Very often, complaints about pressure on the back of the head appear from patients who have suffered for a long time from cervical osteochondrosis. Against the background of this chronic disease, pathological changes occur that provoke disruption of cerebral blood flow. This can contribute to the development of a number of diseases. Let's talk about the most common ones and learn about what to do in such a situation and how to help yourself.
The feeling of pressure in the back of the head can be projected by several negative factors:
- excessive tension of the longitudinal ligaments of the spine, which are attached to the occipital bone;
- overstrain of the muscles of the neck and collar zone against the background of instability of the position of the vertebral bodies, decreased height of the intervertebral cartilaginous discs, etc.;
- displacement of the first cervical vertebra (there is no cartilaginous disc between it and the second vertebra, they are connected by a joint);
- pathology of the articulation of the first cervical vertebra and occipital bone;
- pinching of paired cranial nerves;
- increased blood pressure;
- disturbance of cerebral blood flow, etc.
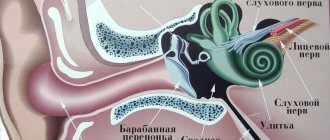
To understand the principle of the development of pain, we suggest delving a little deeper into issues of anatomy and physiology. Let's start with the fact that the cervical spine has 7 vertebrae. The first two are connected to each other using a joint. Between the others are intervertebral cartilaginous discs. They consist of a dense fibrous membrane (ring) and a gelatinous internal body (nucleus pulposus).
This design is responsible for the uniform distribution of shock-absorbing load when making various head movements. It also provides reliable protection for the radicular nerves that extend from the spinal cord located inside the spinal column.
The unique structure of the cervical spine lies in the fact that the vertebral bodies here have additional uncovertebral (hook-shaped) processes. They form channels on the sides of the cervical spine. They contain the posterior vertebral arteries, which are responsible for supplying blood to the structures of the brain.
Any violation of the structure of the cervical spine leads to the fact that the posterior vertebral arteries lose their ability to fully provide blood supply to the brain. To compensate for this process, blood pressure increases. This can provoke the appearance of pressing pain in the back of the head.
The spinal canal is formed by the surface of the vertebral bodies and arcuate lateral processes. Inside there are hard, paranoid and soft shells. Inside them is the spinal cord, placed in the cerebrospinal fluid. Through the foramen magnum, the cerebrospinal fluid communicates with the cavity of the cranium. In this way, partial transmission of the nerve impulse occurs during the interaction of the central and autonomic nervous systems.
If a person experiences instability in the position of the vertebral bodies, a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs, or prolapse of a dorsal intervertebral hernia, then he may experience spinal canal stenosis. This will make it difficult for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the skull. This is often the cause of increased intracranial pressure. This circumstance may also be accompanied by a feeling of pressing pain in the back of the head.
As you can see, the potential causes of such a symptom can be very serious. Therefore, we suggest that you do not self-diagnose. The best way out if you have pressure on the back of your head is to consult a doctor in a timely manner. This could be a neurologist or vertebrologist. These doctors will quickly make an accurate diagnosis and develop effective treatment individually for you.
In Moscow, you can make an appointment for a free appointment with a vertebrologist or neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. Experienced doctors work here. They will conduct a full examination and tell you what examinations are advisable to carry out in your case. After clarifying the diagnosis, an effective and completely safe course of therapy will be developed.
Causes of headaches in the back of the head
Pain is the result of inflammatory reactions, mechanical damage to tissues or pressure on them, impaired blood supply to certain areas of the brain, or ischemia. The cause of pain in the back of the head should be sought not only in this area, but also the condition of the cervical spine should be examined. From time to time it can occur even in a healthy person, regardless of gender and age, but this does not mean that it is safe. If it is relieved by analgesics and does not appear after their action ceases, there is no cause for concern. You should consult a doctor in the following cases:
- pain lasts 5 days or more or a total of 220 days a year;
- there is no response to the use of painkillers, or they bring a short-term effect;
- painful sensations spread to the back of the head, as well as to the neck and upper limbs;
- high intensity pain that occurs frequently.
To understand the cause of pain in the back of the head, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination. Our clinic offers individual programs, as a result of which a definitive diagnosis can be made. However, patients have the right to be informed before the start of treatment and to know what pathologies can cause headaches.
Migraine
Migraines are acute attacks of headache of unknown origin. They are often unilateral, but can be localized in the back of the head. The duration of one attack can range from several hours to several days, and the frequency of their occurrence varies from person to person. Women suffer from migraines more often than men, and the average age of most patients is between 25 and 35 years. It can be triggered by physical activity, changing weather conditions, lack of rest or nervous tension. The attack can be stopped with systemic analgesics - they should be taken immediately after the onset of pain.
Tension headache
This type of headache occurs in most of the population and is less dangerous than other forms. Discomfort in the occipital region is often associated with tension in the neck muscles or prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position. They compress the arteries and nerves that carry blood and impulses to the brain, which is accompanied by a pain reaction in the back of the neck and in the back of the head. Pain of mild or moderate intensity, easily responds to systemic analgesics. It often goes away within a few hours, but its duration can be several days or even a week. In some cases, the provoking factor is emotional tension and stress, which leads to spasm of the neck muscles.
Fluctuations in pressure (arterial and intracranial)
Blood pressure in a healthy adult at rest does not exceed 130/85 mm. rt. Art. If this figure rises to 140/90 mm. rt. Art. and more, we can talk about arterial hypertension. According to statistics, this symptom can be diagnosed in 10-30% of the population, but only a third of patients seek medical help and receive proper treatment. This approach is dangerous to health - hypertension can not only cause acute pain in the back of the head, dizziness and even fainting, but also signal dangerous disorders. In 90% of cases, it is defined as essential, that is, it is an independent pathology that can be easily treated with medication. 10% are due to secondary hypertension. Its causes are diseases of internal organs, and several of its varieties can be distinguished:
- renal - develops with renal failure and accumulation of excess fluid in the body;
- central - indicates damage to certain areas of the brain that regulate blood pressure;
- hemodynamic - we have to talk about this type in case of pathologies and anomalies of the aorta and its valves;
- pulmogenic - manifests itself in chronic lung diseases;
- endocrine - a consequence of diseases of the adrenal glands or thyroid gland.
Another indicator that should be taken into account with chronic pain in the occipital part of the head is intracranial pressure. It is impossible to measure it at home, since accurate data is obtained only by puncturing the spinal cord and determining the speed of fluid flow. Intracranial pressure is a total value that consists of pressure indicators of brain tissue, blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which accumulates in the ventricles of the brain. Its increase is often diagnosed in children and adults, based on ophthalmological examination data and characteristic signs. If hypertension is not associated with organic brain lesions (detected on MRI), treatment consists of adjusting the diet and taking diuretics.
Problems with the cervical spine
One of the causes of headaches concentrated in the back of the head is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. In a healthy person, between the individual vertebrae there are hyaline cartilages, elastic and elastic, which act as a natural shock absorber. Intervertebral discs need sufficient blood supply to maintain their shape and protect the articular surfaces of the bones during movement. Osteochondrosis is a chronic progressive disease associated with thinning and deformation of cartilage. The process is chronic, and it is impossible to completely restore cartilage. Among its reasons are:
- injuries in the cervical spine;
- vertebral displacement, intervertebral protrusions and hernias;
- age-related changes - in older people, cartilage loses its elasticity;
- prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position, excessive physical activity;
- sedentary lifestyle, overweight.
With osteochondrosis, the vertebrae change their usual position. In the initial stages, the disease manifests itself as pain and discomfort directly in the affected area, and then the sensations begin to spread to the back of the head. The reason for this phenomenon is compression of the arteries that carry blood to the brain, and the appearance of ischemic areas. Therapeutic exercises, proper nutrition and drug therapy will improve blood circulation in the brain and prevent further development of osteochondrosis.
Neurological headaches in the back of the head
Occipital neuralgia provokes an acute headache. The greater occipital nerve (or Arnold's nerve) originates from the root of the second spinal nerve and travels under the base of the skull. Its damage, inflammation or compression causes pain in the back of the head. This is a “removing the helmet” type of pain - if the patient indicates in which area he is experiencing pain, he moves his hand from the base of the neck to the front of the head. Discomfort begins in the occipital region, but can spread to the frontal and temporal lobes.
The following factors can cause occipital neuralgia:
- injuries in the upper neck;
- muscle spasms, including those caused by prolonged exposure to a limited position without movement;
- diseases of the cervical spine (osteochondrosis, osteoporosis);
- arthritis that affects the 1st and 2nd cervical vertebrae;
- various tumors, hematomas, neoplasms.
Provoking factors can be incorrect posture, curvature of the cervical spine, working at a monitor or with prolonged concentration on small objects. The process can also begin due to hypothermia or infectious diseases. The pain can be paroxysmal (manifested by attacks) or chronic, requiring timely diagnosis and treatment. At the Clinical Brain Institute you can get more detailed advice about the causes and methods of preventing neuralgia.
Medicinal headaches
Self-medication is dangerous to health. With migraine and other types of headaches, patients often become addicted to the uncontrolled use of systemic analgesics (painkillers), including in excess of recommended dosages. For some time, these actions allow you to get rid of discomfort and continue living as usual, but then they can provoke the development of a medicinal headache. It occurs as a reaction of the body to the frequent intake of active ingredients of analgesics - using them several times a week is enough. Next, patients complain of a continuous headache, which intensifies in the morning and is often localized in the occipital region. It can still be stopped by taking painkillers, but after their effect stops, it manifests itself with renewed vigor.
Other reasons
The cause of a headache can only be identified based on the results of a general examination. Tension headache remains in first place - at least 70% of the population experiences it. Next, it is necessary to exclude possible problems in the cervical spine and diagnose the brain. However, there are several other conditions that can also cause occipital lobe pain. They appear less frequently, but they also cannot be excluded from the list of probable causes of this symptom.
- Cervical myositis is an inflammation of the muscles located in the cervical spine. The process may be aseptic or infectious. It is associated with injuries, curvature of the spinal column, infectious pathologies, as well as hypothermia and excessive physical exertion. Pain occurs in the neck and spreads to the back of the head.
- Atherosclerosis is a decrease in the strength and elasticity of the vessels that carry blood to the brain. Often the process is associated with the deposition of cholesterol and narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, accompanied by an increase in blood viscosity. The most dangerous complications of atherosclerosis include infarction (necrosis of individual areas due to the cessation of their blood supply) and the formation of blood clots in the lumen of blood vessels.
- A history of trauma is one of the reasons why pain can occur even after a long time. Fractures of the skull or cervical vertebrae, closed head injuries and concussions affect the functioning of the nervous system and periodically cause headaches. Patients after trauma often experience weather dependence and suffer from attacks when weather conditions change.
Occipital lobe headaches can be caused by a variety of factors, but present with similar symptoms. The doctors at our clinic specialize in solving such problems and can provide detailed consultations. However, a final diagnosis can only be made after a complete diagnosis.
How to treat if the back of your head hurts
First of all, you need to understand that pain in the back of the head is only a clinical symptom of the disease. Treating it separately is unproductive and dangerous. In this way, you can only suppress the symptom, but the disease will continue to develop. Therefore, it is important to first make an accurate diagnosis, then eliminate the negative factors that provoke the development of the disease and then begin to restore damaged tissues and processes.
The first thing to do if the back of the head hurts and presses against the background of the development of cervical osteochondrosis is to restore the normal height of the intervertebral spaces. To do this, it is advisable to carry out the procedure of manual traction of the spinal column. During this manipulation, the doctor relaxes overly tense muscles, ligaments and tendons, and releases the radicular nerves and their branches from compression. It then restores the height of the intervertebral discs. They take their physiological shape and do not put pressure on surrounding tissues. The pain goes away and the recovery process begins. The patient feels a significant improvement in his condition.
After this, you can carry out a full course of rehabilitation aimed at completely restoring the normal state of the intervertebral discs and surrounding tissues. To do this, the doctor develops an individual course of therapy for each patient. It may include reflexology, osteopathy, massage, therapeutic exercises, kinesiotherapy, laser exposure and much more.
If you have a headache in the back of your head and you are located in Moscow, then make an appointment for a free appointment with a neurologist right now. Fill out the registration form and our clinic administrator will contact you.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
The Clinical Brain Institute offers individualized screening programs to help determine the cause of your headaches. Procedures are prescribed only according to indications. Among them are electroencephalography, radiography of the cervical spine, MRI, Doppler sonography, laboratory blood tests and other techniques.
As a result of a complete examination, a diagnosis can be made and treatment can be prescribed. When selecting medications, doctors at our clinic take into account the patient’s general condition and the body’s response to taking medications. The process takes place under the supervision of specialized specialists, even if it takes place at home.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 40 votes
Share article on social networks