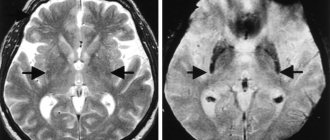
Encephalopathy is a non-inflammatory brain disease. When it comes to the brain and, even more so, its diseases, the answer to the question: are they recruited into the army with encephalopathy or another disease related to the brain, automatically arises in thoughts - of course not.
However, there are many nuances that determine the possibility of releasing a young man with such a disease from service. These include the form and severity of the disease, the functional disorders it provokes in the body and the availability of appropriate documents to confirm the diagnosis.
Types, features of encephalopathy
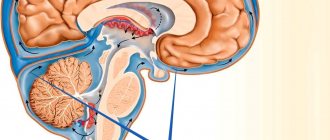
The disease provokes degenerative changes in brain tissue, which leads to dysfunction of the organ. The congenital form of the pathology develops against the background of an unfavorable course of pregnancy in the mother, with a genetic predisposition, or birth trauma. Acquired encephalopathy appears as a result of an infectious, viral, bacterial disease, poisoning, injury, etc.
Experts identify the following causes of encephalopathy:
- Injuries. Numerous bruises lead to the accumulation of amyloids in the brain, which provoke pathology. This type of encephalopathy is also called missed beat syndrome, post-traumatic encephalopathy. It develops more often in boxers, athletes, and American football players.
- Pregnancy, childbirth . It is difficult to prevent pathology in this case, since a large role is played by the genetic factor, the state of health of the mother, and the qualifications of the specialists delivering the child. This type of brain disease is called perinatal encephalopathy.
- Diseases of the vascular, circulatory, venous system . Hypertensive or vascular encephalopathy develops with hypertension, blood dyscirculation, atherosclerosis, inflammatory changes in the walls of blood vessels, and impaired intracranial pressure.
- Chronic intoxication . It develops when toxic substances or components enter the body constantly or frequently. The disease is called toxic encephalopathy and develops when drinking alcohol, drugs, entering the body with heavy metals, poisons, or a large number of medications.
- Liver and kidney diseases . The main organs involved in the breakdown of various substances, removing residues, and cleansing the body as a whole. In severe pathologies, hepatic, uremic encephalopathy develops.
- Oncology, radiation damage . Gradually leads to changes in the structure of brain cells, tissue deformation, and dysfunction of the organ.
- Ischemia. The cause of encephalopathy is oxygen starvation of the brain.
The risk of developing pathology increases in diabetes mellitus, as well as in the presence of a viral infection, HIV.
Doctors distinguish 2 types of encephalopathy, which are often found in patients of different ages - residual (in the lane Residual, formed when other pathologies are “undertreated”), discirculatory . The latter is developing slowly but at a steady pace. Multifocal diffuse damage to brain tissue is observed.
Post-traumatic encephalopathy
Post-traumatic encephalopathy is a condition that includes a complex of mental and neurological disorders caused by the development over a year or more of persistent consequences of a traumatic brain injury due to scarring, atrophic, dystrophic and degenerative changes in brain tissue. Manifestations and severity depend on the location and severity of the injury, the age of the patient, the effectiveness of treatment, the presence or absence of vascular disorders, chronic intoxication, including alcohol.
The following stages can be distinguished in the development of the disease:
- Direct damage to nervous tissue (usually the frontal and temporal lobes) at the time of injury.
- Changes in blood supply to the brain due to cerebral edema.
- Poor circulation of cerebrospinal fluid due to compression of the ventricles.
- In the absence of regeneration of nerve cells, they are replaced by connective tissue with the formation of scars and adhesions.
- A pathological response of the immune system, which begins to perceive its own nerve cells as a foreign agent (autoneurosensitization).
The very first signal indicating possible post-traumatic changes is memory impairment. Another common symptom is problems with attention and concentration. In addition, there are thinking disorders that affect slowness of reaction, inability to analyze, logic and other tools of cognitive processes.
The appearance of vegetative symptoms is also possible. Unreasonable attacks of vomiting and nausea, headaches and dizziness, surges in blood pressure, pallor, cold sweat.
The most common manifestation of encephalopathy of traumatic origin is headache. Dizziness, sleep disturbances, weakness, decreased performance, increased fatigue, emotional lability (unstable, rapidly changing mood), painful sensitivity to weak stimuli (sounds, light, etc.) are also characteristic. Hypochondriacal and depressive disorders are possible.
Psychopathic-like states develop gradually, against the background of a gradual improvement in the patient’s condition in the acute and late period of injury. Previously existing psychopathic character traits are strengthened and “sharpened.” Most often, unmotivated mood swings, a tendency to litigiousness, and explosiveness with bouts of aggression, anger and irritation are observed.
In addition to psycho-emotional disorders, a number of syndromes can develop with post-traumatic encephalopathy:
Hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome (post-traumatic intracranial hypertension). It manifests itself as headache with nausea and vomiting, paroxysmal autonomic disorders.
Episyndrome (post-traumatic epilepsy). Occurs as a result of focal lesions or adhesive-scarring changes in the brain. Attacks of various forms are characteristic - both with loss of consciousness and without it.
Post-traumatic parkinsonism. Develops as a result of prolonged brain hypoxia during the period of injury. There is a constant, steady increase in muscle tone of the extrapyramidal type, akinesia (immobility due to stiffness).
Post-traumatic vestibulopathy. Accompanied by dizziness, vomiting, nausea, uncertainty when standing and walking.
As a result of moderate and severe injuries, motor and speech defects of varying severity, sensitivity disorders, and pelvic disorders can form.
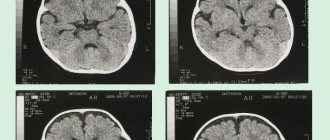
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to perform computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging and neuropsychological testing. With these studies, the doctor receives detailed information about focal or diffuse changes in the brain substance. In addition, this allows us to exclude other pathologies of the central nervous system, accompanied by similar symptoms.
As an additional examination method, it is advisable to perform electroencephalography, which helps to identify the pathological focus of epileptic activity and adjust treatment based on the data obtained.
Treatment of post-traumatic encephalopathy should be aimed at neuroprotection (protection of nerve cells from negative factors), normalization of blood circulation processes, as well as restoration of all cognitive functions and metabolism of brain cells. Symptomatic treatment is also important, especially in the presence of hydrocephalus syndrome (specific drugs that relieve cerebral edema are required), epilepsy (a good selection of antiepileptic drugs and their doses is required). Courses of such complex therapy, depending on the severity of the manifestations of post-traumatic encephalopathy, should be carried out 1-2 times a year.
The prognosis for life, work ability and ability to self-care usually becomes clear within the first year after the injury. It is at this time that it is important to carry out comprehensive rehabilitation measures. The remaining neurological and physical deficit after a specified time is quite difficult to further correct. However, even in the case of gross violations, attempts should be made to compensate them to one degree or another.
Symptoms
Since the causes of the development of the disease are different, the clinical picture has many characteristic manifestations. Symptoms can be pronounced or barely noticeable.
In general, patients with encephalopathy are characterized by:
- Headache is constant or intermittent;
- Disorder of memory, consciousness;
- Decreased mental abilities, concentration, attention, mental activity;
- Lack of initiative;
- Dizziness, fainting;
- Noise in the head;
- Prolonged depression with a desire to die;
- General weakness;
- Rapid fatigue;
- Poor sleep;
- Irritability;
- Tearfulness;
- Absent-mindedness.
In colloquial speech there is verbosity and difficulty in pronouncing some words. The behavior shows apathy, a narrow range of interests, and daytime sleepiness.
In severe cases, in the last stages of the disease, the following is observed:
- Urinary and fecal incontinence;
- Difficulty swallowing food;
- Dementia;
- Forced laughter, crying;
- Voice change;
- Impaired walking, fluency of speech;
- Fluctuations in blood pressure.
Various methods are used to diagnose the disease:
- Rheoencephalography;
- X-ray of the cervical spine with functional tests;
- Ultrasound Dopplerography of the vessels of the neck and brain;
- MRI.
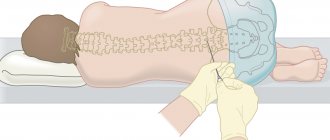
When making a diagnosis, neurological and psychological symptoms, results of blood and cerebrospinal fluid tests are also taken into account.
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, in a hospital setting. Over a year, depending on the severity of the disease, an average of 3 courses of therapy are required. To improve the patient's condition, painkillers, antioxidants, hormones, osteopathy, manual therapy, and physiotherapy are used. As well as physical therapy and surgery. Treatment methods are selected individually in each case, depending on the cause of the disease, severity, and clinical picture.
Treatment of encephalopathy
Treatment of the disease is aimed at ensuring the viability of the patient’s body and is comprehensive. Depending on the type and stage of the disease, as well as the physiological characteristics of the affected organs, medications are prescribed, procedures are performed, and surgery is performed.
Patients are prescribed hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs in combination with blockade injections, and courses of physiotherapy. Operations are prescribed in extremely difficult situations. In some cases, treatment of encephalopathy is a rather lengthy and complex undertaking.
Will people with encephalopathy be drafted into the army in 2021?
Experts distinguish 3 stages of the disease:
- Initial . There is frequent headache, irritability, fatigue, apathy, dizziness, decreased ability to work, depression, insomnia. Troubling noise in the ears.
- Progressive . The clinical picture is clearly expressed. The existing symptoms include complete or partial paralysis of the limbs, impaired vision, hearing, impaired gait, and coordination of movement.
- Heavy . The disease is difficult to treat. Over 1 year, 3 full courses of therapy are required, including in a hospital setting. Neurological symptoms predominate, epileptic seizures appear.
Whether someone with discirculatory, residual encephalopathy will be accepted into the army depends on the severity of the disease, the complexity of the course, the clinical picture, and functional disorders. In the Schedule of Diseases, according to which a conscript is given a deferment, sent to the reserve, or declared unfit for service, encephalopathy is absent. In this case, the decisive role is played by the conclusions of specialists and the severity of the manifestations.
Suitability categories for encephalopathy
The disease can remain in the first stage of development for a long time. Periodically manifested by headache, dizziness, weakness, sleep disturbance, depression, and other manifestations that do not lead to severe functional disorders.
- The mild stage of the disease cannot be diagnosed by a military commission, so the main role is played by entries in the medical book and examination results. A conscript is drafted into the army with category “A” or “B” with minor restrictions on service.
- Conscripts with the second stage of dyscirculatory encephalopathy can be enlisted in the reserve and assigned category “B”. They issue a military ID and have the right to be called up for service in the event of a martial law in the country.
- Conscripts with stage 3 encephalopathy are considered unfit for service, when all functional impairments are visible to the naked eye. They assign category “D”, issue a military ID, and no longer call you to the military registration and enlistment office.
The commission may send the young man for further examination to confirm the diagnosis and treatment if symptoms appear during the examination. In this case, a delay of a maximum of 6 months is given. The next meeting of the members of the military commission makes a decision based on the conclusions of specialists, the results of MRI, CT, and other diagnostic methods. They are assigned category “A”, “B” - they are sent to serve, or “C” - they are enlisted in the reserves.
If the disease begins to progress in the army, the soldier is sent home early.
How to get a military ID for encephalopathy, confirm the diagnosis
Members of the military medical commission are not required to make a diagnosis, therefore, if there are health problems, it is necessary to be examined in advance. A conclusion from a neurologist or vascular surgeon is required. To assign a category, the frequency of exacerbations, duration, and clinical picture play an important role. With mild manifestations of encephalopathy, the conscript will be taken away from service.
If the disease is accompanied by functional disorders, all this should be recorded in the opinions of specialists and in the medical record. You need to seek help from doctors every time your health begins to deteriorate. It is imperative to undergo a full examination of the brain, blood vessels, and cervical spine, and have the appropriate conclusions.
To obtain exemption from the army, 2-3 courses of serious treatment are required, including in a hospital setting. Even in the presence of obvious functional impairments, there must be documentary evidence of the disease. Go to the commission with copies of all extracts from your medical record and specialist reports. Lawyers do not recommend taking the originals to the military registration and enlistment office, since documents are often lost and nothing can be proven later.
If a conscript does not agree with the conclusion of the military commission regarding the assignment of a category, the result can be appealed. You can contact the prosecutor's office directly. The conclusion is revised if violations are identified in the work of the commission.
What is the danger of encephalopathy?
The particular danger of encephalopathy lies in the complications that arise as a result of its development. They may not exist at all, but they can also be very serious, including mental disorders, irreversible brain changes and death.
Important! To prevent the danger to health and life associated with this disease, it is necessary to carry out its prevention to prevent the occurrence of encephalopathy.
Prevention methods are very diverse, they depend on the presence of causes that provoke the development of the disease. A timely consultation with a doctor will allow you to identify individual health problems and take the necessary measures.
General recommendations for the prevention of encephalopathy include:
- timely seeking consultation in the presence of long-term illnesses;
- quitting smoking, drugs, drinking minimal amounts of alcohol;
- playing sports;
- walks in the open air;
- consumption of foods rich in vitamins and beneficial microelements;
- regular examinations by medical specialists.
Prevention of the disease consists of eliminating factors that can provoke it and strengthening the human immune system.
Reviews
Dear readers, you can leave your feedback on whether people with encephalopathy are accepted into the army in the comments; your opinion will be useful to other users of the site!
Andrey:
“I had a concussion, the consequences remained. Periodically I have headaches, weakness, nausea, dizziness, etc. I was examined several times and was hospitalized because I live in a military town. The diagnosis of post-traumatic encephalopathy was confirmed. The military registration and enlistment office again sent me for examination. I had an MRI and everything else. For now they are giving me a deferment because I am in graduate school. The military neurologist said that with such a diagnosis I would be drafted into the army. I consulted with a lawyer, he said they should give category “B”, but a psychiatrist’s opinion is also required. I haven’t noticed any deviations in this area. But the doctor must confirm rapid fatigue, decreased performance, etc. I hope for a "B."
Lily:
“My son is diagnosed with “Consequences of perinatal brain damage...”, as well as VSD. Everything was officially documented, I underwent an appropriate examination from a neurologist. Now they said there will be one more at the request of the military commission. If the diagnosis is confirmed there, they will definitely assign category “B”. We really hope so, my son often has headaches and faints.”
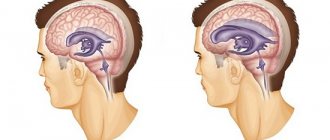
What is cerebral encephalopathy
Encephalopathy is a non-inflammatory disease of the brain.
As a result of various diseases and pathologies, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, and oxygen starvation of the brain tissue occurs. Due to lack of oxygen, nerve cells die, areas of the brain shut down and encephalopathy occurs. The disease can be congenital or acquired:
- Congenital encephalopathy of cerebral vessels occurs due to intracranial birth trauma, abnormalities in brain development, and infection during pregnancy.
- Acquired encephalopathy occurs in adults as a result of illness and injury.