When people talk about cramps, most people mean muscle spasms in the limbs. But in fact, there are many varieties of this pathology. The most common types are tonic and clonic seizures. Both of these types are characterized by involuntary muscle contraction accompanied by pain. But they appear for different reasons, and also have differences in the nature of their course. In the most difficult cases, when neurons in the brain are damaged, mixed tonic-clonic muscle spasms are observed. They occur with epilepsy, hysteria, and some infectious diseases. Despite the fact that most seizures are harmless and cause almost no trouble to patients, treatment of the pathology should begin as early as possible. After all, this condition often indicates health problems.
Determination of tonic muscle spasms
Tonic cramps are unconscious muscle contractions that appear due to severe and sharp pain. There are three types of seizures: clonic, tonic, and tonic-clonic. To accurately determine the type of seizure in a person, timely diagnosis is necessary. Seizures are not always dangerous, but prompt treatment is necessary. An incorrectly functioning body signals that disturbances are occurring within it. In acute forms of the disease, convulsions are considered a factor in blocking the airways and stopping the heart.
Convulsions
Cold
Iron deficiency
Encephalitis
Rheumatism
13121 21 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Cramps are involuntary muscle contractions of a paroxysmal nature.
Almost every person has experienced a single attack of seizures at least once in their life. Most often, this is a sudden painful contraction (spasm) of the muscles lasting from a few seconds to several minutes.
In most cases, a single episode of seizures goes away without consequences or special treatment. But if these episodes recur frequently, you should see a doctor, as this may indicate serious health problems.
The most common cramps are the calf and thigh muscles, as well as the muscles of the feet and hands. Also quite common are spasms of the facial muscles, neck, larynx, and respiratory muscles (convulsive activity in them leads to stuttering).
Types of seizures
There are several types of seizures, classifying them according to different criteria.
The nature:
- tonic
– strong muscle tension, causing you to “freeze” in an unnatural position; - clonic
– rhythmic twitching of a muscle/muscles. Various tics, as well as stuttering (convulsions of the respiratory muscles, larynx) belong specifically to the clonic type; - tonic-clonic
and
clonic-tonic
- characteristic of epilepsy, when during an attack the tonic and clonic phases replace each other.
By prevalence:
- local (focal)
cramps - contraction of individual muscles or muscle groups; - generalized
cramps - contractile activity involves several muscle groups.
According to the development mechanism:
- a convulsive reaction
occurs in response to a deficiency of microelements, infection, insufficient blood supply, intoxication, staying in a stuffy room, etc.; - convulsive syndrome
develops, as a rule, with diseases of the nervous system, which can be identified by studying the electrical activity of the brain; - epilepsy
is a disease characterized by repeated, often generalized (covering the whole body) seizures.
Possible causes of cramps
Muscle cramps can occur as a result of various conditions, such as:
- excessive intake of alcohol, medications (diuretics, antidepressants, etc.), caffeine, nicotine;
- increase in body temperature above 38.5° C – so-called. low-grade seizures, common mainly in young children (up to four years);
- brain tumors and other changes in its structure;
- deterioration of cerebral circulation, traumatic brain injury;
- increased blood pressure and blood glucose levels;
- severe dehydration of the body;
- violation of water-salt metabolism, deficiency of microelements;
- severe overwork, lack of sleep, prolonged psychological stress;
- excessive physical activity or muscle strain;
- pinched nerves;
- intoxication;
- infections;
- hypothermia or overheating;
- anemia (decreased hemoglobin concentration in the blood);
- genetic predisposition to increased seizure activity.
What diseases cause seizures?
Most (up to 90%) seizures occur once and remain in the memory as an unpleasant incident. But if they happen over and over again, most likely, this is the body’s way of signaling about some serious violations. Harmless blepharospasm (tremor of the eyelid) may indicate the development of dangerous dry eye syndrome or even glaucoma (increased intraocular pressure). Clonic convulsions of the hands – about the development of Parkinson’s disease, etc.
Identifying these problems as early as possible and starting timely treatment means prolonging the period of active life, preventing a decrease in its quality and disability.
Convulsions of the same form can occur in various diseases of the nervous system, such as meningitis, encephalitis, brain tumors, aneurysms (protrusion of the wall) of brain vessels, intracerebral hemorrhages, etc. Also, convulsions are often an early symptom of hereditary degenerative diseases of the nervous system, as well as progressive senile dementia.
Often, seizures accompany diseases of the cardiovascular system, autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatism, etc.
Convulsions caused by impaired brain functioning develop during hypo- and hyperglycemic coma, as well as hepatic coma.
Convulsions in young children, not associated with an increase in body temperature, can be a symptom of a malformation of the brain and cardiovascular system, or hereditary diseases.
Which doctors should I contact?
If seizures do not occur for the first time, you must inform your doctor about them:
- or a general practitioner (family doctor);
- ;
- ;
- an ophthalmologist (if you suffer from eyelid tremor);
- or a phlebologist (if the main complaints are cramps of the calf and thigh muscles).
Diagnostics and examinations
Determining the causes of recurring seizures includes examination, history taking, instrumental and laboratory research methods. The doctor will most likely prescribe laboratory tests such as general and biochemical blood tests, analysis of microelements (calcium, potassium, magnesium, iron, blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin.
Seizures
When the body undergoes a tonic spasm, an increase in the frequency of spasmodic contractions is noticed.
The difference between tonic convulsions and other types is that parts of the body change their position, blood pressure increases, the reaction to light stimuli decreases, and breathing quickens. Severe forms of the disease can occur with loss of consciousness.
A characteristic feature of a tonic attack is rigidity of the limbs and torso. This process occurs in a short time, so it does not enter the clonic phase. The duration of convulsions is no more than 3 minutes.
The reason for the appearance of tension in the muscles is the improper functioning of the nervous system. It is influenced by improper development of the fetus during pregnancy and the formation of the body in early childhood, genetics and heredity.
Convulsions can occur with a large loss of fluid from the body, an increase in temperature, a lack of oxygen supplied to the brain, or caffeine poisoning.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Severe and prolonged seizures require mandatory medical intervention. In case of generalized clonic seizures, before the ambulance team arrives, the patient is placed on a flat surface with a pillow under the head, tight clothing is unbuttoned, and air is provided with free access. It is not recommended to resist involuntary movements. Persistent paroxysm is stopped by the administration of anticonvulsants.
Conservative therapy
Treatment of clonic seizures is largely symptomatic, aimed at alleviating the patient's condition by reducing the frequency and severity of attacks. Etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy for most of the described diseases has not been developed, so the emphasis is on supportive treatment. Depending on the clinical situation, medications of the following groups are used:
- Anticonvulsants.
The drugs of choice for the treatment of focal attacks are valproate, carbamazepine, lamotrigine (but the last two are contraindicated in Dravet syndrome). Neonatal seizures are treated with phenobarbital, phenytoin, and benzodiazepines. - Neurometabolic.
For neurodegenerative processes, antioxidants and B vitamins are prescribed as part of complex therapy. Nootropics and vasoactive drugs are contraindicated for many patients due to their ability to provoke seizures. - Antimicrobial.
Etiotropic treatment of infectious diseases consists of the use of antiviral and antibacterial agents. This approach is also practiced for subacute sclerosing encephalitis (immunoglobulin, interferon, isoprinosine). - Detoxification.
Toxic damage to the central nervous system requires infusion therapy, the introduction of sorbents, and specific antidotes. In severe cases, extracorporeal detoxification methods (plasmapheresis, hemosorption, hemodialysis) are used.
Complex therapy of the underlying disease involves the use of physical methods - electrical stimulation of muscles, massage, therapeutic exercises. In case of cognitive impairment, neuropsychological rehabilitation plays an important role. A promising direction in the treatment of hereditary diseases is targeted gene therapy, the possibilities of which are still being studied.
Signs
Medical experts call epilepsy the main disease leading to convulsive syndrome. The approach of a tonic attack can be predicted in advance by several signs: hearing and smell become more acute, and an unpleasant taste appears in the mouth. Epileptics fall into unconsciousness and scream or howl loudly. The muscles experience extreme tension: the jaws tighten, breathing becomes difficult, the face turns blue. The duration of the attack does not exceed 3-5 minutes. After the muscles relax, a sleepy state sets in, and the person is unable to remember what happened.
Localized and generalized tonic seizures
Generalized convulsions : convulsions of the torso, limbs and lungs are added to muscle arrhythmia. The arms twist unnaturally, but the lower limbs remain in a relaxed state. The entire body is under extreme tension. The jaw closes tightly due to the tension on the face, and the head tilts towards the back. A person under such tension is rarely conscious. Generalized tonic convulsions are combined with epileptic seizures. A similar effect can occur due to the penetration of a toxic substance into the body.
Localized seizures are characterized by a paralytic effect on only one part of the body. Contractions do not occur constantly, but in portions, with short intervals. During localized convulsions, the person remains conscious. It is necessary to eliminate the source of irritation and provide rest for the body. No special medical skills are required to eliminate such seizures.
Differences between clonic and tonic seizures
A specific feature of tonic spasms is the sudden tension of all muscles. The body is held in a tense state for a long time. The cause of tonic seizures lies in the cerebral cortex. Convulsions can overtake the patient in his sleep if he was very active the day before. Spasms usually do not affect the facial muscles, respiratory system and arms.
Clonic seizures vary in frequency. Severe spasms are replaced by temporary relaxation. Irregular spasms occur on the face and hands. The torso is involved in a convulsion if the patient has developed attacks of epilepsy. Tonic and clinical convulsions occur alternately in acute epilepsy.
Diagnostics
Sometimes it is possible to guess the cause of clonic seizures clinically - according to the anamnesis and neurological examination. At the same time, attention is paid to the time and circumstances of the attack, its nature, and the presence of accompanying symptoms. But in most cases, an accurate diagnosis is established based on the results of additional procedures:
- Laboratory tests.
For infections, microscopy and culture of biomaterial (nasopharyngeal mucus, sputum, liquor) are prescribed; serological tests; DNA or RNA of the pathogen are detected by PCR. Children with storage diseases undergo enzymatic diagnostics; in case of poisoning, a toxicological analysis is indicated. - DNA diagnostics.
Verification of hereditary diseases is carried out by cytogenetic study of the karyotype, analysis of a panel of genes or individual mutations. The risk of developing pathology in the fetus can be determined through prenatal testing. - Neuroimaging.
Structural defects are detected by tomography. In cases of diffuse damage to brain tissue, MRI shows signs of encephalopathy (hyperintense foci in the cortex, cerebellum or brainstem), atrophy. CT scan of the brain shows scattered calcifications in tuberous sclerosis. - Electroencephalography.
Epileptic and non-epileptic paroxysms are an indication for an EEG. The study makes it possible to establish the localization of seizure activity (focal, multifocal, generalized), its morphology (waves, peaks, “jogs”), frequency and other characteristics.
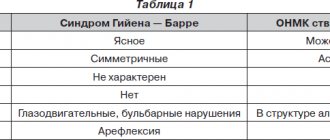
The neurologist is assisted in diagnosis by related specialists. A characteristic sign of Tay-Sachs disease - a red spot on the retina - is determined by an ophthalmologist during ophthalmoscopy; hereditary pathology requires the involvement of a geneticist. It is necessary to differentiate clonic convulsions from paroxysmal conditions of a different origin: stereotypical movements, syncope, pseudoconvulsions.
Causes of tonic seizures
Causes of seizures include:
- Disturbed neurology
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system, swelling.
- Infectious diseases
- Poisoning of the body
- Hysterics
- Sprains and microtraumas
- Overheating and lack of water in the body
- Depletion of the body in vitamins and minerals
- Diabetes, kidney disorders, impaired thyroid function.