According to statistics, the fair half of humanity suffers from depression twice as often as the stronger half. Moreover, every fourth woman has experienced deep depression at least once in her life.
- The essence of depression
- Symptoms of depression in women
- Signs of mania
- Symptoms of mania in women
- Reason for women's predisposition
- Additional risk factors
- Is depression genetic?
- Differences in depression in women
- Depression during pregnancy
- Does depression affect pregnancy?
- Does pregnancy affect the development of depression?
- Tips for pregnant women to relieve symptoms of depression
- Treatment of depressive disorder in pregnant women
- Treatment of postpartum depression
- Depression and menopause
- How to relieve menopause symptoms?
- Treatment of depression in women
- Additional materials. Self-diagnosis tests
The essence and definition of depression
Depression is a common, severe mood disorder. It becomes the cause of sadness, a feeling of helplessness and doom, a state of helplessness that was previously not characteristic of a person. Depression can take a moderate form with symptoms such as apathy, lack of appetite, problems falling asleep, decreased self-esteem, and chronic fatigue. Sometimes depression manifests itself in a more serious form. It can last for several months or several years, disrupting the normal life and activity of a woman, her ability to work, as well as relationships with other people. Depression is also strongly associated with the risk of divorce.
What is the danger of hidden depression?
There is an opinion that SD is dangerous due to the threat of a breakdown, in which long-suppressed negative emotions will burst out, resulting in a person either committing suicide or causing harm to others. Such an outcome cannot be ruled out, but is still considered extremely unlikely.
The real danger of diabetes lies in a sharp decrease in the quality of life, which turns more into “existence” without any joys or at least some positive experiences.
Patients with depressive disorder often compare themselves to robots that “function” mainly for the benefit of their family or close relatives. Days, months and even years merge for them into one hopeless gray spot without a single glimmer of positivity or a desired goal.
Such a life, according to the patients themselves, reminds them of Dante’s 7th circle of hell - and this quite eloquently describes the main threat of latent and untreated depression.
Symptoms of depression in women
- The mood is predominantly sad, which can be briefly described with the word “none.”
- Increased anxiety.
- Lack of interest in any type of activity, including entertainment.
- Decreased libido and sexual activity.
- Feeling restless, irritable, fussy, or tearful.
- Feelings of guilt, hopelessness, futility, hopelessness, helplessness, a general pessimistic attitude.
- Changing sleep patterns: a woman sleeps either much more or much less than before.
- Changes in appetite: a significant increase and the woman gains weight, or a radical decrease and she loses weight.
- Decreased energy level (possibly with increased appetite), constant fatigue, and a feeling of some “slowness.”
- Suicidal thoughts and attempts.
- Difficulty concentrating, difficult to remember anything, difficult to make decisions.
- Other multiple symptoms that cannot be treated with traditional methods, such as persistent headache (possibly also migraine), digestive problems, chronic pain of unknown origin.
Since the above symptoms can characterize depression not only as a separate phenomenon, but also as a gradation of bipolar disorder, let us consider the signs of the opposite gradation - mania.
WHAT PSYCHOLOGISTS SAY
First of all, in order to start fighting depression on your own, you need to know what caused it and neutralize it. The most common “provocateurs” are:
- Personal tragedy experienced at any age.
- Chronic illness.
- Constantly pursuing stressful situations.
- Lack of vitamins.
- Poor nutrition.
- Bad weather, lack of sunlight.
- Problems at work and at home.
- A series of failures.
- Lack of sleep, severe fatigue.
- A sudden significant change in life - the collapse of a business, dismissal, the need to start something over again, moving to another country, etc.
- Loss of a loved one.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages and psychotropic drugs.
We can say for sure: depression does not “pop up” unexpectedly, like a pimple. This is how the psyche responds to negative events that are important to a person. The problems that caused the disorder should not be driven deep into oneself, because then they, poisoning the body from the inside, will become more global and can result in serious mental or somatic illnesses.
Reconsider your views on the situation - as they say, there is no way out of the grave! Life goes on - change your attitude to what is happening, do not pay attention to squabbles and sidelong glances. It's impossible to please everyone. If you need a frank conversation, talk frankly, dot the i's. Work on yourself.
Signs of mania
Bipolar disorder is characterized by the fact that mood can change sharply, occupying completely opposite poles - from mania to depression and vice versa every couple of days, weeks or months. In this case, mania is characterized by a highly energetic state and high spirits. But even if the state of mania may not cause concern due to its inherent positive symptoms, it requires immediate psychotherapeutic help, because at any time it can change to a completely opposite state.
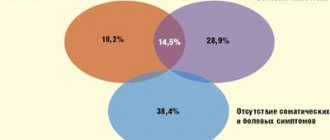
Masked depression: causes of development
Somatized depression, the symptoms of which do not indicate a mental disorder, is considered by experts as the body’s reaction to excessive stress or stress. Masked depression differs from other forms, in particular from endogenous, in the neurotic nature of its course.
Research conducted by German psychiatrists proves the fact that diagnosing latent depression is particularly difficult. Thus, 25% of patients observed by family doctors were diagnosed with somatized depression during the study.
Only a qualified psychiatrist can identify how hidden depression manifests itself. In addition, during the initial consultation, highly qualified specialists at the Yusupov Hospital are able to establish the cause of the development of a mental disorder, even in cases where the patient cannot establish the relationship between masked depression and a traumatic factor.
Symptoms of mania in women include:
- Dominance of high spirits, previously not characteristic of a woman.
- Frequent irritability or intolerance.
- Low need for rest and sleep.
- Generating numerous big ideas.
- Increased need for communication.
- Jumpy formulation of thoughts.
- Excessive, previously unusual, physical activity, including sexual activity (increased libido).
- Noticeably increased overall energy level.
- Lack of judgment, which sometimes leads to undue risk and behavior.
- Inappropriate behavior in public.
What is the reason for women's predisposition to this disorder?
In childhood and pre-puberty, the susceptibility to depression in both sexes is the same. But upon reaching puberty, the risk of this disorder in girls increases significantly and, compared to boys, it occurs almost twice as often.
Most experts tend to consider the cause of such “injustice” to be hormonal changes that occur in the female body throughout life. Changes in hormonal levels become obvious during puberty, pregnancy, premenopause and menopause, as well as in connection with the birth of a child and breastfeeding. Added to this are monthly fluctuations in hormonal balance, which sometimes provoke the occurrence of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), a serious condition similar in nature to depression and a group of anxiety disorders.
Causes of depression
Experts attribute symptoms of depression to environmental factors and genetic predisposition. However, they invariably indicate the impossibility of accurately identifying the cause of the disease. Official medicine recognizes a hereditary trace in more than half of diagnosed cases: in first-degree relatives, identical twins. According to popular theories, the development of a depressive state can be affected by malfunctions of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland or adrenal glands, which produce hormones important for humans. Disturbances in the interaction of these organs can cause prolonged depressive states.
A significant role in the appearance of signs of major or chronic depression is played by the psycho-emotional state, disturbed as a result of experienced problems: divorce, loss of a loved one, financial losses. In the absence of a predisposition to severe mental disorders, these events do not cause prolonged depressive states. If the patient has a tendency to anxiety, the risk of dangerous symptoms increases.
Speaking about women's predisposition to depression, experts point to the following reasons:
- exposure to daily stress due to high mental stress;
- high risk of thyroid dysfunction;
- hormonal changes associated with the menstrual cycle or menopause;
- an increase in the level of monoamine oxidase, an enzyme that promotes the destruction of neurotransmitters that determine the patient’s mood level.
Against the background of clinical depression, the patient may experience signs of somatic diseases: hormonal disorders, brain tumors, strokes, multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's disease.
Additional risk factors
Among the factors that increase the risk of depression are biological (fertility, heredity), characteristics of interpersonal interaction and specific personal characteristics. In addition, if a woman is exposed to increased stress for a long time or is a single mother, this further increases her chances of developing symptoms of depression.
Additional risks include:
- Family experience of mood disorders.
- The presence of a mood disorder in a woman in adolescence or early youth.
- Loss of a parent in childhood.
- Loss of family, friendly support or threat thereof.
- Intense or prolonged psycho-emotional stress (possibly dismissal, problematic interpersonal relationships, separation or divorce).
- Violence experienced in childhood or recently: physical and/or sexual.
- Certain medications.
In addition, some are susceptible to developing postpartum depression, as well as so-called seasonal affective disorder, depending on the time of year.
How is depression different in women?
- It appears earlier, lasts longer, relapses occur more often, is more associated with stressful life circumstances, and is subject to seasonality.
- Female representatives are more predisposed to self-flagellation, experiencing feelings of guilt and are prone to making suicidal attempts.
- Female depression is more often accompanied by various kinds of anxiety disorders and eating disorders (food addiction, psychogenic overeating, nighttime overeating, bulimia (often with a cyclical connection), less often anorexia).
Depression during pregnancy
It is assumed that the expectation of the imminent arrival of a child should be directly correlated with a sense of well-being, which in turn protects a woman from psychological problems. But in practice, it turns out that pregnant women are just as likely to be depressed as other women.
Factors that increase the risk of developing depression during this period include:
- Having depression, severe PMS or PMDD before pregnancy.
- Age of the pregnant woman: the older the woman, the lower the risk.
- Social withdrawal.
- Deprivation of social and friendly support.
- Marital quarrels.
- Uncertainty about the desirability of having a child.
Does depression affect pregnancy?
The following trends are highlighted:
- The insidiousness of this disorder is that a person stops taking care of himself. For a pregnant woman, this may be critical. Pregnant women suffering from depression are less likely to follow doctors' recommendations, sleep and rest patterns, physical activity and a balanced diet.
- This disorder can push a woman to drink alcohol and smoke tobacco, which negatively affects both the health of the expectant mother and her baby.
- Worsening depression may interfere with bonding and bonding with the child.
On the other hand, pregnancy also affects the course of depression:
- An pregnant woman's increased sensitivity to stressful circumstances and their more severe experience may contribute to the development of a depressive disorder or a worsening of existing symptoms.
- Without appropriate therapy, depressive symptoms do not disappear with childbirth, but the name changes - postpartum depression. To assess the signs of depression, take the Test: Postpartum Depression (it is also aimed at pregnant women).
Frequently asked questions about depression
How to get rid of depression on your own?
Attempts to deal with depression on your own usually end in failure and the appearance of signs of a deeper disorder. Only an experienced doctor will be able to determine the type of disease and select the optimal treatment tactics. Folk remedies, uncontrolled use of antidepressants “on the advice of friends,” withdrawal into oneself only tighten the problem and can cause deeper mental disorders with a simultaneous deterioration in physical health.
Why is depression dangerous?
Voluntary refusal of treatment with the intention of independently overcoming the disease can have the most severe consequences: the appearance of suicidal thoughts, deep mental disorders, increased frequency of attacks, personal degradation in professional and family terms, and the emergence of addiction to alcohol and drugs. It is useless to treat all of these symptoms with conventional treatment methods, and taking potent drugs can cause side effects.
How to overcome depression?
It is important to understand that depression is not a temporary deterioration in mood, but a serious mental disorder. And it will be possible to cope with it only after completing a course of complex treatment with the mandatory use of prescribed medications and additional methods for correcting the psycho-emotional state. Treatment under the supervision of an experienced specialist will help to completely cope with the disease and reduce the risk of relapse even when exposed to negative factors.
Tips for pregnant women to relieve symptoms of depression
The preparatory efforts associated with the birth of a baby are energy-intensive and require significant effort and time. But the health of the expectant mother should be given priority. Try not to get hung up on the fact that everything has to be perfect, cut down on current, routine work and do what contributes to your relaxation and calm. Discussing any issues that concern you with your loved ones will help you establish peace of mind and have a beneficial effect on your well-being. Maintain trusting relationships with friends, partner, and loved ones.
If you feel that you are unable to cope on your own, seek professional help from a psychotherapist.
Treatment of depressive disorder in pregnant women
In this case, the treatment plan and the chosen strategy must be carefully thought out, and the risks for the developing fetus and the pregnant woman must be weighed. Only a psychotherapist can effectively cope with such a task, who will either prescribe medications to get results as quickly as possible without the risk of harming the child, or recommend special psychotherapeutic methods for a quick and most reliable result.
Remember, you cannot select and self-prescribe medications, especially for a pregnant woman. This should be done by a doctor based on the results of diagnosing a particular case.
Treatment of postpartum depression
It is treated in the same way as any other form of depression, which involves the use of psychotherapeutic methods and/or medications. If a woman is breastfeeding during therapy, this should be reported to the attending psychotherapist in order to draw up a correct treatment plan. Since it is assumed (not yet confirmed) that the active substances included in antidepressants may pass into breast milk in small quantities, the doctor will need to weigh the possible risks and benefits of using antidepressants and, perhaps, focus more on non-drug therapy for depression.
Since the birth of a child and, in connection with this, a change in lifestyle can affect both the psychological well-being of the woman herself and her relationship with her husband, it is recommended to pay attention to the recommendations of psychologists on how to improve relationships with her husband after the birth of a child, as well as what prejudices the mother should get rid of so as not to drive yourself into depression.
Depressive disorder and menopause
By analogy with other periods of a woman’s life, during menopause there is a close relationship between hormonal levels, physical manifestations and emotional reactions and experiences. Among the physical symptoms, the most common are hot flashes or chills, excessive sweating, dry skin, excess weight gain and a number of others. Mental symptoms include irritability, sleep disturbances, tearfulness, headaches and migraines. These symptoms, together with increased anxiety, cause depression. Most often, menopause begins after 45 years of age, but due to the characteristics of a particular organism (for example, surgical removal of the ovaries), it can begin earlier.
Symptomatic picture of the disease
Signs of depression largely depend on the nature of the disease and help specialists make an accurate diagnosis.
- In a state of major depression, the patient has a tired and sad appearance, lack of eye contact, emotionlessness, depression and restrained speech. Violations of diet and personal hygiene are possible. Also among the characteristic symptoms of depression are: decreased interest in favorite activities, insomnia, weight loss or sudden gain, indecisiveness, inability to concentrate, obsessive thoughts about death or suicide, lethargy.
- In chronic depressive disorder, symptoms of the disease are observed for 2 years or more. The patient has anxiety, obvious personality disorders, increased criticism of himself and others, isolation and low self-esteem. In addition, a chronic condition is indicated by increased fatigue, inability to concentrate, feelings of hopelessness, insomnia or excessive sleepiness, weakness and low mood.
- Against the background of premenstrual depressive disorder, women, a week before the expected date of the start of the cycle, experience sharp mood swings, anger and irritability, a state of anxiety and tension. Interest in usual activities decreases, concentration falls, increased fatigue and a feeling of depression are noted. Up to 6% of women of childbearing age suffer from the listed symptoms of depression in women with PMS at various periods of life.
- In depressive disorders of unknown etiology, patients of both sexes experience anxiety, characteristic manic syndromes (feelings of superiority, talkativeness or high spirits), decreased emotional response to pleasant events, states of delirium or hallucinations, and psychomotor retardation.
The symptomatic picture of different types of depression has an individual coloring for each patient. However, all people suffering from depression invariably share common features of a particular disease, which simplifies the diagnosis.
Complications of depressive conditions
The increase in the pathological situation against the background of the patient’s refusal of professional help can cause the following dangerous phenomena:
- increasing symptoms of depression;
- increased incidence of depression;
- a protracted disease, the duration of which increases as attacks become more frequent;
- cases of double depression, when more “superficial” experiences are superimposed with severe psychological problems and stages of depression develop that are difficult to treat;
- difficulties in selecting appropriate therapy when the disease does not respond to classical methods of correction and requires the use of more “heavy” drugs with a high risk of side effects.
Are you experiencing symptoms of depression?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
How can a woman cope with menopausal symptoms?
- Eat healthy foods and maintain moderate but regular exercise (workout is effective in controlling anxiety levels).
- Get involved in a creative activity, find an interesting hobby that will guide you towards pleasant achievements.
- Find a technique that can balance your mental state: this could be meditation, certain relaxation breathing techniques, yoga (other techniques, strategic self-help for anxiety).
- Try to keep the air in the bedroom at a cool temperature, which will help prevent sweating during sleep and, as a result, sleep disturbances.
- Seek emotional support from friends, close family, or professional help as needed.
- Maintain family relationships, communicate in different interest groups, strengthen friendships with other people.
- Follow your doctor's instructions regarding taking vitamins, dietary supplements, minerals and other medications prescribed to you.
- During periods of frequent hot flashes, give preference to loose-fitting clothing.
PROGRAM FOR OUT OF DEPRESSION BY A PSYCHOTHERAPIST WITH 30 YEARS OF EXPERIENCE
Richard O'Connor, in addition to being a certified specialist in psychiatry, is also the author of many books that have become very popular due to their content and ease of understanding. They talk about many useful things: how to get rid of bad habits, how to become happy and how to get out of depression.
The psychotherapist considers depression not only a mental illness, but also a serious social problem. It should be treated by a specialist, relying on drug therapy and psychotherapy. But professional help is often not enough, since there is always a risk of relapse. An independent way out of depression, the 12 basic principles of which were formulated by O'Connor, will allow you to avoid it. They echo what was said above.
He writes that depression forces a person to think and behave in a certain way, and these become his inalienable habits. They are the ones who dictate an individual’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior. But you can change your thinking, set it on a different course, change your life in a more constructive direction.
So, here are the principles that you need to follow to get out of depression on your own:
1. Don’t avoid expressing feelings, experience them. A person suffering from depression creates a defense mechanism to isolate himself from disturbing emotions, including both unpleasant and pleasant ones. This deprives the individual of important life information - such anesthesia leads to the development of despondency and aggravation of the situation.
Experiencing emotions and expressing them are two different things: we cannot control the first, but we can and should control the second. You can't be sure you need to feel a certain way, because it destroys your personality.
Therefore, you should not be afraid of feelings, because both strong sadness and joy pass very quickly. A person is like a buoy: our emotions are constantly balancing, but eventually stabilize. So you shouldn’t suppress them: crying, laughing, defending your opinion, etc. will improve the condition. You just need to show them where you are understood, and you will certainly find support.
2. Look for the reason. The mood changes for a reason - there is a reason for it and it needs to be identified. If this is difficult to do, it may be advisable to keep a journal and record the events leading up to the episode of depression. Thanks to this, it will be possible to accurately identify the “culprit”. This could be a difficult conversation, a dream, something heard or read, a memory, etc.
Knowing what causes you to feel sad helps you overcome depression. Now the situation can be avoided or changed, and if both fail, then it is better to come to terms with it and not take it too seriously.
3. Practice mindfulness meditation regularly. This will rewire the brain, give you the opportunity to focus on yourself and eliminate obsessive anxiety. Mastering the skills of conscious living, not judging everything in black and white, accepting the world without distortion, not trying to control what is impossible, and enjoying every day is not easy, but it is quite possible.
Repeat the mantra (can be replaced with the phrase) “Lord, give me the serenity to accept what I cannot change, give me the courage to change what I can change, and give me the wisdom to distinguish one from the other” - and everything will work out!
4. Exercise regularly. The brain stores a person's experience, and it changes chemically, electrically, and structurally with every thought, experience, and feeling. Depression damages it by remembering depressive habits. But we are able to create new awareness, “build” other, positive skills, point of view and feelings, thereby improving the brain.
5. Get rid of depressive thinking. Avoid pessimism, blaming yourself for all sins and negative coincidences. Change your way of thinking, bad habits, become confident in your abilities. Keep a diary of dysfunctional thoughts to get rid of them, drive out the inner critic.
6. Get your priorities right. Doing things that are unimportant and uninteresting to you leads to depression. Define values for yourself and strictly follow them, even making an effort. Don’t follow bad habits, don’t let others interfere in your life, strengthen your character.
7. Love yourself. Learn to be proud of yourself - it gives pleasure and a feeling of happiness. Write down your achievements and good deeds in a notebook, whatever they may be - spontaneous or a set task. It is usually quite difficult for a person to feel proud of himself, but such discomfort can be quickly overcome.
Small joys are very important: delicious food, a pleasant smell, a comfortable chair, etc. Just pay mindless attention to them - the main thing here is the sensations.
You need to learn to relax. Yoga, dancing, singing in a choir, swimming, aerobics will help with this.
Eat well, take care of your body and health, do not smoke or drink alcohol.
8. Be direct. To be understood correctly, you need to express your desires to your loved one. The language must be unambiguous: what you say and how you say it must match.
Depressed people, as a rule, think that they are not understood, that they are tongue-tied, prefer not to continue the conversation, become silent, and withdraw into themselves. However, if you cannot express your thought, it is better to pause, concentrate, and even ask your interlocutor to ask questions.
In turn, you should listen carefully to what they tell you and ask again for a better understanding.
Communicate more, smile at people, be friendly. It has been proven that extroverts are happy.
9. Find a hero. You need to identify a role model for yourself. This could be someone whom everyone respects for his kindness, courage, self-sacrifice. Such a person can be among both those living and those who have passed away. Of course, he definitely has some shortcomings, but they deserve admiration for their actions.
Try to be like this person and thereby you will begin to respect yourself.
10. Be generous. Of course, it is impossible to find a way out of depression by simply distributing money, showing participation and sympathy. But an outstretched helping hand to another person in need of funds will help get rid of the disorder. If you don’t have the opportunity to do charity work, then you can become a volunteer.
The habit of generosity will break through self-isolation and make you respect and feel better about yourself.
11. Don’t be afraid of intimacy, open up to your loved one. Intimacy opens you up more to him, he gets to know your doubts, secret fears, shameful secrets. This gives birth to harmony in the couple - there is nothing secret anymore, the masks are removed and you are loved for who you really are.
12. Ask for help in a timely manner. Learn to understand the signs that precede a depressive episode. The “bell” may be discomfort in the stomach, irritability, or a lump in the throat. Each person has a different signal, and if you notice it, then immediately, without delay, contact a specialist. Sometimes just one visit to a therapist can prevent a serious relapse.
Take medications prescribed by your doctor - this is not a sign of weakness, but a guarantee that nothing bad will happen.
Attend support groups and give your loved ones instructions in case you get really sick.
Shame to seek help is a symptom of depression and needs to be addressed.
Of course, as Richard O'Connor argues, it is very difficult to live exactly according to these principles. Yes, and they are not easy to master. These new skills need to be constantly practiced, but this requires your great desire to overcome depression.
It will take patience, time, and a lot of work on yourself, which will be accompanied by discomfort and anxiety. But gradually new habits will become commonplace, and then recovery will come.