The vestibular apparatus is an organ of balance. Together with the visual and motor receptor systems (a receptor is an anatomical formation that converts perceived irritation into nerve impulses), it plays a leading role in a person’s orientation in space. The vestibular apparatus perceives information about acceleration or deceleration that occurs during any type of movement, as well as when the position of the head changes in space. The sense of gravity is also analyzed here, which is why the vestibular apparatus is also called the organ of gravity. Under resting conditions, the receptors of the vestibular apparatus are not excited. Irritation of the receptors occurs when the head is tilted or moved. In this case, reflex muscle contractions occur, helping to straighten the body and maintain balance.
General information
Vestibulopathy is a disorder of the normal functioning of the vestibular apparatus , in which characteristic symptoms appear.
The ICD-10 code for vestibulopathy is H81 (Vestibular function disorders). The normal orientation of a person in space and his balance in a vertical position is ensured by the vestibular apparatus. Disturbances in its work lead to a person experiencing confusion, dizziness , and the inability to remain in a standing position. This condition is also called labyrinthopathy. It can develop due to various reasons and diseases, developing at any age in every person. Sometimes vestibulopathy is a congenital pathology.
It may manifest itself as a separate syndrome or as a sign of neuropsychiatric disorders. In the second case, it is more difficult to treat this disease. How this pathology manifests itself, and what treatment methods are advisable to practice, will be discussed in this article.
Pathogenesis
Vestibular insufficiency can occur at any age. Sometimes this is a congenital pathology. The pathological process is localized in the inner ear. The vestibular apparatus, which is a complex receptor of the vestibular analyzer, consists of three arches. They are located at an angle of 90 degrees to each other. They contain liquid, which is distributed through the channels depending on the position of the human body, gravity, the force of attraction, as well as the influence of a number of other factors. The brain receives impulses that determine the movements of different parts of the body. Vestibular insufficiency develops when the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is impaired.
Vestibulopathy can develop with a variety of pathogenetic variants of damage to the peripheral or central part of the vestibular analyzer, which performs three important functions - maintaining balance, spatial orientation, and image stabilization.
Location and structure of the vestibular apparatus
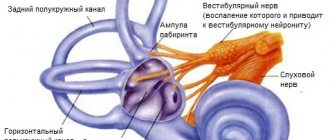
Labyrinth The vestibular apparatus is located inside the temporal bone and is closely connected with the organ of hearing. In the thickness of the temporal bone there is a complex labyrinth, which is a system of interconnected canals and cavities. There is a bone labyrinth and a membranous labyrinth located inside it, which has a connective tissue wall and basically repeats the shape of the bone labyrinth. Between the bony and membranous labyrinths there is a gap filled with fluid - perilymph. The membranous labyrinth is filled with dense endolymph, the viscosity of which is 2–3 times greater than that of water.
The labyrinth contains the vestibule and semicircular canals, in which the vestibular receptors are located, as well as the cochlea, where the auditory receptors are located. There are three semicircular canals, and they lie in mutually perpendicular planes, which makes it possible to analyze the position in three-dimensional space. Each semicircular canal has two legs, one of which expands in front of the vestibule, forming an ampulla. The vestibule is an oval cavity into which the semicircular canals open on one side and the cochlea on the other.
In the corresponding bony semicircular canals lie the membranous semicircular ducts; in the vestibule there are membranous spherical and elliptical sacs. In the semicircular ducts and vestibular sacs there are clusters of receptor cells. Vestibular receptors are located on elevations, which are present only in the ampoules of the ducts in the form of scallops and in the sacs in the form of spots. The fluid contained in the labyrinth moves when the head and body move (first perilymph, and then endolymph) and irritates the receptor cells. The latter in the ampoules of the semicircular ducts are excited during the movement of the endolymph, mainly during angular accelerations, and in the spots of the sacs - during linear accelerations.
Receptor cells In spots, the part of the receptor cell protruding into the cavity of the sac ends in one longer mobile hair and 60–80 glued immobile hairs. These hairs are immersed in a jelly-like membrane containing calcareous crystals - otoliths. The receptor cells of the spots are irritated due to the sliding of the otolithic membrane along the hairs during the movements of the endolymph. The sensitivity of receptor hair cells is high: the threshold for distinguishing head tilt to the side is only about 1°, and forward and backward is 1.5–2°. When the rotation accelerates, a person notices a change of 2–3° per 1 s2.
It is believed that receptor cells in the spots of the sacs perceive the force of gravity and primarily regulate the balance of the head and body at rest (static balance), and the receptors in the ampullae of the semicircular ducts react to acceleration or deceleration of movement, that is, they regulate the balance of the body moving in space ( dynamic equilibrium).
Classification
Depending on the nature of its origin, vestibulopathy is divided into several types:
- Vertebrogenic – develops against the background of pathologies of the cervical spine. It can be observed with osteochondrosis , osteoporosis , intervertebral hernia , etc. This form is the most common. This condition is characterized by prolonged dizziness and a feeling of head instability. When trying to focus your gaze on moving objects, discomfort occurs. Spontaneous attacks of eye rotation may occur when a person tries to turn his head sharply. They last no longer than 30 seconds.
- Peripheral - develops as a consequence of the inflammatory process in the nerve ganglia in the inner ear. Most often this occurs due to allergies or infections. With such a lesion, in addition to vestibular disorders, the patient may experience tinnitus and causeless fear. Prolonged dizziness and bouts of eye rolling are noted.
- Central - develops if disturbances occur in the function and structure of the vestibular nuclei of the medulla oblongata and cortex.
- Post-traumatic – develops after traumatic brain injury if hemorrhage occurs in the labyrinth of the inner ear. As a result, tissue damage is noted. The eardrums may also be damaged, and the ganglia of the brain may be shaken and damaged. In this case, both dizziness and other characteristic signs are noted - spontaneous eye movements, nausea, vomiting. In addition, a patient with such a lesion has an unstable gait - it is difficult for him to stand on his feet.
Cochleovestibular syndrome is also distinguished . In this condition, auditory and vestibular function is impaired. Cochleovestibular disorders are accompanied by tinnitus, hearing loss, dizziness, and imbalance.
Causes of vestibular apparatus disorders
The causes of dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus can be very different. Basically, vestibulopathy is provoked by the following factors:
- Cervical osteochondrosis - due to displacement of discs and vertebrae, the functioning of the vertebral artery is disrupted, which impairs blood supply. In addition, with osteochondrosis, the nerves are pinched, which also leads to dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus. Also, problems with the vestibular apparatus can be observed with intervertebral hernia, osteoporosis, etc.
- Pathologies of the inner ear - this may be a violation of lymph flow in the middle ear, inflammatory processes, otitis media, etc.
- Labyrinthitis is an inflammatory disease that provokes the development of periodic dizziness.
- Meniere's disease - during the development of the disease, pathological changes in the inner ear are noted.
- Infarction of the labyrinth – leads to impairment of hearing and function of the vestibular apparatus.
- Vestibular neuronitis is a consequence of herpetic damage to nerve fibers. If a person is diagnosed with vestibular neuronitis, it should be taken into account that signs of the disease appear periodically - during exacerbation. As a rule, this happens in spring and autumn. Also, vestibular neuritis can develop as a consequence of acute respiratory infections, influenza , etc.
- Migraine - with this disease, the symptoms are similar to vestibulopathy, but the hearing does not change.
- Diseases of the central nervous system - can cause pathological processes in the membranous labyrinth.
- Traumatic damage to the thin bone membranes of the labyrinth , in which the eardrum ruptures or hemorrhage in the middle ear - this can happen with severe coughing, straining, diving.
- Vertebrobasilar insufficiency - manifests itself mainly in older people, causing damage to the vestibular analyzers. With this pathology, the blood vessels, cerebellum and brain stems are affected. The duration of such an attack is several minutes, during which the person loses balance and orientation in space, he develops weakness, and his limbs go numb.
- Intoxication of the body due to taking certain medications.
- Neurotic disorders.
- Neuromas are tumors that form and grow from nerve cells.
- Occupational diseases – working in conditions of constant vibration or noise.
How does the balance organ work?
Although the vestibular system is located inside the bone box, this does not prevent it from collecting information not only about the position of the head, but also the arms, legs and other organs of the human body. The connection with the balance apparatus is especially secure at the nerve endings, gastrointestinal tract, and cardiovascular system. That is why, after being nervous and drinking too much coffee, many people feel dizzy.
Under the influence of attraction, the jelly-like liquid and the crystals in it will shift, affecting the balance receptors. The villi will immediately transmit information to the brain about changes in balance, and from there instructions will come to other organs: change muscle tone, move your leg or arm to the right, stand up straighter. It is very interesting that the vestibular system is configured only for horizontal movement of the body, so when going up in an elevator or flying on an airplane, many experience severe nausea, ringing in the ears, and dizziness.
Functions
In close proximity to the optic nerves and auricles, the balance system has nothing to do with either hearing or vision. The main function of the vestibular apparatus is to analyze changes in the position of the arms, legs, torso or head and transmit data to the brain. The organ quickly reacts to minimal external influence, detecting even the slightest changes in the gravitational field of the planet, helping to maintain balance in complete blindness or navigate in unfamiliar space.
Symptoms of vestibulopathy
The basis of vestibulopathy are four main symptoms:
- systemic dizziness;
- vegetative manifestations - nausea, vomiting, hyperhidrosis , heart rate disturbances, etc.;
- imbalance;
- spontaneous nystagmus .
However, disorders of the vestibular system can manifest themselves differently in different diseases. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the following manifestations:
- I feel dizzy from time to time, and this symptom occurs quite often.
- Difficulties appear in maintaining balance - it seems that the body “does not obey” while walking or trying to move.
- Vision deteriorates, spots and goosebumps appear in the eyes.
- of migraines increases .
- Hearing deteriorates, tinnitus bothers me.
- Nystagmus is periodically observed - the movement of the eyeballs in one direction.
- Periodic nausea and vomiting.
If a person does not know what vestibular neuritis and how it manifests itself, then he can ignore the symptoms of vestibular neuritis for a long time, believing that these are just signs of overwork.
Bibliography
- "Biological encyclopedic dictionary." Ch. ed. M. S. Gilyarov; Editorial team: A. A. Babaev, G. G. Vinberg, G. A. Zavarzin and others - 2nd ed., corrected. - M.: Sov. Encyclopedia, 1986.
- "Otorhinolaryngology". Textbook ed. I.B. Soldatov and V.R. Hoffman. – St. Petersburg, 2000. – p.41-45, p.75-96.
- Soldatov I.B. "Lectures on otorhinolaryngology: Textbook." – M.: Medicine, 1994. – pp. 40-56., pp. 261-277.
- How the vestibular apparatus works - https://theoryandpractice.ru (Access date: 07/01/2019)
- How to train the vestibular apparatus at home - www.sovsport.ru (Date of access: 07/02/2019)
Tests and diagnostics
To establish a diagnosis, the patient must see a doctor, who first conducts a detailed survey and examination. Further, if necessary, further studies will be prescribed.
The study of the vestibular apparatus can be carried out using different methods. There are three main tests to check how the vestibular apparatus works: rotational , thermal and mechanical . In addition, you can undergo simple testing to determine the presence of coordination disorders.
With the help of such tests, a study of the functions of the vestibular apparatus for VVC in Moscow (Khimki, etc.) and other cities is carried out.
- Rotation test - to conduct it, a person sits in a chair and tilts his head forward. After this, 10 rotations are carried out over 20 seconds, then the chair suddenly stops. After this, nystagmus develops. Having measured its duration, the procedure is repeated again with rotation in the opposite direction. Normally, nystagmus will last the same amount of time - 20-50 seconds. If the difference between the two results is 25%, then we can talk about balance disorders.
- Mechanical examination - for this purpose, a rubber bulb is used, with the help of which the external auditory canal is filled with oil to displace the air from it. Next, the pear is compressed and unclenched, checking for damage to the bone capsule of the labyrinth.
- Thermal examination - the patient's ear canals are washed with water for 30 seconds.
At this time, nystagmus occurs, and assessing its duration makes it possible to determine the sensitivity of the vestibular apparatus.
Tests are carried out to determine coordination. This could be walking in a straight line with your eyes closed, trying to touch the tip of your nose with your eyes open and closed, etc.
There are other tests to determine whether the vestibular apparatus is weak or strong.
- Nystagmus can be measured using so-called Frenzel glasses . These are special magnifying glasses with bulbs equipped with light bulbs that illuminate the eyes.
- Also for this purpose, the method of electronystagmography - measuring nystagmus using electrodes.
- A neurological examination is also carried out, aimed at determining the condition of the nerve trunks of the eyeball and the muscles of the facial skull.
- MRI allows you to determine the condition of the spine.
- The inner ear and eardrum are also examined.
Other studies may be prescribed. The doctor will tell you during the consultation where to undergo such a study and what the conclusion looks like.
How does the vestibular apparatus work?
The components of the system are three semicircular tubules - the utriculus and the otolith organ - the sacculus. The channels are filled from the inside with a viscous liquid and have the shape of a shell, at the base of which there is a seal - jelly-like cupules. The sacculus is divided into two sacs: round and oval. Above them are small crystals of calcium carbonate - otoliths.
Under the sealing valve there are ciliated cells of the inner ear, with the help of which two types of signals are transmitted: static and dynamic. The first are associated with the position of the body, the second with the acceleration of movement. In general, the coordination organ is formed in such a way that at the slightest tilt and turn of the head or walking, all the component parts interact at once.
Treatment with folk remedies
Some folk remedies can be used as auxiliary methods during the period of treatment and recovery for vestibulopathy.
- Melissa tea . 1 tbsp. l. Dried lemon balm pour 1 cup boiling water. After 10 minutes, drink with honey. It is recommended to drink this tea for dizziness twice a day.
- Infusion of parsley seeds . Finely grind parsley seeds, 1 tsp. pour the raw material into 1 glass of water and leave for 8 hours. Drink 50 ml 4 times a day.
- Infusion of nettle leaves . 1 tbsp. l. Pour dry nettle leaves into a thermos and pour 200 ml of boiling water. After two hours, strain by squeezing out the nettle leaves. Combine the resulting liquid with the same amount of fresh apple juice. Drink throughout the day. Take for two weeks.
- Essential oils . Mix 50 ml of camphor oil with 25 ml of fir oil and 10 ml of juniper. Mix thoroughly and lubricate the lymph nodes on the neck, nose and mouth with the resulting product. Please note that this product should not be applied to open wounds.
- Infusion of mistletoe and Japanese Sophora . The dry raw materials of both plants need to be crushed and mixed with 15 g of each component. Pour 500 ml of boiling water. When the product is infused, drink 100 ml before meals.
What to do if the vestibular system is damaged
When the balance organs fail and signal this in every possible way, a person should first undergo an examination and visit an ENT doctor’s office. Mandatory diagnostics include:
- special hardware tests for audiometry and electronystagmography;
- CT or MRI of the brain;
- blood analysis;
- ultrasound examination of blood flow;
- vestibular tests.
Training
If the dizziness is minor and only bothers you when traveling on a boat, going up in an elevator, or making sudden turns of the body, your balance apparatus needs to be trained. Exercises for the vestibular apparatus can be mastered by anyone if desired:
- Sit on a chair or armchair. Extend your index finger forward and fix your gaze on it. Start turning your head in different directions, gradually increasing the pace.
- Next exercise: take two cards in your hands, straighten your elbows. It is necessary to alternately focus your gaze on one of the cards, while your head must remain motionless.
- Stand up, spread your legs, and focus your gaze straight ahead. Start making circular movements with your body. First with a small amplitude, then with a large circle diameter.
- All exercises for training the vestibular system should be performed daily with several approaches.
Treatment
If imbalances progress and other symptoms are added to the momentary dizziness, gymnastics will not help. Urgent medical treatment of vestibular vertigo is necessary. The choice of drug and method of therapy will depend on the reasons that caused this:
- If damage to the balance apparatus is caused by peripheral polyneuropathy, then diabetes must be treated.
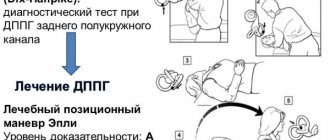
- For paroxysmal vertigo, the ENT specialist chooses a special technique: he turns the patient in a certain sequence, the crystals change location, after which an improvement in well-being occurs.
- Treatment of dizziness with Meniere's syndrome cannot be done without effective antihistamines and antiemetic drugs. In addition, the patient necessarily needs nutritional correction and a special diet.
- Migraines in children can be treated with aspirin, ergotamine, beta blockers and antidepressants.
- If disorders appear at retirement age, the doctor may suggest implanting implants that will restore the lost balance.
Folk remedies for dizziness
Along with drug therapy and preventive gymnastics, it is possible to treat the vestibular apparatus with folk remedies. For example, make ginger tincture:
- Take 4 tsp. grated ginger root, mix with a pinch of dried mint, fennel seeds, pumpkin seeds, chamomile flowers and orange zest.
- Pour hot water over the herbal mixture, let it brew for 15 minutes and drink if you feel dizzy, lose balance, or other signs of systemic disorders.
In case of persistent dysfunction of the balance apparatus, a balm made from three tinctures helps strengthen a weak body at home:
- For half a liter of alcohol, take 4 tablespoons of clover inflorescences. Wrap the container with foil and leave for 2 weeks.
- For the same amount of alcohol, take 5 tbsp. l. Dioscorea root. Insist as in the previous recipe.
- Fill the propolis with alcohol and put it in a dark place. After 10 days, strain the tincture.
- Mix all three components and take 1 tbsp three times after meals. l.
Prevention
The following prevention methods should be practiced:
- Limit situations that provoke an attack of vestibulopathy.
- Eat right, avoiding lack of vitamins and minerals. If necessary, take vitamin-mineral complexes periodically.
- Get proper rest, sleep at least 7 hours a day.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Exercise daily, do yoga, Pilates, swimming.
- Treat bacterial and viral diseases in a timely manner.
- If vestibulopathy occurs, consult a doctor.
Diet
Salt-free diet
- Efficiency: 5-10 kg in 13 days
- Time frame: 13 days
- Cost of products: 4500-8000 rubles for 13 days
For some diseases that provoke vestibulopathy, it is recommended to adhere to a salt-free diet or limit the amount of salt in the menu.
In general, nutrition should be rational and varied, and the diet must include fresh fruits and vegetables, meat, fish, dairy products, nuts, and vegetable oils.
You should give up alcohol.
Consequences and complications
A severe complication of vestibulopathy can be purulent labyrinthitis , which, in turn, sometimes develops into meningitis . Therefore, inflammation in the inner ear must be treated under the close supervision of a doctor.
Vestibulopathy, moreover, negatively affects the overall quality of life. Dizziness and migraines impair work ability. In addition, such manifestations can cause accidents and traffic accidents.
In advanced stages, the auditory nerve may be affected, leading to the development of hearing loss.
This condition can also lead to cognitive impairment.
List of sources
- Zamergrad M.V., Grachev S.P., Gergova A.A. Acute vestibular vertigo in old age: stroke or peripheral vestibulopathy. Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry. S.S. Korsakov. Special issues. 2018; 118(6-2): 46-49.
- Parfenov V.A., Abdulina O.V., Zamergrad M.V. Differential diagnosis and treatment of vestibular vertigo // Neurology, neuropsychiatry, psychosomatics. - 2010. - No. 2. - P. 49-54.
- Suslina Z.A., Varakin Yu.Ya., Vereshchagin N.V. Vascular diseases of the brain. M. 2006.
Sources
- Wu X., Liu M., Zhuang HW., Chen KT., Yang ZY., Xiong GX. [Cochleo-vestibular lesions and prognosis in patients with profound sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a comparative analysis]. // Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi - 2021 - Vol55 - N5 - p.472-478; PMID:32842361
- Rawlins KW., Zhan KY., Mattingly JK., Feldman AZ., Adunka OF. Fibrous dysplasia mimicking a pediatric endolymphatic sac tumor. // Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol - 2021 - Vol129 - NNULL - p.109785; PMID:31770666
- Rajeshwari B., Shanmugam S., Sadiya N., Mitra G., Chendilnathan B. “Endolymphatic sac tumor”: A case report with review of literature. // Indian J Pathol Microbiol - 2021 - Vol62 - N4 - p.608-610; PMID:31611452
- Eguchi S., Hirose G., Miaki M. Vestibular symptoms in acute hemispheric strokes. // J Neurol - 2021 - Vol266 - N8 - p.1852-1858; PMID:31037419
- Lee JY., Kim CH., Park JS., Kim MB. Peripheral Vestibulopathy Presenting as Acute Vertigo and Spontaneous Nystagmus with Negative Video Head Impulse Test. // Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg - 2021 - Vol160 - N5 - p.894-901; PMID:30665325
- Strupp M., Mandalà M., López-Escámez JA. Peripheral vestibular disorders: an update. // Curr Opin Neurol - 2021 - Vol32 - N1 - p.165-173; PMID:30562267
- Wang HW., Guo Y., Zhou J., Zhou HF. . // Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi - 2021 - Vol32 - N2 - p.99-102; PMID:29757553
- Sonoda S., Yoshimura M., Abe C., Morita H., Ueno H., Motojima Y., Saito R., Maruyama T., Hashimoto H., Tanaka Y., Ueta Y. Effects of hypergravity on the gene expression of the hypothalamic feeding-related neuropeptides in mice via vestibular inputs. // Peptides - 2021 - Vol105 - NNULL - p.14-20; PMID:29751050
- Park JS., Kim CH., Kim MB. Comparison of Video Head Impulse Test in the Posterior Semicircular Canal Plane and Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential in Patients With Vestibular Neuroitis. // Otol Neurotol - 2021 - Vol39 - N4 - p.e263-e268; PMID:29494469
- Tamás LT., Lundberg YW., Büki B. Vergence increases the gain of the human angular vestibulo-ocular reflex during peripheral hyposensitivity identified by cold thermal irrigation. // J Vestib Res - 2021 - Vol27 - N5-6 - p.265-270; PMID:29400687