EEG
The abbreviation EEG in the medical community refers to electroencephalography of the brain: one of the methods for studying the state of the brain, which is used when one or another pathology or malfunction is suspected. Using EEG, you can also track the degree of participation of the central nervous system in pathologies of other systems and organs. The principle of the study itself is simple, and is based on the study of electrical impulses emitted by individual areas of the brain.
Reference. The “product” of such an analysis will be an electroencephalogram: a graph of the biopotentials of the brain. From the curve of this graph, an experienced specialist can determine how coordinated the work of individual brain zones is and how actively it functions.
The specialist refers the patient to an EEG if:
- dizziness and headaches;
- neuroses, mental disorders;
- neurotoxin poisoning;
- paroxysmal hemicrania;
- sleep disorders, insomnia;
- epileptic seizures;
- panic attacks;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia, etc.
As for the diagnostic procedure itself, it is carried out absolutely painlessly for the patient who lies or sits in a relaxed position with his eyes closed. Sometimes an EEG is performed directly during sleep, so the patient must fall asleep either naturally or with the help of special medications before the procedure.
Once the patient is ready for the procedure, a “helmet” equipped with electrodes is placed on his head, capable of recording electrical activity in various areas of the head. Diagnostic results are displayed on paper or simply on a computer screen. By deciphering the result obtained in the form of a graph, the doctor determines the presence or absence of certain deviations from the norm.
Methods for diagnosing brain diseases
The quality of our life depends on many nuances of the state of the body. The most important of these is the functioning of our brain. Stress, depression, poor ecology are constant companions of almost every inhabitant of the Earth, so many diseases, including brain diseases, are much more common than a hundred years ago. In addition, diseases are “getting younger” and are observed in a huge number of adolescents and even children. Sometimes we no longer pay attention to the symptoms, get used to frequent headaches, ignore dizziness, try once again not to “listen” to our feelings, and mindlessly take pills. It is important not to numb the pain with medications, but to understand the cause by examining the brain for the presence of structural and functional disorders. Maria Yuryevna Alekseeva , a functional diagnostics doctor, a doctor of the highest category, told how to do this
If you have any complaints, you should immediately consult a doctor. It will help determine the necessary path of examination. But, there are a number of studies that can be done before the consultation to save time. I would like to remind you a little about such diagnostic techniques as EEG, REG and ECHO-EG.
All of them are screening tests, as they have a number of positive properties: painless, harmless, without age restrictions, low cost, quick, and informative. With the results of these studies, the specialist will have a more complete picture of what is happening in your body.
What is EEG?
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method for studying the functioning of the brain, based on recording its electrical activity. Brain activity can be normal and pathological. So, when recording an EEG, we provide a description of normal brain activity taking into account age-related assessment criteria, and also indicate the presence or absence of pathological activity, which includes epileptic activity.
What are the indications for an electroencephalogram?
Mainly it is the diagnosis of epilepsy.
It can also be any complaints about the head (headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, loss of consciousness, panic attacks), seizures, any sleep disorders, a constant feeling of fatigue.
EEG is prescribed for various brain diseases: traumatic brain injuries, meningitis, encephalitis, strokes, brain tumors, autism, speech disorders, delayed psychomotor development, tics, neuroses, Down syndrome, cerebral palsy, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
In addition, EEG allows you to observe the dynamics of the disease, adjust treatment methods and evaluate the effect of drugs. It is also included in the screening program when passing a medical examination.
Is EEG performed on children?
This examination is very common in childhood, since the onset of many diseases of the nervous system occurs in children. Even for an infant, this technique is completely safe and does not harm health. Thanks to a timely EEG, it is often possible to defeat a serious illness at the earliest stages of its development.
How is the procedure performed?
No special preparation is needed, the procedure will not take much time and will not cause any discomfort. A special cap is placed on the head, to which electrodes are attached. Before applying them, the electrodes are moistened with a special gel so that the contact with the scalp is more dense.
The procedure lasts approximately 15-20 minutes. When recording an EEG, functional tests are usually carried out, “provocations” of hidden pathological conditions, convulsive attacks: photostimulation (light flashes at different frequencies), hyperventilation (deep breathing). These are different types of stress for the brain, which help to identify violations of its functioning.
What is REG? What is the essence of the method?
Rheoencephalography is a study of cerebral circulation, namely the functional state of blood vessels, their walls (tone), how they (quickly or not) fill with blood, venous outflow. The reaction of blood vessels to turning and tilting the head and holding the breath is also assessed. The procedure is based on recording the electrical resistance of brain tissue.
What are the indications for the procedure?
This study has wide application in childhood. After all, vascular disorders, unfortunately, are often found in modern children.
Rheoencephalography is advisable to use in the diagnosis of cerebrovascular pathology of a functional nature (vegetative-vascular dystonia, migraine), in atherosclerosis, acute and chronic cerebrovascular disorders, as well as in assessing the effectiveness of certain medications and non-drug treatment methods. REG studies are highly informative in identifying the effect on cerebral vessels in pathologies of the cervical spine (osteochondrosis, spondylitis, consequences of injury, etc.).
REG can be prescribed both for diagnostic purposes and routinely, since it is absolutely safe. This is especially true for mature and elderly patients, since over time the characteristics of blood vessels only worsen, and any pathology is best recognized in advance.
How is the examination carried out?
REG does not require special training. In general, the procedure is similar to an EEG: electrodes are installed on the patient’s head and connected to a machine that records the results. The whole procedure lasts 5-10 minutes.
What are the advantages of REG?
There is an opinion that REG research has been used for quite a long time and can be considered obsolete, especially with the advent of ultrasound and tomographic techniques. However, the simple conditions for the procedure and its painlessness for the patient are the main advantages of REG. At the same time, the device takes readings about the work of arteries and veins separately, which simplifies diagnosis at any stage of the disease.
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography, as well as Doppler ultrasound, are more detailed, but not as accessible to the public. In addition, there are categories of patients who need to undergo such research regularly, for example, during the postoperative period.
REG in childhood is especially relevant, since sitting in a rubber cap for 5 minutes in the presence of parents is much easier for a child than being alone inside a huge humming device (tomograph). Therefore, doctors do not stop turning to rheoencephalography.
What is ECHO-EG of the brain?
Echo-EG of the brain (ECHO-ES or Echoencephalography) is a method of one-dimensional ultrasound diagnosis of the brain followed by computer processing.
ECHO-EG reveals displacement of the midline structures of the brain, which occurs due to head injuries or neoplasms. The midline structures include the ventricles of the brain (these are natural cavities between the hemispheres). In case of pathological processes on the right or left, they shift to the healthy side.
This method also helps in diagnosing increased intracranial pressure.
In what cases should an ECHO-EG be done?
Mainly traumatic brain injuries.
Also, ECHO-EG is indicated:
- for severe regular headaches,
- general weakness, the causes of which are not clear;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- fainting.
In addition, echoencephalography allows you to see indirect signs of increased intracranial pressure.
How is the procedure performed?
No special preparation is required. The doctor places small ultrasound sensors on the patient’s head and periodically moves them during the examination. In this case, the patient does not experience any discomfort. It is done very quickly (5-10 minutes), the result is given immediately.
What are the advantages of ECHO-EG?
Echoencephalography is a simple, safe and harmless diagnostic method that has no contraindications or age restrictions. It is especially relevant in patients with contraindications to MRI (for example, an installed pacemaker, or built-in metal structures). Or in early childhood with head injuries, which happen quite often. In such cases, global examinations such as MRI are not always justified, and ECHO-encephalography comes to the rescue.
What are the features of conducting EEG, REG and ECHO-EG at the Center for New Medical Technologies?
To conduct these studies, our Center uses the latest equipment, and modern computer programs are used for analysis. Patients are received by highly qualified specialists by appointment, without queues. We have extensive experience working with children of different ages (including newborns), and with various pathologies. Research results are prepared quickly.
In conclusion, I would like to draw your attention to the fact that, whatever the reason why you or your child needs an EEG, REG or ECHO-EG, after the examination you must consult a neurologist to interpret the results and treatment. Be healthy!
EchoEG
This concept refers to the term “echoencephalography”, which is based on the study of the state of the brain using the ultrasound method. The method is based on the fact that different tissues of the human body (skin, bone, etc.) can reflect ultrasonic waves differently.
Using this study, doctors identify various hemorrhages, abscesses, edema and tumors, as well as hydrocephalus and intracranial hypertension. The study itself is carried out by applying a special sensor to various points of the head and analyzing the results displayed on a computer screen. The patient should be in a sitting or lying position at this time.
Reference. An echoencephalogram is a diagram of ultrasound signals converted into electrical impulses.
Features of the diagnostic method
The study is completely safe and non-invasive; it does not require lengthy preparation. The essence of the research: a special device acts on the plates with ultrafrequency electrical impulses.
The plates that are fixed on the patient's head begin to move. The movement of the plates produces ultrasound, which propagates to the tissues of the brain and skull. In areas where environments are differentiated by density, signals undergo echolocation. The device registers waves that are reflected from the structures under study. A graph of reflected structures appears on the computer screen; this graphic image is called an echoencephalogram.
Content:
- Features of the diagnostic method
- Indications of echo-EG of the brain
- Carrying out echoencephaloscopy
- Research results
Different tissues of the human body react differently to ultrasonic waves: adipose tissue and skin create one type of signal, tissue damage, neoplasms and tumors create a completely different one. These indicators are recorded on a graph, so the doctor can determine where the areas under study are healthy and where they are affected by the disease.
During the study, it is possible to examine certain brain structures, assess the condition of the periosteal space, and record median pulsations when intracranial pressure changes. Echoencephalography makes it possible to assess the condition of blood vessels and examine the displacement of brain structures. It is advisable to use the technique to make a diagnosis and prescribe further treatment for the found diseases and lesions. The study is necessary to obtain the most accurate information about the state of the patient’s brain.
There are two modes in which the study is carried out: one-dimensional (internal areas of the brain are examined) and two-dimensional (the brain is scanned in 2 planes and two-dimensional visualization is displayed on the screen). A two-dimensional examination is done for children under the age of 1 year, it is called neurosonography.
The result of the study is a high-quality and accurate echoencephalogram, which is a recording of ultrasound signals that are constantly changing. The study is prescribed by a doctor if serious brain diseases are suspected.
What common
In fact, there is not much in common between these two methods of studying the brain and central nervous system activity. Both of them have the same “object” of research, but different goals. Both studies require the patient to be at rest (the latter should sit or lie in a relaxed state). The results of both studies need to be deciphered, and only a qualified specialist can identify this or that pathology.
Both procedures are absolutely safe and painless for the patient. They can be prescribed to both adults and children, pregnant and lactating women, etc.
Carrying out echoencephaloscopy
There is no need to prepare for echoencephalography of the brain. The examination takes place lying down or in a sitting position. If you need to examine a newborn baby, you will need the help of mom and dad. They must carefully hold the baby's head in the desired position.
The examination of adult patients and children lasts from 10 to 15 minutes. Depending on the examination mode, 1 or 2 sensors will be recorded. During transmission diagnostics, 2 sensors are attached to the head (on the right and on the left side), they must be on the 1st axis. One of the sensors sends a signal, the second receives it. Emission research is carried out using only one sensor; it is fixed on a certain area of the head.
During diagnosis, you need to listen to the specialist and not move. If you experience discomfort, pain in the head or other reactions, you should inform your doctor. The diagnosis is completely safe and painless, so no side effects or reactions should occur.
What is the difference between EEG and EchoEG
The main and main difference between the research methods under consideration will be the nature of their impact on body tissues. If EEG works with electrical impulses, which any human or animal brain inevitably produces during operation, then EchoEG uses exclusively ultrasonic signals that are reflected differently from different tissues.
As a result, the goals of diagnosis also differ. In the case of an EEG, an assessment is made of brain activity and the degree of coordination of nervous processes (this way, for example, syndromes of developing epilepsy can be identified), while an EchoEG is aimed at detecting pathological formations of the brain (tumors, abscesses, etc.).
Reference. Since the ultrasound-based method involves external influence on the body, many patients believe that it is more harmful than EEG, but this is not the case. Ultrasound examination does not have any negative effect on organs and tissues; it is safe for both children and adults. EEG can also be called completely safe.
According to many modern doctors, echoEG has recently become outdated, and is being replaced by many more modern methods. However, echoencephalography is still used in many medical organizations and makes it possible to diagnose and prevent the development of many pathologies.
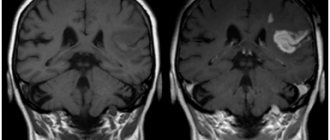
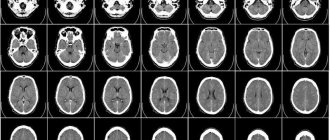
Magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography of the brain is better
The level of darkening and lightening of areas is the result of the activity of impulses passing under the influence of a magnetic field from the examined areas of the brain during MRI. Hydrogen is the main element that changes the radio frequency signal when exposed to a strong magnetic field. The number of hydrogen particles inside the tissue determines the power of the pulse that is detected by the gradient coil. Water, which contains two hydrogen atoms, displays the signal in the picture in light tones. Bone tissue, on the contrary, does not have hydrogen atoms inside itself, so it gives an insignificant signal. Areas that do not contain hydrogen particles appear dark in the images.
It is definitely difficult to answer the question of MRI or CT scan of the brain - which is better. It is not the patient, but the specialist who can choose the right examination method. The magnetic resonance imaging machine will produce images that will most effectively highlight lesions in the soft tissue of the brain. Errors in MRI of the brain are caused by human mobility during scanning. MRI is highly informative during ischemic stroke, nerve fiber disorders, and pathologies of the inner ear.
Computed tomography is prescribed in the presence of defects in the hard parts of the skull.
MRI and CT have their pros and cons, so each of them, in its own way, is indispensable when diagnosing diseases of the head area.