Heart pain or spinal problems? Find out everything about your health!
"Novoklinik" does not treat pinched thoracic nerve! If you notice symptoms similar to those described in the article, contact your doctor.
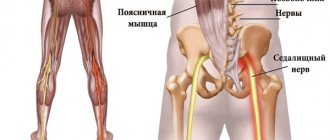
Compression of the spinal cord nerve roots by various structural elements of the spine - vertebrae, intervertebral discs and spinal muscles - is called pinched nerves.
Causes of the disease
In general, all reasons can be divided into two groups. Namely:
- Mechanical damage.
- Degenerative processes.
In the first case, it is enough to turn or bend over unsuccessfully to encounter manifestations of pinching. Also, sometimes pathology is provoked by excessive physical exertion and lack of dosage of work and rest. Degenerative processes include scoliosis, osteochondrosis and other diseases. They lead to disturbances in the structure of the vertebrae and the cartilage between them, accompanied by severe pain and a host of other manifestations.
Physical exercise
Symptoms of a pinched nerve in the thoracic spine can easily arise if, for example, you take on a load that is too heavy for you. You may experience pain if you lift a load too quickly or if you lift it incorrectly and put strain on your back.
Osteochondrosis
It is a dangerous disease, the manifestation of which is often a pinched nerve in the thoracic spine. The pathology causes the cartilage tissue between the vertebrae to wear out and become thinner, which significantly impairs shock absorption. Untimely treated osteochondrosis can lead not only to pinched nerves, but also to the occurrence of intervertebral hernia.
Sensitivity of nerves
The sensitivity of the nerves tends to change over time, and the position of the spine changes in the same way. There are cases when, with age, people experience various types of curvature of the spinal column, which provokes pinched nerves. To eliminate this condition, you will need to stop the displacement and strengthen your back muscles.
General information
In official medicine, damage to the spinal roots is also called radiculopathy. It is always based on compression of the nerve. This may be caused by an increase in size or displacement of certain anatomical formations bordering the spinal cord, the emergence of neoplasms or a reflex reaction of the body to irritants, manifested by muscle spasms, etc. There are many, and quite diverse, reasons for the development of radicular syndrome, but more on them later .
Radiculopathies have always been and remain common. But if previously they occurred mainly in people aged 40-60 years, today they are often diagnosed at a younger age, including teenagers. Damage to the spinal nerves and bundles can be observed in any part of the spine, on the basis of which radiculopathy is distinguished:
- cervical;
- chest;
- lumbosacral spine.
In all cases there is pain of varying severity and nature. But the place of its concentration and the area to which it will irradiate (give off) directly depends on which specific spinal root is infringed. This also has a direct impact on the nature of other symptoms that will accompany radicular syndrome. After all, the nerve roots extend in pairs at the level of each of the 33 vertebrae, each of which is responsible for transmitting sensory and motor impulses to the corresponding part of the body.
The pain associated with radiculopathy can be very similar to that characteristic of heart disease, including myocardial infarction, or other life-threatening conditions, such as peritonitis. This significantly complicates diagnosis and often leads to the prescription of treatment that is completely inappropriate for the patient.
Pain in radicular syndrome can reach such intensity that it deprives the patient of rest and completely immobilizes them. This can be combined with spastic muscle tension, forced posture, the appearance of sensory disturbances, for example, a feeling of numbness in the corresponding part of the body, impaired mobility up to paralysis, and other symptoms. Without intervention, this can lead to irreversible changes in the structure of the nerve and disability, so it is important to diagnose radicular syndrome as early as possible, determine the cause of its development and eliminate it conservatively or surgically, depending on the complexity of the situation.
Symptoms
The symptoms of this phenomenon can be either obvious or disguised as diseases of internal organs and other pathologies. Often, treatment for a pinched nerve in the thoracic spine is needed by people who have gone to the doctor with complaints about the heart, stomach and other internal organs, since the pain innervates them. It is worth knowing how a pinched nerve manifests itself in order to recognize the condition in time and consult a neurologist
.
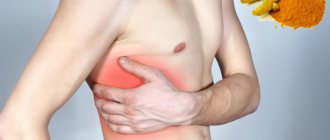
Chest pain
Symptoms of pinching in the thoracic spine are often very similar to symptoms of an angina attack. The person complains about the following:
- there is severe pain and burning under the shoulder blade and in the chest;
- there is not enough air and you can’t breathe in completely;
- hands go numb;
- Cold sweat appears on the body.
To exclude the condition that occurs with angina pectoris, you can put two nitroglycerin tablets under your tongue. If you have heart problems, this remedy will eliminate them within 5 minutes, but if you have a pinched nerve, then the situation will not improve. In this case, there will be severe pain in the vertebral area.
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract
A person who is experiencing digestive problems due to back pain may need to find out what the symptoms and treatment of pinched thoracic spine may be. A person may note:
- Pain in the intestines when trying to change position.
- Spasmodic pain in the abdomen.
- Stool disorders.
Such symptoms may indicate not only pinching, but also a more serious condition - prolapsed intervertebral hernia or displacement of the vertebrae.
Pinched vessel in the thoracic spine
Another dangerous condition is pinching of a vessel in the thoracic spine, which can lead to the development of paralysis of the body and death due to cessation of respiratory and cardiac activity.
Pinching of large blood vessels in the thoracic spine occurs inside the spinal canal. This is a cavity that runs from the foramen ovale at the base of the occipital bone to the coccyx. Inside is the spinal cord, encased in a dural membrane. The paired radicular nerves depart from it. They are responsible for innervation of the human body and regulation of the autonomic nervous system.
The spinal cord is supplied with blood through several large arteries and veins. They are also located inside the spinal canal.
The walls of the spinal canal are not only the bone tissue of the vertebral bodies and their arcuate processes. These are also the fibrous rings of the intervertebral discs. With degenerative-dystrophic destruction, the intervertebral disc can extend beyond the vertebral bodies into the cavity of the spinal canal. Thus, it narrows its lumen and primarily pinches large blood vessels.
The structures of the spinal cord located below and the radicular nerves extending from them do not receive sufficient arterial blood (enriched with oxygen and nutrients). Ischemia (starvation) begins. In this case, a gradual accumulation of venous blood occurs, which also cannot be drained in a timely manner. Excessive internal pressure occurs in the canal, which further aggravates the patient's condition.
Pinched blood vessels in the spinal canal of the thoracic spine is a condition that requires immediate medical attention.
How to treat?
It is necessary to choose a treatment method depending on what preceded the pinched nerve in the thoracic spine. However, there are general rules for treating pinched nerve roots that will help you get rid of the unpleasant condition.
Drug treatment
If you go to the doctor with complaints of back pain and you are found to have an injury, you will be prescribed a list of medications. These will be:
- antispasmodics;
- drugs to improve blood circulation;
- medications for inflammation;
- vaso-strengthening.
Additionally, painkillers may be prescribed depending on the general condition of the patient. As soon as the condition improves, other treatment methods can be used.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is combined with gymnastic exercises, which allow you to recover and prevent recurrent injuries in the future. If you are experiencing pinching in the thoracic spine, you may be prescribed physical therapy:
- ultrasonic;
- laser;
- electrical stimulation of muscle tissue.
However, all these treatment methods can be used only after the patient’s general condition has improved and pain has been relieved.
Surgical intervention
As a rule, during the treatment of pinched nerve tissue, surgical interventions are avoided. But they will be indicated in a number of cases when there is no improvement in the condition for a long time, and the situation is getting worse. Radical treatment methods will be indicated if:
- conservative treatment was not effective;
- the pain spread further;
- the muscles began to atrophy;
- complications have appeared that affect the functioning of internal organs;
- pathological processes occurred in the intervertebral discs.
In such a situation, in addition to surgically eliminating the cause of the pain, surgery may be necessary to enlarge the hole in the intervertebral disc. But most often, treatment with medications and exercises for severe pinching of the thoracic spine can achieve the desired result, and surgery is a last resort.
Diagnosis of radiculopathy
For an experienced neurologist, it is not a problem to detect signs of radicular syndrome. In addition to the characteristic symptoms, the results of an examination of the patient (the doctor evaluates the posture that the person involuntarily assumes, muscle tone, the presence of painful sensations on palpation) and specific neurological tests carried out help him make a diagnosis. But in order to accurately determine at what level compression of the spinal root occurs and what causes it, a number of instrumental studies are required. The neurologist will determine which of them are necessary and write a prescription:
- radiography of the spine in 2 projections;
- CT;
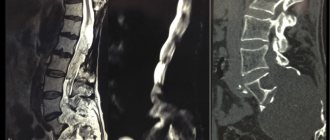
- MRI;
- electroneuromyography.
If there is a suspicion of the presence of diseases of the heart, gastrointestinal tract or others, ultrasound, blood tests, urine tests, etc. may be additionally prescribed.
For diagnosing intervertebral disc pathologies, MRI is considered the most informative method. With its help, you can detect even the slightest changes in the structure of the discs, which will not be visible with any other type of examination. But if it is necessary to accurately examine bone elements and detect their deformations, an X-ray, or better yet a CT scan, is required.
Prevention
In order not to think about how to remove pinching in the thoracic spine, prevent pathology. Maintain good posture, keep your weight under control, lift weights correctly - do not bend over, but squat. If your work involves a computer or long periods of sitting at a desk, do exercises and breaks. In addition, you need to monitor your diet, adequate intake of vitamins and minerals, basic physical activity, and lead the healthiest lifestyle possible. In this case, it will be possible to maintain the health of the spine even in old age.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis and its prevention
Conservative treatment of osteochondrosis in the thoracic spine is intended to stop or at least slow down degenerative changes, restore normal back mobility and eliminate symptoms that cause discomfort to the patient.
Therapeutic treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis involves the simultaneous use of:
- medications
(chondroprotectors, neuroprotectors, muscle relaxants, anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics); - methods of physiotherapeutic complex
; - therapeutic exercises
; - orthopedic regime
.
Patients are also advised to change their diet and lifestyle.
In case of severe irreversible changes in the intervertebral joints , in which pain and nerve conduction disorders are not relieved by medications,
surgery is recommended for patients
. It helps stop the death of nerve tissue and prevent life-threatening or disabling consequences of thoracic osteochondrosis. Depending on the situation, complete or partial resection of the intervertebral disc or its replacement with an artificial one, narrowing of the spinal canal or other surgery may be indicated.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
Physiotherapy
The objectives of physiotherapy for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region are to reduce pain and inflammation, relieve spasms, strengthen the muscle corset, restore the function of the nerve roots and normal blood circulation.
To relieve the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, the following are successfully used:
- Magnetic therapy
is one of the most effective anti-inflammatory techniques. Improves metabolic processes in tissues and relieves swelling. - Laser therapy
. Promotes biological activation of regenerative processes. Helps eliminate the consequences of trophic disorders and relieve inflammation. - Drug electrophoresis
. Allows you to restore tissue nutrition and relieve inflammation - the effect of the procedure depends on the medications used. - Medicinal phonophoresis
. Ensures deep penetration of the active ingredients of medications into soft tissues. - Massotherapy
. Helps relax muscles, eliminate tension and improve the supply of nutrients to the tissues of the spine. In the early stages, it eliminates the main symptom of thoracic osteochondrosis - a feeling of pain in the sternum - in a few sessions. - Acupuncture
. Stimulation of muscles and nerve endings helps relieve pain, restore sensitivity and eliminate swelling. - Ultrahigh frequency therapy
. Increases the permeability of capillary walls, improves blood flow and ensures the flow of protective cells into the site of inflammation. - Shock wave therapy
. It starts the processes of restoration of bone and cartilage tissue, prevents the deposition of calcium salts on the vertebral surfaces. - Balneotherapy
. As a rule, mud and ozokerite applications are used, less often paraffin. Radon and hydromassage baths are also recommended for patients. They help improve metabolism and restore sensitivity in affected tissues. - Amplipulse therapy
. It has a neurostimulating, analgesic and trophic effect, activates metabolic processes, and facilitates breathing. - Kinesiotherapy
(physical therapy, massage, traction therapy, kinesiotaping). Allows you to strengthen ligaments and skeletal muscles, restore mobility in the back and eliminate even persistent spasticity. Prevents the formation of osteophytes and narrowing of the canals in which the spinal roots are located.
In addition to physical therapy sessions, for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, patients may be recommended an orthopedic corset, which allows them to relieve the load on the spine.
Exercise therapy and massage
Therapeutic exercises and massage help strengthen the back muscles and relieve stress on the spine. With daily sessions, they help achieve stable drug-free remission, increase range of motion, and eliminate neurological manifestations of the disease. These treatment methods also prevent complications of osteochondrosis.
. For example, congestion in the lungs (with thoracic osteochondrosis it is difficult to breathe deeply), due to which patients are susceptible to pneumonia, as well as coronary heart disease.
Dosed physical activity helps relieve compression of the nerve roots, improve blood circulation and nutrition of the intervertebral discs. The optimal frequency and duration of gymnastic classes is determined by the exercise therapy instructor. As a rule, 3-4 exercises of 10-15 minutes a day are enough.
.
The exercises recommended for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis include the following:
- Stand straight, feet together, hands at your sides. As you exhale, raise your arms up and bend back, then inhale deeply. Lower your arms and lean forward, slightly arching your back in a dome-shaped manner (to do this, lower your head and shoulders as you exhale).
- Sit on a chair and, while inhaling, place your hands behind your head. Bend back and rest your shoulder blades on the back of the chair, exhaling.
- Get on all fours and arch your back. After maintaining the position for 3 seconds, bend your back with a crampon.
- Lying on the floor on your stomach, place your palms on the floor and, raising yourself on your arms, try to move your head as far back as possible, lifting your chest off the floor.
- Lie on your stomach and extend your arms at your sides. Perform the “yoke” exercise, trying to simultaneously raise your head and legs.
- Sit on the floor and stretch your legs in front of you. Reach the fingers of your right hand to the toe of your left foot and vice versa.
- Do a plank exercise (about 30 seconds).
- Perform hangs on the horizontal bar (or, in the absence of a horizontal bar, secure your fingers on the door frame and try to stretch your back as much as possible).
Bends to the side while raising your arm will also be helpful. All exercises should be performed 8 to 10 times
.
To treat thoracic osteochondrosis, various massage techniques are used, incl. acupressure and vacuum massage. For self-massage at home, patients are recommended the following movements:
- stroking the cervical-collar, scapular and axillary areas
; - squeezing with the thumb and index finger
(grabbing the skin and soft tissues); - trituration
; - kneading
(it should be done extremely carefully, it is advisable to entrust this technique to a specialist).
Massage should not be performed during exacerbations of the disease or during severe inflammation.
Drug treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
To treat the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- help relieve pain, calm inflammation and disperse swelling. They can be used both systemically (in the form of tablets, capsules and injections) and locally (in the form of ointments, gels, creams, compresses and solutions for medicinal electrophoresis). - Hormonal drugs
- to eliminate acute and chronic neurological pain. Used in cases where NSAIDs demonstrate insufficient effectiveness. - Muscle relaxants
are prescribed to reduce muscle tone and eliminate spasms of skeletal muscles. This helps alleviate pain and has a positive effect on tissue trophism. - Blood circulation correctors
- strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve blood circulation in small capillaries that nourish the periosteum and other structural elements of the vertebral joints. Reduce discomfort and reduce the risk of complications. - Neuroprotectors
- to preserve and restore sensitivity during compression of nerve roots and relieve neurological symptoms. This group also includes cholinesterase inhibitors, which improve nerve impulse transmission and help restore normal muscle tone.
For structural restoration of tissues affected by the degenerative process, the following are used in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis:
- chondroprotectors (Artracam)
are essential bioactive substances that trigger the processes of regeneration of cartilage and bone tissue. Serves to prevent the growth of osteophytes and narrowing of the spinal canal. They help a weakened body grow stable and resilient cartilage cells. Taking Artracam significantly improves the shock-absorbing properties of intervertebral discs, making them more elastic and resistant to damage; - vitamin complexes
- help normalize metabolic processes and prevent excess oxidation in tissues.
To relieve excruciating pain that interferes with the patient’s daily activities, the doctor may recommend a medical blockade with anesthetics. Diuretics are used to eliminate swelling and relieve compressed nerves and blood vessels.
Prevention of thoracic osteochondrosis
To prevent symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, you should:
- Take care to maintain healthy posture. This is facilitated by walking, swimming and therapeutic exercises to strengthen the muscles of the back, chest, abs, and shoulder complex.
- When working sedentarily, properly arrange your workplace and perform physical warm-up whenever your back and neck begin to become stiff (ideally, bend to the sides, stretch, and rotate your shoulders every 2 hours).
- Avoid back injuries and promptly seek help from an orthopedic traumatologist, even in the case of a seemingly insignificant bruise. Other diseases of the musculoskeletal system should not be triggered, especially in the joints of the lower extremities.
- If possible, unload the spine during the day (to do this, just lie on the floor for 40 minutes).
- Protect yourself from hypothermia and stress.
- Take chondroprotectors to protect joints for at least 3 months a year. Regardless of the strength of the muscular corset, the human spine is anatomically not adapted to vertical loads, and therefore requires additional support.
- Adjust weight if it is overweight. In addition to maintaining a low-carb diet, you should eat a diet high in vitamins and minerals. In the spring-autumn period they can be taken in tablet form.
- Sports activities that involve jumping from heights or lifting heavy weights should be limited.
- It is advisable to sleep on a semi-rigid bed, and for prolonged sitting, choose hard furniture. This helps maintain muscle tone and relieve stress on the spine. If possible, you should purchase an orthopedic mattress and shoe insoles.
- Do not lift loads weighing more than 10 kg. The load should be distributed evenly, with muscle tension and without transferring to one side. If necessary, use a special sports corset. It is undesirable to hold loads in outstretched arms for a long time.
- Women should avoid wearing high-heeled shoes. The optimal heel height is 2-4 cm.
These recommendations will also be useful for those who are already sick - they will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the spine and will help to significantly slow down pathological changes.
And remember: the main thing in the prevention of thoracic osteochondrosis is consistent adherence to healthy habits.
Let chest pain never bother you!
Treatment
Having learned about the diagnosis, patients begin to wonder what to do if the spinal nerve is pinched and what complications this leads to. Treatment of pathology requires an integrated approach. In mild cases of the disease, medications are prescribed to relieve pain and relieve inflammation. Additionally, the specialist recommends attending physiotherapeutic procedures that will improve blood flow to the affected area.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy methods allow you to quickly get rid of the symptoms of the disease, since their action is aimed at improving blood microcirculation. Increased blood flow to the site of inflammation allows you to relieve muscle tension, eliminate inflammation and soreness.
Among all physiotherapeutic techniques, the following are distinguished:
- massage – the procedure is carried out by a specialist or independently using applicators and massage rollers;
- manual therapy is a procedure that is characterized by deep work on the back muscle tissue;
- electrophoresis - a method in which a direct electric current helps deliver medications when they are administered;
- acupuncture – acupuncture, in which a specialist acts on the active points of the patient’s back, improving microcirculation;
- Exercise therapy is a set of exercises that helps cure pathology and reduce the severity of symptoms.
If the patient does not have the opportunity to go to appointments with a massage therapist or chiropractor, then he can independently work out the back muscles using massage rollers or applicators (Kuznetsova or Lyapko)
Drug treatment
Treatment of compressed nerve tissue involves taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. As a rule, with a mild pathogenesis, the therapist prescribes local anesthetics - ointments and gels, which have an analgesic and warming effect.
No ads 2
These ointments include:
- Diclofenac (Dolobene, Voltaren, Deep Relief);
- Finalgon;
- Ketoprofen (Ketonal, Valusal, Fastum, Ultrafastin);
- Nicoflex (Ben-Gay);
- ointments based on bee or snake venom (Viprosal B, Apizartron).
All local products are applied in a thin layer so that the active substance is better absorbed by the skin and reaches its destination. Warming ointments should not be chosen independently, as there are contraindications to their use. In this regard, it is better for the patient to clarify in advance whether it is possible to heat the sore spot or whether other medications should be used.
In addition to ointments, much attention is paid to oral medications and injections. The active ingredient in the preparations may not differ from that in ointments and gels, so Diclofenac can be used simultaneously in the form of injections and ointments.
Surgical intervention
In advanced cases, the patient may require surgery to restore the integrity of the nerve roots. Depending on the etiological factor, types of radical therapy are distinguished. If the cause of compression of the nerve fibers is an intervertebral hernia or a benign formation, the structure is removed and the affected area is cleaned. This operation allows you to get rid of the oppressive factor and begin the recovery process.
The rehabilitation period takes 1–3 months until the functions of the spinal column return to normal. In cases where the pathological process is caused by a rupture of the spinal nerve, surgery is prescribed to restore its integrity. Neurosurgical operation is performed on damaged nerve tissues, after the patient consents to surgery. There is a certain risk that is associated with the anatomical feature of the spinal column.
No ads 3
After the operation, the patient undergoes a rehabilitation course to restore the functionality of the spinal column. To do this, he is prescribed a set of physical exercises and wearing orthopedic corsets or bandages. Posture correctors are mandatory, since weakened muscles cannot take a large load on the spine.
Microdiscectomy, or surgery to remove a herniated disc, is prescribed by a doctor when conservative treatment methods do not have a therapeutic effect.
First aid
If a nerve of the chest is pinched, you must call an ambulance.
A pinched nerve of the chest can occur anywhere and under any life circumstances. In this case, you must immediately call an ambulance and provide first aid.
It is necessary to lay the patient on a flat and hard surface, ensuring complete immobility of the victim. A person should take a body position in which he will experience as little pain as possible. It is important to provide access to fresh air.
As a rule, pinching of a nerve is accompanied by severe unbearable pain, so you need to relieve the symptom with the help of an anesthetic drug. Due to the suddenness of the incident, victims often experience painful shock and nervous shock. In this case, it is recommended to give the patient a sedative tablet.
Upon arrival of the ambulance, it is important to tell the doctors about all the medications that were given to the victim. Hospitalization is required only in the most difficult cases. More often, the doctor locally anesthetizes the inflamed area and recommends undergoing a thorough medical examination.
Symptoms of a pinched nerve in the chest
Pain from a pinched nerve is often confused with attacks of heart pain, manifestations of cholecystitis or pancreatitis
. If a person has a pinched chest, the pathological process will be accompanied by quite specific symptoms. An experienced specialist can quickly distinguish neuralgia from, for example, myocardial infarction, exacerbation of pancreatitis, angina pectoris and pneumonia (pneumonia).
The development of the disease is accompanied by the following clinical picture:
- Painful sensations are sudden and sharp, mainly localized in the intercostal spaces.
- Pain can occur during physical activity and in a state of complete rest, but most often the pain is caused by sudden changes in body position - bending or turning. Symptoms often manifest themselves when running, sneezing and coughing.
- The duration of a painful attack may vary depending on the characteristics of the pinching and the general condition of the body. May last from a few minutes to several days.
- The skin and soft tissues located over the inflamed nerve often become numb.
- During an exacerbation of the condition, it is possible to relieve symptoms or reduce their manifestations by using a comfortable position of the torso or holding your breath.
Sharp attacks of pain are often confused with disturbances in the functioning of the heart and cardiovascular system as a whole. To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor must pay attention to one important point - with neuralgic abnormalities, the pain intensifies when trying to cough or change body position.
A pinched nerve is observed with the development of herpes zoster. A characteristic feature of the disease is the formation of bubbles along the nerve. The pathological condition is not contagious, but requires a different therapeutic course than intercostal neuralgia.