Stroke is a common neurological pathology with many manifestations. Some consequences of a stroke can be treated and restored with adequate medical care. These consequences include seizures that occur in women and men after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
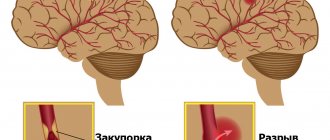
The development of convulsive syndrome is caused by the death of brain neurons and the formation of a focus of necrosis. The body's response to this process is the activation of other neurons to restore blood circulation and stop the pathological process. Necrotic tissue is replaced by a cavity filled with fluid; when a cyst forms, a person does not feel discomfort. However, when neurons are irritated by the cyst, seizures can occur.
Treatment of seizures and other consequences of stroke is carried out by neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital, who offer patients individual therapy programs. Specialists are able to improve the quality of life and restore the functions of even those patients who were abandoned in other medical institutions.
Features of treatment
The therapeutic approach depends on the type of seizure.
If these are warning signs, specific anticonvulsants are not prescribed. The main goal of treatment is to eliminate the narrowing of the artery. Depending on the cause of the pathology, the patient is prescribed anticoagulant medications (aspirin), blood pressure pills, and neuroprotectors. Early seizures do not require immediate specific treatment. They usually disappear on their own once the metabolism in the brain has stabilized. Antiepileptic drugs are prescribed exclusively to patients with repeated unprovoked seizures.
Isolated late attacks also require observation. If episodes of seizures are repeated, there is a possibility of developing post-stroke epilepsy, a chronic disease manifested by periodic convulsive conditions. If the diagnosis is confirmed, patients are prescribed anticonvulsants:
- carbamazepine (tegretol, finlepsin);
- valproates (convulex, convulsofin, depakine, valparin);
- topiramate (maxitopyr, topsaver, topamax);
- lamotrigine (convulsan, lamitor, lamictal);
- Levetiracetam (Keppra).
First aid
Forecasts and chances of surviving after a third stroke
If the attack occurred at home and had no prerequisites, then the first thing to do is call an ambulance. After this, they begin to provide first aid, which consists of:
- Lay the patient horizontally with a cushion under his head.
- Remove food debris, vomit, and saliva from the oral cavity using any piece of tissue.
- To prevent tongue injury, insert a pencil or any stick that can be clamped between the jaws.
- Impaired respiratory function requires artificial respiration, as well as turning the patient on his side.
- To prevent self-injury, it is better to hold the patient firmly. During the peak of the attack, inexplicable forces appear, when even strong men cannot hold the patient.
After the attack stops, it is important to calm the person down, since he does not remember what happened to him. It is not recommended to move the patient
To ensure comfort, you can cover your body with a blanket. It is strictly forbidden to give anything to drink or eat until the doctors arrive. The same applies to the administration of medications. Failure to comply with these rules may provoke the development of a recurrent attack.
In cases where the attack is mild and does not cause loss of consciousness, pain due to muscle stiffness can be relieved by actively rubbing the skin. You can use alcohol tinctures of calendula and sea buckthorn oil.
Types of post-stroke seizures
Antiphospholipid syndrome: causes, treatment
Depending on the time of occurrence of seizures, there are 3 types of post-stroke seizures, which have different development mechanisms:
- Precursors (vascular precursive epilepsy) - develop several months, years before the appearance of other symptoms of stroke. The reason for their occurrence is narrowing/partial blockage of the main vessel of the head. Precursor seizures may be the only sign of a micro-stroke or “silent” stroke, which does not lead to noticeable permanent disorders and is diagnosed by chance during a routine MRI or CT scan of the brain.
- Early (epilepsy of irritation). They account for 20-25% of all post-stroke seizures. Occurs during the acute period of rehabilitation (the first 7 days). Their appearance is associated with disruption of the functioning of neurons that have experienced oxygen starvation. Due to disruptions of the antiepileptic system, a small group of nerve cells is formed that produce pathological electrical impulses that cause the muscles to contract unnaturally.
- Late (scarring epilepsy) is the most common type (65-70%). Appear weeks, months, years after a stroke. Caused by the restructuring of nervous tissue. Characteristic of patients who have a cyst or atrophy of the cerebral cortex formed in the affected area. If late-onset seizures first appear weeks or months after an ischemic stroke, there is a high likelihood of their regularity in the future.
Late seizures may occur:
- after emotional stress, physical strain;
- during sleep;
- be a side effect of some medications.
According to the characteristics of their manifestation, convulsive contractions are:
- tonic – prolonged contraction of individual muscle groups;
- clonic (convulsions) - alternating strong contraction and relaxation of muscle fibers.
Risk factors for the development of post-stroke epilepsy include:
- hemorrhagic form of cerebral stroke;
- impregnation of infarction zones with blood components (hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic stroke);
- cardioembolic nature of the disease;
- damage to the cerebral cortex;
- significant area of damage;
- thrombosis of central veins, sinuses;
- severe course of the pathology.
Emergency measures for seizures
Registration of disability after a stroke
Success in treatment depends on taking primary measures to stabilize the patient's condition.
- During an attack, you need to remove your dentures and remove any remaining food from your mouth;
- You should raise your head and put a bag or other handy item under it. The head is held higher than the body;
- Such conditions are accompanied by hoarse breathing. The patient is turned on his side, facilitating respiratory function;
- If a cramp occurs in muscle tissue, you should rub and warm it up. Perform massage movements. At home, you can use olive oil and dry mustard. The homogeneous mixture is rubbed in with massage movements;
- You need to take aspirin. It normalizes body temperature and accelerates blood circulation through the vessels.
These are the primary measures. If even short-term convulsive attacks occur, be sure to consult a doctor.
What to do first?
When the first symptoms appear, it is necessary to provide the patient with first aid as quickly as possible. The success of all further treatment directly depends on the speed of measures taken. First aid to the patient will consist of the following steps:
- Provide the victim with oxygen, ventilate the room, free the person from constrictive clothing;
- Clear the patient’s mouth of food and foreign objects, if any;
- Keep the head higher than the body level, place the person on a pillow;
- If wheezing and heavy breathing occur, carefully turn the person on his side;
- If the patient is experiencing severe pain, massage the affected area and warm up the muscle;
- Give aspirin to eliminate elevated body temperature, fever, eliminate muscle spasms and normalize blood circulation.
The above steps will not only help alleviate the patient’s general condition and slightly eliminate pain, but in some cases they can also gain time before the ambulance arrives.
If the attack was minor and went away on its own after first aid, the patient should still be shown to a specialist and the necessary examinations should be carried out to prevent recurrent hemorrhage.
Complications
Seizures are dangerous accompaniments of a stroke, indicating an acute cerebrovascular accident. The intensity and duration of the seizures may indicate which part of the brain is damaged and how severely it is damaged. In the period after a stroke, convulsions may appear slightly, and after 2-3 months they may increase in speed. This does not indicate incorrect treatment, but indicates the presence of extensive foci of brain damage.
In the absence of proper treatment and extensive brain damage, complications such as:
- Recurrence of stroke - seizures are a characteristic sign of how damaged the brain is and whether the recovery process is underway.
- Coma state - against the background of prolonged attacks, a coma develops, in which all reflexes are reduced, and vital processes slow down.
- Development of disability and inability to self-care - people with frequent attacks must be under constant supervision, as they pose a danger not only to others, but also to themselves. They need constant care and attention.
- Lethal outcome is a consequence of prolonged disruption of cerebral circulation, which leads to tissue necrosis and non-viability of the brain.
Elderly people are at risk, since as natural aging processes progress, regeneration occurs extremely slowly. In such patients, the risk of recurrent stroke increases several times.
It is important to pay attention to the performance of the cardiovascular system and eat right. Prevention consists of taking vitamin complexes, periodic examination by a specialist, and reducing the likelihood of stroke
source
Dangerous complications
Lack of adequate treatment for seizures after stroke can cause complications. Such patients are at risk:
- Repeated stroke, which not everyone manages to survive;
- Comatose state - attacks of muscle spasms lead first to a short-term and then to a longer loss of consciousness. With frequently recurring seizures, the patient falls into a coma;
- Loss of ability to work - the regular occurrence of seizures that do not disappear when taking standard medications indicates necrotization of large areas of the brain. Rehabilitation of such a patient is not effective, the person becomes disabled;
- Fatal outcome - constant relapses of convulsive attacks, the lack of positive dynamics during treatment indicates the likelihood of internal bleeding. It is practically impossible to eliminate this condition. Therefore the patient dies.
To prevent the development of dangerous consequences of seizures during a stroke, you should immediately seek medical help, undergo a comprehensive examination and begin treatment.
Features of treatment
The therapeutic approach depends on the type of seizure. If these are warning signs, specific anticonvulsants are not prescribed. The main goal of treatment is to eliminate the narrowing of the artery. Depending on the cause of the pathology, the patient is prescribed anticoagulant medications (aspirin), blood pressure pills, and neuroprotectors.
Early seizures do not require immediate specific treatment. They usually disappear on their own once the metabolism in the brain has stabilized. Antiepileptic drugs are prescribed exclusively to patients with repeated unprovoked seizures.
Isolated late attacks also require observation. If episodes of seizures are repeated, there is a possibility of developing post-stroke epilepsy, a chronic disease manifested by periodic convulsive conditions. If the diagnosis is confirmed, patients are prescribed anticonvulsants:
- carbamazepine (tegretol, finlepsin);
- valproates (convulex, convulsofin, depakine, valparin);
- topiramate (maxitopyr, topsaver, topamax);
- lamotrigine (convulsan, lamitor, lamictal);
- Levetiracetam (Keppra).
Possible complications
Older people, who make up the bulk of those affected, are more sensitive to the side effects of anticonvulsant medications. It's connected with:
- simultaneous use of 3 or more medications of different pharmacological groups that can interact with each other;
- unsatisfactory condition of the liver, kidneys;
- the presence of cognitive impairment;
- accumulation of antiepileptic drugs in blood serum.
Most common side effects
| Active substance | Violation |
| Carbamazepine, phenytoin |
|
| Valproate |
|
| Topiramate |
Types of post-stroke seizures
Depending on the time of occurrence of seizures, there are 3 types of post-stroke seizures, which have different development mechanisms:
- Precursors (vascular precursive epilepsy) - develop several months, years before the appearance of other symptoms of stroke. The reason for their occurrence is narrowing/partial blockage of the main vessel of the head. Precursor seizures may be the only sign of a micro-stroke or “silent” stroke, which does not lead to noticeable permanent disorders and is diagnosed by chance during a routine MRI or CT scan of the brain.
- Early (epilepsy of irritation). They account for 20-25% of all post-stroke seizures. Occurs during the acute period of rehabilitation (the first 7 days). Their appearance is associated with disruption of the functioning of neurons that have experienced oxygen starvation. Due to disruptions of the antiepileptic system, a small group of nerve cells is formed that produce pathological electrical impulses that cause the muscles to contract unnaturally.
- Late (scarring epilepsy) is the most common type (65-70%). Appear weeks, months, years after a stroke. Caused by the restructuring of nervous tissue. Characteristic of patients who have a cyst or atrophy of the cerebral cortex formed in the affected area. If late-onset seizures first appear weeks or months after an ischemic stroke, there is a high likelihood of their regularity in the future.
Late seizures may occur:
- after emotional stress, physical strain;
- during sleep;
- be a side effect of some medications.
According to the characteristics of their manifestation, convulsive contractions are:
- tonic – prolonged contraction of individual muscle groups;
- clonic (convulsions) - alternating strong contraction and relaxation of muscle fibers.
Risk factors for the development of post-stroke epilepsy include:
- hemorrhagic form of cerebral stroke;
- impregnation of infarction zones with blood components (hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic stroke);
- cardioembolic nature of the disease;
- damage to the cerebral cortex;
- significant area of damage;
- thrombosis of central veins, sinuses;
- severe course of the pathology.
WHY DO PATIENTS HAVE SEIZURES AFTER A STROKE?
A blocked or ruptured blood vessel can lead to seizures. In both cases, blood flow in the brain is disrupted and sufficient oxygen ceases to flow. Some time after a stroke, the following factors can cause seizures:
- blood clot formation;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure;
- insufficient nutrition of brain cells;
- necrosis of the damaged area;
- cyst in the frontal lobe of the brain;
- nervous tension, stress;
- depression;
- infections and inflammation;
- physical stress;
- increased stress on the body;
- long-term use of certain types of drugs;
- drug overdose;
- incompatibility of medications.
Features of occurrence and symptoms
Cramps are involuntary twitches or contractions of muscles that can last several tens of minutes. Generalized seizures after a stroke are characterized by muscle contractions throughout the body. After such attacks, the patient often falls asleep or loses consciousness, since generalized convulsions are a stressful situation for the body.
After a stroke, seizures can manifest in patients in the form of:
- numbness of one or both limbs at the same time, feeling of a wooden leg or arm;
- contractions of the muscles of the face and neck, resulting in a “mask-like face”, tilting of the head to one side or asymmetry of the face on one side;
- contractions of the facial muscles against the background of numbness of the limbs.
Some patients experience mild tremors after a stroke, while other patients experience short-term cramps throughout the body. This circumstance is taken into account by neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital; additional therapeutic measures are prescribed to patients to treat seizures.
Convulsive syndrome appears not only in acute circulatory disorders; its signs are noted by some patients during the first months of rehabilitation, when exacerbations occur. If seizures occur, a patient who has suffered a stroke requires medical care in a hospital setting.
Make an appointment
Treatment options
To relieve seizures, complex therapy is used, which includes:
- Antiepileptic drugs - reduce the sensitivity of nerve receptors to irritants, blocking the transmission of neural impulses.
- Nootropic drugs - normalize brain activity, improving microcirculation and reducing the need for oxygen by brain cells. Acceleration of metabolic processes allows for faster regeneration of damaged areas of the brain, which has a positive effect on the rehabilitation process.
- Thrombolytics – help thin the blood and prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Hepatoprotectors and drugs that affect lipid metabolism stimulate the production of good cholesterol and reduce the synthesis of bad cholesterol, which reduces the likelihood of developing atherosclerosis.
- Vitamin complexes with a high content of B vitamins improve connections between neurons, taking part in the restoration of the peripheral and central nervous system.
Symptomatic therapy is aimed at reducing muscle pain and relieving cephalgia. In these cases, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which have an analgesic effect. When severe muscle pain develops, ointments and creams may be prescribed, which contain natural ingredients that have a warming effect.
After seizures, various complications may develop that affect the patient’s motor activity. This dictates the need for a number of rehabilitation measures aimed at full recovery. This includes physical therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, saturating the diet with vitamins and completely abandoning bad habits.
The duration of medications and their dosage are selected individually, taking into account the age, gender and characteristics of the patient.
Traditional medicine recipes are not used due to their danger and unproven effectiveness. Some rubs and alcohol tinctures can be used for external use by kneading the limbs. Self-medication can be life-threatening and cause a number of irreversible processes.
Only medical workers can stop seizures by administering special medications. It is impossible to fully help a person at home and with the help of improvised means.
The patient is shown complete rest and constant monitoring of his condition. If possible, in the post-stroke period there should always be close people nearby who can quickly react and provide help.
If the attack is severe, the first step is to call an ambulance
First aid for seizures
Sometimes seizures occur as one of the symptoms of a stroke. Very often the attack is accompanied by a loss or disturbance in the level of consciousness. Before the ambulance arrives, such a patient must:
- lay on your side, place a small pillow under your head or build a platform from available materials (jacket, sweater, bag, backpack);
- hold your head so that vomit and saliva can flow down freely;
- wipe off discharge with a napkin;
- Hold the victim’s arms and legs without using brute force. This will prevent involuntary injuries to others and to oneself;
- If at the end of the seizure the patient stops breathing, proceed to chest compressions and artificial respiration.
- put any objects into your mouth. They can damage teeth and oral mucosa;
- try to immobilize the patient, unclench his fingers;
- give water - the victim may choke on it;
- offer any medications, except in cases previously agreed upon with the doctor;
- offering ammonia can cause respiratory arrest.
Urgent Care
What to do with cramps after a stroke - if a muscle spasm occurs, you must:
- Call an ambulance immediately;
- If convulsions are accompanied by loss of consciousness, you need to put the patient on the sofa;
- Open the window and remove tight clothing from the patient to ensure oxygen access;
- Place a pillow or cushion under your head, remove hard or sharp objects that could cause injury;
- Remove food or vomit from the mouth and remove dentures;
- If breathing is impaired and wheezing occurs, the patient should be placed on his side;
- If a seizure continues for a long time, you will have to restrain the patient to prevent accidental injury;
- If the patient is conscious and suffers from strong muscle contractions, it is recommended to prepare a mustard compress with olive oil or gently rub the legs.
Attention!
Basic treatment of seizures after a stroke can only be prescribed by a neurologist after a comprehensive diagnosis.
First aid rules for seizures after a stroke
Manifestations of pathology
1. Epilepsy due to stroke is not such a common type of complication, but among elderly and senile people it is being recorded more and more often. It manifests itself as a convulsive attack of varying intensity. As a rule, it is preceded by a series of difficult-to-define symptoms, collectively called an “aura.”
2. The attack usually begins suddenly and can happen anywhere, including on the street. The person lets out a strong cry and falls backward. If a seizure occurs at home, then it is advisable to have time to grab the person so that he does not hurt himself by falling on the floor. If this does happen, then he should put a pillow under his head so that during sudden movements the victim does not injure himself. The teeth should be fixed so that he does not bite his tongue during a seizure.
Seizures after a stroke: causes
Patients and their families often wonder why seizures occur after a stroke. And this is not entirely correct, since similar involuntary muscle contractions may also indicate the approach of trouble (primary or repeated blows).
Common reasons include:
- death of brain cells;
- infections;
- accompanying inflammatory processes;
- presence of a tumor;
- cysts in the brain;
- intense physical activity;
- excessive emotional and mental stress;
- approach of secondary cerebral infarction;
- side effect from taking certain groups of medications (for example, diuretics);
- lack of individual microelements (magnesium, potassium, iron).
A detailed study of the problem helped doctors come to the conclusion that the main cause is the formation of a hollow space in the brain filled with fluid, which occurs in response to tissue necrosis.
Such self-defense of the body does not in any way affect the functioning of the body and the state of human health, but can provoke a reduction in muscle mass.
Seizures after a stroke: why do they occur at night?
Night attacks, in addition to severe pain, also cause insomnia, which entails negative consequences for health. The reason for this is an attempt to completely involuntarily relax the body during sleep.
At the same time, the muscles do not allow the body to relax 100% due to lack of oxygen. The process of sudden spasms at night is called muscle ischemia.
Medicines used to relieve seizures:
- anticonvulsants (diazepam, sodium thiopental, valproic acid, carbamazepine, finlepsin);
- potassium-containing drugs (asparkam, etc.);
- iron-containing series (sorbifer, etc.);
- vitamins of group B6.
A light relaxing massage of “problem” areas before bed (done with oil) helps prevent muscle spasms. A sufficient daily amount of fluid intake also minimizes the risk of seizures (the volume of water consumed should correspond to body weight).
How to treat clonic seizures after a stroke?
Unlike the tonic variety, in which the spasm is not replaced by relaxation, the clonic type is characterized by a change in tone, which is felt as a rapid twitching of the muscle (there are periods of relaxation). They are treated according to the scheme described above.
source
Features of the manifestation of cramps in the legs
The manifestation of convulsive phenomena after stroke is classified into:
- Limited occurrence of cramps, when after a stroke, cramps in the toes, calf muscles or foot. Such spasms are called cramps;
- Vivid and prolonged spasms, accompanied by numbness or complete loss of sensation in the lower limb (the so-called “cotton leg”).
The appearance of such symptoms indicates serious necrotic lesions of the brain or the death of cells of the motor center in the cerebral cortex.
On a note!
Seizures after a stroke occur in the limbs on the side opposite to the area of brain damage.
Manifestation of seizures
Convulsive syndrome, including epileptic seizures, occurs to the patient if the frontal lobes of the brain are damaged by an impact, or if a subarachnoid hemorrhagic attack occurs. The patient's seizures vary in duration and can last from 10–20 seconds to several minutes. In most cases, a prolonged attack ends in sleep, after which the patient does not remember the onset of the convulsive syndrome. In general, seizures during and after a cerebral stroke manifest themselves as follows:
- The patient loses the ability to communicate with his immediate environment.
- Tension develops in certain muscles of the body and/or limbs.
- Muscle tone sharply develops into cramps.
- The patient may lose consciousness.
- The patient experiences involuntary urination.
All seizures during and after a stroke are divided into two types:
- Tonic. Prolonged, characterized by patients as a feeling of complete numbness of the limb.
- Clonic. They have a short duration and are expressed in twitching of some muscles of the face or body.
Additionally, convulsions and twitching of the limbs can be divided into three main groups:
- Premonitory seizures. They can manifest themselves several months or even years before apoplexy. As a rule, this indicates vascular insufficiency. Most often, such convulsions foreshadow an ischemic stroke.
- Early cramps. They are mainly formed during an attack and within a week after it.
- Late convulsions and epileptic seizures. They are the result of impaired cerebral circulation and the death of a certain number of neurons.
For stroke
Most often, during a stroke, twitching of the body and limbs occurs after the patient loses consciousness. People who may experience an attack of apoplexy should immobilize the patient's body as much as possible and call an ambulance. In addition, you need to free the patient from constricting clothing, provide an influx of fresh air, and raise the patient’s head 30 degrees from the floor or other flat surface. A convulsive state during apoplexy is considered one of the main symptoms of a stroke.
It is worth knowing that convulsions and twitching are observed in the part of the body opposite the affected hemisphere of the brain. For example, if a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere occurs, then convulsions will be observed in the left limbs, and vice versa.
After a stroke
If convulsions and twitching appear in a patient after an attack, this in no way indicates the incompetence of the attending physician. It's all about impaired blood circulation in a certain area of the brain. Moreover, such symptoms require special attention, since they indicate the following conditions:
- Formation of neoplasms in dead parts of the brain. It could be a cyst, etc.
- Risk of recurrent apoplexy.
- Inflammatory processes of the central nervous system against the background of infection.
- Degradation and pathological changes in neural connections in the central nervous system.
What is the danger of post-stroke seizures?
According to statistics, stroke is a disease that ranks 3rd in the world as a cause of death. Repeated hemorrhage often provokes coma and destruction of brain cells, which is not comparable to human life.
After a stroke, persistent cramps on the affected side are a clear sign of the progress of a pathological disorder, which can provoke a recurrence of hemorrhage.
Leg cramps at night after a stroke definitely require treatment. Ischemic stroke and convulsions within a week indicate an exacerbation of the disease and its further development.
The consequences can be extremely severe and dangerous not only for health, but also for the life of the patient as a whole. Post-stroke seizures can lead to:
- recurrent stroke (systematic recurrence of seizures indicates incorrect or ineffective post-stroke treatment, it must be urgently corrected. Otherwise, a generalized convulsive seizure may occur, which leads to repeated cerebral hemorrhage);
- death (the intensity and frequency of repetitions of convulsive seizures indicates a danger - ischemic damage to brain tissue. This leads to continued hemorrhage, increased intracranial pressure, coma and death);
- coma (convulsions during or after a cerebral stroke can become more frequent and cause short-term or long-term loss of consciousness, that is, coma);
- disability (leg cramps after a stroke or other limbs are extremely dangerous for a sick person, since he ceases to control the movements of his body and can harm himself, for example, cut himself or bite off a piece of his tongue, and become disabled).
Clinical picture
The seizures are usually short in duration and appear in the part of the body affected by the stroke; in rare cases, the entire body may be affected. The duration of the convulsions varies from approximately 15 seconds to 15 minutes, and if the body is affected for a long time, the patient may faint. As a rule, a severe attack ends with the patient sleeping for a long time; it can last about an hour.
Visually, convulsive conditions are similar to tremors of the limbs, but in severe cases, when the whole body is affected, the condition resembles an epileptic seizure. Serious seizures occur in a patient when the frontal part of the brain is damaged.
In general, convulsive conditions are divided into two types:
- Tonic - long-lasting and large-scale in size of the affected area of the body;
- Clonic - short-term, only individual muscles of the limb are affected;
- Generalized - tonic and clonic types alternate in a row.
Signs of seizures after a stroke include the following conditions:
- Loss of ability to contact and communicate;
- Involuntary urination;
- Fainting;
- Severe muscle tension in the area of the cramp.
Associated symptoms
The clinical picture of seizures after a stroke depends on the cause that provoked them. Some patients experience slight twitching of the feet and hands, while in others the seizures develop into an epileptic attack.
It is necessary to know the symptoms of seizures. This will help prepare for an attack and prevent the development of severe consequences. The convulsive state is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The reaction to other people is lost, the patient stops answering questions;
- The patient complains of dizziness;
On a note!
Some patients experience loss of consciousness (fainting) before the seizure.
- The muscles of the legs and arms harden, their tone increases;
- Mild tremors appear in the limbs;
- During an attack, the patient may bite his tongue. With pronounced convulsions, uncontrolled urination or defecation is possible.
Attention!
Sometimes leg cramps during a stroke are accompanied by severe pain. This symptom is caused by impaired cerebral circulation.
Symptoms of seizures after a stroke
In most cases, the duration of an epileptic attack is 5-7 minutes. After the convulsions disappear, the patient faints. Resembling deep sleep.
There are two types of seizures after a stroke:
- Clonic - a spasm develops in the upper or lower limb on one side, or the attack affects a limited number of muscles. A severe attack alternates with a period of muscle relaxation;
- Tonic - a sharp and strong muscle spasm that lasts for a long time. Typically, a tonic attack is characteristic of the muscles of the legs, but it also happens in other parts of the body.
FOLK METHODS IN COMBATING CONVIVUS SEIZURES AFTER STROKE
Phototherapy acts as an additional treatment method. Convulsive attacks caused by tension can be reduced with decoctions of the following herbs:
Medicinal plants have contraindications, so it is recommended to consult a doctor before use. A specialist will help you choose the appropriate complex.
Conclusion
Seizures are one of the warning signs and symptoms of stroke.
Malaise may indicate the onset of bleeding in the brain. Also, seizures are often a consequence of poor circulation and lack of nutrition to brain cells. The disorder requires treatment, so you need to contact a specialist to select the optimal set of restorative measures. It is worth considering that seizures some time after a stroke, namely during the rehabilitation period, may indicate that the prescribed drug therapy does not help or the drugs are poorly compatible. source
Spasticity after stroke: features and rehabilitation
Not everyone experiences spasticity after a stroke. But, if a muscle is in spasm all the time, it can shorten. If the muscles of the injured arm or leg are not stretched, pain will begin over time. Contracture may develop - the muscle will shorten and the limb cannot be straightened without surgery.
How to avoid complications:
1. You should stretch muscles that have increased tone.
- You should stretch very carefully, slowly and gradually.
- The patient should not experience pain.
- Stretching is done several times a day, every day.
- Stretching can be done by the patient himself or by an assistant.
2. For spasticity, medications are used for treatment - botulinum therapy.
- It is very effective in reducing muscle tone and is safe.
- Botulinum therapy is successfully used in all countries with developed medicine.
- Botulinum therapy is carried out by additionally trained doctors. They give injections to those muscles that have high muscle tone.
- The effect does not occur immediately, but within several weeks, and lasts for an average of 3 months.
- If the patient's spasticity is severe, then botulinum therapy should be carried out 2-4 times a year.
- Botulinum therapy can be used to reduce tone, relieve pain and limited mobility. It can also help restore movement
These drugs are quite expensive, but they can be obtained free of charge through the state program if the patient has a disability group.
After 2 weeks of botulinum injections, the patient’s muscle tone decreases and a “rehabilitation window” opens.
At this time, rehabilitation will be very effective.
The secret is that the better the patient moves his arm or leg, the less muscle tone. You can get rid of spasticity through proper use of the affected arm for dressing, preparing and eating food, washing the body, and also when walking.
Therefore, in rehabilitation it is important to combine botulinum therapy with non-drug therapy:
- physical therapy
- classes with a speech therapist
- occupational therapist
- psychologist
- rehabilitation nurse
In some cases, after a series of botulinum injections and rehabilitation courses, the patient manages to get rid of spasticity completely.
Pyotr Ivanovich had just such a case. He managed to regain hand function using botulinum therapy and rehabilitation. Good interaction between specialists, doctors, psychologists, occupational therapists and physical therapists allows you not to waste time and effectively plan rehabilitation after botulinum therapy.
Write to us what difficulty you encountered, and we will suggest further steps for rehabilitation or provide the missing information.
WHY DO PATIENTS HAVE SEIZURES AFTER A STROKE?
A blocked or ruptured blood vessel can lead to seizures. In both cases, blood flow in the brain is disrupted and sufficient oxygen ceases to flow. Some time after a stroke, the following factors can cause seizures:
- blood clot formation;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure;
- insufficient nutrition of brain cells;
- necrosis of the damaged area;
- cyst in the frontal lobe of the brain;
- nervous tension, stress;
- depression;
- infections and inflammation;
- physical stress;
- increased stress on the body;
- long-term use of certain types of drugs;
- drug overdose;
- incompatibility of medications.
FOLK METHODS IN COMBATING CONVIVUS SEIZURES AFTER STROKE
Phototherapy acts as an additional treatment method. Convulsive attacks caused by tension can be reduced with decoctions of the following herbs:
Medicinal plants have contraindications, so it is recommended to consult a doctor before use. A specialist will help you choose the appropriate complex.
Conclusion
Seizures are one of the warning signs and symptoms of stroke.
Malaise may indicate the onset of bleeding in the brain. Also, seizures are often a consequence of poor circulation and lack of nutrition to brain cells. The disorder requires treatment, so you need to contact a specialist to select the optimal set of restorative measures. It is worth considering that seizures some time after a stroke, namely during the rehabilitation period, may indicate that the prescribed drug therapy does not help or the drugs are poorly compatible. source
Rehabilitation after a stroke at the Almadeya Clinic
Almost every day patients come to us with the problem of increased muscle tone in the arm or leg after a stroke.
We carried out botulinum therapy, stretched the muscles, gave exercises and tasks to restore the arm.
The hand recovered best when Pyotr Ivanovich received his working tools and performed exercises with them. The nurses walked around and were amazed at how Pyotr Ivanovich easily copes with the repairs, although he is still undergoing a rehabilitation course.
We managed to restore his hand and Pyotr Ivanovich remained to work in the hospital.
This story shows that spasticity can be managed through movement and drug therapy. Using familiar activities can help restore activity to your sore arm.
Treatment regimen
Before starting therapy, the patient must undergo a series of examinations: MRI, CT, general urine and blood tests.
After studying the examination results, the neurologist makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes medication, which includes:
- Anticoagulants to prevent blood clots (Heparin, Klivarin).
- Nootropics for active nutrition of brain cells and normalization of blood supply (Phenotropil).
- Anticonvulsants (Carbamazepine, Finlepsin).
Your doctor may also prescribe injection procedures:
- To reduce blood clotting - heparin, warfavin.
- To normalize blood circulation albumin.
- To reduce pressure Cavinton, Instenton.
It is important to remember that the simultaneous use of anticonvulsants with anticoagulants can lead to bleeding. Any medications must be taken strictly according to your doctor's prescription.
Treatment of convulsive conditions should occur strictly under the supervision of a neurologist and be comprehensive. In addition to medications, the patient is prescribed rehabilitation therapy:
- Gymnastics and physical therapy. It is performed under the supervision of a rehabilitation specialist and is aimed at restoring motor activity and coordination of movements.
- Special procedures in the physiotherapy room that stimulate muscles.
- Massage and warming up the affected areas of the body.
- Hydrotherapy and acupuncture.
- Speech restoration with the help of exercises from a speech therapist or neuropsychologist.
In some cases, when a patient experiences depression due to pathology, it may be necessary to work with a psychologist and use antidepressants.
Proper comprehensive treatment will give results within a couple of weeks of daily therapy; the intensity and frequency of seizures will significantly decrease. In addition to eliminating convulsive conditions, such rehabilitation measures will be an excellent prevention of recurrent stroke.
Together with rehabilitation therapy and drug treatment, traditional medicine can be used, for example, a herbal mixture of mint, yarrow, knotweed and shepherd's purse. Hot baths from this decoction are effective for cramps and spasms of the limbs.
Take a teaspoon orally three times a day.
To reduce spasms, bay ointment is suitable. To prepare it, mix 20 g of bay leaf and 150 g of oil; this mixture needs to steep for about a month, then boil and thoroughly rub the affected areas.
Before starting to use traditional recipes, you should consult your doctor to avoid possible side effects and complications.
Causes
The cause of convulsive pathology lies in the death of cells in the affected area of the brain, as a result of which cysts and cavities form.
Neoplasms negatively affect neighboring healthy cells and provoke the appearance of spasms in individual limbs.
Also, the causes of convulsive conditions may be:
- Severe nervous tension and stress;
- Psycho-emotional and physical exhaustion;
- Side effects of medications, their overdose or incorrect combination.
In addition to the above factors, the cause of convulsive conditions can be infectious infections of the brain that occur during or after surgery.
How do they manifest themselves?
Post-stroke seizures occur due to poor blood circulation in the affected part of the body and tissue necrosis.
Symptoms of such pathological conditions may include frequent dizziness, spatial disorientation, and headaches.
After a hemorrhage in the brain, a new growth (cyst) appears in the area of tissue death, which can put pressure on neighboring tissues and interfere with their normal nutrition.
Convulsive states and spasms arise as a result of a brain reaction.
In most cases, the pathology manifests itself at night, and the victim may experience severe pain. Typically, patients experience spasms of the lower extremities: the calves, feet, and toes become numb, and sometimes the entire leg may become numb. The face is also sometimes affected: the muscles of the cheeks and eyelids twitch. The hands are rarely affected, with spasms appearing only on the palms.