Vascular tone is the tension of blood vessels, supported by smooth muscles, an important factor in the blood supply to internal organs, one of the tools for general blood circulation. Vascular tone is influenced by the endothelium, the inner layer of blood vessels. Very thin (one cell thick), but plays a significant role in regulating vascular and cardiac tone, as well as in angiogenesis (formation of new vessels) and immune defense.
The fact that the endothelium is formed by a single layer of flat mesenchymal cells should seem to mean its insignificance, “microscopicity”. In fact, it is the largest organ in humans, present in all tissues. It affects blood clotting, kidney filtration, brain nutrition, and many other processes.
What is vegetative-vascular dystonia?
Vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD)
) is a malfunction in the functioning of the whole organism. By and large, this is not a disease, but a malfunction of the autonomic nervous system, a violation of the regulation of the dynamic constancy of the internal environment of the body and the stability of its basic physiological functions: breathing, blood circulation, digestion, thermoregulation, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, etc. This is a functional failure of the body that can turn into disease.
VSD is a very common disease. About half of all women and a fifth of men are susceptible to autonomic dysfunction syndrome. Complaints can be very diverse: patients complain of weakness, pain in the heart area and under the left shoulder blade, headache, pressure surges and neurological disorders. If no measures are taken, the patient only gets worse. In the future, more serious surges in pressure, disruption of brain function and panic attacks are possible - acute stressful conditions characterized by a serious disturbance in a person’s mental state. If left untreated, functional disorders of VSD can cause more serious diseases, such as hypertension.
Quite often, vegetative-vascular dystonia is situational in nature: this means that an exacerbation of symptoms occurs against the background of stress, during weather changes, menstruation or other ordinary situations.
To date, doctors have described about 150 symptoms and 32 syndromes of clinical disorders with the diagnosis of “vegetative-vascular dystonia”. This is too much for an accurate diagnosis of any disease, and this is why diagnosing VSD is very difficult.
Many patients do not understand what serious consequences vegetative-vascular dystonia can lead to. Unfortunately, feeling unwell and having headaches is considered a “habitual” occurrence that can be alleviated with painkillers.
The availability of medications does its job: it’s easier to go to the pharmacy and relieve pain with pills, but medications only eliminate the symptoms of VSD and have nothing to do with treatment.
The mechanism of development of vegetative-vascular dystonia is as follows: in a normal state, the autonomic nervous system regulates the activity of internal organs, ensuring their adequate response to processes occurring in the body. In turn, the activity of the human autonomic nervous system is regulated by two subsystems: parasympathetic and sympathetic.
The parasympathetic subsystem is responsible for sleep and restoration of the body's strength, and the sympathetic subsystem is responsible for the period of wakefulness. Their work “alternates,” allowing a person to expend energy during the day and recover at night, during sleep and rest. The systems are closely connected to the brain and spinal cord and their failure affects the activity of the entire nervous system. The disruption of the relationship between these subsystems and the body’s incorrect response to natural processes is called vegetative-vascular dystonia. Since we are talking about malfunctions of the nervous system, VSD is very difficult to diagnose. The patient visits several specialists without success, but his condition continues to worsen. At the same time, the test results or cardiogram are in perfect order, but the patient feels worse and worse.
Muscular regulation of vascular tone
The actively maintained tension assigned to the vessel segment by smooth muscles resists surges in blood pressure and does not allow changes in the internal lumens of the vessels - and, consequently, their capacity. This stabilizes blood circulation within an organ or in a separate area of internal tissue. Regardless of pressure surges, the blood supply here remains uniform.
To ensure such regulation, both parasympathetic nerve connections and myogenic mechanisms are involved. The subtleties of paracrine secretion also have an effect.
Paracrine is the third type of secretion, along with endocrine and exocrine.
- Endocrine cells, which are part of the endocrine glands, produce hormones that are released into the blood. They spread through the circulatory system and act within the body.
- Exocrine cells that make up the exocrine glands produce substances that are secreted outward (sweat, saliva, tears) or into internal cavities (for example, pancreatic juices secreted by the pancreas into the intestines).
- Paracrine cells secrete substances that are directly consumed by neighboring cells.
Such close transmission is important, for example, for the development of a receptor response of local cells to the effects of regulatory hormones delivered along with the blood flow.
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia?
The symptoms of autonomic dysfunction are very diverse: the patient’s condition is characterized by a variety of symptom complexes. Symptoms appear against the background of physical and mental stress, family worries, problems at work and general weakness of the body. Most often, VSD is characterized by vague pain in the heart, sweating, rapid heartbeat, a feeling of shortness of breath and fluctuations in blood pressure. The painful condition may be accompanied by fear, weakness, trembling in the limbs, slight dizziness, irritability, anxiety, tinnitus and decreased appetite - even fainting and sudden emotional swings. These symptoms can be the cause of a variety of diseases. The diagnosis of VSD is made by excluding those diseases that the patient complains of. If the patient’s complaints are not confirmed by the examination results, the doctor excludes a specific disease and continues to look for the cause of the ailment. If consistent work based on the patient’s complaints and examination results does not allow one to draw a specific conclusion about the causes of the disease, the doctor makes a diagnosis of VSD. One of the most well-known symptoms of VSD is meteorological dependence - the patient feels unwell when the weather changes.
Types of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is manifested by many symptoms, varying in nature and intensity.
Based on patient complaints and doctors’ experience, several types of vegetative-vascular dystonia can be classified, among which the following types are the most common:
VSD of mixed type:
the patient complains of headache, nervousness, anxiety and fear, dizziness and changes in heart rate.
VSD according to cardiac type:
the predominance of complaints of pain in the area of the heart and left shoulder blade, rapid heartbeat. In this case, blood pressure can deviate either upward or downward, or be stable.
VSD according to the vagotonic type:
causeless abdominal pain, nausea, lack of appetite, digestive problems. The patient may complain of insomnia, increased swelling, fatigue, sweating and psychological sensitivity.
VSD of the hypertensive type:
one of the most common types, when the disease occurs with high blood pressure. Most often, the patient complains of headaches, nausea and dizziness.
VSD of hypotonic type:
manifests itself in the form of weakness, increased sweating, and is characterized by decreased ability to work. In this case, blood pressure is steadily reduced.
Each type of VSD has its own symptoms of the disease and their list is quite extensive. To one degree or another, the initial signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia are present in every person and most people simply do not pay attention to them. If you have a headache, you take medicine, but the true cause of the ailment remains unclear.
This is the main danger of vegetative-vascular dystonia. Lack of proper treatment and self-medication leads to the progression of VSD: gradually the whole body is involved in the process, and if no action is taken, the disease has consequences on the internal organs. Over time, it becomes more and more difficult for a person to maintain a comfortable rhythm of life: the manifestations of the disease become more acute, and more and more medications are required to relieve symptoms.
In an advanced stage, vegetative-vascular dystonia leads to kidney problems, varicose veins, thrombosis, as well as a significant increase in the risk of heart attack. In the chronic stage, VSD leads to complete disability and causes serious mental illness.
Systematizing all cases, doctors conclude that the following factors can cause the disease:
- Hereditary constitutional factor: the likelihood of VSD increases if one of the parents suffers from this disease. In addition, those people who grew up in single-parent families, or where they were raised in an environment of frequent quarrels and scandals, are more susceptible to the disease.
- Psychophysiological changes that can occur due to stress, heavy physical or intellectual work. There is a high probability of the occurrence and development of VSD against the background of viral infections, alcohol abuse and smoking. Chronic stress, alcohol abuse and smoking contribute to the deterioration and progression of the condition. The most likely causes of vegetative-vascular dystonia may be the inability to rest and relax after hard work, a sedentary lifestyle or a violation of the daily routine. We can draw the following conclusion: everything that weakens the immune system and does not benefit the body can cause the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Hormonal changes: VSD can occur during puberty and during menstruation.
- Organic somatic diseases: the disease is aggravated by diseases of the heart and blood vessels, respiratory system, liver dysfunction, gastrointestinal tract and processes affecting mental activity; VSD can occur against the background of viral infections and disorders of the musculoskeletal system - problems with the spine often coexist with autonomic dysfunction.
- Diseases of the nervous system: VSD accompanies many diseases of the nervous system.
- Occupational diseases: physical factors of the working environment - electromagnetic radiation, increased noise levels, foreign odors, etc. – can cause VSD.
- Neuroses: one of the most common factors causing the manifestation of autonomic dysfunction syndrome.
- Mental illnesses: cause emotional and personal disorders, which also provoke the onset and course of VSD.
From the above it is clear that there are many reasons for the occurrence of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Brakes and accelerators of vascular tone
Hormones produced by the adrenal medulla circulating along with the blood are important for maintaining tone (especially of peripheral vessels). Adrenaline is well known. But to maintain vascular tone, norepinephrine, which is the biological precursor of adrenaline, is more important. It has a more active effect on blood vessels - but is much gentler on the heart, bronchi and intestines, and does not harm metabolism.
Norepinephrine regulates both blood pressure and peripheral vascular resistance. If the position of the body changes abruptly (for example, a person is lying down and suddenly stands up), the amount of norepinephrine increases many times. It strongly constricts the blood vessels - this maintains the pressure inside the arteries, which, in theory, should drop when the body is transferred from a horizontal to a vertical position (it is one thing if the blood spreads horizontally, another thing when it needs to be pumped upward).
An increased level of norepinephrine affects the vascular muscles - it stabilizes the blood vessels. But with an increase in its level, the reaction of presynaptic adrenergic receptors slows down - which immediately leads to a sharp decrease in the secretion of norepinephrine. The pressure in the arteries is regulated, and there is no longer a need for smooth muscles to compress the vessels. Consequently, there is no need for norepinephrine - it “calms down”. Self-regulation of pressure is due to self-regulation of functions for the production of norepinephrine.
This is a very complex biochemical balance; its maintenance involves not only the hormones dopamine and tyrazine, from which norepinephrine is synthesized, but also adenosine, acetylchodine, histamine, serotonin, prostaglandin, and angeotensin. Moreover, if some hormones (angeotensin) spur the synthesis of norepinephrine, others (prostaglandin, etc.), on the contrary, inhibit it. The process develops cyclically, under the influence of brakes and accelerators.
This “device” is very important for vascular areas that are characterized by frequent and sudden changes in pressure.
The reaction of smooth muscles that regulate pressure in blood vessels is also ensured by the content of ion exchange. The positive ions of potassium and calcium are of particular importance. Their complex transformations in interaction with arachidonic acid and substances stimulate contraction (contraction) or relaxation of vascular muscles, adapting to pressure surges.
How to treat vegetative-vascular dystonia with the ALMAG-01 device
IMPORTANT: the ALMAG-01 device can only be used for the treatment of VSD due to hypertension. Treatment must begin after the acute phase of the vegetative crisis.
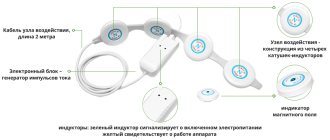
THE DESIGN OF ALMAG-01 INCLUDES THE FOLLOWING ELEMENTS:
Physiotherapeutic procedures with the ALMAG-01 device are carried out once a day. The standard course of treatment lasts three weeks: after every six days, a one-day break is required. The course of treatment is 18 procedures. A repeated course can be carried out after 30-40 days, and a maintenance course - 3-4 months after completion of treatment.
The treatment procedure is simple and does not require special knowledge. Inductor coils are sequentially applied to the projection area of the adrenal glands and the collar zone, and the exposure time is set according to a table developed by specialists.
Fortunately, vegetative-vascular dystonia is a curable disease. To do this, it is necessary not only to undergo treatment, but also to change your lifestyle, reconsidering your views on your daily routine, rest and physical activity.
Therapeutic effect of ALMAG-01 in the treatment of VSD
The running pulsed magnetic field of the ALMAG-01 device improves blood circulation in the affected area, increases the activity of cells and the endocrine system, which has a positive effect on the production of hormones and enzymes. And this, in turn, allows you to normalize the functions of the human cardiovascular and nervous systems. The device has a general calming effect.
The use of the ALMAG-01 device for the treatment of VSD can significantly reduce the intake of medications, or even do without their use, and prevent the development of hypertension.
Exposure to the zone of a traveling pulsed magnetic field reduces vascular tone, the opened capillaries begin to let more blood through and trigger the mechanism for restoring metabolic processes.
The magnetic pulses of the device penetrate deep into the tissue and are able to have a complex effect on all tissue capillaries. Normalizing blood circulation and metabolic processes can improve the quality of sleep, the general well-being of the patient and relieve the main symptoms characteristic of attacks of VSD.
In the ALMAG-01 device there is no problem of the patient getting used to the physiological procedure: sequential activation of the field generators allows you to create the effect of a “running” field, and the constant change in the intensity of the inductor coils does not allow the body to get used to the therapeutic effect.
Regulation of vascular tone through surrounding tissue
The neighboring tissue, which is supplied with blood through these vessels, also participates in pressure regulation. Metabolic factors that arise in the tissue during energy production or, conversely, during its consumption, affect blood vessels. The channel for such an effect is either the endothelium or vascular smooth muscle. Reactions of the endothelium and smooth muscles lead to the expansion or contraction of blood vessels, which normalizes the pressure inside them.
In addition to direct metabolic products, blood vessels can also be affected by other factors related to tissue functions. For example, skeletal muscle secretes the enzymes nitric oxide (NO synthase) and cyclooxygenase (COX). This is in addition to "pure" nitric oxide and prostaglandins, which are also typical of skeletal muscle. During heavy physical activity (that is, with regular tension of the striated muscles), these products are released in particularly large quantities, can reach local vessels, affect their tension or elastic relaxation of the walls, the width of the internal lumen, and pressure.
The extent of this influence (significant or insignificant) is not yet known to pathologists. Various hypotheses have been put forward - but be that as it may, the influence of skeletal muscles on the regulation of vascular tone cannot be excluded.
Moreover, new factors of such influence are constantly being identified. Thus, it became known that certain cells that make up the heart muscle (cardiomyocytes) also regulate vascular tone in their own way. These cells also secrete nitric oxide (NO), which spreads through the internal tissues to the vessels, primarily the coronary vessels. Thus, the heart regulates the pressure inside the vessels not only by supplying blood, but also additionally, through nitric oxide, making the lumens of the vessels optimal for a specific level of blood flow.
Advantages of the ALMAG-01 device in the treatment of VSD
- ALMAG-01 improves microcirculation and normalizes blood pressure. Even at the initial stage of treatment, the patient's increased vascular tone decreases and blood circulation improves.
- Eliminates the main cause of VSD - normalizes a person’s mental state.
- By reducing the sensitivity of peripheral nerve receptors, the device has a calming effect and restores sleep quality.
- Treatment allows you to normalize blood pressure, and in the case of tachycardia, reduce the heart rate.
- The course of treatment does not require special knowledge and can be carried out by the patient independently, at home.
- The device is able to enhance the effect of medications used and even completely eliminate them.
How does the endothelium affect vascular tone?
Among the products of endothelial activity, nitric oxide (NO) attracts attention. It regulates vascular tone. The production of nitric oxide increases with increasing pressure at a given vascular site. Blood pressure may rise due to increased physical activity or under the influence of certain hormones (for example, acetylcholine).
Increased pressure on the vessel wall activates a special set of enzymes called endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS). These enzymes spur increased production of NO. Nitric oxide molecules are freely released through cell membranes and penetrate into smooth muscle. Under the influence of NO, muscle tissue relaxes - the walls of blood vessels, without encountering resistance from smooth muscles, expand, and the pressure inside these vessels drops.
A decrease in pressure weakens eNOS activity in the endothelium. Less nitric oxide is released - the vascular muscles tense again, maintaining the pressure at the working level.