The cause of PA is the release of adrenaline into the blood
It is because of the strong release that a state of adrenaline overdose occurs and a vegetative crisis appears. Therefore, treatment of panic attacks in the initial stages is aimed at reducing and regulating the amount of adrenaline in the blood. Then symptomatic treatment is carried out and work with fear of a recurrence of panic.
How adrenaline affect the human body? This is a substance that is secreted by the adrenal glands and provokes a stressful state in humans. When released into the blood, adrenaline is quickly destroyed, entering into various biochemical reactions. Therefore, as soon as the adrenal glands stop producing adrenaline, the state of stress goes away. However, a person himself can cause relapses of this condition, being under the influence of an experienced event.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a panic attack can vary from person to person. This is due to the fact that symptoms are the results of the human body’s struggle with unexpected chemical processes, and exactly how this struggle will manifest itself depends on the individual characteristics of the person. During a panic attack, you may experience difficulty breathing (a feeling that your throat is swelling), rapid heartbeat, and pulsating blood in your temples. A person may feel sick, feel either hot or cold, or feel uncontrollable trembling. But in the end, the most difficult feeling is a feeling of sudden and overwhelming fear or panic.
Treatment
Treatment of panic attacks is currently very successful and effective. When treating phobias and panic attacks, treatment is initially aimed at the root cause of the state of panic - the release of adrenaline, and therefore adrenergic blockers are used. However, before therapy it is necessary to exclude diseases with similar symptoms, among which sympathoadrenal crisis can be distinguished. In one case, a vegetative crisis may occur due to an adrenal adenoma - this is a benign tumor, due to which excess adrenaline can be released into the blood. In another case, a symptomatic adrenal crisis may occur against the background of neurosis, and disturbances of the autonomic nervous system may also be observed. The crisis is triggered by an incorrect command from the human brain addressed to the adrenal glands, as a result of which they mistakenly release adrenaline. However, a modern psychiatric clinic has a sufficient range of equipment, and thanks to the work of highly qualified specialists, it will not be difficult to confirm or refute this diagnosis. Psychotherapy plays an important role in the treatment of panic attacks, since drug treatment alone cannot eliminate the underlying cause of the disease. Drug therapy will help temporarily eliminate or mitigate the symptoms of the disease, but intensive psychotherapy can find and eradicate the true causes of panic attacks.
Anaprilin
Beta blockers should not be used in patients with untreated chronic heart failure until the condition has stabilized.
Before using the drug, patients with heart failure (early stages) must use cardiac glycosides and/or diuretics.
Monitoring of patients taking the drug should include monitoring heart rate and blood pressure (daily at the beginning of treatment, then once every 3-4 months), recording an electrocardiogram.
In elderly patients, it is recommended to monitor renal function (once every 4-5 months).
In case of increasing bradycardia (less than 60 beats/min), arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure less than 100 mm Hg), atrioventricular block, bronchospasm, ventricular arrhythmias, severe liver and/or kidney dysfunction in elderly patients, it is necessary reduce the dose of the drug or stop treatment.
Use the drug with caution in patients with first degree atrioventricular block.
The patient should be trained in the method of calculating heart rate and instructed about the need for medical consultation if the heart rate is less than 60 beats/min.
It is recommended to discontinue therapy if depression caused by taking beta-blockers develops.
Patients who use contact lenses should take into account that during treatment with beta-blockers, there may be a decrease in the production of tear fluid.
Treatment of coronary heart disease and persistent arterial hypertension should be long-term - taking the drug is possible for several years.
Discontinuation of treatment is carried out gradually, under the supervision of a physician: abrupt withdrawal can dramatically increase myocardial ischemia, anginal syndrome, and worsen exercise tolerance. Cancellation is carried out gradually, reducing the dose by 25% every 3-4 days for 2 weeks or more.
When deciding on the use of the drug Anaprilin in patients with psoriasis, one should carefully weigh the expected benefits and the possible risk of exacerbation of psoriasis.
In thyrotoxicosis, propranolol may mask certain clinical signs of thyroid hyperfunction (for example, tachycardia). Abrupt withdrawal in patients with hyperthyroidism is contraindicated as it can worsen symptoms.
Isolated reports of myasthenia gravis have been reported during propranolol therapy. If muscle weakness occurs, consult a doctor. In patients with diabetes mellitus, the drug is used under the control of blood glucose concentration (once every 4-5 months). Use with caution simultaneously with hypoglycemic agents, since hypoglycemia may develop during prolonged breaks in food intake, as well as during insulin therapy. Moreover, its symptoms such as tachycardia or tremor will be masked due to the action of the drug. The patient should be instructed that the main symptom of hypoglycemia during treatment with the drug is increased sweating. There is also a risk of hyperglycemia when taking oral hypoglycemic agents.
When taking clonidine concomitantly, it can be discontinued only a few days after discontinuation of the drug.
Beta blockers may increase sensitivity to allergens and the severity of anaphylactic reactions. Propranolol may cause severe reactions to a number of allergens when administered to patients with a history of severe anaphylactic reactions to these allergens. These patients may not respond to the usual doses of epinephrine (adrenaline) used to treat anaphylactic shock.
For pheochromocytoma, it is used only in combination with alpha-blockers. Concomitant use with antipsychotics (neuroleptics) and tranquilizers is contraindicated.
Drugs that reduce catecholamine levels (for example, reserpine) may enhance the effect of propranolol. Therefore, patients taking combinations of drugs should be under constant medical supervision to detect arterial hypotension and bradycardia.
During treatment, intravenous administration of verapamil and diltiazem should be avoided.
Use with caution in combination with psychotropic drugs, for example, MAO inhibitors, when their course is used for more than 2 weeks.
A few days before general anesthesia with chloroform or ether, it is necessary to stop taking the drug (increased risk of depression of myocardial function and the development of arterial hypotension). It is necessary to warn the anesthesiologist that the patient is taking Anaprilin.
The effectiveness of beta-blockers in smokers is lower than in non-smoking patients. The drug Anaprilin should be discontinued before testing the content of catecholamines, normetanephrine and vanillylmandelic acid in the blood and urine, and titers of antinuclear antibodies.
Therapy with the drug should be suspended if there is a respiratory infection of the lower respiratory tract accompanied by difficulty breathing. The use of beta2-agonists and inhaled glucocorticosteroids is allowed. Resumption of use of the drug is possible only after the patient has completely recovered. In case of repeated infection, as well as in the case of isolated bronchospasm, the use of the drug should be stopped completely.
It is not recommended to drink alcohol during treatment.
Beta-blockers should be used with caution in patients with peripheral circulatory disorders, as these symptoms may worsen.
Natural licorice should be avoided: foods rich in protein may increase the bioavailability of propranolol.
Propranolol may give a positive result in a doping test.
Panic attacks and willpower
There are a number of common points in the treatment of panic attacks and neuroses - their therapy involves searching for the internal cause of the attacks. Usually these reasons are psychological trauma and severe stress. However, if a person with a strong will was able to suppress them and displace the strongest experiences into the subconscious, then deeply hidden emotions will make themselves felt. Since a person has not allowed himself to fully experience a strong emotion - joy, grief, excitement, etc., this feeling will find a way out for the realization of nervous excitement. As a result, a panic attack may develop. But having found out the true cause of the disease, the psychotherapist can, using the patient’s volitional qualities, eliminate the source of the panic state. Therefore, treating panic attacks through psychotherapy is quite successful and effective, as it combats the underlying cause of the disease.
Not every sympathoadrenal crisis is a panic attack.
There are three main types of sympathoadrenal crises:
Suppressed anxiety, a suppressed reaction to stress leads to the accumulation of nervous tension. The body is preparing to respond to danger; all this is experienced as a panic attack. This lends itself to psychotherapy.
An adrenal adenoma, a benign tumor that produces more adrenaline than necessary, may be the cause of panic attack symptoms. For diagnosis, an ultrasound or MRI is performed and tests are prescribed. It is treated promptly.
An epileptic seizure may be the cause of the symptoms. A connection between epileptic brain activity and a panic attack is established using an EEG study.
The symptoms of psychogenic panic attacks and the other two types of sympathoadrenal crises are similar, but their treatment is different.
People with a strong will, who hide negative emotions, suppress them, and do something “because I can’t” are more susceptible to panic attacks. Unlived emotions can be repressed, but the body does not forget them. The accumulated excitement can be released in the form of a panic attack.
Outpatient and inpatient treatment
The Mental Health Clinic successfully combines the treatment of panic attacks both with medication and through psychotherapy. Most often, treatment for panic attacks is carried out on an outpatient basis, but there are also options for inpatient placement. The attending physician will select an antidepressant that will help relieve acute symptoms and draw up a treatment plan, including the prevention and relief of possible recurrences of panic attacks. Patients who clearly know how to help themselves when the disease manifests itself experience significantly less fear of the manifestation of a crisis, which reduces general anxiety and raises the emotional background in general. However, the most important psychiatric help for panic attacks is to conduct active psychotherapeutic work with the patient. This will allow you to find the root cause of the disease and, by completely eliminating it, get rid of the disease forever.
We can help you! Call us
Quick help for a panic attack
Benzodiazepine tranquilizers
The most effective and fastest-acting medications for panic attacks are a group of benzodiazepine tranquilizers
. These include:
- alprazolam (Xanax),
- clonazepam,
- diazepam (Relanium),
- bromodihydrochlorophenylbenzodiazepine (phenazepam).
These are potent drugs and therefore are not commercially available. They can be purchased using special prescriptions, which can only be prescribed by certified doctors in licensed clinics.
The action of benzodiazepine tranquilizers provides rapid relief of anxiety, vegetative manifestations (rapid pulse and breathing, sweating, trembling, chills and heat waves, dizziness, etc.), normalization of sleep and appetite.
Since the basis of any panic attack is anxiety and excessive activation of brain structures responsible for the protective anxiety reflex, then, regardless of the causes, mechanism of development and manifestation of panic, tranquilizers always have a quick effect. They will either prevent the development of a panic attack, or (if it has already begun) stop it.
Benzodiazepine tranquilizers are used once - as an ambulance, or in short courses (usually no more than a week). With long-term use, dependence is formed, one of the manifestations of which will be “increasing tolerance” - the need to increase the dose to achieve an effect.
These drugs are often used in tablet form. As a rule, taking one tranquilizer tablet ensures the development of a therapeutic effect in 20-40 minutes.
Some of these drugs (diazepam, bromodihydrochlorophenylbenzodiazepine) exist in the form of a solution, which allows them to be used as injections intramuscularly or intravenously, in which case the effect occurs very quickly - from a few seconds to several minutes.
Advantages of benzodiazepine tranquilizers: pronounced anti-anxiety effect, rapid onset of action, well tolerated.
Disadvantages: difficult to purchase (you need a doctor's prescription, a special prescription form), a common side effect is drowsiness and lethargy; if taken regularly, they can cause physical and mental dependence.
Non-benzodiazepine tranquilizers
The next group is non-benzodiazepine tranquilizers
. They are distinguished from the first group by a different chemical structure. The most common representatives:
- hydroxyzine (atarax),
- mebicar,
- etifoxine,
- meprobamate.
In terms of potency, they are inferior to the drugs of the previous group. But they also have their advantages: they are well tolerated, do not cause drowsiness, do not develop dependence, and are easier to purchase in pharmacies (no special prescriptions are needed).
The most common remedy in this group is ATARAX
. They can be used once to prevent or relieve a panic attack. It is also used for long-term use, which can prevent the recurrence of a panic attack.
Thus, tranquilizers
- the most common and popular group of pills for panic attacks. It has been noticed that many people who have long gotten rid of panic attacks, but remember these unpleasant anxiety states, try to carry a tranquilizer pill with them “just in case.”
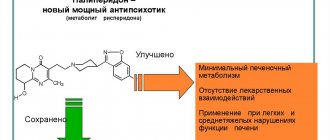
Neuroleptics
Neuroleptics with sedative action. This is the next group of drugs that have a sedative effect and can relieve a panic attack. The most common tablets are:
- Thioridazine (Sonapax);
- Periciazine (neuleptil);
- Chlorprothixene (Truxal);
- Quetiapine (Seroquel);
- Alimemazine (teraligen);
- Sulpiride (eglonil).
The general sedative effect of these drugs allows, when taken continuously, to prevent the development of panic attacks, and when taken once, to relieve a panic attack.
The disadvantage of this group of drugs is that, in addition to anxiety, other emotional reactions (joy, surprise, delight, pleasure, curiosity, melancholy, etc.) can be suppressed.
Antidepressants with sedative effects
Despite the fact that antidepressants are the most prescribed pills in the complex treatment of panic attacks, they can also be used as an “ambulance” - once to stop a panic attack. For this purpose the following are most often used:
- Amitriptyline;
- Clomipramine (Anafranil);
- Mianserin (lerivon)
Unlike antipsychotics and tranquilizers, the effect of antidepressants does not develop as quickly, but is longer lasting.
Other drugs for quick relief of an attack
- aminophenylbutyric acid (phenibut),
- glycine,
- ethyl alcohol (alcohol),
- valocordin or corvalol (and their analogues),
- beta-blockers (anaprilin, atenolol),
- alpha-blockers (clinidine), etc.