Diagnosis and treatment of cerebellar disorders
The neurologist examines and tests superficial and deep reflexes.
Electronystagmography and vestibulometry are performed. A general blood test is prescribed. A lumbar puncture is performed to detect infection in the cerebrospinal fluid, as well as markers of stroke or inflammation. The head is held. The condition of the cerebellar vessels is determined using Dopplerography. Treatment of cerebellar diseases in ischemic stroke is carried out using thrombus lysis. Fibrinolytics (streptokinase, alteplase, urokinase) are prescribed. To prevent the formation of new blood clots, antiplatelet agents (aspirin, clopidogrel) are used.
For ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, metabolic drugs (Mexidol, Cerebrolysin, Cytoflavin) improve metabolism in brain tissue. To prevent recurrent strokes, drugs that lower blood cholesterol are prescribed, and in case of hemorrhagic hemorrhage, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed.
- Causes of cerebellar ataxia
- Causes and signs of weak development of reflexes
- How does a “normal” cerebellum work?
- Cerebellar ataxia with acute onset
- Diagnostics
- Consequences of the disease and prevention
- Cerebellar diseases
- Palmar chin reflex Marinescu Radovici
- Study of oral automatism reflexes in neurology
Neuroinfections (encephalitis, meningitis) require antibiotic therapy. Pathologies of the cerebellum caused by intoxications require detoxification therapy, depending on the nature of the poisons. Forced diuresis, peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis are performed. In case of food poisoning - gastric lavage, administration of sorbents.
For oncological lesions of the cerebellum, treatment is carried out in accordance with the type of pathology. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgical treatment are prescribed. If the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted, causing cerebellar syndrome, an operation is performed with craniotomy and shunting of the pathways for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
Conclusion
Damage to the cerebellum, the consequence of which can be disability, the patient’s need for care, requires timely and thorough treatment, as well as care and rehabilitation of the patient. If there is a sudden disturbance in gait or speech disorder, it is necessary to visit a neurologist.
Coordination motor disorder caused by cerebellar pathology. Its main manifestations include gait disorder, disproportionality and asynergy of movements, dysdiadochokinesis, and changes in handwriting such as sweeping macrography. Typically, cerebellar ataxia is accompanied by scanned speech, intention tremor, postural tremor of the head and torso, and muscle hypotonia. Diagnosis is carried out using MRI, CT, MSCT, MAG of the brain, Dopplerography, cerebrospinal fluid analysis; if necessary, genetic research. Treatment and prognosis depend on the causative disease that caused the development of cerebellar symptoms.
Clinical signs
The symptom complex of cerebellar ataxia takes first place in the clinic. Patients are characterized by static disorder - falling backward or to the sides in the Romberg stance. A slight disturbance in gait, “shooting” pain in the legs and lower back indicate the onset of the disease. Next, tremors of the hands, head, and unconscious contractions of the muscles of the face and torso occur. With a significant decrease in muscle strength, sensitivity remains. The clinic is accompanied by a lack of coordination of movements, handwriting becomes large, uneven and sweeping. Speech becomes difficult, becomes intermittent and slow, and has a chanting character.
Classic clinical cases are not without oculomotor disorders and decreased visual function. The gradual death of the optic nerves leads to a narrowing of the visual fields. All these signs are steadily progressing. Drooping of the upper eyelid is recorded. The patient raises his eyebrows in an attempt to reduce ptosis - this gives the face a surprised look. Often the disease is expressed by strabismus, impaired binocular vision, which leads to paresis of the abducens nerve.
Mental ailments are gradually joining the listed disorders. The course of the disease is aggravated by a decrease in mental processes and memory, and a depressive neurotic state develops. In severe clinical cases, epileptic seizures occur.
Causes of cerebellar ataxia
Ataxia may be a consequence of:
- severe head injury (traumatic brain injury);
- accumulation of fluid in the cavities of the brain, spinal canal (hydrocephalus);
- congenital malformation of the brain/skull;
- infectious disease of the brain (encephalitis);
- cerebrovascular accidents (ischemic stroke);
- cerebral palsy;
- epilepsy in children;
- malignant neoplasms;
- abscesses.
Sensitive ataxia syndrome develops as a result of damage to:
- posterior brain stems,
- peripheral nodes,
- posterior nerves, optic thalamus,
- parietal lobe of the brain.
Cerebellar ataxia is a consequence of damage to the cerebellar vermis, its peduncles and hemispheres. Occurs in encephalitis, sclerosis.
The vestibular form of the disease is caused by damage to any part of the vestibular apparatus - nuclei in the brain stem, cortical center in the temporal lobe of the brain, vestibular nerve, labyrinth.
Cortical ataxia occurs when the frontal lobe of the brain is damaged, which is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the fronto-pontine-cerebellar system.
The best doctors for the treatment of ataxia
8.4 13 reviews
NeurologistHirudotherapistDoctor of the highest category
Zanegin Dmitry Andreevich Experience 14 years 8.4 7 reviews
NeurologistCardiologistGastroenterologistArrhythmologistTherapistDoctor of the highest category
Karmanov Sergey Sergeevich Experience 12 years Candidate of Medical Sciences9 2 reviews
VertebrologistReflexotherapistNeurologistDoctor of the highest category
Sbitneva Natalya Georgievna Experience 39 years 8.6 7 reviews
Neurologist
Bondareva Anastasia Nikolaevna Experience 9 years 8.2 2 reviews
NeurologistDoctor of the first category
Kubyshta Svetlana Mikhailovna Experience 14 years 8.7
NeurologistNeurophysiologistFunctional diagnostics doctor First category doctor
Seleznev Fedor Alekseevich Experience 9 years Candidate of Medical Sciences8.8 41 reviews
NeurologistManual therapist
Podryadov Nikolay Evgenievich Experience 34 years 8.8 124 reviews
Neurologist
Gadaborsheva Tamara Magomedovna Experience 41 years 9.5 76 reviews
ReflexologistNeurologistManual therapistDoctor of the highest category
Shnigirist Alexander Ilyich Experience 27 years Candidate of Medical Sciences8.8 14 reviews
Neurologist Chiropractor Hirudotherapist Reflexotherapist Doctor of the first category
Derzhavina Irina Nikolaevna Experience 35 years
Most often, the main cause of the development of acute cerebellar ataxia is ischemic stroke, which is caused by atherosclerotic occlusion or embolism of the cerebral arteries that supply the cerebellum. A hemorrhagic stroke, compression of the cerebellum under the influence of an intracerebral hematoma or traumatic damage to the cerebellum resulting from a head injury cannot be excluded.
Late cerebellar ataxia of the subacute form often occurs as a symptom of an intracerebral tumor, which is located in the cerebellum. These are astrocytoma, hemangioblastoma, medulloblastoma, ependymoma. It can also develop as a result of normal pressure hydrocephalus arising from subarachnoid hemorrhage.
One of the reasons is meningitis and brain surgery. In addition, this form of ataxia can occur with a lack of vitamins, an overdose of anticonvulsants, an endocrine disorder, for example, with hyperparathyroidism or hypothyroidism. It may be a paraneoplastic syndrome for malignant tumors that are localized outside the brain. This could be lung cancer, ovarian cancer, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and some other forms of oncology.
Danger of ataxia
Ataxia is a disease in which coordination of movements is impaired. Its progression can lead to disability and even death. Tremor of the arms and legs, severe dizziness, inability to move independently, disturbances in swallowing and defecation - all these are symptoms of pathology. In addition, ataxia leads to respiratory failure, chronic heart failure, weakened immunity and a tendency to recurrent infectious diseases.
However, it should be understood that not all patients experience obvious complications. In some cases, if you follow medical recommendations, constantly take medications and timely eliminate signs of ataxia, the quality of life of patients does not decrease and they manage to live to an old age.
Causes and signs of weak development of reflexes
It is advisable to study information about what reflexes a newborn should have; in some cases, they may not manifest themselves to an insufficient extent.
The reasons for this situation may be the following:
- received birth injuries;
- dysfunction of the nervous system;
- premature birth of a child;
- spine pathologies;
- previous asphyxia.
A sign of weakening is insufficient expression or one-sided manifestation of symmetrical reflexes. In some cases, the baby is not ready to respond to the stimulus; for example, if the child has no desire to eat, the sucking reflex will not be pronounced.
Spinocerebellar ataxia in a child
Spinocerebellar ataxia is a neurodegenerative pathology that combines several types of autosomal dominant diseases, each of which is considered separately. A feature of the pathology is the rapid increase in clinical manifestations. Symptoms of ataxia include: awkwardness of movements and unsteadiness during gait, tremors of the hands, inability to perform precise movements. As the disease progresses, problems with urination arise, muscle atrophy and paralysis occur.
On our website you will find more information on the topic “spinocerebellar ataxia in a child” and you can make an appointment with a doctor. Reception is conducted by specialists of the highest category.
How does a “normal” cerebellum work?
Before approaching the description of diseases of the cerebellum, it is necessary to briefly talk about how the cerebellum is structured and how it functions.
The cerebellum is located at the bottom of the brain, under the occipital lobes of the cerebral hemispheres.
It consists of a small middle section, the vermis, and hemispheres. The vermis is an ancient section, and its function is to ensure balance and statics, and the hemispheres developed along with the cerebral cortex, and provide complex motor acts, for example, the process of typing this article on a computer keyboard.
The cerebellum is closely connected to all the tendons and muscles of the body. They contain special receptors that “tell” the cerebellum what state the muscles are in. This sense is called proprioception. For example, each of us knows, without looking, in what position and where his leg or arm is, even in the dark and at rest. This sensation reaches the cerebellum via the spinocerebellar tracts that ascend in the spinal cord.
In addition, the cerebellum is connected with the system of semicircular canals, or the vestibular apparatus, as well as with the conductors of the joint-muscular sense.
The olivocerebellar pathway passes through the inferior cerebellar peduncle, which connects it with unconscious movements. The reverse, efferent pathway is the path from the cerebellum to the red nuclei.
It is this path that works brilliantly when, having slipped, a person “dances” on the ice. Without having time to figure out what is happening, and without having time to get scared, the person restores his balance. This triggered a “relay” that switched information from the vestibular apparatus about changes in body position immediately through the cerebellar vermis to the basal ganglia, and then to the muscles. Since this happened “automatically”, without the participation of the cerebral cortex, the process of restoring balance occurs unconsciously.
The cerebellum is closely connected to the cerebral cortex, regulating conscious movements of the limbs. This regulation occurs in the cerebellar hemispheres
Indications for classes
As we have already found out, cerebellar stimulation is an excellent solution to learning problems . It increases intellectual and mental abilities, becoming a good method of assistance for children with learning problems.
However, this method is much more widely used for correctional classes in the presence of very specific problems. Thus, cerebellar stimulation is indicated for the following conditions:
- ZRR of varying severity.
- The problem of dysgraphia or dyslexia.
- ZPR and ZPRR.
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
- Autism and other autism spectrum conditions.
- Alalia.
- Logoneurosis (stuttering).
- Delays in the development of motor skills and coordination.
- Imperfect functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
- Behavioral disorders.
- Lack of concentration, increased distractibility.
- Posture disorders.
- Learning difficulties.
Cerebellar ataxia with acute onset
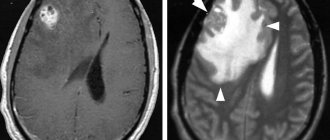
Stroke appears to be the most common cause of acute ataxia in clinical practice. Lacunar infarctions in the area of the pons and supratentorial can cause ataxia, usually in the picture of ataxic hemiparesis. Ischemia in the area of the thalamus, posterior limb of the internal capsule and corona radiata (area of blood supply from the posterior cerebral artery) can manifest as cerebellar ataxia. At the same time, “silent” lacunar infarcts are often found in the cerebellum. Cerebellar infarction may also present with isolated dizziness. Cardiac embolism and atherosclerotic occlusion are the two most common causes of cerebellar stroke.
Hemiataxia with hemihypesthesia are characteristic of strokes in the thalamus (branch of the posterior cerebral artery). An isolated ataxic gait sometimes occurs when the penetrating branches of the basilar artery are affected. Hemiataxia involving certain cranial nerves develops with damage to the upper parts of the pons (superior cerebellar artery), inferolateral parts of the pons and lateral parts of the medulla oblongata (anterior inferior and posterior inferior cerebellar arteries), usually in the picture of brainstem alternating syndromes.
Extensive cerebellar infarctions or hemorrhages are accompanied by the rapid development of generalized ataxia, dizziness and other brainstem and cerebral manifestations, often in connection with the development of obstructive hydrocephalus.
Cerebellar tumors, abscesses, granulomatous and other space-occupying processes sometimes manifest themselves acutely and without severe symptoms (headaches, vomiting, mild ataxia when walking).
Multiple sclerosis sometimes develops acutely and rarely occurs without cerebellar symptoms. There are usually other signs (clinical and neuroimaging) of multifocal damage to the brainstem and other parts of the nervous system.
Guillain-Barré syndrome occurs as a rare form of lesion involving the cranial nerves and ataxia. But even here, at least mild hyporeflexia and an increase in protein in the cerebrospinal fluid are detected. Miller Fisher syndrome occurs acutely with the development of ataxia, ophthalmoplegia and areflexia (other symptoms are optional) followed by good recovery of impaired functions. These manifestations are very specific and sufficient for clinical diagnosis.
Encephalitis and post-infectious cerebellitis often involve the cerebellum. Cerebellitis in mumps is especially common in children with premorbid cerebellar anomalies. Chickenpox can cause cerebellitis. Epstein-Bar virus causes infectious mononucleosis with secondary acute cerebellar ataxia. Acute post-infectious ataxia is especially common among the consequences of childhood infections.
Intoxication is another common cause of acute ataxia. As a rule, there is an ataxic gait and nystagmus. If ataxia is detected in the limbs, it is usually symmetrical. The most common causes: alcohol (including Wernicke encephalopathy), anticonvulsants, psychotropic drugs.
Metabolic disorders such as insulinoma (hypoglycemia causes acute ataxia and confusion) are fairly common causes of acute ataxia.
Hyperthermia in the form of prolonged and intense heat stress (high fever, heat stroke, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, malignant hyperthermia, lithium toxicity hyperthermia) can affect the cerebellum, especially in the rostral region around the vermis.
Obstructive hydrocephalus, which has developed acutely, is manifested by a whole complex of symptoms of intracranial hypertension (headache, drowsiness, stupor, vomiting), among which acute cerebellar ataxia often occurs. With the slow development of hydrocephalus, ataxia can manifest itself with minimal cerebral disorders.
[], [], [], [], [], []
Etiology and course of the disease
Hereditary cerebellar ataxia is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner and develops when a pathological gene is received from one of the parents. External causes contribute to the development of the disease and significantly aggravate the course. The causes can be a variety of infections (typhoid fever, brucellosis, dysentery, pyelonephritis, pneumonia), various injuries to the brain and skeletal bones, intoxication, and pregnancy.
Symptoms appear non-stop and progress steadily without significant periods of exacerbation and remission. Pierre-Marie ataxia can modify its clinical manifestations under the influence of external factors or after infections. The variability of the clinic makes it much more difficult to draw a conclusion. After an infectious disease, a sharp exacerbation may occur, and later a partial recovery, which is mistakenly taken for improvement.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing ataxia, the following methods are used:
- MRI of the brain (detects atrophy of the brain stems and spinal cord, the upper parts of the vermis);
- electroencephalography of the brain (diagnoses reduction of alpha rhythm, diffuse theta and delta activity);
- electromyography (reveals axonal demyelinating damage to sensory fibers of peripheral nerves);
- DNA diagnostics (used to determine hereditary types of ataxia). By conducting indirect DNA diagnostics, doctors determine whether the ataxia pathogen can be inherited by other children in the family;
- magnetic resonance angiography (allows you to assess the integrity and patency in the cranial cavity and identify brain tumors).
Additional diagnostic procedures include consultation with a neurologist, ophthalmologist, and psychiatrist. Laboratory diagnostics for ataxia show a violation of amino acid metabolism - a reduced concentration of alanine and leucine, a decrease in their excretion in the urine.
Since the etiology of this disease involves a fairly wide range of diseases and its congenital nature cannot be ruled out, diagnosing the disease involves consulting the following specialists:
- neurosurgeon;
- neurologist;
- traumatologist;
- oncologist;
- endocrinologist
The diagnostic program may include the following activities:
- spinal puncture and cerebrospinal fluid analysis;
- functional tests;
- CT and MRI of the brain;
- Dopplerography of the brain;
- electronystagmography;
- PCR studies;
- MSCT;
- DNA diagnostics.
In addition, genetic counseling may be needed.
Due to the fact that the etymology of cerebellar pathologies is very diverse, diagnosis is carried out by several specialists with a narrow focus, namely a traumatologist, neurosurgeon, oncologist, geneticist, and endocrinologist. A thorough neurological examination allows not only to determine the cerebellar nature of the ataxia, but also to identify approximately the affected area.
In order to exclude vestibular disorder, it is necessary to conduct a study of the vestibular analyzer. A neurologist may prescribe stabilography, vestibulometry, and electronystagmography. If there is a suspicion that ataxia has arisen as a result of an infectious lesion, a blood sterility test or PCR test is required.
DNA testing and genetic analysis can detect the hereditary nature of ataxia in the cerebellum. The treatment is presented below.
When conducting a full range of examinations, making a diagnosis does not cause difficulties.
A functional test, assessment of tendon reflexes, and blood and cerebrospinal fluid testing are required.
A computed tomography and ultrasound scan of the brain is prescribed, and an anamnesis is collected.
Treatment of ataxia
Independent treatment of ataxia, regardless of its type and severity of symptoms, is impossible. A consultation with a neurologist is required.
Treatment is usually aimed at eliminating the causative disease, for example:
- tumor removal,
- elimination of hemorrhage,
- decreased pressure in the posterior fossa (Arnold-Chiari malformation),
- abscess removal,
- normalization of blood pressure.
In addition, it includes:
- selection of a special set of gymnastic exercises that help reduce incoordination and strengthen muscles;
- prescription of general strengthening agents - B vitamins, cerebrolysin, anticholinesterase drugs, ATP.
For ataxia telangiectasia, medications that correct immunodeficiency are prescribed, and a course of immunoglobulin is administered. Treatment of Friedreich's ataxia involves the use of medications that support mitochondrial function (vitamin E, riboflavin, succinic acid, coenzyme Q10).
Consequences of the disease and prevention
Treatment of cerebellar ataxia will be successful only if the true cause of the development of the disease is correctly established. The disease can be completely cured only in rare cases. Most often, patients remain with symptoms characteristic of the disease, which periodically worsen. In cases where it was possible to start therapy for the underlying disease in a timely manner, the prognosis will be as positive as possible. The patient’s age, general health, and the form of manifestation of cerebellar ataxia have a significant influence.
There is no specific prevention against the development of ataxia. Experts recommend timely treatment of infectious and viral pathologies, vaccination against serious diseases, and monitoring the functioning of the thyroid gland and cardiovascular system. Before planning a pregnancy, you should definitely consult a geneticist if there are cases of this disease in the family.
general information
The disease was first described in great detail by Pierre Marie in 1893. The scientist identified the disease in a special form and identified manifestations different from Friedreich's ataxia. Pierre-Marie ataxia has other distinctive clinical symptoms, a different mode of inheritance, and an older age of manifestation. The disease is found in people 20-45 years old, regardless of gender. There is 1 case of the disease in 200,000 people. Pathological transformations in the structure during cerebellar ataxia are located in the substance of the cerebellar nuclei and cortex. The spinal tract and lateral branches of the spinal cord are not clearly expressed. Degenerative transformations can affect the nuclei of the pons of the medulla oblongata.
Cerebellar diseases
Violations in the functioning of the organ are manifested by a diverse clinic. But problems associated with impaired coordination, gait, and muscle tone predominate.
Congenital pathologies appear from the first minutes of life. They are associated with underdevelopment of the cerebellum or one of its parts. The lesion becomes noticeable as motor skills develop. Ataxia almost always appears.
Hereditary problems are associated with a gene defect. They are transmitted from parents in an autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive manner. Among these pathologies are:
- Friedreich's ataxia;
- Ataxia-telangiectasia;
- Ataxia with vitamin E deficiency;
- Abetalipoproteinemia.
One type of ataxia is spinocerebellar disorders. They include a whole range of diseases with a hereditary transmission mechanism. In addition to the main symptoms, disturbances in walking, tone, and coordination dominate.
Acquired diseases of the cerebellum arise as a result of circulatory disorders in the organ, viral and bacterial infections. The toxic effects of alcohol, heavy metal salts, lithium, and anticonvulsants also lead to cerebellum problems. Atrophic phenomena in the organ appear from a lack of vitamin E and B12, with hypothyroidism.
Tumors develop in the cerebellum. They manifest themselves as symptoms of compression and loss of coordination. The most common types of tumors that develop are astrocytomas and meduloblastomas.
What results can you get by studying F. Belgau's program?
- improved concentration and attention;
- increasing endurance and performance in classes;
- improved hand-eye coordination;
- development of spatial perception and imagination;
- development of motor abilities: reaction speed, dexterity;
- development of all types of memory: visual, visuospatial, sound, figurative, and especially motor and others;
- development of perception of oral and written speech, their automation, which in turn is the basis for the formation and development of one’s own speech and writing skills;
- optimization of rote reading skills;
- development of intellectual abilities;
- development of mathematical and logical abilities;
- development of abilities to plan and control one’s activities;
- harmonization of the emotional-volitional sphere;
- normalization of behavior;
- personal changes.
The most effective is cerebellar stimulation in combination with classes of a speech therapist, psychologist, speech pathologist, or neuropsychologist. Exercises on a balancing board allow you to speed up the solution of correctional problems in speech therapy and psychology.
Palmar chin reflex Marinescu Radovici
The Marinescu-Radovici reflex (palmomental) is a typical reflex of oral automatism. It occurs normally in children up to 12-18 months, ensuring the cooperative performance of two different functions: grasping the mammary gland with the hands and simultaneous sucking of milk.
Determining this reflex during a neurological examination allows us to understand the cause of the disease and determine the location of the pathological process in the brain. The reflex was first described in 1920 by two neurologists Marinescu and Radovici.
Phenomena of oral automatism
The Marinescu-Radovic reflex refers to the reflexes of oral automatism. These are pathological reflexes on the face that occur during the phenomena of central (spastic) paralysis or paresis of the facial muscles, which are innervated by the cranial nerves.
The appearance of these reflexes indicates bilateral supranuclear damage to the brain stem, subcortical structures or cerebral cortex.
These reflexes, including Marinescu-Radovic, normally appear in children up to 18 months of age. This is due to the immaturity of brain structures and the ongoing differentiation of parts of the central nervous system.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=45bMF78O-iQ
Oral automaticity reflexes include:
- Marinescu-Radovic reflex, or palmomental reflex. It can be caused by streaking movements with a blunt object on the skin of the palm at the base of the thumb. In response to this, a slight upward displacement of the skin of the chin occurs on the patient’s face, which is associated with contraction of the mentalis muscle.
- Nasolabial (nasolabial) reflex. It is caused by tapping the back of the nose with a neurological hammer. In response to this, the person extends his lips slightly anteriorly, which is mediated by contraction of the orbicularis oris muscle.
- Proboscis reflex. Completely identical in appearance to nasolabial, but is caused by tapping on the upper or lower lip.
- The sucking reflex is manifested by sucking movements of the lips when touching or stroking the lips.
- Distance-oral Karchikyan syndrome. If you slowly bring a hammer closer to the patient’s lips, they will stretch out in the form of a “proboscis” without contact with the object.
All these reflexes are observed in newborns and children in the first year and a half of life, but then fade away and can occur in adults against the background of damage to brain structures.
Information about the Marineski-Radovici reflex
The reflex was first described in the 20s of the twentieth century by two Romanian neurologists Marinescu and Radovici. Observing this phenomenon in their patients, they established that the appearance of the reflex is associated with damage to the brain stem and is a reflection of the rudimentary synergy of grasping and sucking, or chewing.
The reflex consists of contraction of the mental muscle on the face with a gentle stroke of irritation of the palm in the area of the base of the thumb. As was revealed later, the nuclei of the seventh pair of cranial nerves are involved in this reflex.
A characteristic feature of this reflex is the one-sidedness of the reaction: when the skin on the right is irritated, the response is observed on the right half of the face, despite bilateral brain damage.
Use in diagnostics
As mentioned above, the palmar-chin reflex occurs in adults and children over one and a half years old with damage to brain structures: the brain stem, subcortical formations and the cerebral cortex.
Its appearance is associated with damage to the central motor neuron or its axon, and the occurrence of spastic or central paralysis in a certain muscle group in the patient. In this case, the inhibitory effect of the cerebral cortex neuron on the muscles disappears, as a result of which the reflex readiness of the muscles increases and pathological reflexes arise that are normally absent.
Most often this occurs as a result of the following diseases:
The appearance of any phenomena of oral automatism, incl. and the Marinescu-Radovic reflex, a serious warning sign indicating irreversible brain damage. Therefore, if such symptoms appear, you must immediately contact a medical facility to receive qualified medical care.
Prevention of ataxia
In order to prevent the birth of people with ataxia, it is necessary to avoid the birth of children in families where there are patients with a hereditary form of this pathology. Disease prevention also includes:
- exclusion of consanguineous marriages,
- timely treatment of infectious diseases,
- blood pressure control,
- refusal to engage in sports that can lead to traumatic brain injury,
- compliance with the work and rest regime, rational nutrition.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.