Cerebral palsy is a broad concept that unites a group of movement disorders that progress against the background of damage to brain structures in the perinatal period. The pathology is characterized by intellectual impairment, mental disorders, gait disturbances and motor coordination. In the first year of life, children noticeably lag behind their peers in motor and mental development. People with cerebral palsy need lifelong rehabilitation, medication, physiotherapy and surgical treatment as indicated.
General information about the disease
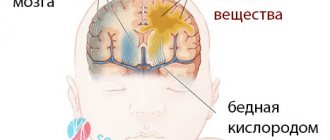
Cerebral palsy is a motor function disorder that occurs as a result of serious changes in brain structures. According to statistics, the frequency of this diagnosis is 2-7 cases per 1000 people among children under 1 year of age. The prevalence among premature newborns increases 10-fold.
Depending on the area of localization of the affected area of the brain, there are 5 types of lesions.
- Spastic diplegia. Prevalence is about 40% of the total number of cases. Characteristic damage to the motor centers leads to the development of paresis affecting the legs. The hemiparetic form is characterized by damage to the motor centers of one of the hemispheres.
- Hyperkinetic form. Characterized by damage to subcortical structures. Hyperkinesis intensifies against the background of excessive excitement or fear of the child.
- Atonic-astatic form. Diagnosed when a lesion is detected in the cerebellum. This form is characterized by impaired statics and coordination, muscle atony.
- Double hemiplegia. The most severe form, resulting from volumetric damage to both hemispheres of the brain. Children are unable to sit or stand and cannot hold their head up on their own.
- Mixed forms. Characterized by a combined manifestation of symptoms inherent to varying degrees in each type.
In the first few days or even months of life, the child is no different from his peers. Symptoms of cerebral palsy may appear much later. Their severity depends on the degree of brain damage, timely diagnosis and treatment. The clinical picture inherent in the pathology looks like this:
- decreased or increased muscle tone;
- skeletal deformity;
- preservation of reflexes that disappear in healthy children under 6 months of age;
- convulsions;
- problems in the functioning of the organs of vision and hearing;
- violation of the swallowing reflex.
The main reason provoking the disease is the negative impact of various damaging factors on the child. This influence provokes the death of certain parts of the brain. The prerequisites for the development of the disease appear against the background of pathologies of pregnancy and infections.
Are you experiencing symptoms of cerebral palsy?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Diagnosis of cerebral palsy begins with a full examination by a pediatric neurologist. If neurological spectrum disorders are suspected, instrumental diagnostics are used:
- encephalography;
- transcranial magnetic stimulation;
- electromyography;
- electroneurography.
The listed methods allow us to differentiate the pathology and exclude other congenital defects of a neurological nature.
The most common consequences include:
- disability;
- violation of social adaptation;
- arthrosis;
- muscle contracture;
- lack of positive dynamics;
- Difficulty eating due to impaired swallowing.
If a child has a risk of developing cerebral palsy, prevention of its development is provided immediately after birth (if the condition is critical, after its normalization). In their practice, rehabilitators use several schemes, determining the optimal one, depending on the risk group into which the child falls.
If the risk is low, use fitball exercises, developmental gymnastics, aquatherapy, baby yoga, dynamic gymnastics, massage, and physiotherapy with caution. At high risk, neurological physiotherapy, aqua therapy, massage, and physiotherapy are used. Courses are conducted every month until the child is 1.5 years old. Parents reinforce the effectiveness of sessions at home by conducting classes according to the recommended scheme.
Forecast
The prognosis, which determines whether it is possible to cure cerebral palsy in a child, depends on the type of disease, the degree of damage to the limbs and brain. All patients with cerebral palsy - young children, adolescents, adult patients - are observed by doctors and rehabilitated throughout their lives.
Warning signs should be analyzed based on the following aspects:
- whether deviations appear during repeated inspections;
- assessment of the nature of deviations - pathological nature or the possibility of considering them as an option for individual development;
- whether there is an increase in the deficit of changes in development or, conversely, there is a tendency to their decrease.
Treatment information
Treatment of cerebral palsy with restoration of quality of life to a full level is possible if you follow the doctor’s recommendations. You shouldn’t count on achieving quick results; these involve many years of training, courses of therapy, and sometimes operations. Much depends on the severity of the disease and how early cerebral palsy is detected. If symptoms are detected early, the prognosis is encouraging.
During the first months after the birth of a child (if a presumptive diagnosis is not established immediately after birth), the following signs help to suspect the disease:
- hypotension;
- pain syndrome (characterized by a loud cry);
- tremor;
- chaotic movements of limbs;
- taking unnatural poses;
- grimaces;
- convulsions;
- reflex disorders.
A neurologist diagnoses the disease. Additionally, consultations with specialized specialists are indicated: ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, psychiatrist, orthopedist. If the causes of cerebral palsy have not been established, and the diagnosis must be differentiated from other hereditary diseases, genetic and biochemical methods are used.
It is impossible to determine the time frame for recovery. Each case is unique. The classification of cerebral palsy includes several forms of the disease, each with a different prognosis. The most severe is for children with double hemiplegia. Full recovery is impossible.
Causes
The child’s brain in the embryonic period and in the first few months of life is still immature, undeveloped, and has a very limited number of responses with which it can respond to damage. In other words, harmful factors cause significant changes. The reasons can be divided into the following categories.
- Prenatal - factors that occur during pregnancy - various infections, x-rays, especially irradiation of the abdominal cavity, exposure to toxic substances, drugs. These causes are the most risky, especially during the first 3 months of pregnancy.
- Perinatal - adverse conditions that occur during childbirth - all factors that impair the supply of blood to the fetal brain are dangerous. For example, long-term, multiple births, premature births, injuries to the child during childbirth.
- Postnatal – occurring in the first weeks after birth – the newborn is at risk of jaundice due to Rh factor incompatibility, especially with repeat pregnancies. The following problems include cerebral hemorrhage, infectious diseases, because... In such a short period after birth, the blood-brain barrier has not yet been formed; toxins easily penetrate the brain.
Symptoms of cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy presents with a variety of symptoms. The clinical picture always depends on the depth and localization of damage to brain structures. In the first days of a baby’s life, the following signs may be observed:
- freezing in one position;
- involuntary movements (for example, frequent head nodding);
- asymmetry of the body (one arm can be very tense, while the other is motionless and relaxed);
- different length/thickness of limbs;
- convulsions;
- restless sleep;
- sluggish breastfeeding.
At about 3 months, the symptoms of cerebral palsy become more pronounced. Among them:
- delay in the formation of motor skills;
- inability to hold your head up and roll over;
- lack of interest in toys;
- inability to consciously move limbs;
- inability to hold toys.
If a child with cerebral palsy is put on his feet, he immediately stands on his tiptoes, and not on his full foot.
Insufficient innervation of the speech apparatus in cerebral palsy causes disturbances in the pronunciation aspect of speech. Paresis during paralysis can be only on one side or cover all limbs. If there is weakness in the muscles of the larynx and pharynx, the patient has problems swallowing. Over time, a lag in physical development of paretic limbs is diagnosed - they become thinner and shorter than healthy ones. Skeletal deformities typical for cerebral palsy (chest curvature, scoliosis) develop.
In some cases, cerebral palsy occurs with limited passive movements in the joints of paretic limbs, which further aggravates existing motor disorders. Skeletal deformities and motor disorders associated with the disease lead to chronic pain in the neck, shoulders, feet and back. Other symptoms of cerebral palsy in children include:
- functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- strabismus;
- involuntary motor attacks (nods and turns of the head, grimaces on the face, twitching, pretentious movements and poses);
- urinary incontinence;
- respiratory function disorders;
- epilepsy (in 20-40% of patients);
- vision problems (60% of patients);
- complete deafness or hearing loss;
- endocrine pathologies (half of the children are diagnosed with obesity, growth retardation, hypothyroidism, etc.).
Cerebral palsy is often accompanied by oligophrenia (degrees may vary), perception disorders, mental retardation, and learning disabilities. 35% of sick children have a normal level of intelligence, 33% have minor deviations in mental development.
Cerebral palsy is a chronic but non-progressive disease. Over the years, the child may develop previously hidden symptoms of pathology, causing parents to think that the condition has worsened. In fact, this is a “false progression.” Deterioration in health is usually due to secondary complications - stroke, epilepsy, hemorrhage, somatic diseases, and the use of anesthesia.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Child with cerebral palsy: where to go to study?
Children with cerebral palsy are not ordinary individuals. They do not communicate with everyone; they act and think very slowly. It is difficult for them to concentrate and remember something, so they have difficulty making friends and, as a rule, do not know how to play. However, they grow and develop. And one day the moment comes when it’s time for them to go to school. Where is the best place for a child with cerebral palsy to study?
Most often, experts recommend sending such a student to a specialized institution where the necessary conditions for his education and maintenance exist - ramps, special door handles, toilets. However, you rarely see such equipment in Russian schools. In addition, neither the majority of domestic teachers are prepared for the presence of a “special child” in the classroom, nor do their peers themselves know how to communicate with him. True, such difficulties arise only in elementary school, since by the age of 10-12 years a child with cerebral palsy usually achieves normal mental development, and peers gradually get used to his presence and even make friends with him.
This is a fact - not all secondary schools are ready to accept a child with cerebral palsy. But in some of them there are still experimental classes where wheelchair users study together with regular schoolchildren. As a rule, these are private institutions with individual programs and a small number of students per class. But not every Russian parent is ready to accompany their child to a regular school until he is 10-12 years old, until he becomes independent. For this reason, the majority of disabled children graduate from boarding schools under the mass program and only a small part of them become students. In addition, so far in Russia there are only a few universities that are fully equipped to train wheelchair users.
When choosing a profession, a young person with cerebral palsy must take into account the degree of the disease. If this is a mild form, then many specialties are suitable - economist, junior medical staff, teacher. People with moderate cerebral palsy should choose freelance professions - programmers, copywriters, seamstresses. Severe cases of the disease, unfortunately, do not allow you to find a job. But this does not exclude the possibility of creativity and development.
Compensation methods
If a child suffers from an advanced form of cerebral palsy, it is necessary to use assistive and prosthetic devices in accordance with the individual needs of the patient. These include:
- orthoses;
- adjustable devices for sitting, strollers, etc.
Their goal is to compensate for musculoskeletal disorders, minimizing their impact on the patient’s daily life.
Care for a patient with cerebral palsy should be comprehensive, including treatment of complications and associated problems, their solutions with the participation of many specialists:
- neurologist;
- orthopedist;
- ophthalmologist;
- ENT specialist;
- psychiatrist;
- neurosurgeon;
- gastroenterologist;
- psychologist;
- speech therapist;
- endotherapist;
- teacher;
- prosthetic care specialist;
- social worker, etc.
Treatment results depend on early diagnosis and are proportional to the quality and complexity of rehabilitation.
Myths about the causes of cerebral palsy
Before the myths about the causes of cerebral palsy, there is a contradiction in the fact that only children from dysfunctional families suffer from cerebral palsy. In fact, the development of cerebral palsy occurs due to the indifference of various factors, so every child with a prosperous family is not immune from the development of the disease.
Another myth that can be expanded is that cerebral palsy causes cerebral palsy. There is no reason to think about this against scientific evidence. Insanely, before splinters it is necessary to place them carefully, closely follow the vaccine container and are obviously contraindicated before vaccination in a child. If the vaccine is clear and has no contraindications, then side effects from vaccination will be excluded or reduced to a minimum.
There is also a myth that cerebral palsy is a genetic disease. In fact, cerebral palsy is not transmitted by depression. I want genetic factors to take their share in the development of illness. Another myth is that cerebral palsy is more common. But in reality, it is impossible to completely overcome cerebral palsy.
Treatment for childhood paralysis includes drug therapy, massage, physical exercise, therapy, aquatherapy and other types of treatment. By following all the doctor's recommendations, it is possible to significantly change the symptoms of illness and improve the quality of life of the child.
3
3
3
Stat rating:
4.14 out of 5 based on 7 ratings
Author: Volvach Yuriy Ivanovich
Children's doctor orthopedist-traumatologist. Qualification category. Work experience 25 years.
Should I have surgery?
This disease cannot be completely cured. This is what experienced and qualified doctors say. But there are real examples where a child, almost sentenced to life in a wheelchair, learned to walk, and his gait is indistinguishable from the gait of healthy children, and he succeeds just as well in his studies.
This can be called a real miracle, but they really do take place in our lives. The main thing is to start treatment on time, even in the early stages. It should be comprehensive, include various physical procedures, orthopedic therapy, and if necessary, you can and should decide on surgical intervention. Typically, such operations are successfully carried out abroad.
Doctors say that a child can be operated on at about 5-10 years of age, when the skeletal system has already formed. Sometimes physical procedures, although they give noticeable results, do not relieve the baby from excessive muscle tension, and this leads to deformation and immobilization of the joints. There are many good clinics in Russia with competent specialists who have experience in such operations. Their patients are now indistinguishable from healthy children.