily accompany hypotension all the time, but occur with a sudden change in position. This occurs due to the fact that the heart does not have time to deliver blood to large vessels, which is necessary for the normal functioning of all systems in the body. But even if you experience a condition where you have low blood pressure and feel dizzy, don’t despair. A problem noticed in time and immediately taken measures will help protect against more serious diseases, often accompanied by hypotension.
Important! Every person needs to know their normal blood pressure, since sometimes generally accepted norms deviate in one direction or another. Your attending physician or local therapist in a regular clinic will help with this.
Orthostatic hypotension
Can you count how many times over the past few days, when getting out of a chair or bed, you felt dizzy, your vision went dark, or you had a slight ringing in your ears? A popular piece of advice comes to mind: don’t stand up abruptly. But you did not notice any excessive sharpness in your movement. Getting up from a lying or sitting position constantly causes you similar problems, which go away after a few seconds. In this case, you suffer from orthostatic hypotension.
Orthostatic hypotension is not a disease. In essence, this is an inadequate response of the body to changes in body position, characteristic of men and women of any age. With a sudden change in position, blood accumulates in the veins of the torso and legs, causing a decrease in blood circulation, a decrease in cardiac output and a temporary decrease in blood pressure.
Typical symptoms of orthostatic hypotension:
- dizziness;
- short-term visual impairment;
- fainting.
If you experience severe dizziness and risk of fainting, the following action will help: sit on a chair, put your elbows on your knees, bend your head between your knees.
Orthostatic hypotension in hypertension
Orthostatic hypotension may occur in patients being treated for hypertension. If this condition occurs, you should consult a doctor. Problems disappear or are significantly reduced after adjusting the dosage of the medication taken (lowering the dose or dividing it into several daily doses).
In most cases, 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring is required as part of diagnosis and treatment. The patient's condition during a routine visit to the doctor often cannot be objectively assessed, since about 1/3 of patients have white coat syndrome.
Orthostatic hypotension with low blood pressure
Orthostatic hypotension is more common in people suffering from low blood pressure. In these patients, when changing position (from sitting or lying to standing), it decreases even more. There are no universal preventive or therapeutic measures.
The occurrence or current state of orthostatic hypotension is also influenced by external factors. Mostly, we are talking about situations that can lead to dehydration. These include:
- high ambient temperature;
- excessive physical activity;
- overdose of diuretic drugs.
In older people, orthostatic hypotension occurs more often on hot summer days.
Risks of orthostatic hypotension
More often, young people, especially girls, suffer from orthostatic hypotension. It often intensifies during menstruation. The next group is the elderly, in whom this condition causes severe dizziness and falling.
But orthostatic hypotension can also accompany diseases that damage the nervous system, such as diabetes, diseases of the brain and spinal cord. Therefore, if it suddenly appears (especially if there are no problems with low blood pressure before), it is advisable to consult a doctor.
In other cases, low blood pressure is not considered an emergency, except in cases of loss of consciousness, leading to dangerous falls.
Dizziness with high blood pressure
Hypertension is widespread among the adult population of the Earth, so it is easily called the most common disease. Sometimes people do not realize that they are sick, attributing poor health to overwork. Dizziness with hypertension occurs in every second patient, and this symptom cannot be ignored. Along with it, patients also complain of:
- noise in ears;
- intoxication;
- weakness;
- throbbing pain in the head area.
Prevention
Low or high blood pressure and dizziness can be easily prevented if you promptly treat diseases accompanied by these symptoms. For this, not only pills, which today can be purchased freely in pharmacies, are suitable, but also self-discipline. In particular, the following rules must be adhered to:
- Avoid overwork and don’t get nervous over trifles. Walk more in the fresh air, especially before bed. You definitely need to get enough sleep at night. You can also do sports - walking, yoga or swimming.
- Adhere to the principles of a healthy diet - remove all unhealthy foods that contain a lot of salt, fat and traces of smoking. Eat more fruits and vegetables, as well as foods rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Control your calorie intake, as excess weight causes high blood pressure. It is better to eat more often, but in small portions, than to starve all day and gorge yourself in the evening.
- Monitor your blood pressure readings and keep a record of measurements to calculate your operating pressure. Any deviation from this indicator will be a reason to consult a doctor.
What to do
Before looking for a “universal pill,” you need to understand that hypertension and hypotension are different diseases and therefore cannot be treated with the same remedy. The same can be said about dizziness, which is a consequence of surges in blood pressure. The first step to recovery is to measure your blood pressure. His readings will help determine why it is necessary to treat – high blood pressure or low blood pressure. The doctor will be able to immediately explain what is best to take for low blood pressure and dizziness, or what medicine to take for high blood pressure.
After the call, the attending physician needs to calm down and take a comfortable position. At home, it is better to lie down on the sofa and free yourself from tight fasteners that are squeezing blood vessels. Free air circulation promotes rapid penetration of oxygen into the body. Therefore, if there is someone else in the room, you can ask to open the window. If you have anti-nausea medications in your medicine cabinet, you should take them and calmly wait for medical help to arrive.
If the problem occurs unexpectedly at work or on the street, then you need to look for a quiet place that allows you to take a horizontal position - a bench in the park or a desk in the office, leaning on the wall. This will allow you to maintain your balance and focus on one point. At this time, you need to breathe calmly and deeply. In addition, before the doctors arrive, you can use folk wisdom and eat dark chocolate - for hypotension, or drink valerian tincture - for hypertension.
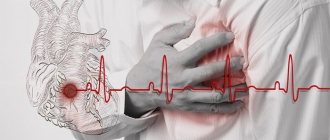
You should not ignore dizziness, as they may be the first symptoms of heart disease, which, in turn, often lead to serious complications and death. Timely consultation with a doctor will help prevent the development of hypertension or hypotension, and therefore prevent or delay the onset of heart attack and stroke.
Constant dizziness and its causes
Dizziness is a feeling of uncertainty in determining the position of your body in space. It may be accompanied by a seeming swaying or spinning of the environment or one’s own body, disorientation in space, a feeling of instability, and “floating” of the ground from under one’s feet. In most cases, dizziness can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, rapid breathing, increased sweating, increased heart rate, surges in blood pressure, hearing and vision impairment (nystagmus - involuntary high-frequency oscillatory movements of the eyes). Attacks of uncertainty can last from a few seconds to several hours.
Dizziness and impaired coordination of movements are one of the most common complaints of patients and the most “unloved” symptom for doctors. They can be signs of various diseases: neurological and mental, musculoskeletal and vestibular, diseases of the cardiovascular system or ears and eyes. Therefore, the doctor’s primary task is to clarify the nature of dizziness and correctly diagnose the disease.
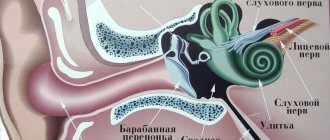
Receptors responsible for coordination of movements are located in all extremities of the body, and vision is responsible for orientation in space. Next, all reflex impulses are collected in the brain, where the body’s response is formed. Disruption or distortion of any impulse leads to incorrect information for the brain, and, consequently, a feeling of dizziness.
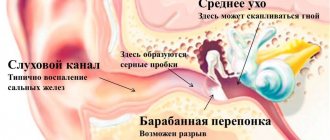
Systemic dizziness is characteristic of damage to the vestibular apparatus (peripheral or central parts). It is considered normal to have an imbalance after a long ride in vehicles (sickness), swimming or riding on a swing. Some people suffer from such disorders from a very early age.
Causes of constant dizziness
The main causes of dizziness can be:
- Vestibular pathologies of the central or peripheral parts. An apparent sensation of rotation, falling, swaying, tilting of the environment or one’s own body is experienced. As a rule, it is accompanied by nausea, hearing and balance problems, and rapid illusory vibration of surrounding objects.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. There is a feeling of lightheadedness, impending clouding of consciousness, loss of consciousness, and fainting. Quite often accompanied by pale skin, increased heart rate, darkening of the eyes, a feeling of fear, “cold sweat,” and a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
- Neurotic disorders or pinched nerve fibers in the cervical spine. In this case, there is an inability to maintain balance (body balance), instability and unsteadiness of gait, impaired sensitivity of the limbs up to complete paresis (weakening of a muscle or group of muscles due to damage to the pathways of the nervous system and motor centers of the spinal cord and/or brain). Symptoms of dizziness and loss of balance are worse when the body is upright (walking or standing), much less pronounced when sitting, and disappear completely in a horizontal position.
- Cervicogenic disorders. Dizziness and headaches that occur against the background of pain and limited mobility of the cervical segment of the spine. Treatment of headaches and dizziness in this case begins with treatment of the spine and postural disorders (position of the head relative to the entire body).
- Quite often, dizziness precedes migraine attacks. Circulatory disorders in certain areas of the brain associated with the work of the vestibular apparatus cause impaired coordination of movements, irritability, slow reaction and headache. Migraine treatments in many cases relieve all disturbing symptoms.
- Vertebrogenic pathologies. Circulatory disorders or pinched nerve roots caused by osteochondrosis, osteoporosis, spinal stenosis, scoliosis, herniated intervertebral discs and other diseases of the spine or postural curvature can cause dizziness, pain syndromes, weakness in the limbs and other unpleasant sensations. In this case, it is necessary to consult a vertebrologist, treat spinal diseases, and the disturbing symptoms will subside on their own after proper therapy.
- Traumatic brain injuries, tumors and brain diseases. Accompanied by severe dizziness, headache, tinnitus, darkening of the eyes, poor health, nausea.
Also, the causes of frequent dizziness may be:
- hypertension or hypotension – high or low blood pressure;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- strict diets low iron content in the body, anemia;
- long-term use of certain medications (vasoconstrictors, sedatives, anticonvulsants, psychotropic drugs, etc.);
- diseases of the inner ear (otitis media, etc.);
- constant stressful situations and nervous overstrain.
Quite often, dizziness is accompanied by temporary mental disorders: hysteria, hysteria, panic or anxiety, depersonalization.
First self-help for dizziness
If you experience dizziness or imbalance at home, it is advisable to lie down immediately. At the same time, try to keep your head and shoulders at the same level; place a small cushion under your neck. This will help straighten the spine, release restrictions, if any, and stabilize the blood supply to the brain.
When dizziness occurs on the street, you urgently need to sit down, close your eyes, relax, try not to make sudden movements so as not to lose your balance and fall. If the attack does not go away for more than ten minutes, seek help from others and ask them to call an ambulance.
If attacks of dizziness become a frequent occurrence or last for several days, these are the first signs of serious disorders in the body and you should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
This could be a local therapist, a neurologist, a neurologist, a vertebrologist, a doctor who treats the spine, etc. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr