03.11.2017
1. Features of positional vertigo
1.2. Causes of BPPV development
2. Anatomy of the vestibular organ
3. Symptoms
4. Diagnosis of paroxysmal positional vertigo
4.5. Differential diagnosis
5. Treatment of benign paroxysmal vertigo
Dizziness is one of the most common symptoms of neurological origin. Of all types of dizziness, the most common is benign positional vertigo, which is detected in more than 80% of all patients who complain.
This type of dizziness is associated with pathology of the inner ear and vestibular apparatus. Usually this type of dizziness occurs suddenly, the patient cannot indicate the specific reason that provoked the development of an attack of instability. Although during the examination, attention is drawn to the formation of instability as a result of sudden movements of the patient’s head or body, after which an attack is formed. This type of dizziness has a paroxysmal character due to its short duration, i.e. This condition is characterized by a rapid increase in symptoms and an equally rapid disappearance.
Essence and basic principles
The Epley maneuver or exercises are a special maneuver used to treat benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).
This procedure is often carried out in a physiotherapy office, but it can also be done at home after a specialist shows all the basics of the technique. This maneuver was developed by Dr. John Epley, after whom it was named. The first time it was talked about was back in the 80s of the last century.
The Epley maneuver is a series of exercises that help relieve symptoms of dizziness. Numerous studies have proven that this technique is the simplest, safest and most effective in the treatment of dizziness caused by the deposition of calcium salts in the inner canal of the ear.
All these exercises do not eliminate the presence of otoliths, but only change their location. Such manipulations cause them to move to other areas of the inner ear that do not cause dizziness.
The essence of the technique is to place your head at an angle at which gravity helps relieve unpleasant symptoms. Tilt of the head helps remove crystals from the semicircular ear canals. This means that they stop displacing fluid, which is what causes nausea and dizziness in a person.
As a result, it turns out that this maneuver relieves all symptoms, but you need to do the set of exercises several times. The thing is that the first time the crystals can move a small distance.
It is worth remembering that the Epley maneuver requires special concentration from a person, all actions must be precise, no sudden movements.
There are a number of rules that must be followed:
- classes should take place in a well-lit room;
- there should not be any objects with sharp corners, carpet paths, or objects that could cause a person to fall near the patient;
- It is better to perform the exercise on a soft surface; a couch, yoga mat, or thick-pile carpet are suitable for this;
- the clothes a person wears should be loose, not restricting movements, so that he can move easily and freely;
- shoes on feet should be without heels;
- while performing exercises, someone must be present next to the person; it is unknown how his body will react to the exercise; someone needs to provide backup;
- if a person feels unwell or has symptoms of other diseases, then therapy is postponed until the person feels better;
- Even after the Epley maneuver is successfully performed, when the results sought are obtained, you will need to visit the doctor several more times to prevent a relapse.
Experts who recommend the Epley maneuver to their patients for symptoms such as dizziness note that after the first use of a set of exercises, serious changes are observed. The symptoms go away, but only if you follow all the prescribed recommendations for several days after them.
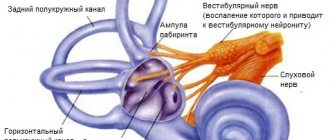
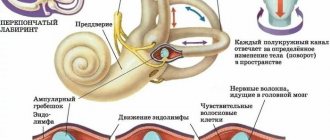
The structure of the vestibular apparatus
We are talking about the sensory organ of the labyrinth of the inner ear, responsible for the perception of balance (serves similarly to the statocyst in invertebrates). It develops in the embryonic period from the ear placode. The entire system is filled with endolymph inside and surrounded by perilymph on the outside. In some parts there are sensory cells (neuromasts).
The vestibular system consists of several clearly defined parts, of which the best known are:
- semicircular canals – perception of angular acceleration of the head;
- spherical sac (sacculus) – perception of direct vertical acceleration;
- elliptical sac (utriculus) – perception of linear horizontal acceleration.
Indications for use
The Epley maneuver is prescribed by a doctor only after examination, examination and an accurate diagnosis. It is also worth remembering that these exercises can only be recommended for stable, non-progressive illness.
Among these pathologies:
- period after a stroke;
- benign positional paroxysmal vertigo;
- violation of movement coordination;
- osteochondrosis;
- recovery period after injury to the spine or brain;
- ear diseases;
- infectious pathologies.
Gymnastics does not affect muscle function in any way. Its main goal is to teach a person to control attention, so regular use does not cause any unwanted manifestations.
Contraindications for use
The Epley maneuver for dizziness is a safe therapeutic procedure, but it does have a number of contraindications.
It is prohibited to carry out manipulations if the patient:
- with active manifestations of symptoms: confusion, disorientation;
- respiratory function is impaired if there are problems with the functioning of the heart, blood vessels, and respiratory organs;
- worsening after exercise.
In other cases, the maneuver can be carried out, but it is better to do this under the supervision of a specialist.
Features of treatment of the disease
During therapy, the following approaches are used.
Positional maneuvers:
- Semont maneuver (relaxation) - under medical supervision;
- Epley maneuver (repositioning) - under medical supervision;
- Brandt–Daruff habituation maneuvers (at home, independently).
Regime measures:
- sleep in a semi-sitting position, in which you should:
- avoid provoking positions;
- do not lie on the affected ear;
- avoid complete darkness.
The following treatment methods:
- medications (antiemetics, vasodilation therapy);
- surgical therapy - surgery of the damaged canal.
Useful tips for patients
There are some recommendations that will help you complete the procedure successfully with maximum results and without any inconvenience:
- Before starting the exercises, the specialist recommends that the patient take a vestibulolytic drug. It will help reduce the severity of symptoms. Take dimenhydrinate in a dosage of 100 mg half an hour before the start of the procedure.
Take 2 Dramamine tablets 30 minutes before the Epley maneuver for dizziness. - All exercises should be performed quickly, but without sudden movements.
- When performing the maneuver, the neck should be extended as much as possible, thereby protecting against re-entry of calcium salts into the semicircular canal.
- The patient may need to perform the maneuver several times in 1 session.
Main complex
Back in the early 80s of the last century, a set of exercises was developed, which today is called the Epley maneuver.
Its use allows calcium carbonate crystals to move out of the semicircular tubules under the influence of gravity. During this maneuver, the patient often experiences an increase in autonomic symptoms, which can be explained by the fact that otolith fragments are forced to move.
It is better to perform the maneuver for the first time only in the presence of a specialist. Its main feature is a clear trajectory, slow movement from one position to another, without any sudden movements.
The Epley maneuver for dizziness requires precise adherence to all exercise techniques:
- The patient sits straight on the couch, turns his head towards the ear (45˚), in which an accumulation of otoliths is detected.
- Without turning your head, you need to lie down on the couch with your head thrown back slightly. You need to stay in this position for at least 1 minute.
- Turn your head 90˚ towards your healthy ear and hold for 30 seconds.
- The body and head in a fixed position are turned in the same direction by another 90˚. The patient's face at this moment should be directed downward. Stops again for 30 seconds.
- Again the person returns to the starting position, sitting on the couch.
While performing the maneuver, the person should feel slightly dizzy. If such a symptom appears, it means that he is doing everything correctly. All the exercises described above should be performed several times for 10 minutes. Only in this case can the full effect be achieved.
The Epley maneuver for dizziness does not accept any sudden movements; all manipulations must be smooth. After exercise, you should definitely rest. Regular exercise will allow you to gradually dissolve all the salts and forget about dizziness.
If after the first session of the Epley maneuver there are no results or the patient experiences frequent relapses, then in this case a modified procedure can be used at home. If you follow all the rules for doing the exercises, the symptoms disappear after a few days.
The Epley maneuver can also be used as a diagnostic tool in people who cannot be definitively diagnosed with BPPV but are strongly suspected to have it. But it is carried out only if the Hallpike tests are negative.
Diagnostics
In addition to a good medical history (occurrence of dizziness with typical movements) and a standardized neurological examination, the presence of characteristic nystagmus on the Dix–Hallpick test is a key factor in the diagnosis of BPPV.
Physical examination
The survey includes the following measures:
- internal (blood pressure measurement, heart rhythm disturbances, heart defects, anemia, orthostatic dysregulation: Schelling test);
- neurological (examination of cerebellar symptoms, sensory polyneuropathy with loss of position perception, damage to the trigeminal or facial nerve):
- gait study - falling on one side (on the affected side - vestibular causes, on the healthy side - cerebellar causes);
- Romberg test - positive (in the case of proprioceptive and sensory ataxia), negative (in the case of cerebral vertigo);
- Unterberger test – positive (for cerebral and vestibular damage);
- nystagmus (with the vestibular type - nystagmus in one direction, never vertical; with the central type - complex, changing direction);
- ear examination with an otoscope (herpes zoster, otitis media, perforation);
- hearing test (one-sided deafness is usually of vestibular etiology).
Instrumental studies
This method includes the following approaches:
- ECG – if there is a suspicion of heart rhythm disturbances;
- laboratory examination - blood test, glycemia, creatinine, liver tests, basal TSH (with a targeted examination, all studies are not necessary);
- if necessary, examination by an ENT specialist, neurologist, ophthalmologist, orthopedist.
Consolidate the result
After exercise, you need to sit for 10 minutes. This is necessary to ensure that all the contents of the inner ear remain in place and do not move. This is the only way to protect yourself from repeated attacks of dizziness. You should wear a soft pillow around your neck for the rest of the day. With its help, you can limit head movements and record the results of the Epley maneuver for a long time.
In the days following the exercises, you need to sleep with your shoulders and head straightened. It is better to sleep in a position where your head is turned 45˚. During the day, after the Epley maneuver, the head should be kept upright. You should not visit a hairdresser or dentist at this time, who will ask you to tilt your head back.
You should not perform exercises that require sudden movements and throwing your head back.
After the Epley maneuver, you should wait a week and not provoke attacks of dizziness during this period. Check to see if symptoms appear if you take a position that previously caused them. If there is no recurrence of symptoms, then the procedure was successful.
Causes of dizziness
In clinical practice, a distinction is made between secondary and primary dizziness.
The secondary form of vertigo is characterized by the release of excess otoconia from the otoliths. Almost every disease that directly or indirectly affects the inner ear leads to this process.
BPPV often occurs after vestibular neuritis. In this case, it is sometimes confused with recurrent neuritis, characterized by dizziness even at rest.
The “classic” one is post-traumatic BPPV. Dizziness can occur immediately after injury, but most often the event only disrupts the diaphragm and releases the otoconia over several days or weeks. Post-traumatic vertigo often affects both labyrinths at the same time.
When to expect an effect
After the first session, within 3 days, and after a month, the patient is recommended to visit a specialist. If symptoms do not go away, you may need to repeat the maneuver or need to look for other causes and remedies to get rid of dizziness.
Relapses occur in 20 patients out of 100.
The Epley maneuver may not produce the desired results if:
- neck extension is insufficient, due to which calcium salts return to their place;
- the patient has blockage of the posterior semicircular canal with a conglomerate;
- the diagnosis was incorrectly made and the patient does not have canalolithiasis of the posterior semicircular canal, but cupulolithiasis, as a result of which, after performing the maneuver, the pressure goes in the opposite direction;
- transformation of BPPV of the posterior canal into BPPV of the anterior canal.
The table below shows other types of vestibular maneuvers that can be used if the Epley maneuver does not give the desired result. But they are used only on the recommendation of a doctor.
| Maneuver name | Peculiarities |
| Semonta | It is carried out only under the supervision of medical personnel. Often during it, patients experience a pronounced autonomic reaction, manifested in the form of nausea, vomiting and heart rhythm disturbances. It is carried out like this: sitting on the couch, legs hanging, the patient turns his head towards the healthy ear. The head in this position must be fixed with the help of hands. The patient in this position moves to a lying position on the side of the sore ear. Stay for a couple of minutes, relax. Afterwards, the patient quickly sits down again, the head remains fixed, and turns over to the other side. Head down, lie down again for 2 minutes, and then return to the starting position. |
| Lempert | This maneuver is very similar in technique to the Epley maneuver. The difference is that after turning the patient’s torso on its side, with the healthy ear down, the rotation of the torso continues. The patient lies on his stomach face down, and then on the sore eye with his ear down. At the end of the complex, he returns to a sitting position. Its actions strongly resemble rotation around its axis. After performing this maneuver, you should avoid bending your body for several days and sleep only on a raised head of the bed or on a hard pillow. |
In rare cases, relapses may occur or the complex needs to be repeated, but after talking with the patient it turns out that he did not adhere to the recommendations. The maneuver is truly an excellent opportunity to remove otoliths from the inner ear, because they are the ones that cause an unpleasant symptom, but a favorable result is guaranteed only if all the rules are followed.
The Epley maneuver is an effective complex that helps a person get rid of dizziness without any harm to health.
Thanks to this technique, it is possible to normalize the vestibular apparatus if the problems are associated with the deposition of calcium salts in the inner ear. But it should only be carried out on the recommendation of a doctor, there is no self-medication and it is better to do everything the first time in the presence of a specialist.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Symptoms
BPPV develops more often in women. The most likely cause of the disease is the deposition of calcium salts (otoliths) in the inner ear canal. Head movements (tilts, turns, tilts) provoke short-term attacks of dizziness. Between episodes, the patient may experience nausea, fluctuations in blood pressure, loss of balance, and impaired thermoregulation. Regular intense attacks can cause such great inconvenience that the question of what to do with dizziness is in the first place for the patient. With timely treatment, BPPV does not cause lasting harm to health; the benign nature of the disease implies a decrease in the severity of the episodes.