Intercostal neuralgia
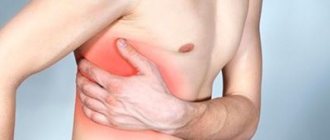
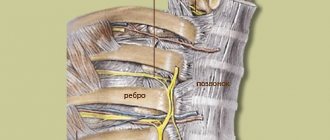
This is a pain syndrome caused by damage to the peripheral nerves of the chest. Appears due to inflammation, irritation or pinching of the nerve roots in the intercostal space. Intercostal neuralgia is not a disease - it is a syndrome that can appear against the background of various pathologies. Vertebrogenic thoracalgia (as intercostal neuralgia is called) is a general concept that refers to pain that occurs in the chest area. They can appear for no particular reason, or can serve as a sign of various diseases.
Symptoms may resemble pain from a heart attack, pneumonia or pleurisy, diseases such as pancreatitis and others. A characteristic symptom is an increase in pain when coughing, laughing, moving, bending the body and decreasing at rest and with muscle relaxation. This is a distinctive feature of intercostal neuralgia, which allows it to be differentiated from symptoms of heart disease or other pathologies. But you shouldn’t take risks and try to diagnose yourself. The cost of a mistake can be higher than the prolonged pain syndrome.
The principles of treatment and symptoms of intercostal neuralgia in men and women are similar. The main manifestation is pain:
- Paroxysmal, occurring on its own.
- Monotonous, aching.
- Intensified by movement, deep breathing and exhalation, laughter, coughing.
- Occurs when pressing on individual points on the front of the chest or side.
- A burning sensation in the area where the nerve is damaged.
- Numbness, “pins and needles” sensation.
The pathology is more common on the left side of the body, and in women, intercostal neuralgia is a fairly common companion to pregnancy. During this period, the growing fetus puts pressure on the organs in the abdominal cavity, which can lead to pinched nerves.
Main complex
Basic exercises for intercostal neuralgia:
- Starting position: lying on your back. The limbs are stretched in opposite directions - the arms should be extended behind the head, while the legs should be pulled down. The exercise should be performed at a slow pace, like morning stretching. It should be performed several times at the very beginning of the workout.
- Lying on your back, your legs must be bent so that your feet are in full contact with the floor and your knees are shoulder-width apart. The body must be gradually raised so that only the feet, head and neck remain on the floor.
- Lying on your back, you need to connect your straightened legs together. Next, they need to be pulled up to the chest so that the knees are as close to the forehead as possible.
- Squats are the most important element of exercise therapy. They need to be performed with a straight posture. Shallow squats are allowed. If it is difficult to perform them without support, you can hold on to a chair.
- Starting position: lying on your stomach. It is necessary to simultaneously raise the upper and lower limbs. Ascents should be slow. At the top point you need to linger for 10 seconds, then return to the starting position.
- Starting position: sitting, legs extended forward. Your hands should be clasped together and raised above the top of your head, stretching them upward. There is no need to strain your legs.
Causes
Intercostal neuralgia can be caused by various reasons. Basic:
- Poor posture, injuries, intervertebral hernias, osteochondrosis.
- Hypothermia, which led to poor circulation.
- Infectious and other diseases that lead to nerve damage. For example, destruction of the nerve sheath in multiple sclerosis.
- Neoplasms that compress nerve roots.
- Muscle spasms, prolonged tension during sudden movements or prolonged uncomfortable body posture.
- Operations.
- Pathologies of internal organs.
When gentle loads help
The indication for exercises for neuralgia of the thoracic spine is the rehabilitation period after an exacerbation. Most often, the attack goes away within 3-4 days. An important condition for the effectiveness of the effect is the absence of inflammation. Before starting training, you must consult with a surgeon (orthopedist) and make sure that there is no hernia or swelling.
Separately, contraindications to physical activity should be noted. First of all, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition. The specialist’s task is to make sure that the patient does not have concomitant diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus), heart and blood vessels. A jump in blood pressure in this case can provoke a sharp deterioration in the condition.
It is necessary to highlight the fact that exercises for thoracic neuralgia do not help get rid of pain. On the contrary, stress aggravates the patient’s condition and causes disturbances in blood flow in the problem area. The list of contraindications also includes women during pregnancy.
Diagnostics
Intercostal neuralgia can be a symptom of many diseases - from cardiovascular pathologies to diseases of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity and chest. It is impossible to independently determine the cause only from existing complaints. A consultation with a neurologist and a comprehensive diagnosis is necessary to ensure that there are no diseases of the heart, lungs, or digestive system.
Particular attention is paid when diagnosing and treating intercostal neuralgia on the left side. Acute pain in the heart may be a sign of a heart attack. Symptoms usually differ - for example, with heart problems, cold sweat appears and shortness of breath bothers you, the pain does not decrease with rest when the muscles relax. But making a diagnosis based only on symptoms is wrong. The doctor is responsible for the life and health of the patient, which means he needs confidence in the diagnosis and correctness of treatment.
The procedure for examining a patient with suspected intercostal neuralgia is as follows:
- Questioning the patient about complaints and the characteristics of their occurrence.
- Examination to find the location of the pain.
- Setting up a preliminary diagnosis.
- Carrying out examinations to confirm intercostal neuralgia, its causes and prescribe the treatment that will be required in a particular case.
The following diagnostic methods can be used:
- Magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography is a study that will provide detailed and highly accurate images of tissues and pathology in them.
- ECG – monitoring of heart function to exclude cardiovascular diseases.
- Ultrasound of the heart or other internal organs, diseases in which may have similar symptoms.
- X-ray of the lungs to exclude pneumonia, pleurisy and other diseases in which there are complaints of chest pain.
Diagnostic methods are selected individually depending on the nature of the pain and its location, and the patient’s condition. In some cases, other specialists are involved in diagnosis and treatment - a cardiologist, gastroenterologist, pulmonologist.
Additional complex
Exercises performed from the starting position lying on your back:
- The limbs are extended along the body. You need to bend your legs and pull them towards your chest, hugging them with your hands under your knees, then do a few rolls on your back. The load on the cervical spine is unacceptable.
- While in a lying position, you need to clasp your hands and pull them up, while your legs are relaxed. Then, on the contrary, the toes of the feet are pulled away from you, the arms are relaxed.
Starting position - feet shoulder-width apart:
- The arms are stretched forward, then you should take a deep breath and, turning to the right side, extend your right arm. All steps are repeated for the left side.
- You need to bend your left leg and place your right palm on it. The left arm remains relaxed, then the body turns to the left. The twist must be repeated for the right side.
- A tilt is made so that the right hand reaches the floor and the left is extended upward. The head should be turned towards the outstretched arm. The exercise is performed followed by alternating hands.
- You need to bend forward, try to reach the floor with both hands. Legs should be straight. After bending over, you need to wait 10 seconds and slowly return to the starting position.
Starting position sitting:
You need to straighten your lower back and, bending your legs, bring them so that your heels are near your buttocks. Your palms should be placed under your kneecaps. Then, as you inhale, you need to begin to descend, pressing your body to your knees, and as you exhale, rise again. It is better to do the exercise at least three times.
With your legs crossed “Turkish”, you need to put your hands in front of you. The body leans forward, while the lower back is completely relaxed.
Treatment
The goals of therapy for intercostal neuralgia: reduce pain, eliminate the cause of pinching or inflammation.
For this purpose, drug treatment is prescribed using:
- Muscle relaxants to relieve muscle spasms.
- Neuroprotectors for the protection and restoration of nerve cells.
- Painkillers and injection therapeutic blockade with various drugs. It has a strong analgesic effect, relieves swelling and eliminates muscle spasms.
Drug treatment of intercostal neuralgia is complemented by physiotherapy. The following physiotherapeutic procedures can be used:
- Exercise therapy is an individually selected set of exercises to relax spastic muscles, improve blood circulation and lymph flow in the problem area. Exercise therapy is effective for the treatment and prevention of neuralgia, but it can only be done if there are no contraindications. It is important not to cause harm, which is possible with home exercises. What exercises will be effective, how exactly to do them, the number of repetitions - all this will be advised by a physical therapy doctor. The safest and most effective classes are under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor in individual or group classes.
- Laser therapy uses light energy to increase blood circulation, relax muscles, and reduce pain and inflammation.
- Magnetotherapy - the effect of an electromagnetic field on the body leads to the elimination of congestion, improvement of blood circulation, and reduction of pain syndromes.
- Diadynamic therapy, galvanization, exposure to interference currents and other procedures with electric current of varying power and frequency. They have a healing effect on soft tissues, improving blood circulation and lymph outflow, relaxing muscles and providing an analgesic effect.
- Electrophoresis is a procedure that improves the penetration of drugs into soft tissues and accelerates their action.
- Therapeutic massage and manual therapy are methods of influencing the body with the hands of a doctor. They allow not only to reduce or completely relieve pain, but also to treat the causes of intercostal neuralgia - pathologies of the spine, functional blocks in its work. What exactly to use - acupressure, segmental or other types of massage - is decided by a chiropractor or massage therapist.
- Acupuncture (acupuncture) – injections with thin needles into biologically active points on the body to relieve pain and normalize the functioning of internal organs.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia on the right or left side of the chest, in the side with the help of physiotherapeutic procedures is carried out in several procedures. A full course usually consists of 10-15 sessions. Appointments are always individual.
Contraindications
As with any treatment, you should consult your doctor before engaging in physical therapy as there are some limitations.
Main contraindications:
- compression of the spinal cord and spinal nerves;
- hernias;
- fractures;
- injuries and curvature of the spine.
With intercostal neuralgia, exercise can begin only a few days after the acute pain has been relieved with the help of medications and physiotherapy.
Prevention
The following recommendations help to avoid the appearance of intercostal neuralgia:
- Moderate physical activity to strengthen the muscle frame and maintain their elasticity.
- Maintaining correct posture.
- Healthy eating.
- Daily routine and alternation of work and rest time.
- Protection against hypothermia.
You should not endure the pain of intercostal neuralgia and worry about its causes - consult a doctor to be sure that there are no serious pathologies and for quick relief of symptoms.
Symptoms of the disease
The main manifestation of the pathology is pain (paroxysmal, girdling) localized in the right or left part of the sternum. With active activities and coughing, the pain intensifies.
If the cause is overstrain of one or more muscles, the pain increases when bending forward. In some cases, the disease is accompanied by numbness or burning along the nerves, radiating to the back, lower back and shoulder blade.
Depending on which nerves are affected, the syndrome may resemble stomach pain and the pain of acute appendicitis. If the upper segments of the sternum are affected, the patient will complain of a feeling of a foreign body in the throat, interfering with the swallowing process.
On our website Dobrobut.com you can make an appointment with a doctor who will tell you about the signs of intercostal neuralgia in the back and methods of its treatment.